本文主要是介绍边界检测方法总结,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1:经典的边界检测方法有sobel,拉普拉斯,canny等。
sobel:
def get_sobel(in_chan, out_chan):filter_x = np.array([[1, 0, -1],[2, 0, -2],[1, 0, -1],]).astype(np.float32)filter_y = np.array([[1, 2, 1],[0, 0, 0],[-1, -2, -1],]).astype(np.float32)filter_x = filter_x.reshape((1, 1, 3, 3))filter_x = np.repeat(filter_x, in_chan, axis=1)filter_x = np.repeat(filter_x, out_chan, axis=0)filter_y = filter_y.reshape((1, 1, 3, 3))filter_y = np.repeat(filter_y, in_chan, axis=1)filter_y = np.repeat(filter_y, out_chan, axis=0)filter_x = torch.from_numpy(filter_x)filter_y = torch.from_numpy(filter_y)filter_x = nn.Parameter(filter_x, requires_grad=False)filter_y = nn.Parameter(filter_y, requires_grad=False)conv_x = nn.Conv2d(in_chan, out_chan, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)conv_x.weight = filter_xconv_y = nn.Conv2d(in_chan, out_chan, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)conv_y.weight = filter_ysobel_x = nn.Sequential(conv_x, nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chan)) # 自定义修改卷积核的权重sobel_y = nn.Sequential(conv_y, nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chan))return sobel_x, sobel_ydef run_sobel(conv_x, conv_y, input):g_x = conv_x(input) # (1,1,15,20)g_y = conv_y(input) # (1,1,15,20)g = torch.sqrt(torch.pow(g_x, 2) + torch.pow(g_y, 2) + 1e-6).clone()return g
拉普拉斯:
self.laplacian_kernel = torch.tensor([-1, -1, -1, -1, 8, -1, -1, -1, -1],dtype=torch.float32).reshape(1, 1, 3, 3).requires_grad_(False).type(torch.cuda.FloatTensor)
2:《Holistically-nested edge detection》,HED经典的采用CNN进行边缘检测,通过边界损失进行约束。
论文地址
backbone的每一个输出后接一个side_output,输出通道为1,上采样到原图大小,GT进过提取边界后与上采样的side_output进行损失计算。
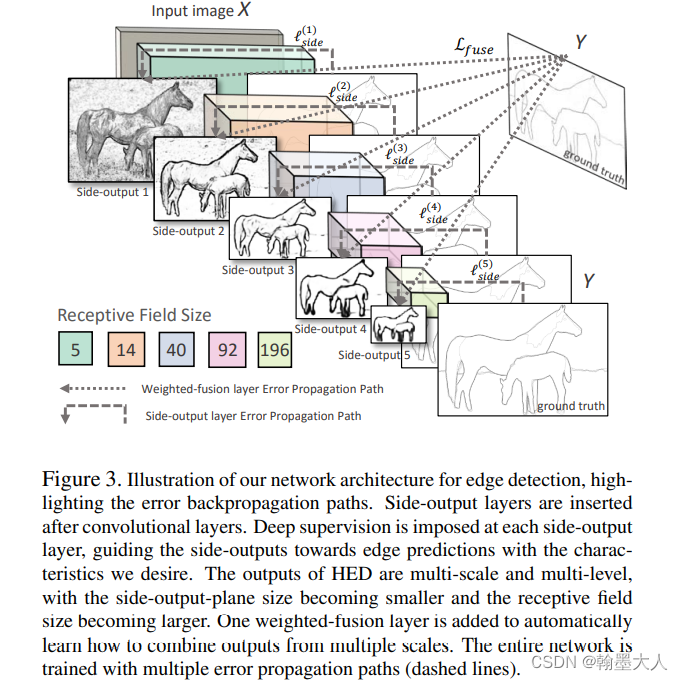
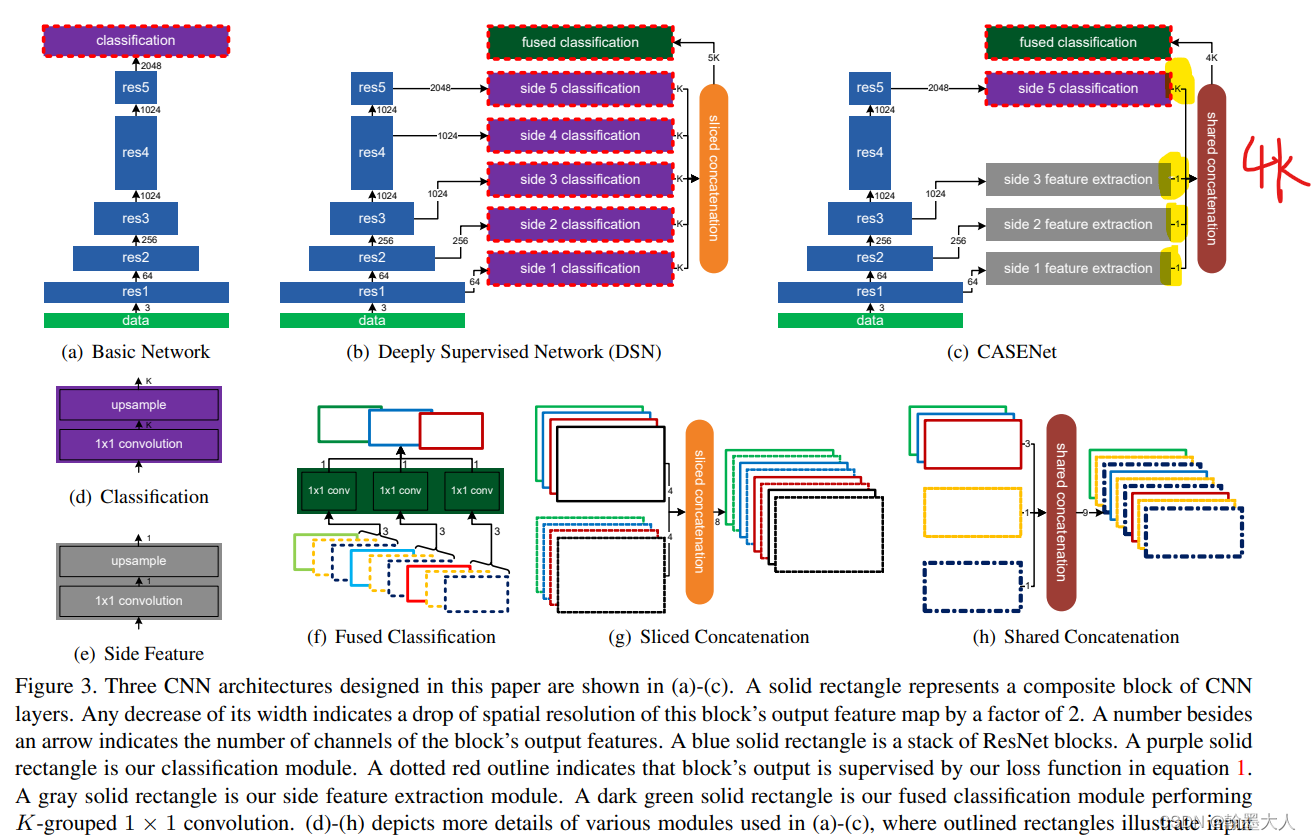
3:CASENet:CASENet: Deep Category-Aware Semantic Edge Detection
相比于多标签监督,CASENet采用了多类别即(category-aware)进行监督,考虑的是一个像素点可能同时属于多个类别,因此采用的不是one-hot编码,而是按RGB三通道的bit进行编码,在模型中前几个stage输出通道为1的边缘图,最后一个stage生成通道为num_class的特征图,然后通过slice_concat,将num_class的每一个通道与其他三个通道为1的特征图进行拼接,这样就有4num_class个通道,再经过融合层。
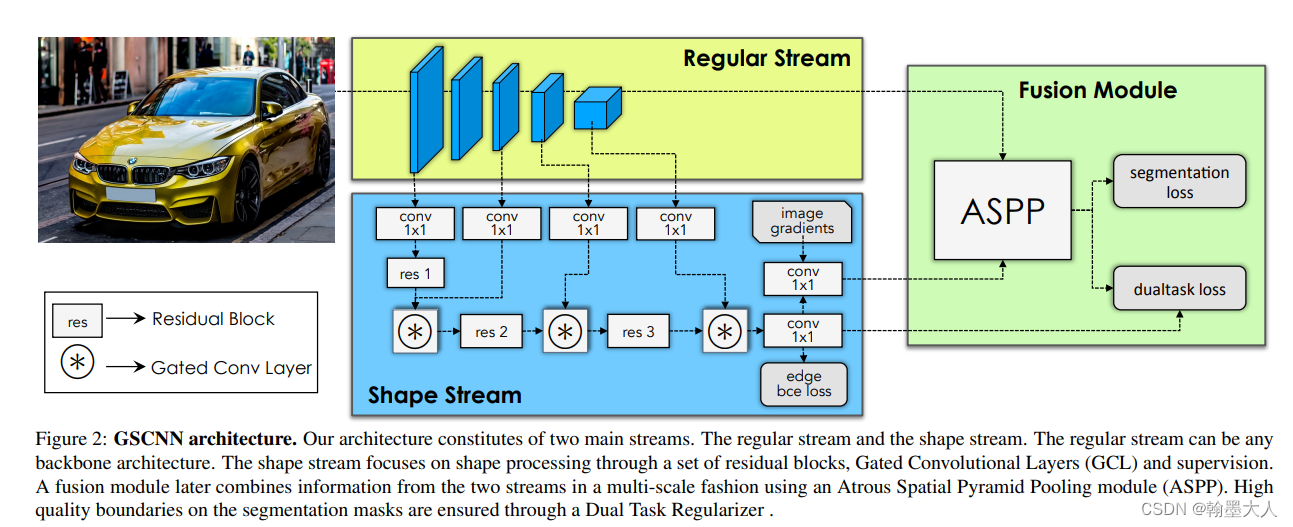
4:Gated-SCNN:Gated Shape CNNs for Semantic Segmentation
模型分为两条支路,regular stream和shape stream,shape stream只学习图像的shape信息,在shape分支通过edge bce loss进行约束,在regular通过segmentation loss进行约束。将第一个stage的输出,不断的和其他分支进行融合,最后输出通道为1的边界图,计算边界损失。和CASENet不同的是,每个side_output都不断地进行特征的交互。
5:基于CASENet*的结构,有很多的应用,比如SwinNet,FusionNet,BES-Net等。
5.1:
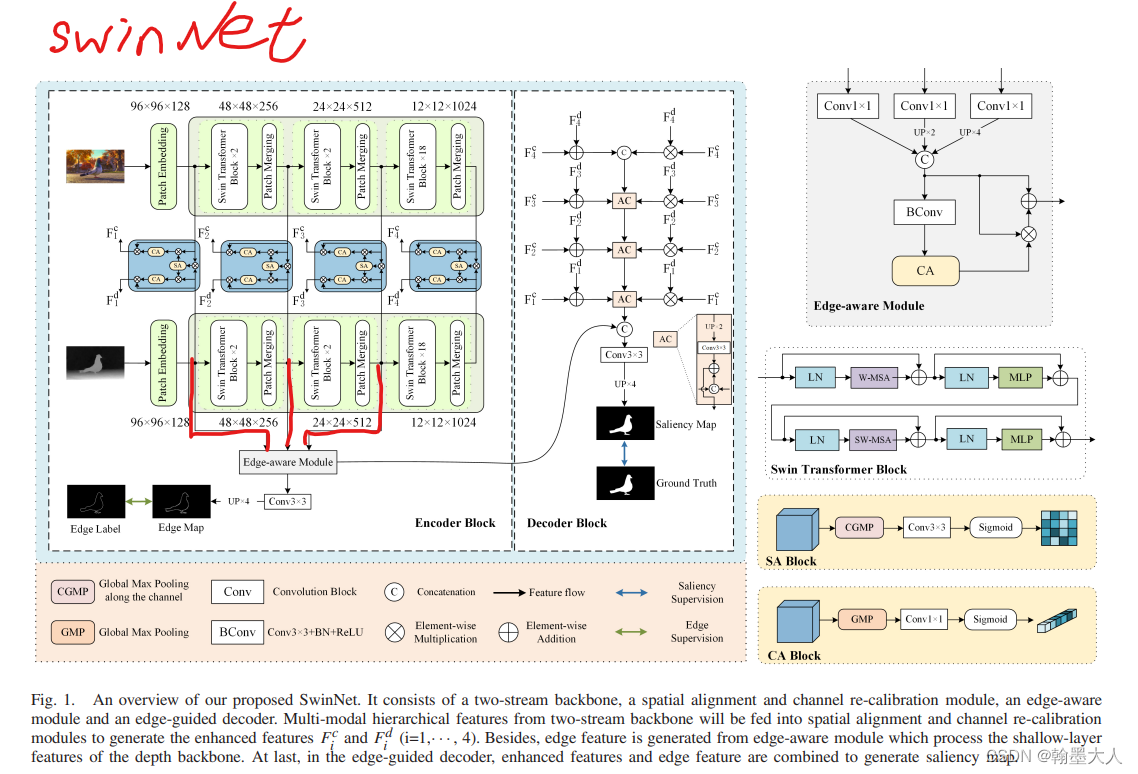
5.2:BES-Net: Boundary Enhancing Semantic Context Network for High-Resolution Image Semantic Segmentation和Pixel Difference Networks for Efficient Edge Detection
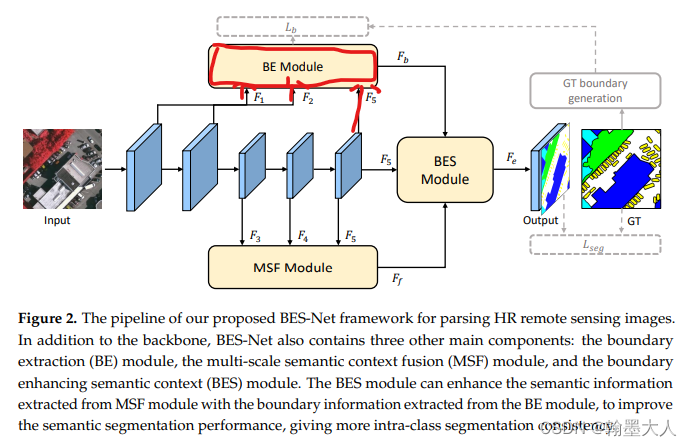
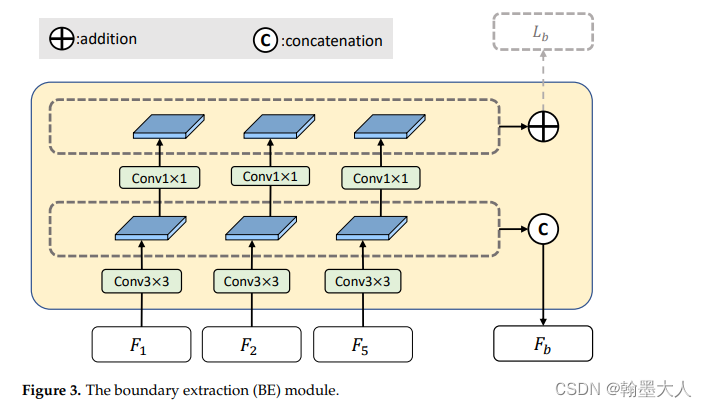
6:基于HED的有Pixel Difference Networks for Efficient Edge Detection,Boundary-Aware CNN for Semantic Segmentation
6.1:Pixel Difference Networks for Efficient Edge Detection:
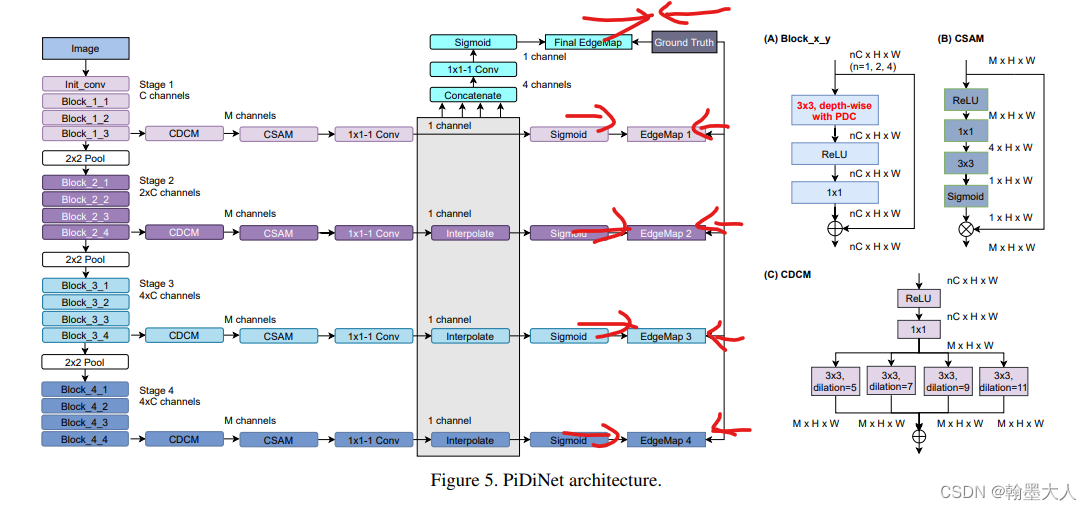
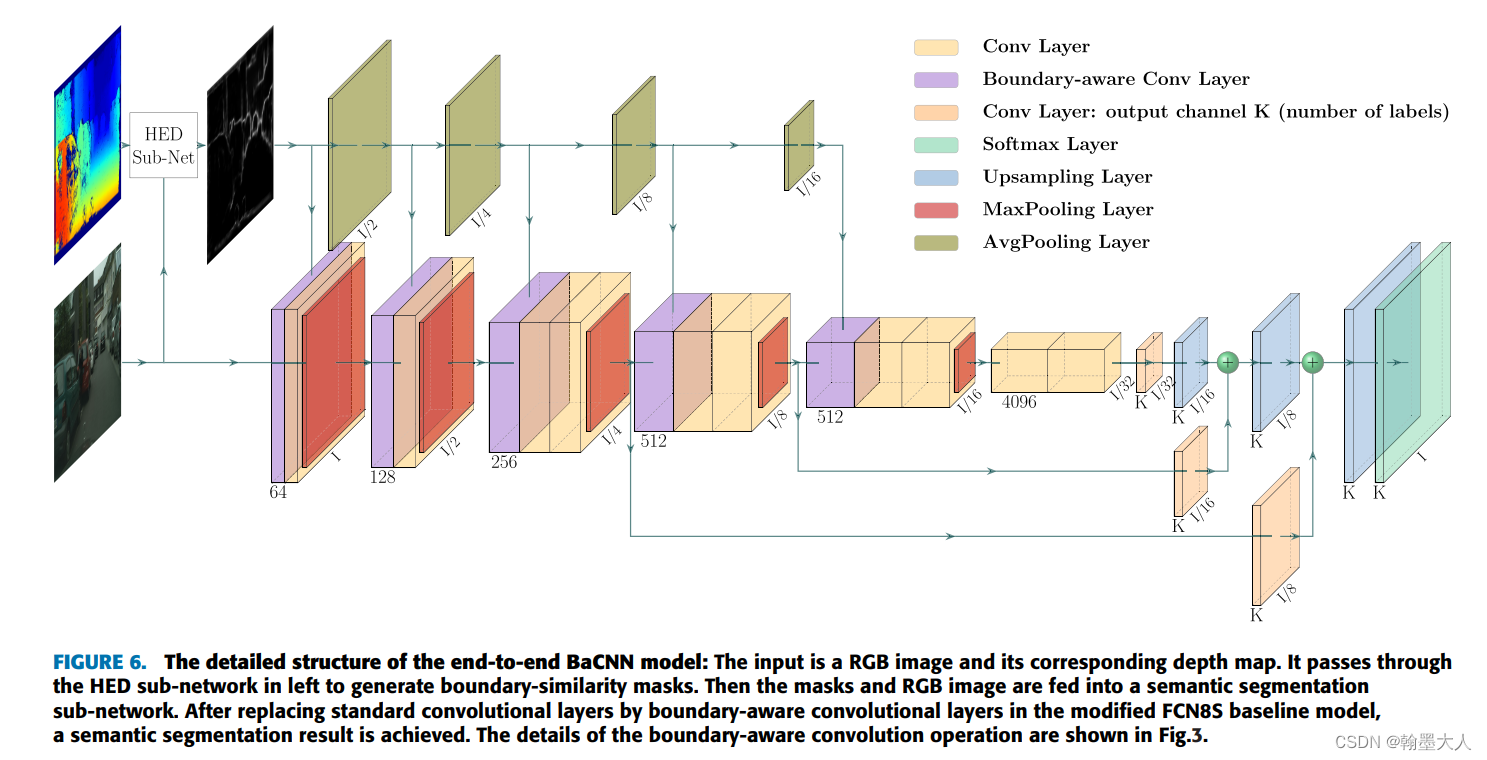
6.2:Boundary-Aware CNN for Semantic Segmentation:depth和RGB首先经过一个子网络HED,生成的边界图通过平均池化不断下采样和RGB分支融合,其中还提出了Boundary-Aware卷积,类似于depth-aware卷积
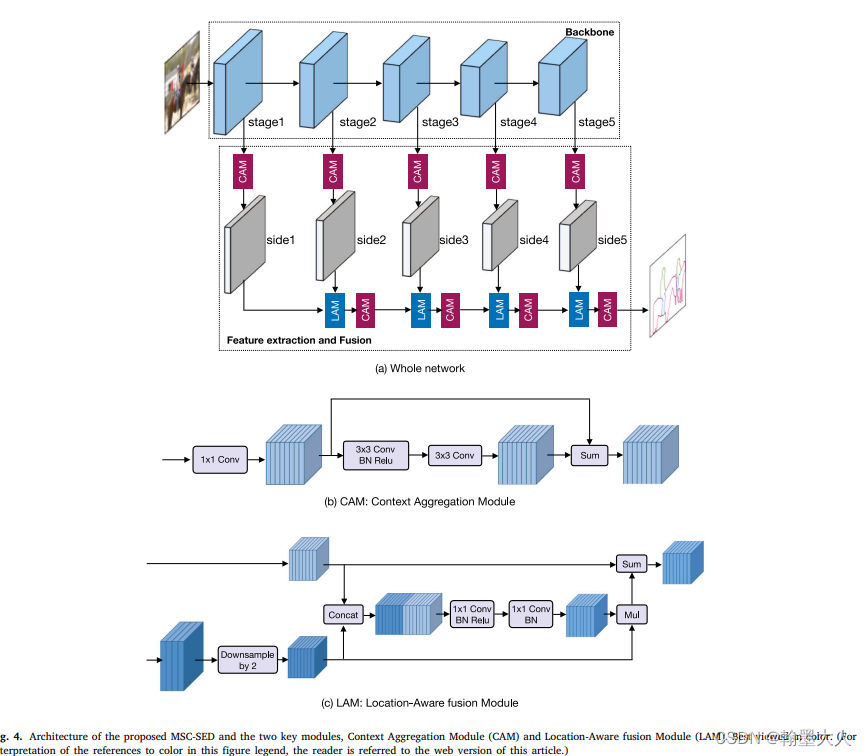
7:基于Gated-SCNN的有
7.1:Multi-scale spatial context-based semantic edge detection,通过CAM提取,通过LAM融合,其中LAM结构和Gated-SCNN的Gate-layer几乎一样。
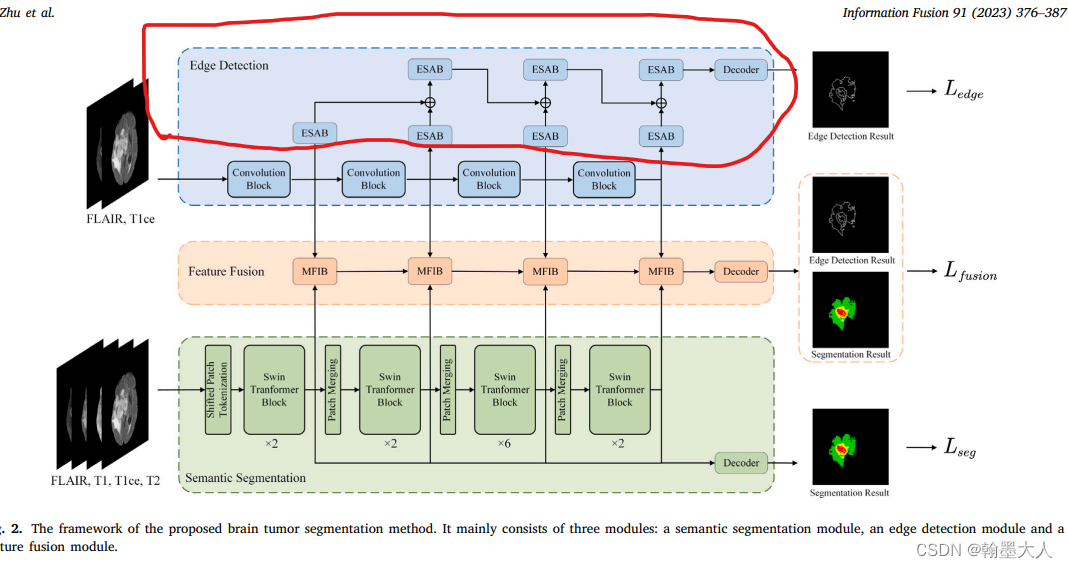
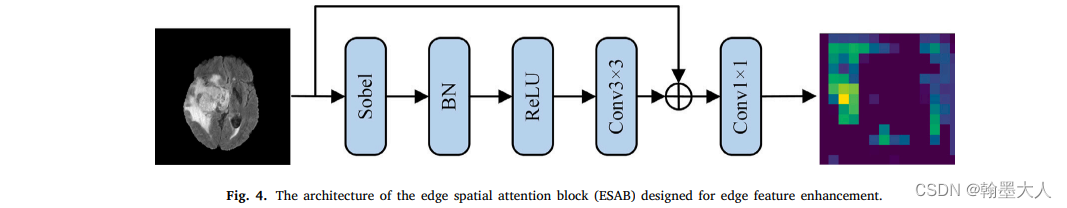
7.2:Brain tumor segmentation based on the fusion of deep semantics and edge information in multimodal MRI:
因为他图片是医学的核磁共振图像,对于图片的性质和特点不太理解。他结合了sobel和卷积进行边缘的提取。
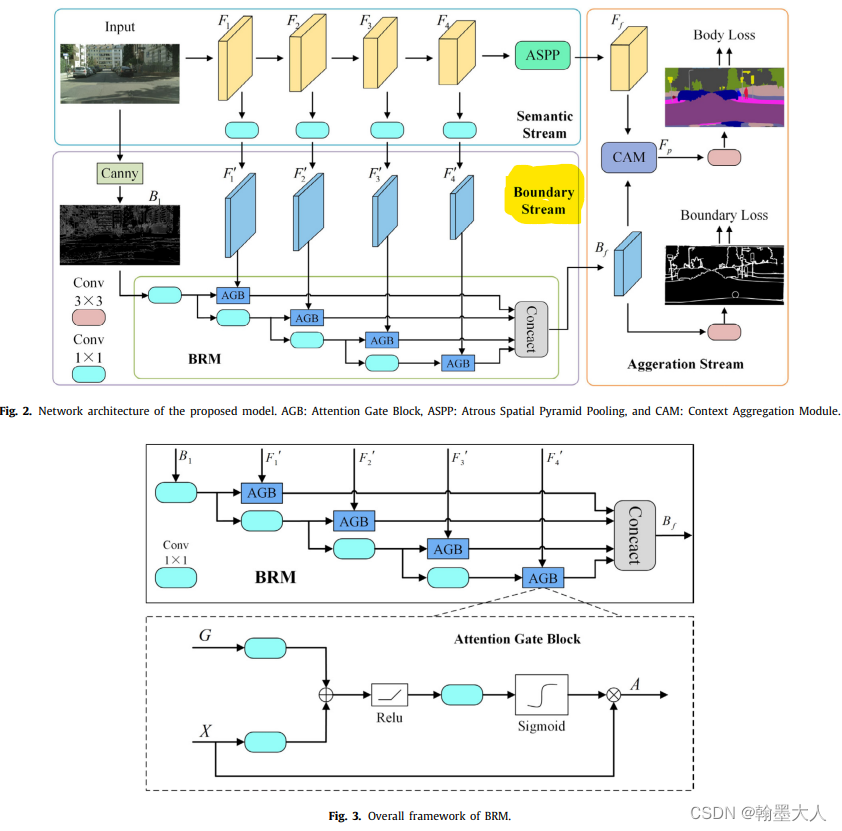
7.3:BASeg:也是两条分支,第二条分支开始是对RGB图进行Canny操作,然后和语义分支的每一个stage输出进行融合,最后和语义分支共同输入到CAM中,相当于边缘信息融合到语义信息中,使得最终的分割图可以有一个清晰的边缘。
这篇关于边界检测方法总结的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



