本文主要是介绍三、SpringBoot的日志--bilibili雷丰阳笔记,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
三、springboot与日志
抽象层 SLF4j 实现类logback
日志记录方法
给系统导入slf4j的jar和logback的jar
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;public class HelloWorld {public static void main(String[] args) {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);logger.info("Hello World");}
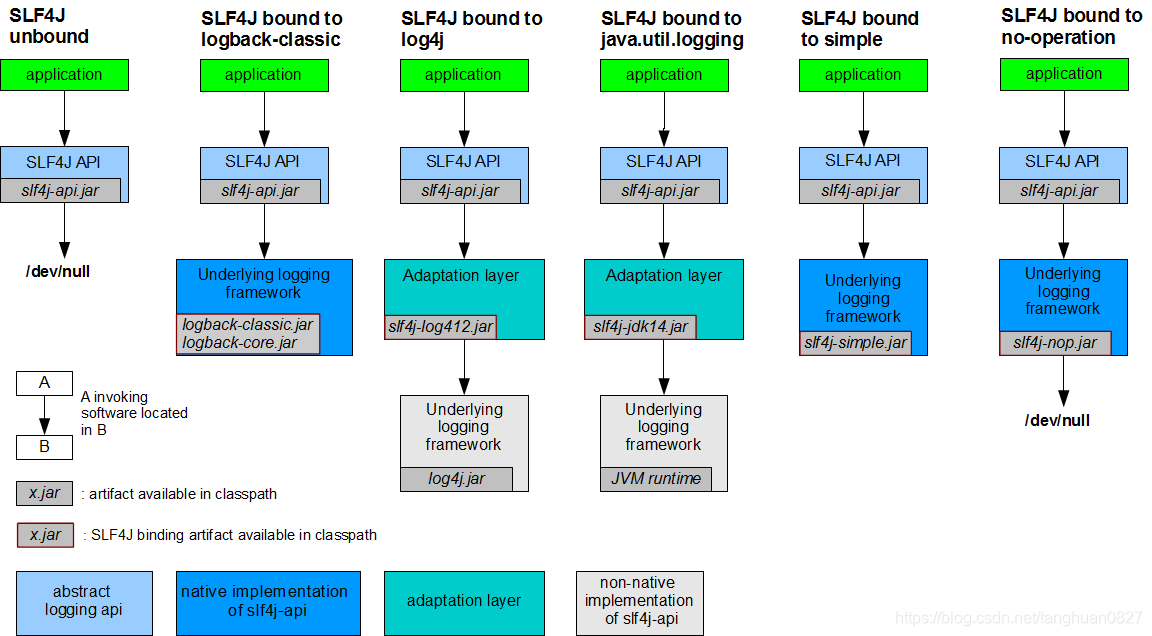
统一日志记录,即使别的框架
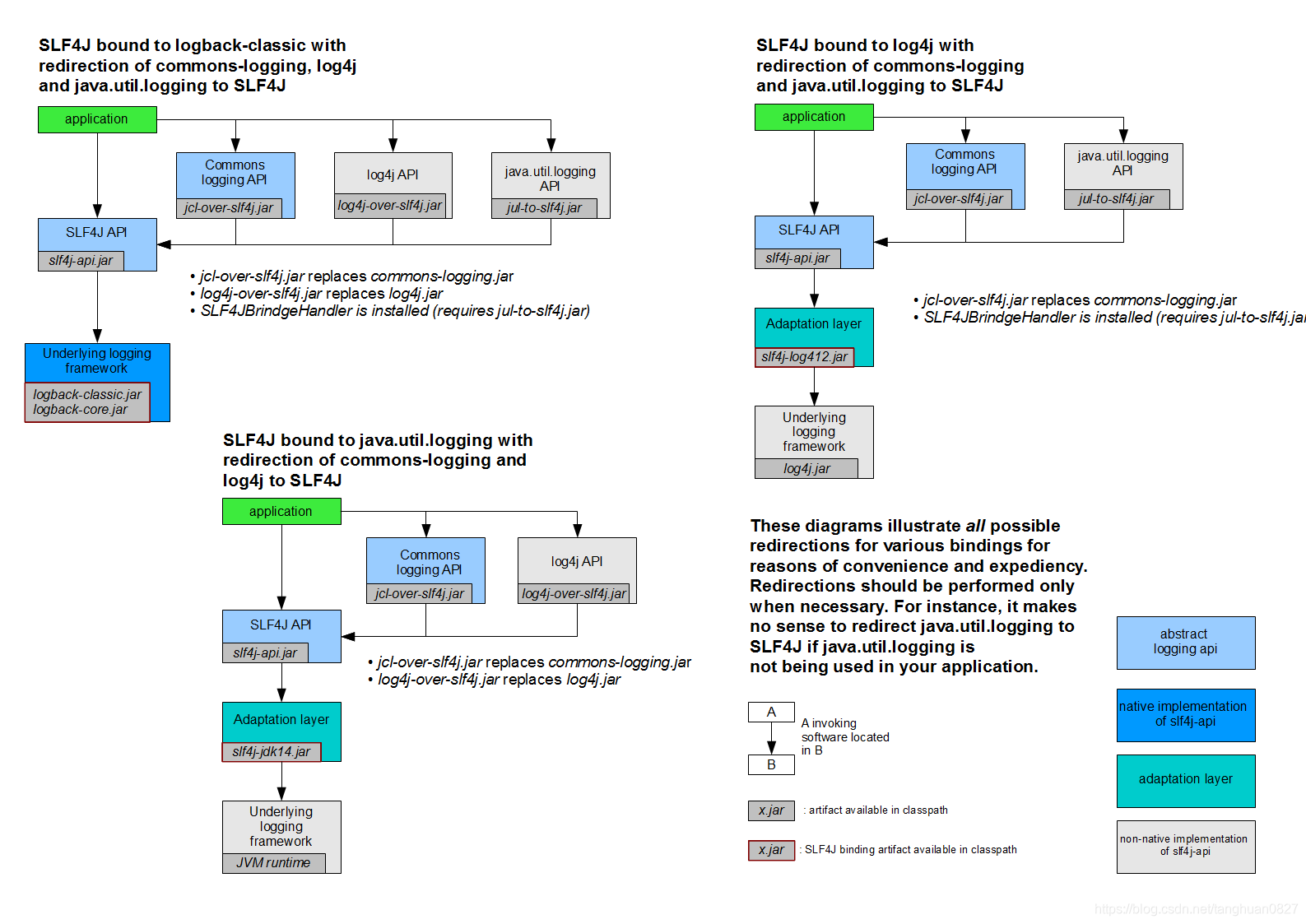
1 将系统中其他日志框架先排除
2 用中间包来替换原有的日志框架
3 我们导入slf4j其他的实现
idea中

springboot的底层方式 slf4j+log4j的方式

中间的转换包

我们要引入其他框架,一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉

适配器
/*** 在编码的时候进行容器注入*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBootApplicationTest {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());@Testpublic void contextLoads(){//日志级别logger.trace("这是trace日志");logger.debug("这是debug日志");logger.info("info日志");logger.warn("warn日志");logger.error("error日志");}
}
springboot默认日志级别是info
logging.level.com=trace
#logging.file=springboot.log
logging.file=d:/springboot.log
logging.path=/spring/log #在e:/根目录下logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level [%thread] %logger{15} - %msg%nlogging.pattern.file=
logging.file和logging.path取其一,一般logging.file为主
2、指定配置
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件:SpringBoot就不使用他默认配置
记录系统 定制
Logback logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml, or logback.groovy
Log4j2 log4j2-spring.xml or log4j2.xml
JDK (Java Util Logging) logging.properties
logback-spring.xml
<springProfile name="staging"><!-- configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active -->
</springProfile><springProfile name="dev | staging"><!-- configuration to be enabled when the "dev" or "staging" profiles are active -->
</springProfile><springProfile name="!production"><!-- configuration to be enabled when the "production" profile is not active -->
</springProfile>

spring.profiles.active=dev
文件名没有logback-spring.xml spring就报错
排除依赖

这篇关于三、SpringBoot的日志--bilibili雷丰阳笔记的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




