本文主要是介绍uva 580 Critical Mass,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
原题:
Critical Mass
During the early stages of the Manhattan Project, the dangers of the new radioctive materials were not widely known. Vast new factory cities were built to manufacture uranium and plutonium in bulk.Compounds and solutions of these substances were accumulating in metal barrels, glass bottles and cardboard box piles on the cement oors of store rooms. Workers did not know that the substances they were handling could result in sickness, or worse, an explosion. The o cials who new the danger assumed that they could ensure safety by never assembling any amount close to the critical mass estimated by the physicists. But mistakes were made. The workers, ignorant of the the dangers, often
did not track these materials care- fully, and in some cases, too much material was stored together {an accident was waiting to happen.Fortunately, the dangers were taken seriously by a few knowledgeable physicists. They drew up guidelines for how to store the materials to eliminate the danger of critical mass accumulations. The system for handling uranium was simple. Each uranium cube was marked \ U “. It was to be stacked
with lead cubes (marked \ L “) interspersed. No more than two uranium cubes could be next to each other on a stack. With this simple system, a potential for the uranium reaching critical mass (three stacked next to each other) was avoided. The second constraint is that no more than thirty cubes can be stacked on top of each other, since the height of the storage room can only accommodate that many.One of the physicists was still not completely satis ed with this solution. He felt that a worker, not
paying attention or not trained with the new system, could easily cause a chain reaction. He posed the question: consider a worker stacking the radioactive cubes and non radioactive cubes at random on top of each other to a height of n cubes; how many possible combinations are there for a disaster to
happen?
For example, say the stack is of size 3. There is one way for the stack to reach critical mass { if all three cubes are radioactive.
1: UUU
However, if the size of the stack is 4, then there are three ways:
1: UUUL
2: LUUU
3: UUUU
Input
The input is a list of integers on separate lines. Each integer corresponds to the size of the stack and
is always greater than 0. The input is terminated with a integer value of 0 .
Output
For each stack, compute the total number of dangerous combinations where each cube position in the
linear stack can either be \ L ” for lead, or \ U ” for uranium. Output your answer as a single integer on
a line by itself.
Sample Input
4
5
0
Sample Output
3
8
大意:
有一些装有铀(用U表示)和铅(用L表示)的盒子,数量均足够多。要求把n(n≤30)个盒子放成一行,但至少有3个U放在一起,有多少种放法?例如,n=4, 5, 30时答案分别为3,8和974791728。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//fstream in,out;
int n;
int f[31];
int PowerTwo[31];
int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);PowerTwo[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<=30;i++)PowerTwo[i]=PowerTwo[i-1]*2;f[0]=f[1]=f[2]=0;f[3]=1;for(int i=4;i<=30;i++){int tmp=0;for(int j=2;j<=i-2;j++)tmp+=PowerTwo[i-4]-PowerTwo[i-j-2]*f[j-2];f[i]=tmp+PowerTwo[i-3];}while(cin>>n,n){cout<<f[n]<<endl;}return 0;
}
解答:
lrj小白书上的例题,很好的一道题目,解答来源于书上。
设答案为f(n)。既然有3个U放在一起,可以根据这3个U的位置分类——对,根据前面的经验,要根据“最左边的3个U”的位置分类。假定是i、i+1和i+2这3个盒子,则前i-1个盒子不能有3个U放在一起的情况。设n个盒子“没有3个U放在一起”的方案数为g(n)=2^n -f(n),则前i-1个盒子的方案有g(i-1)种。后面的n-i-2个盒子可以随便选择,有2 n-i-2 种。根据乘法原理和加法原理,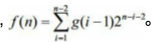
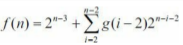
这篇关于uva 580 Critical Mass的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




