本文主要是介绍机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑→汇总篇←,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
有困惑,说明还在思考,麻木才是最恐怖的自我放弃。
如果在思想上不能做自己的主人,那么在身体上就只能做他人的奴仆。
还挺拗口的O(∩_∩)O
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“卷”
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“歧视”
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“取舍”
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“学历与待遇”
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“学历与待遇”补充
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“阶段小结”
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“要求越来越高”
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“效果越来越差”
☞ 机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑“以学生为中心”
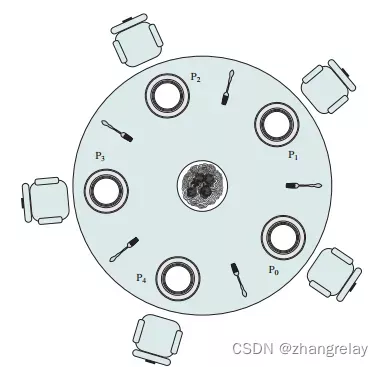
#include<stdio.h>#define n 4int compltedPhilo = 0,i;struct fork{
int taken;
}ForkAvil[n];struct philosp{
int left;
int right;
}Philostatus[n];void goForDinner(int philID){ //same like threads concept here cases implemented
if(Philostatus[philID].left==10 && Philostatus[philID].right==10)printf("Philosopher %d completed his dinner\n",philID+1);
//if already completed dinner
else if(Philostatus[philID].left==1 && Philostatus[philID].right==1){//if just taken two forksprintf("Philosopher %d completed his dinner\n",philID+1);Philostatus[philID].left = Philostatus[philID].right = 10; //remembering that he completed dinner by assigning value 10int otherFork = philID-1;if(otherFork== -1)otherFork=(n-1);ForkAvil[philID].taken = ForkAvil[otherFork].taken = 0; //releasing forksprintf("Philosopher %d released fork %d and fork %d\n",philID+1,philID+1,otherFork+1);compltedPhilo++;}else if(Philostatus[philID].left==1 && Philostatus[philID].right==0){ //left already taken, trying for right forkif(philID==(n-1)){if(ForkAvil[philID].taken==0){ //KEY POINT OF THIS PROBLEM, THAT LAST PHILOSOPHER TRYING IN reverse DIRECTIONForkAvil[philID].taken = Philostatus[philID].right = 1;printf("Fork %d taken by philosopher %d\n",philID+1,philID+1);}else{printf("Philosopher %d is waiting for fork %d\n",philID+1,philID+1);}}else{ //except last philosopher caseint dupphilID = philID;philID-=1;if(philID== -1)philID=(n-1);if(ForkAvil[philID].taken == 0){ForkAvil[philID].taken = Philostatus[dupphilID].right = 1;printf("Fork %d taken by Philosopher %d\n",philID+1,dupphilID+1);}else{printf("Philosopher %d is waiting for Fork %d\n",dupphilID+1,philID+1);}}}else if(Philostatus[philID].left==0){ //nothing taken yetif(philID==(n-1)){if(ForkAvil[philID-1].taken==0){ //KEY POINT OF THIS PROBLEM, THAT LAST PHILOSOPHER TRYING IN reverse DIRECTIONForkAvil[philID-1].taken = Philostatus[philID].left = 1;printf("Fork %d taken by philosopher %d\n",philID,philID+1);}else{printf("Philosopher %d is waiting for fork %d\n",philID+1,philID);}}else{ //except last philosopher caseif(ForkAvil[philID].taken == 0){ForkAvil[philID].taken = Philostatus[philID].left = 1;printf("Fork %d taken by Philosopher %d\n",philID+1,philID+1);}else{printf("Philosopher %d is waiting for Fork %d\n",philID+1,philID+1);}}}else{}
}int main(){
for(i=0;i<n;i++)ForkAvil[i].taken=Philostatus[i].left=Philostatus[i].right=0;while(compltedPhilo<n){
/* Observe here carefully, while loop will run until all philosophers complete dinner
Actually problem of deadlock occur only thy try to take at same time
This for loop will say that they are trying at same time. And remaining status will print by go for dinner function
*/
for(i=0;i<n;i++)goForDinner(i);
printf("\nTill now num of philosophers completed dinner are %d\n\n",compltedPhilo);
}return 0;
}
#include<iostream>#define n 4using namespace std;int compltedPhilo = 0,i;struct fork{
int taken;
}ForkAvil[n];struct philosp{
int left;
int right;
}Philostatus[n];void goForDinner(int philID){ //same like threads concept here cases implemented
if(Philostatus[philID].left==10 && Philostatus[philID].right==10)cout<<"Philosopher "<<philID+1<<" completed his dinner\n";
//if already completed dinner
else if(Philostatus[philID].left==1 && Philostatus[philID].right==1){//if just taken two forkscout<<"Philosopher "<<philID+1<<" completed his dinner\n";Philostatus[philID].left = Philostatus[philID].right = 10; //remembering that he completed dinner by assigning value 10int otherFork = philID-1;if(otherFork== -1)otherFork=(n-1);ForkAvil[philID].taken = ForkAvil[otherFork].taken = 0; //releasing forkscout<<"Philosopher "<<philID+1<<" released fork "<<philID+1<<" and fork "<<otherFork+1<<"\n";compltedPhilo++;}else if(Philostatus[philID].left==1 && Philostatus[philID].right==0){ //left already taken, trying for right forkif(philID==(n-1)){if(ForkAvil[philID].taken==0){ //KEY POINT OF THIS PROBLEM, THAT LAST PHILOSOPHER TRYING IN reverse DIRECTIONForkAvil[philID].taken = Philostatus[philID].right = 1;cout<<"Fork "<<philID+1<<" taken by philosopher "<<philID+1<<"\n";}else{cout<<"Philosopher "<<philID+1<<" is waiting for fork "<<philID+1<<"\n";}}else{ //except last philosopher caseint dupphilID = philID;philID-=1;if(philID== -1)philID=(n-1);if(ForkAvil[philID].taken == 0){ForkAvil[philID].taken = Philostatus[dupphilID].right = 1;cout<<"Fork "<<philID+1<<" taken by Philosopher "<<dupphilID+1<<"\n";}else{cout<<"Philosopher "<<dupphilID+1<<" is waiting for Fork "<<philID+1<<"\n";}}}else if(Philostatus[philID].left==0){ //nothing taken yetif(philID==(n-1)){if(ForkAvil[philID-1].taken==0){ //KEY POINT OF THIS PROBLEM, THAT LAST PHILOSOPHER TRYING IN reverse DIRECTIONForkAvil[philID-1].taken = Philostatus[philID].left = 1;cout<<"Fork "<<philID<<" taken by philosopher "<<philID+1<<"\n";}else{cout<<"Philosopher "<<philID+1<<" is waiting for fork "<<philID<<"\n";}}else{ //except last philosopher caseif(ForkAvil[philID].taken == 0){ForkAvil[philID].taken = Philostatus[philID].left = 1;cout<<"Fork "<<philID+1<<" taken by Philosopher "<<philID+1<<"\n";}else{cout<<"Philosopher "<<philID+1<<" is waiting for Fork "<<philID+1<<"\n";}}}else{}
}int main(){
for(i=0;i<n;i++)ForkAvil[i].taken=Philostatus[i].left=Philostatus[i].right=0;while(compltedPhilo<n){
/* Observe here carefully, while loop will run until all philosophers complete dinner
Actually problem of deadlock occur only thy try to take at same time
This for loop will say that they are trying at same time. And remaining status will print by go for dinner function
*/
for(i=0;i<n;i++)goForDinner(i);
cout<<"\nTill now num of philosophers completed dinner are "<<compltedPhilo<<"\n\n";
}return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>int current[5][5], maximum_claim[5][5], available[5];
int allocation[5] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
int maxres[5], running[5], safe = 0;
int counter = 0, i, j, exec, resources, processes, k = 1;int main()
{
printf("\nEnter number of processes: ");scanf("%d", &processes);for (i = 0; i < processes; i++)
{running[i] = 1;counter++;}printf("\nEnter number of resources: ");scanf("%d", &resources);printf("\nEnter Claim Vector:");for (i = 0; i < resources; i++)
{scanf("%d", &maxres[i]);}printf("\nEnter Allocated Resource Table:\n");for (i = 0; i < processes; i++)
{for(j = 0; j < resources; j++)
{scanf("%d", ¤t[i][j]);}}printf("\nEnter Maximum Claim Table:\n");for (i = 0; i < processes; i++)
{for(j = 0; j < resources; j++)
{scanf("%d", &maximum_claim[i][j]);}}printf("\nThe Claim Vector is: ");for (i = 0; i < resources; i++)
{printf("\t%d", maxres[i]);
}printf("\nThe Allocated Resource Table:\n");for (i = 0; i < processes; i++)
{for (j = 0; j < resources; j++)
{printf("\t%d", current[i][j]);}
printf("\n");}printf("\nThe Maximum Claim Table:\n");for (i = 0; i < processes; i++)
{for (j = 0; j < resources; j++)
{printf("\t%d", maximum_claim[i][j]);}printf("\n");}for (i = 0; i < processes; i++)
{for (j = 0; j < resources; j++)
{allocation[j] += current[i][j];}}printf("\nAllocated resources:");for (i = 0; i < resources; i++)
{printf("\t%d", allocation[i]);}for (i = 0; i < resources; i++)
{available[i] = maxres[i] - allocation[i];
}printf("\nAvailable resources:");for (i = 0; i < resources; i++)
{printf("\t%d", available[i]);}printf("\n");while (counter != 0)
{safe = 0;for (i = 0; i < processes; i++)
{if (running[i])
{exec = 1;for (j = 0; j < resources; j++)
{if (maximum_claim[i][j] - current[i][j] > available[j])
{exec = 0;break;}}if (exec)
{printf("\nProcess%d is executing\n", i + 1);running[i] = 0;counter--;safe = 1;for (j = 0; j < resources; j++)
{available[j] += current[i][j];}break;}}}if (!safe)
{printf("\nThe processes are in unsafe state.\n");break;}
else
{printf("\nThe process is in safe state");printf("\nAvailable vector:");for (i = 0; i < resources; i++)
{printf("\t%d", available[i]);}printf("\n");}}return 0;
}这篇关于机器人工程的工作与考研之困惑→汇总篇←的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





