本文主要是介绍【Java 多线程】从源码出发,剖析Threadlocal的数据结构,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- example
- set(T value)
- createMap(t, value);
- set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value)
- ThreadLocalMap和Thread的关系
- 全貌
ThreadLocal是个很重要的多线程类,里面数据结构的设计很有意思,很巧妙。但是我们平时使用它的时候常常容易对它的使用感到迷惑,因为它跟其它的API很不一样,使用很不一样,设计也很不一样。
但是不用担心,这篇文章将从源码出发,一步步深入剖析ThreadLocal内部构造,理清楚它的来龙去脉。
example
还是从一个使用用例出发:
public class ThreadLocalExample {// 声明一个 ThreadLocal 变量private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();public static void main(String[] args) {// 在主线程中设置变量值threadLocal.set(10);// 创建并启动一个新线程Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {// 在新线程中获取变量值System.out.println("ThreadLocal value in new thread: " + threadLocal.get());});thread.start();// 在主线程中获取变量值System.out.println("ThreadLocal value in main thread: " + threadLocal.get());}
}打印结果:
ThreadLocal value in main thread: 10
ThreadLocal value in new thread: null
可以看出同一个threadLocal 对象,在不同的线程里面调用get方法,获取的是不一样的结果!也就是说,threadLocal 对象存储了不同线程的私有变量。
现在可能我们还是觉得云里雾里,那现在我们就从源码出发,来一步步进行分析。
从threadLocal.set(10);方法进去:
set(T value)
/*** Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}* method to set the values of thread-locals.** @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of* this thread-local.*/public void set(T value) {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null)map.set(this, value);elsecreateMap(t, value);}
创建map或者设置key&value。
createMap(t, value);
先来看看假如map==null它怎么做:
/*** Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in* InheritableThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map*/void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);}
这里把new出来的ThreadLocalMap赋值给了t.threadLocals,t是个线程。
/*** Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.*/ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);size = 1;setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);}
这里是ThreadLocalMap的构造方法,可以看出ThreadLocal作为key,传进来的参数作为value。
set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value)
现在回退一下,看看map.set(this, value);做了什么:
/*** Set the value associated with key.** @param key the thread local object* @param value the value to be set*/private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at// least as common to use set() to create new entries as// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast// path would fail more often than not.Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}if (k == null) {replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}}tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);int sz = ++size;if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)rehash();}
这里有必要知道的是该方法位于ThreadLocalMap类里面:
看下Entry 的实现代码:
/*** The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using* its main ref field as the key (which is always a* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.*/static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}}
Entry 是个弱引用的子类。设计为弱引用,说明它跟内存泄漏有关。这里先不深入探讨。
到这里我们可以得知set方法执行的时候以ThreadLocal对象作为key,以value入参作为value,传到了ThreadLocal的 Entry[] 里面,设置的时候根据threadLocal对象的hash值来确定其在ThreadLocalMap中的位置。
ThreadLocalMap和Thread的关系
还记得前面的这行代码吗?
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
它createMap(t, value);里面,来看看ThreadLocalMap和Thread的关系:
java/lang/Thread.java
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained* by the ThreadLocal class. */ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
也就是说ThreadLocalMap 其实是属于线程的成员变量。
全貌
其实到这里,我们已经有能力知道整体的数据结构的设计了,下面我们通过前面给出的example代码,通过画图的方式把它们之间关系全貌绘制出来:
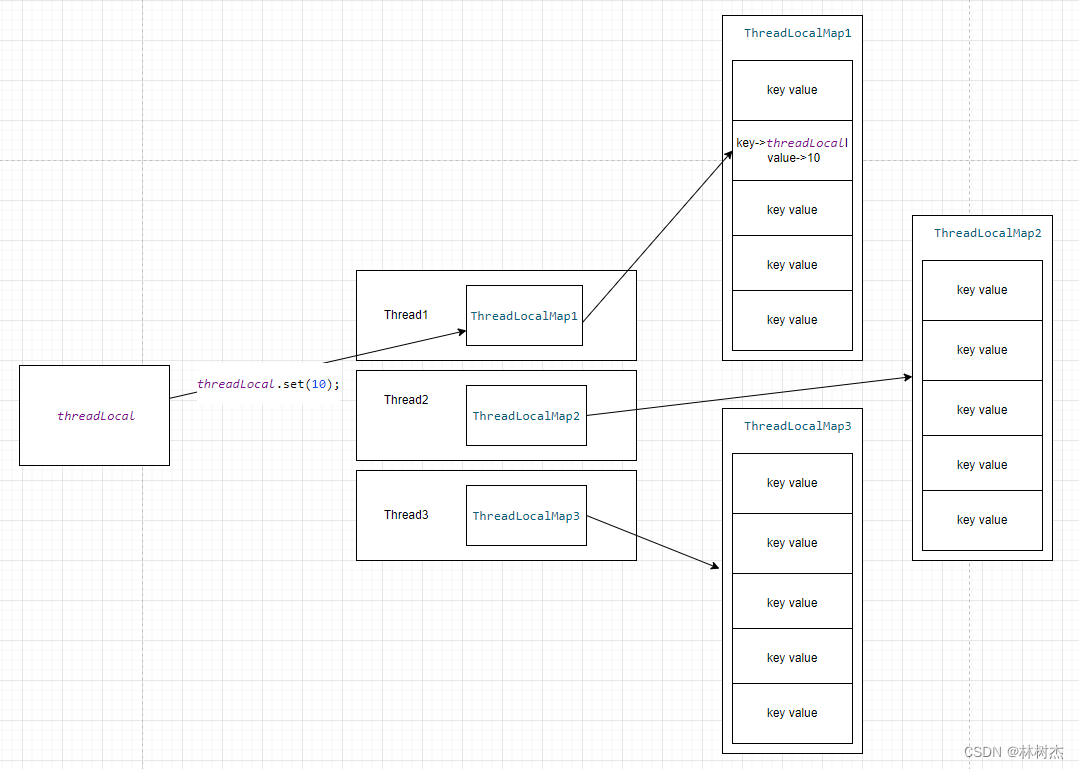
ThreadLocalMap里面是Entry数组,那么其它Entry元素怎么用呢?
这是个好问题,我们迭代下前面的example:
class ThreadLocalExample {// 声明一个 ThreadLocal 变量private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal2 = new ThreadLocal<>();public static void main(String[] args) {// 在主线程中设置变量值threadLocal.set(10);threadLocal2.set("hello");// 创建并启动一个新线程Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {// 在新线程中获取变量值System.out.println("ThreadLocal value in new thread: " + threadLocal.get());System.out.println("ThreadLocal2 value in new thread: " + threadLocal2.get());});thread.start();// 在主线程中获取变量值System.out.println("ThreadLocal value in main thread: " + threadLocal.get());System.out.println("ThreadLocal2 value in main thread: " + threadLocal2.get());}
}
运行结果:
ThreadLocal value in main thread: 10
ThreadLocal value in new thread: null
ThreadLocal2 value in main thread: hello
ThreadLocal2 value in new thread: null
再来一个图:
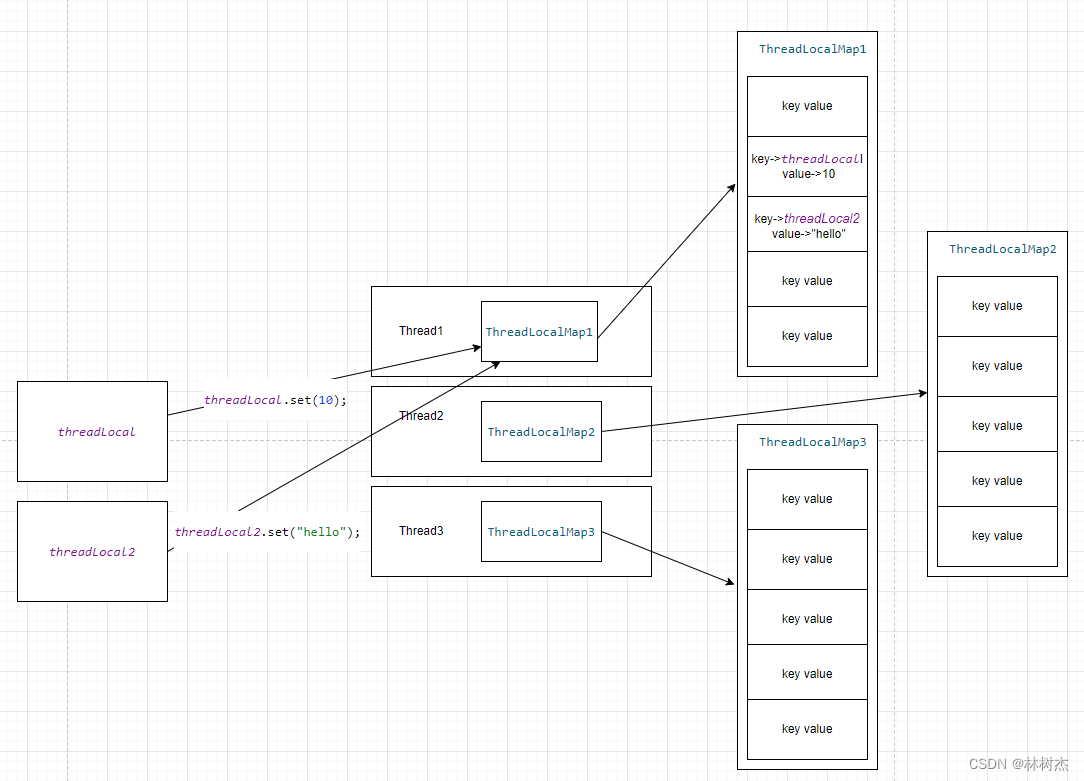
一图胜千言,到这里我们应该对ThreadLocal这个线程类的整体有个清晰的把握了。
enjoy it。
这篇关于【Java 多线程】从源码出发,剖析Threadlocal的数据结构的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





