本文主要是介绍【链表】Leetcode 138. 随机链表的复制【中等】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
随机链表的复制
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
- val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
- random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
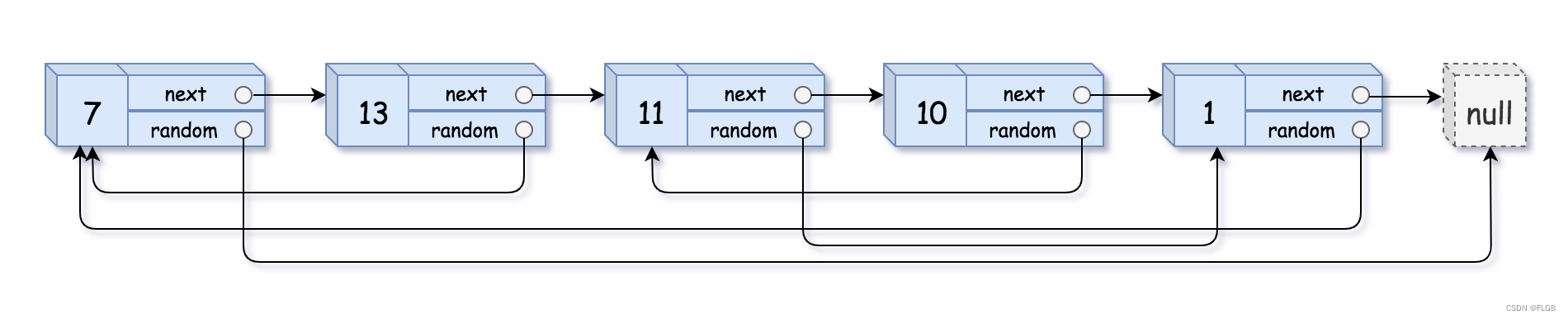
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
解题思路
-
使用哈希表来存储原链表节点和复制链表节点的对应关系。
-
第一次遍历:创建新节点并构建原链表节点和新节点的映射关系。同时,复制节点的 val 值和 next 指针。
-
第二次遍历:根据原链表的 random 指针,为复制链表的对应节点设置 random 指针。
java实现
class Node {int val;Node next;Node random;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;this.random = null;}
}public class DeepCopyLinkedList {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}// 第一次遍历:创建新节点并构建原链表节点和新节点的映射关系Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();Node current = head;while (current != null) {map.put(current, new Node(current.val));current = current.next;}// 第二次遍历:根据原链表的 random 指针,为复制链表的对应节点设置 random 指针current = head;while (current != null) {Node copyNode = map.get(current);copyNode.next = map.get(current.next);copyNode.random = map.get(current.random);current = current.next;}return map.get(head);}public static void main(String[] args) {// 构造链表 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5Node head = new Node(1);head.next = new Node(2);head.next.next = new Node(3);head.next.next.next = new Node(4);head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);// 设置 random 指针head.random = head.next.next; // 1.random --> 3head.next.random = head.next.next.next; // 2.random --> 4head.next.next.random = head; // 3.random --> 1head.next.next.next.random = null; // 4.random --> nullhead.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // 5.random --> 2// 调用 copyRandomList 方法进行深拷贝DeepCopyLinkedList solution = new DeepCopyLinkedList();Node copiedHead = solution.copyRandomList(head);// 打印复制链表while (copiedHead != null) {System.out.print("[" + copiedHead.val +", " + (copiedHead.random != null ? copiedHead.random.val : "null") +"] ");copiedHead = copiedHead.next;}// 输出:[1, 3] [2, 4] [3, 1] [4, null] [5, 2]}
}时间空间复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),需要额外的空间存储新节点
这篇关于【链表】Leetcode 138. 随机链表的复制【中等】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





