本文主要是介绍文献速递:深度学习乳腺癌诊断---使用深度学习改善乳腺癌组织学分级,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Title
题目
Improved breast cancer histological grading using deep learning
使用深度学习改善乳腺癌组织学分级
01
文献速递介绍
乳腺癌组织学分级是乳腺癌中一个确立的临床变量,它包括来自三个方面的信息,即小管形成程度、核多态性和有丝分裂计数。与其他只考虑单一方面如年龄、肿瘤大小或淋巴结状态的广泛使用的预后因素相比,组织学分级同时考虑了形态学和增殖,因此具有独特的预后意义,在临床决策中被广泛应用。最广泛采用的分级分类系统是诺丁汉分级系统,由Elston和Ellis从Bloome Richardson分级系统修改而来,其预后价值已在不同人群的研究中得到验证。
较高的诺丁汉组织学分级(NHG)与不良预后相关,并且是进行更积极治疗的指示,而较低的分级表明复发风险较低,允许进行更保守的治疗。然而,分级是由病理学家手工进行的,与之相关的是大量的不确定性,表现为大的评估者间变异。先前的研究发现在识别最具侵袭性肿瘤(NHG 3)时一致性更高,而在区分NHG 1和2肿瘤时一致性较低。
中间组(NHG 2)占大约一半的患者人群,但与NHG 1和3相比,在形态学模式和生存结果方面表现出更大的变异。由于组织学分级在确定治疗方案中仍然处于核心位置,NHG 2组的异质性为决定个别患者的最佳治疗方案带来挑战。因此,已经提出了多种方法来解决这些不确定性,以减少过度治疗和治疗不足。基因表达分型已被用于将NHG 2肿瘤患者二分为不同结果的组。也有人建议完全取消NHG 2。包括Oncotype Dx和Prosigna在内的基因表达测验可以预测中间风险肿瘤患者的复发和死亡风险。然而,与基于组织病理学的诊断相比,分子诊断仍然昂贵且耗时。
数字病理学的出现和高分辨率全幅组织病理学图像(WSIs)的常规获取现在使得在标准临床设置中应用高级图像分析成为可能。人工智能的进步也为使用深度学习进行组织病理学图像分析开辟了新的机会。深度卷积神经网络(CNNs)最近已成功地用于检测和病理分类,涵盖多种癌症类型,包括乳腺癌。深度CNNs为基于常规组织病理学幻灯片图像的癌症诊断提供了成本效益的解决方案。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种基于深度学习的新方法,DeepGrade,用于基于数字化的苏木精和伊红(HE)染色的WSIs对乳腺癌进行组织学分级,特别关注于改善NHG 2肿瘤的预后分层。该模型针对NHG 1和NHG 3的形态学模式进行了开发分类,随后根据学习到的模式对NHG 2肿瘤进行重新分层。提出的模型已在关于患者结果的独立内部和外部测试数据中得到验证。
Results
结果
DeepGrade provides independent prognostic information for stratification of NHG 2 cases in the internal test set, where DG2-high showed an increased risk for recurrence (hazard ratio [HR] 2.94, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.24- 6.97, P ¼ 0.015) compared with the DG2-low group after adjusting for established risk factors (independent test data).DG2-low also shared phenotypic similarities with NHG 1, and DG2-high with NHG 3, suggesting that the model identifies morphological patterns in NHG 2 that are associated with more aggressive tumours. The prognostic value of DeepGrade was further assessed in the external test set, confirming an increased risk for recurrence in DG2-high (HR 1.91, 95% CI1.11-3.29, P ¼ 0.019).
DeepGrade为NHG 2例的分层提供了独立的预后信息,在内部测试集中,与DG2-低风险组相比,经调整已建立的风险因素后,DG2-高风险组显示出复发风险增加(风险比[HR] 2.94,95%置信区间[CI] 1.24-6.97,P=0.015)(独立测试数据)。DG2-低风险组也与NHG 1具有表型相似性,而DG2-高风险组则与NHG 3相似,这表明该模型识别了NHG 2中与更具侵袭性肿瘤相关的形态学模式。在外部测试集中进一步评估了DeepGrade的预后价值,确认了DG2-高风险组复发风险增加(HR 1.91,95% CI 1.11-3.29,P=0.019)。
Methods
方法
In this observational retrospective study, routine WSIs stained with haematoxylin and eosin from 1567 patients were utilised for model optimisation and validation. Model generalisability was further evaluated in an external test set with 1262 patients. NHG 2 cases were stratified into two groups, DG2-high and DG2-low, and the prognostic value was assessed. The main outcome was recurrence-free survival.
在这项观察性回顾性研究中,利用1567名患者的常规WSIs(用苏木精和伊红染色)进行模型优化和验证。模型的普适性进一步在包含1262名患者的外部测试集中进行评估。NHG 2例被分为两组,DG2-高风险组和DG2-低风险组,评估了预后价值。主要结果是无复发生存率。
Conclusions
结论
The proposed model-based strati fication of patients with NHG 2 tumours is prognostic and adds clinically relevant information over routine histological grading. The methodology offers a cost-effective alternative to molecular profiling to extract information relevant for clinical decisions. Key words: breast cancer, digital pathology, deep learning, artificial intelligence, histological grade
提出的基于模型的NHG 2肿瘤患者分层具有预后意义,并且在常规组织学分级的基础上增加了临床相关信息。该方法提供了一种成本效益高的替代方案,用于分子分型,以提取对临床决策相关的信息。
关键词:乳腺癌,数字病理学,深度学习,人工智能,组织学等级
Fig
图

Figure 1. Schematic overview of the optimisation, application and evaluation of the DeepGrade model.
Stained histopathology slides from breast cancer surgical specimens were scanned, tumour regions were segmented and image tiles were extracted. Patients with tumours graded as Nottingham histological grade (NHG) 1 and 3 were used to optimise the DeepGrade model, a convolutional neural network (CNN) ensemble including 20 base models. The DeepGrade model was subsequently applied to re-stratify NHG 2 cases. Finally, time-to-event analysis was applied to evaluate the prognostic performance. DG, DeepGrade; WSI, whole-slide histopathology image.
图1。DeepGrade模型优化、应用和评估的示意概览。
从乳腺癌手术标本中取得的染色组织病理学幻灯片被扫描,肿瘤区域被分割并提取图像瓦片。被评为诺丁汉组织学分级(NHG)1级和3级的肿瘤患者被用来优化DeepGrade模型,一个包括20个基础模型的卷积神经网络(CNN)集成体。随后,DeepGrade模型被应用于对NHG 2病例进行重新分层。最后,应用生存时间分析来评估预后性能。DG, DeepGrade;WSI, 全幅组织病理学图像。
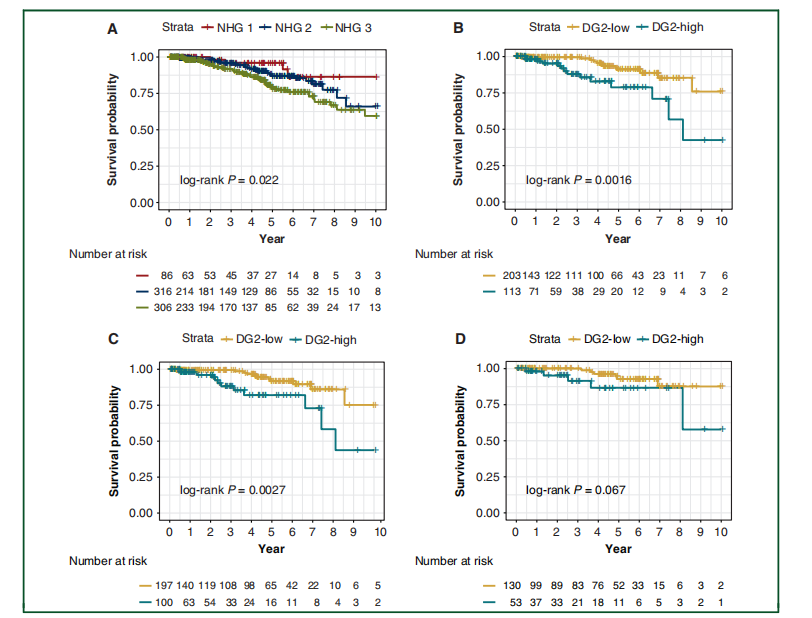
Figure 2. Recurrence-free survival outcomes for breast cancer patients by Nottingham histological grade, and by DeepGrade-re-stratified Nottingham histological grade (NHG) 2 patients. (A) KaplaneMeier curves for patients stratified by NHG 1-3. NHG 2 had an intermediate survival rate, whereas the NHG 3 had the worst prognosis. (B) KaplaneMeier curves for DeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 cases. Worse prognosis was observed in the DG2-high group. (C) KaplaneMeier curves for the DeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 ER-positive subgroup. (D) KaplaneMeier curves for the DeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 ER-positive and node-negative subgroup. DG, DeepGrade; ER, estrogen receptor.
图2。根据诺丁汉组织学分级以及通过DeepGrade重新分层的诺丁汉组织学分级(NHG)2级患者的乳腺癌患者无复发生存结果。(A) 根据NHG 1-3分层的患者的Kaplan-Meier曲线。NHG 2显示出中等的生存率,而NHG 3有最差的预后。(B) DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2病例的Kaplan-Meier曲线。在DG2-高风险组观察到更差的预后。(C) DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2 ER阳性亚组的Kaplan-Meier曲线。(D) DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2 ER阳性且淋巴结阴性亚组的Kaplan-Meier曲线。DG, DeepGrade; ER, 雌激素受体。
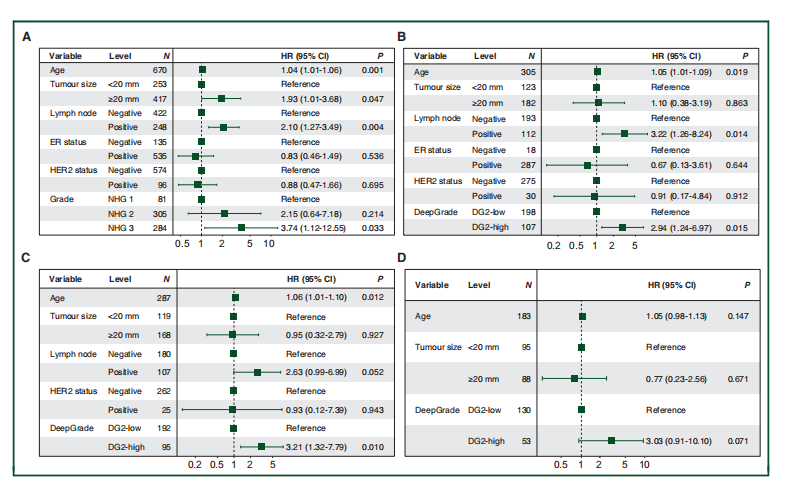
Figure 3. Forest plots from multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression. (A) Results from multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analysis of patients stratified by Nottingham histological grade (NHG) 1-3. NHG 2 was not significantly different from NHG 1, while the hazard ratio (HR) between NHG 1 and 3 was 3.74 (95% CI 1.12-12.55, P ¼ 0.033). (B) Results from multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analyses of DeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 cases. The estimated HR between DG2-low and DG2-high was 2.94 (95% CI 1.24-6.97,P ¼ 0.015). (C) Results from Cox proportional hazard regression in the DeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 ER-positive subgroup (HR 3.21, 95% CI 1.32-7.79, P ¼ 0.010). (D) Results from Cox proportional hazard regression of the DeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 ER-positive and node-negative subgroup (HR 3.03; 95% CI 0.91-10.10, P ¼ 0.071). All Cox proportional hazard models were adjusted for age, tumour size, lymph node metastases, ER status and HER2 status. CI, confidence interval; DG, DeepGrade; ER, estrogen receptor; HR, hazard ratio.
图3。多变量Cox比例风险回归的森林图。
(A) 根据诺丁汉组织学分级(NHG)1-3分层的患者的多变量Cox比例风险回归分析结果。NHG 2与NHG 1之间没有显著差异,而NHG 1与3之间的风险比(HR)为3.74(95% CI 1.12-12.55, P = 0.033)。(B) DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2病例的多变量Cox比例风险回归分析结果。估计的DG2-低与DG2-高之间的HR为2.94(95% CI 1.24-6.97, P = 0.015)。(C) DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2 ER阳性亚组的Cox比例风险回归结果(HR 3.21, 95% CI 1.32-7.79, P = 0.010)。(D) DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2 ER阳性且淋巴结阴性亚组的Cox比例风险回归结果(HR 3.03; 95% CI 0.91-10.10, P = 0.071)。所有Cox比例风险模型均根据年龄、肿瘤大小、淋巴结转移、ER状态和HER2状态进行了调整。CI, 置信区间;DG, DeepGrade;ER, 雌激素受体;HR, 风险比。
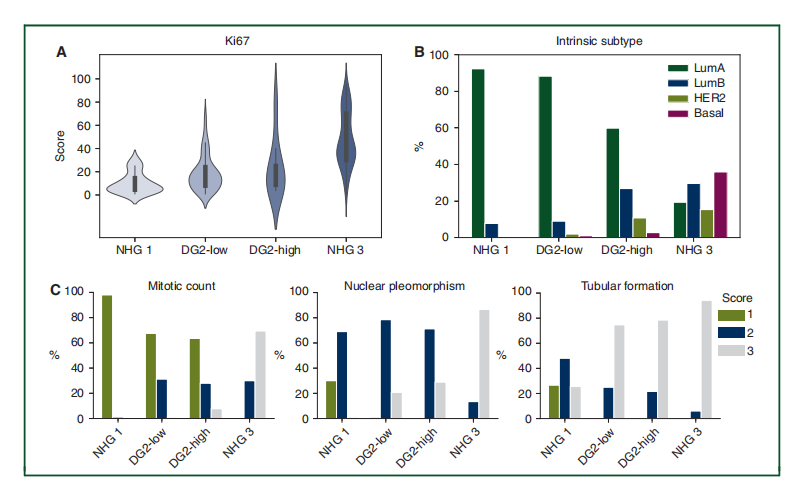
Figure 4. Ki67 score, intrinsic subtype distribution and NHG subcomponent score distribution across NHG 1, DG2-low and DG2-high, and NHG 3 patient groups.
(A) Violin plot showing distribution of Ki67 (data only available in ClinSeq-BC). The distribution was different between NHG 1 and DG2-low (P ¼ 2.80 10 3 , ManneWhitney U test), and different between DG2-high and NHG 3 (P ¼ 2.94 10 4 , ManneWhitney U test). No significant difference between DG2-low and DG2-high was observed (P ¼ 0.625, ManneWhitney U test). (B) Distribution of intrinsic subtypes. DG2-low was similar to NHG 1 with the majority being luminal A ( P ¼ 0.618, Fisher’s exact test). DG2-high has a larger proportion of HER2 and basal type compared with DG2-low. The subtype distribution for NHG 3 is signi ficantly different with DG2-high(P¼ 2.20 10 16, Fisher’s exact test). (C) Distribution of three NHG subcomponent scores with respect to mitotic count, nuclear polymorphism and tubular formation.Only the score for mitotic count was found to be signi ficantly different between DG2-low and DG2-high (P ¼ 6.54 10 3 , Fisher’s exact test). Basal, basal-like; DG,DeepGrade; Her2, Her2-enriched; LumA, luminal A; LumB, luminal B; NHG, Nottingham histological grade.
图4。Ki67评分、固有亚型分布和NHG亚组分数分布在NHG 1、DG2-低、DG2-高和NHG 3患者组中的分布。(A) 小提琴图显示Ki67的分布(数据仅在ClinSeq-BC中可用)。NHG 1与DG2-低之间的分布不同(P = 2.80 × 10^-3,Mann-Whitney U检验),DG2-高与NHG 3之间的分布也不同(P = 2.94 × 10^-4,Mann-Whitney U检验)。DG2-低与DG2-高之间未观察到显著差异(P = 0.625,Mann-Whitney U检验)。(B) 固有亚型的分布。DG2-低与NHG 1相似,大多数为Luminal A(P = 0.618,Fisher精确检验)。与DG2-低相比,DG2-高有更大比例的HER2和基底型。NHG 3的亚型分布与DG2-高显著不同(P = 2.20 × 10^-16,Fisher精确检验)。(C) 三个NHG亚组分数的分布,关于有丝分裂计数、核多态性和管状形成。只有有丝分裂计数的评分在DG2-低和DG2-高之间被发现显著不同(P = 6.54 × 10^-3,Fisher精确检验)。Basal, 基底样;DG, DeepGrade;Her2, Her2富集型;LumA, Luminal A;LumB, Luminal B;NHG, 诺丁汉组织学分级。
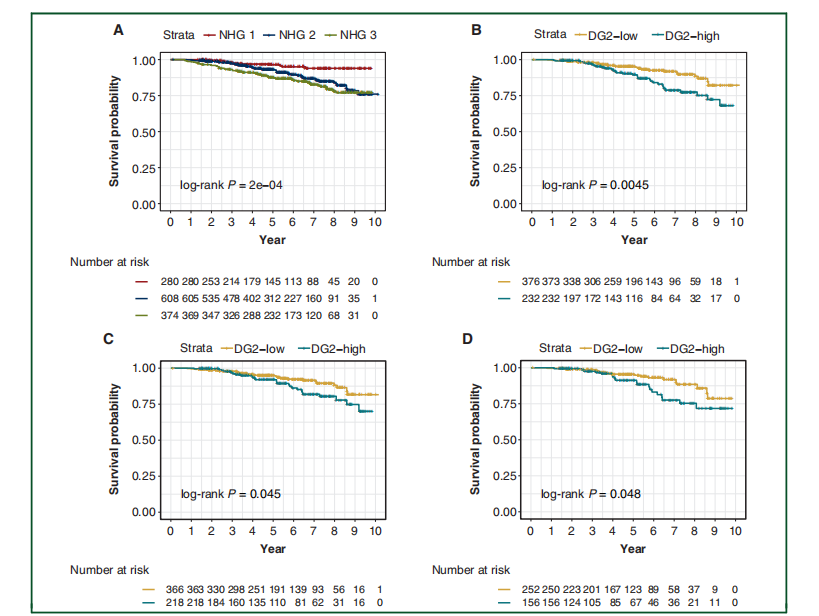
Figure 5. Recurrence-free survival outcomes for breast cancer patients from the external test set by Nottingham histological grade, and by DeepGrade re-stratified NHG 2 patients.(A) KaplaneMeier curves for patients stratified by NHG 1-3. NHG 2 had an intermediate survival rate, whereas the NHG 3 had the worst prognosis. (B) KaplaneMeier curves for DeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 cases. DG2-high displayed significantly worse prognosis compared with the DG2-low group. (C) KaplaneMeier curves for theDeepGrade-re-stratified NHG 2 ER-positive subgroup from the external test set. (D) KaplaneMeier curves for the DeepGrade re-stratified NHG 2 ER-positive and node negative subgroup from the external test set. DG, DeepGrade; ER, estrogen receptor; NHG, Nottingham histological grade.
图5。根据诺丁汉组织学分级以及通过DeepGrade重新分层的诺丁汉组织学分级(NHG)2级患者的外部测试集中乳腺癌患者的无复发生存结果。
(A) 根据NHG 1-3分层的患者的Kaplan-Meier曲线。NHG 2显示出中等的生存率,而NHG 3有最差的预后。(B) DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2病例的Kaplan-Meier曲线。与DG2-低风险组相比,DG2-高风险组显示出显著更差的预后。(C) 外部测试集中DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2 ER阳性亚组的Kaplan-Meier曲线。(D) 外部测试集中DeepGrade重新分层NHG 2 ER阳性且淋巴结阴性亚组的Kaplan-Meier曲线。DG, DeepGrade;ER, 雌激素受体;NHG, 诺丁汉组织学分级。
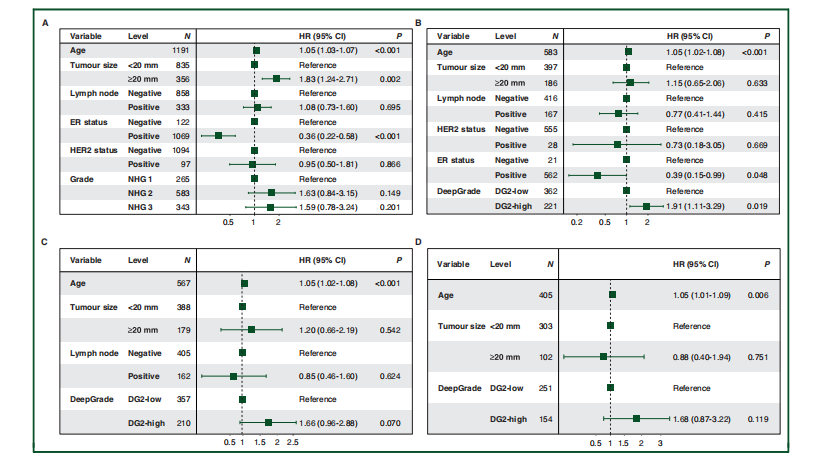
Figure 6. Forest plots from multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analysis in the external test set.(A) Stratification of all patients by routine NHG 1-3. (B) Stratification of NHG 2 cases by DeepGrade. (C) Stratification of patients in the NHG 2 and ER-positive subgroupsby DeepGrade. (D) Stratification of patients in the NHG 2, ER-positive and node-negative subgroups by DeepGrade. DG, DeepGrade; ER, estrogen receptor; NHG,Nottingham histological grade.
图6。外部测试集中多变量Cox比例风险回归分析的森林图。(A) 根据常规NHG 1-3对所有患者进行分层。(B) 通过DeepGrade对NHG 2病例进行分层。(C) 通过DeepGrade对NHG 2且ER阳性亚组的患者进行分层。(D) 通过DeepGrade对NHG 2、ER阳性且淋巴结阴性亚组的患者进行分层。DG, DeepGrade;ER, 雌激素受体;NHG, 诺丁汉组织学分级。
这篇关于文献速递:深度学习乳腺癌诊断---使用深度学习改善乳腺癌组织学分级的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





