本文主要是介绍Silverlight之我见——数据批示(1),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

特性在使用的时候,可以忽略“Attribute”,如上面的,可以写成Flags。
Silverlight(银光)中的“数据批示”概念现在不陌生了,那么,它为何要叫数据批示呢?
因为这些特性类都是用于定义实体类的元数据的,它很像SQL里面的字段属性,如是否为只能,是否为自增长,是否为主/外键等。
这些类都定义在System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations命名空间里面,有兴趣的可以查阅MSDN,这里当然不会逐个列举,我们只挑常用的来讨论。

好的,今天我们讨论第一个,相信也是使用频率最高的——DisplayAttribute。
Name属性:在UI中显示字段标签,下面看了示例你就明白了。
Description:对字段(属性)的描述,可以在UI中向用户显示工具提示信息。
Order:字段在用户界面的显示顺序,这个不用介绍了,和以前的ListView或DataGridView类似(System.Windows.Forms中)。
OK,就这几个,其实的属性不那么重要,其实使用Name和Description就足够了,来,看看下面这个实体类(实体类这玩意儿嘛,你就理解为对客观事物的一种抽象,相当于数据库中的表,用E-R图画出来可能生动一点)。
public class Song
{
string m_Name = "";
string m_Singer = "";
public Song(string songName, string singer)
{
this.m_Name = songName;
this.m_Singer = singer;
}
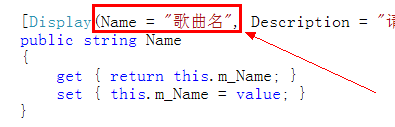
[Display(Name = "歌曲名", Description = "请输入歌曲名。")]
public string Name
{
get { return this.m_Name; }
set { this.m_Name = value; }
}
[Display(Name = "歌手", Description = "请输入歌手姓名。")]
public string Singer
{
get { return this.m_Singer; }
set { this.m_Singer = value; }
}
}
这是一个歌曲类,它有两个属性:歌名和歌手,在上面的代码中,你应该看到了DisPlayAttribute的用法了。
但你一定有些迷惑,不要紧,所见即所得,运行程序一看便知晓。
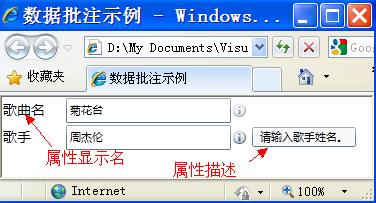
上面用到了Label控件,这个控件不在.NET类库中定义,它在SDK的System.Windows.Controls.Data.Input.dll中,所以,使用前一定要把它添加到项目的引用列表中,这个就不用说了,玩VS的人都知道,省去38个字。
好,看看上面的截图,发现了没?Label上显示的,正是我们刚才定义的DisPlayAttrbute的Name属性。
我们把两个TextBox分别绑定到Name和Singer属性。
你一定发现,在文本框的右侧有一个像“i”的符号,然后你把鼠标移到上面,别动,你就看到那几个字,记得吗?这几个字在哪里定义的?对了,就是DisPlayAttribute的Description属性。

现在,你感悟了没有?那么,Label是如何绑定起来的呢?
把Target设置为要绑定的控件名就行了,如这里是绑定到文本框,因为绑定路径不复杂,所以,无需设置属性路径。
好了,现在我就把XAML放出来,亮亮相。
大家不妨自己动手试试,很有意思的。
<UserControl x:Class="数据批注示例.MainPage"
xmlns=" http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation "
xmlns:x=" http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml "
xmlns:d=" http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008 " xmlns:mc=" http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006 "
mc:Ignorable="d" d:DesignWidth="640" d:DesignHeight="480"
xmlns:sdk="clr-namespace:System.Windows.Controls;assembly=System.Windows.Controls.Data.Input">
<Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="auto"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="27"/>
<RowDefinition Height="27"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<sdk:Label x:Name="lbName" Target="{Binding ElementName=txtName}" Grid.Column="0"
Grid.Row="0" FontSize="14" Margin="1,1,20,1"/>
<sdk:Label x:Name="lbSinger" Target="{Binding ElementName=txtSinger}" Grid.Column="0"
Grid.Row="1" FontSize="14" Margin="1,1,20,1"/>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="0" Orientation="Horizontal">
<TextBox x:Name="txtName" Margin="1,1" Width="165"
Text="{Binding Name}"/>
<sdk:DescriptionViewer Target="{Binding ElementName=txtName}" />
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1" Orientation="Horizontal">
<TextBox x:Name="txtSinger" Margin="1,1" Width="165"
Text="{Binding Singer}"/>
<sdk:DescriptionViewer Target="{Binding ElementName=txtSinger}"/>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
这篇关于Silverlight之我见——数据批示(1)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





