本文主要是介绍Linux课程____进程管理,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
记录工作日志
script 240319.log
CTRL+d 退出
cat 240319.log //查看
一、查看进程
1.静态
ps -aux
ps -elf
2.动态
top
3.pgrep 查看特定条件的进程
pgrep -l “log”

pgrep -l "ssh"
pgrep -l -U redhat
4.pstree 查看进程树
pstree -aup 所有用户、进程id\详细信息
pstree -ap redhat 查看redhat用户的进程
任务调度和进程管理
5.后台启动,加 & 字符
#cp /dev/sr0 mycd.iso &
6.查看后台任务
jobs

7.调度任务
fg [任务序列号]
8.启动后台停止进程:
bg [任务序列号]
9.终止进程
前台进程终止:crtl + c
后台进程终止:kill -9 进程号, killall -9 进程名称
杀死特定条件进程。
pkill -9 -U “用户名”
如果文件被非正常退出,会生成一个隐藏的缓存文件
例如:file1 文件被中断,会生成.
file1.swp 隐藏文件file2-->.file2.swp
10.监控系统
#uptime 负载、运行时间,用户数。
#lscpu 查看cpu数量,参数等。
二、控制服务和守护进程
含systemd 第一个进程
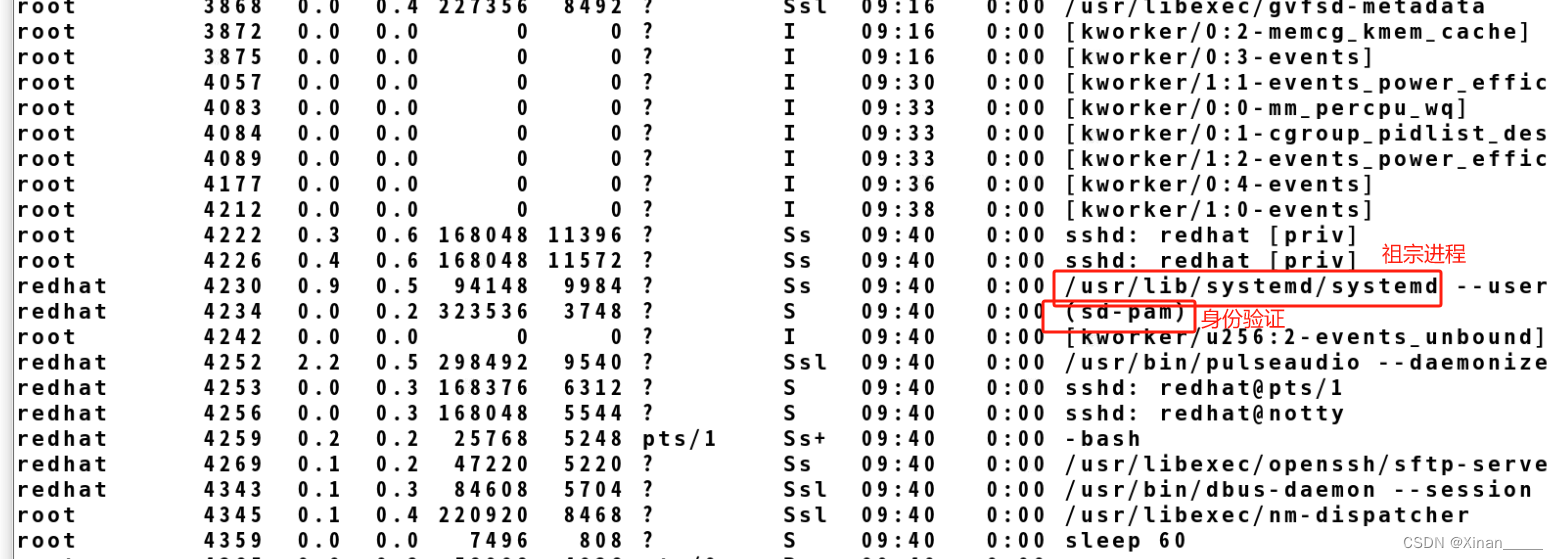

在后台运行

1.systemctl 查看进程
systemctl 列出所有已经加载且运行的单元
systemctl --version 查看版本
systemctl get-default 系统运行级别
systemctl --help
systemctl list-units --type=service 列出服务单元
--type=socket
systemctl list-unit-files 列出服务单元所有的文件
Systemctl status sshd.service 查看某个具体的服务单元的运行状态。
2.小实验
打印机的管理服务:cups.service 手动打开关闭和自动打开关闭
systemctl status cups.service //查看状态
systemctl stop cups.service //手动关闭服务systemctl status cups.service //查看状态
systemctl start cups.service //手动开启服务
禁止系统引导时启动
systemctl disable cups.service //自动关闭服务(开机时关闭)重新启动操作系统
systemctl status cups.service //查看状态
允许系统引导时启动。
systemctl enable cups.service //自动开启服务(开机时开启)
重新启动操作系统systemctl is-active cups.service //查看 cups.service 状态
三、计划任务管理
让设备在指定时间完成指定任务
1.一次性任务计划
at
#date 查看日期
#at 计划时间
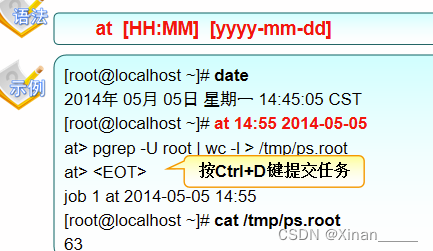
#atq 查询计划序列
#atrm 任务序号 删除计划
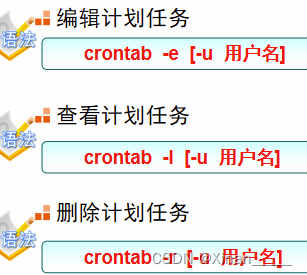
2.crontab周期性任务计划

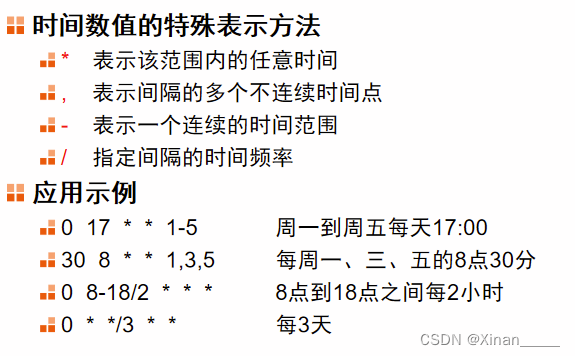
注意:日和星期不可同时设置,无法保证日和星期相对应。
# crontab -U username -e //为username用户设置任务
#crontab -e 编辑(对齐)
50 7 * * * systemctl start sshd.service
10 17 * * * systemctl stop sshd.service
0 0 */5 * * /bin/rm -rf /var/ftp/pub
查看任务计划列表
#crontab -l
任务保存位置:
cat /var/spool/cron/[用户名】
如:cat /var/spool/cron/root
10 17 * * * systemctl stop sshd.service
这篇关于Linux课程____进程管理的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





