本文主要是介绍Day18:LeedCode 513.找树左下角的值 112. 路径总和 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
513. 找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:

输入: root = [2,1,3] 输出: 1
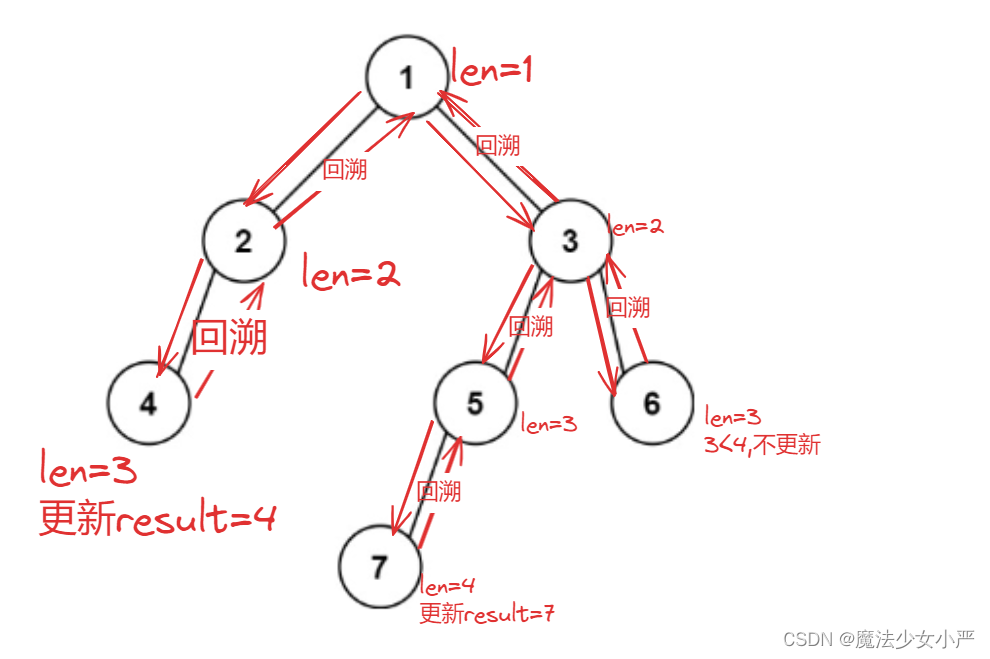
思路:出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值=找出深度最大的第一个结点(左结点先遍历)
方法一:递归法
如何找出深度最大的结点:回溯法,设置两个全局遍历maxlen,result记录最长深度,结果
图解:
递归三部曲:
1.确定返回值和参数的类型
用一个全局变量记录最长深度,result记录结果,递归函数无返回值,参数为int len(当前深度),和传入结点TreeNode cur;
2.确认终止条件:
我们采用左优先遍历 ,遇到叶节点则return,如果该叶节点是深度更大的结点,则更新result;
3.单层递归逻辑:
用回溯法计算每个结点的深度
代码参考:
class Solution {int maxlen=-1;int result=0;public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {//本题结点个数至少为1个travelsal(root,1);return result;}void travelsal(TreeNode cur,int len){// if(root==null)return;if(cur.left==null&&cur.right==null){if(len>maxlen){//找到第一个深度更大的结点则更新resultresult=cur.val;maxlen=len;}return;}if(cur.left!=null){travelsal(cur.left,len+1);}//回溯,下一结点深度+1//本节点深度不变if(cur.right!=null){travelsal(cur.right,len+1);}//回溯,下一结点深度+1}
}方法二:迭代法,层序遍历找到最后一排的第一个结点
层序遍历模板:
Day15:二叉树层序遍历 LeedCode 102.二叉树的层序遍历 199二叉树的右视图 637.二叉树的层平均值 101.对称二叉树 226.翻转二叉树-CSDN博客
代码参考:
class Solution {int result=0;public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> myQ=new LinkedList<>();TreeNode cur=root;myQ.offer(cur);while(!myQ.isEmpty()){int len=myQ.size();for(int i=0;i<len;i++){//每层的第一个元素用来更新resultTreeNode temp=myQ.poll();if(i==0)result=temp.val;if(temp.left!=null){myQ.offer(temp.left);}if(temp.right!=null){myQ.offer(temp.right);}}}return result;}
}112. 路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
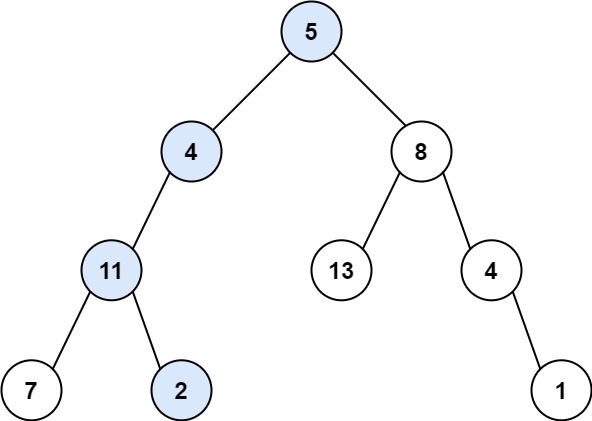
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
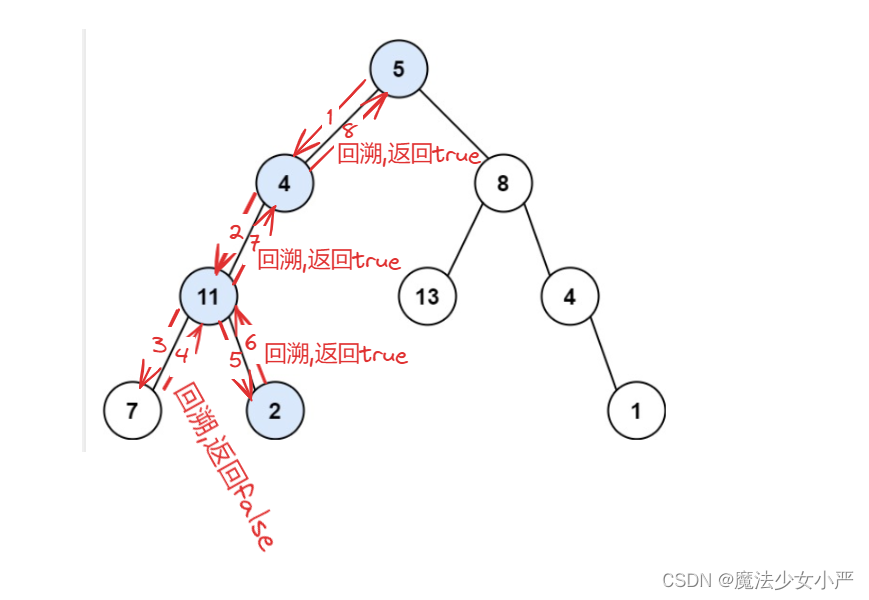
思路:用回溯法遍历所有路径
递归三部曲:
1.确定返回值和参数类型
返回一个boolean类型,参数为int sums(用targetSum依次减去路径上的值)和TreeNode cur(记录当前遍历到哪个结点)
因为targetSum不是全局变量,我们不能用sums==targetSum来判断是否找到路径,用targetSum依次减去路径上的值,sums==0代表找到
2.确定终止条件
遇到叶子结点判断sums是否等于0
if(cur.left==null&&cur.right==null&&sums==0){return true;}
if(cur.left==null&&cur.right==null)return false;
3.确定单层递归逻辑:
找到了就立即返回false,没找到就找其他路径,当所有路径都遍历完时,返回false
if(cur.left!=null){
if(travelsal(cur.left,sums-cur.left.val))return true;
}
if(cur.right!=null){
if(travelsal(cur.right,sums-cur.right.val))return true;
}
class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if(root==null)return false;return travelsal(root,targetSum-root.val);}boolean travelsal(TreeNode cur,int sums){if(cur.left==null&&cur.right==null&&sums==0){return true;}if(cur.left==null&&cur.right==null)return false;if(cur.left!=null){if(travelsal(cur.left,sums-cur.left.val))return true;}if(cur.right!=null){if(travelsal(cur.right,sums-cur.right.val))return true;}//遍历完所有路径均没找到,返回falsereturn false;}
}方法二:迭代法
用栈来模拟回溯的过程:
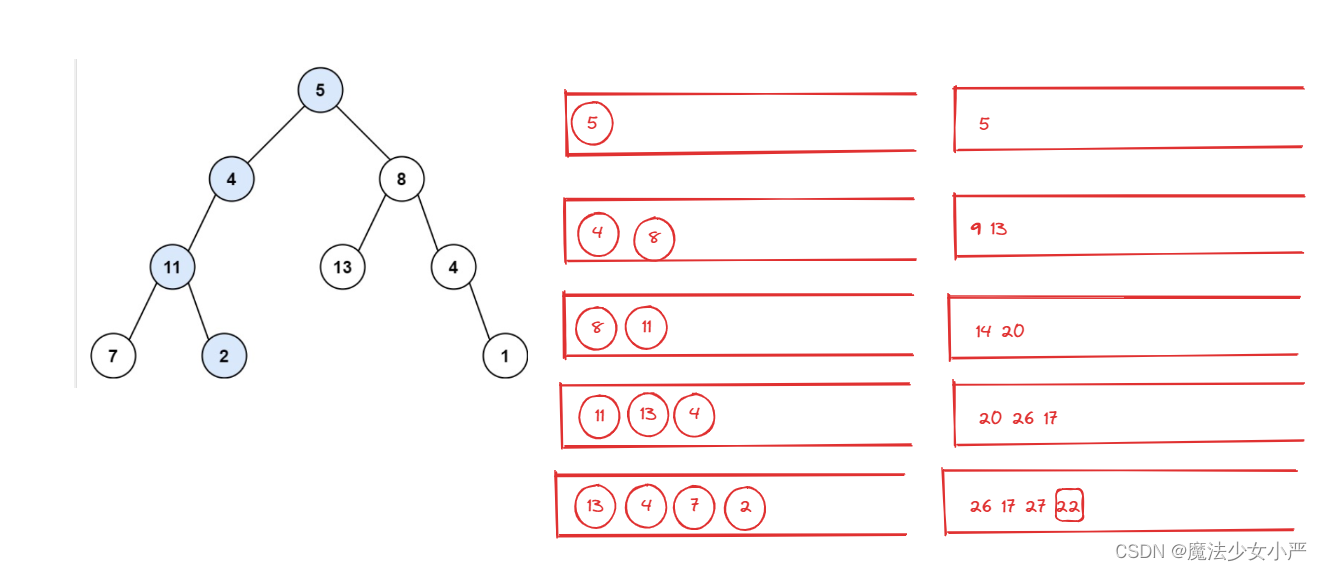
思路:用一个栈放入所有分支路径,一个栈放入这些路径的总和值
class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if(root==null)return false;Stack<TreeNode> stack1=new Stack<>();Stack<Integer> stack2=new Stack<>();stack1.push(root);stack2.push(root.val);while(!stack1.empty()){TreeNode cur=stack1.pop();Integer curSum=stack2.pop();//如果该节点为叶节点,且路径值==target 返回true;if(cur.left==null&&cur.right==null&&curSum==targetSum)return true;if(cur.left!=null){stack1.push(cur.left);stack2.push(curSum+cur.left.val);}if(cur.right!=null){stack1.push(cur.right);stack2.push(curSum+cur.right.val);}}return false;}
}106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
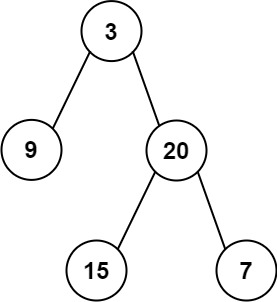
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
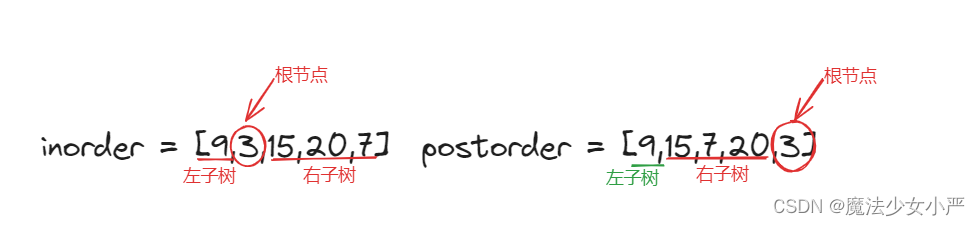
思路:
-
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
-
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
-
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
-
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
-
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
-
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
图解:
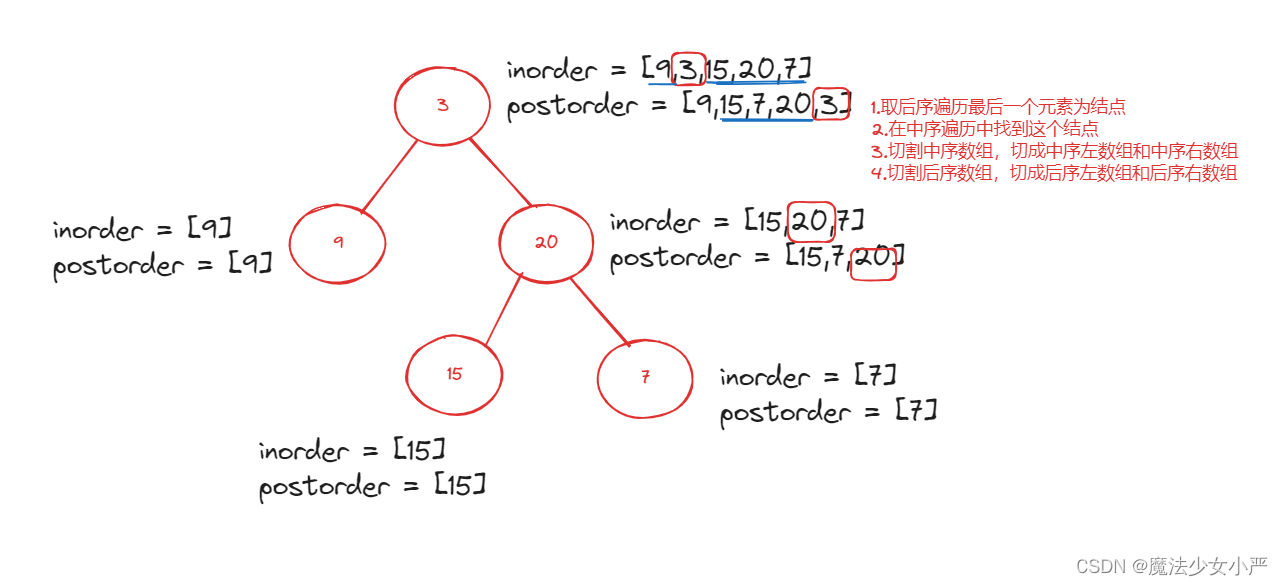
代码:
class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {if(inorder.length==0)return null;//根据后序遍历找到根节点int rootValue=postorder[postorder.length-1];TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootValue);//在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置int index=0;for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++){if(inorder[i]==rootValue) index=i;}//切割中序数组,中序数组在rootValue左边的值是左子树,在rootValue右边的值是右子树int[] left_inorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0,index);int[] right_inorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,index+1,inorder.length);//切割后序数组int[] left_postorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,0,index);int[] right_postorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,index,postorder.length-1);root.left=buildTree(left_inorder,left_postorder);root.right=buildTree(right_inorder,right_postorder);return root;}
}注意:Arrays.copyOfRange()主要用于对一个已有的数组进行截取复制,复制出一个左闭右开区间的数组。
相似题目:
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
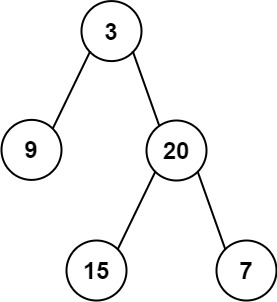
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]

代码:
class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {if(inorder.length==0)return null;//根据先序遍历找到根节点int rootValue=preorder[0];TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootValue);//在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置int index=0;for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++){if(inorder[i]==rootValue) index=i;}//切割中序数组,中序数组在rootValue左边的值是左子树,在rootValue右边的值是右子树int[] left_inorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0,index);int[] right_inorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,index+1,inorder.length);//切割先序序数组int[] left_preorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,1,1+index);int[] right_preorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,index+1,preorder.length);root.left=buildTree(left_preorder,left_inorder);root.right=buildTree(right_preorder,right_inorder);return root;}
}
这篇关于Day18:LeedCode 513.找树左下角的值 112. 路径总和 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





