本文主要是介绍glibc-2.23 puts源码分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在分析puts代码之前先看一些基本的知识:
一些flag:
#define _IO_USER_BUF 1 /* User owns buffer; don't delete it on close. */
#define _IO_UNBUFFERED 2 /* 无缓冲,此时会使用_IO_FILE内部的shortbuf作为缓冲区 */
#define _IO_NO_READS 4 /* Reading not allowed */
#define _IO_NO_WRITES 8 /* Writing not allowd */
#define _IO_EOF_SEEN 0x10 //读到末尾了
#define _IO_ERR_SEEN 0x20 //出错了
#define _IO_DELETE_DONT_CLOSE 0x40 /* Don't call close(_fileno) on cleanup. */
#define _IO_LINKED 0x80 /* Set if linked (using _chain) to streambuf::_list_all.*/
#define _IO_IN_BACKUP 0x100 //不太明白这个
#define _IO_LINE_BUF 0x200 //行缓冲#define _IO_TIED_PUT_GET 0x400 /* Set if put and get pointer logicly tied. */#define _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING 0x800 //当前正在输出......什么时候会被设置.
#define _IO_IS_APPENDING 0x1000 //append fopen的时候mode里面有 +
#define _IO_IS_FILEBUF 0x2000 //不太明白
#define _IO_BAD_SEEN 0x4000 //出错了.#define _IO_USER_LOCK 0x8000 //有锁????
_IO_FILE结构 :
struct _IO_FILE {int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. *///高两字节是固定的magic,低两字节被用来储存flags/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. *//* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. *///读相关char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. *///写相关char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. *///缓冲区char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. *//* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */ //撤销操作???//什么时候会有撤销操作char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */struct _IO_marker *_markers;struct _IO_FILE *_chain; //File 链int _fileno; //fd文件描述符
#if 0int _blksize;
#elseint _flags2; //
#endif_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */#define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary *//* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */unsigned short _cur_column; //signed char _vtable_offset; //虚表偏移char _shortbuf[1]; //无缓冲的时候要用这个作为缓冲区./* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */_IO_lock_t *_lock; //🔒
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
vtable:
#ifdef _LIBC
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_do_write, _IO_do_write, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_attach, _IO_file_attach, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_close_it, _IO_file_close_it, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_finish, _IO_file_finish, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_fopen, _IO_file_fopen, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_init, _IO_file_init, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_setbuf, _IO_file_setbuf, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_sync, _IO_file_sync, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_overflow, _IO_file_overflow, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_seekoff, _IO_file_seekoff, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_underflow, _IO_file_underflow, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_write, _IO_file_write, GLIBC_2_1);
versioned_symbol (libc, _IO_new_file_xsputn, _IO_file_xsputn, GLIBC_2_1);
#endifconst struct _IO_jump_t _IO_file_jumps =
{JUMP_INIT_DUMMY,JUMP_INIT(finish, _IO_file_finish),JUMP_INIT(overflow, _IO_file_overflow),JUMP_INIT(underflow, _IO_file_underflow),JUMP_INIT(uflow, _IO_default_uflow),JUMP_INIT(pbackfail, _IO_default_pbackfail),JUMP_INIT(xsputn, _IO_file_xsputn),JUMP_INIT(xsgetn, _IO_file_xsgetn),JUMP_INIT(seekoff, _IO_new_file_seekoff),JUMP_INIT(seekpos, _IO_default_seekpos),JUMP_INIT(setbuf, _IO_new_file_setbuf),JUMP_INIT(sync, _IO_new_file_sync),JUMP_INIT(doallocate, _IO_file_doallocate),JUMP_INIT(read, _IO_file_read),JUMP_INIT(write, _IO_new_file_write),JUMP_INIT(seek, _IO_file_seek),JUMP_INIT(close, _IO_file_close),JUMP_INIT(stat, _IO_file_stat),JUMP_INIT(showmanyc, _IO_default_showmanyc),JUMP_INIT(imbue, _IO_default_imbue)
};puts函数
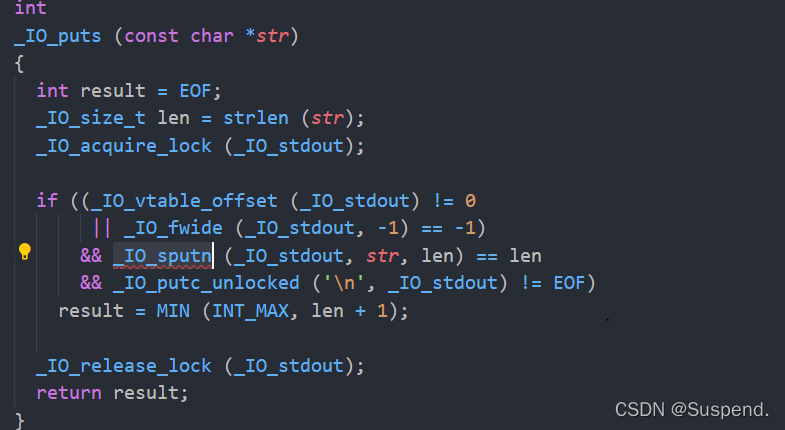
接着puts函数进入了_IO_sputn,看一下它的定义

是调用了vtable里面的 xsputn函数,从上面的那个结构体初始化可以看出,就是_IO_file_xsputn函数,也就是_IO_new_file_xsputn函数
转到_IO_new_file_xsputn函数看一下:
_IO_size_t _IO_new_file_xsputn (_IO_FILE *f, const void *data, _IO_size_t n)
{const char *s = (const char *) data;_IO_size_t to_do = n; //to_do是剩余要输出的长度int must_flush = 0; //标是否要输出缓冲区内容_IO_size_t count = 0; //输出缓冲区剩余部分大于 所要输出的长度if (n <= 0)return 0;if ((f->_flags & _IO_LINE_BUF) && (f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING)){count = f->_IO_buf_end - f->_IO_write_ptr;//看一下缓冲区剩余的空间还有多少,如果无法把data拷贝进去,那么会输出缓冲区内容,//这里是看一下把data可以全部拷贝到缓冲区的情况,若指定了行缓冲,那么就找一下是否存在\n,//存在的话就需要flush 输出缓冲区。if (count >= n){const char *p;for (p = s + n; p > s; ){if (*--p == '\n'){count = p - s + 1;must_flush = 1;break;}}}}else if (f->_IO_write_end > f->_IO_write_ptr)count = f->_IO_write_end - f->_IO_write_ptr; /* Space available. *//* Then fill the buffer. */if (count > 0){if (count > to_do) //先尽可能的把数据拷贝到缓冲区count = to_do;
#ifdef _LIBCf->_IO_write_ptr = __mempcpy (f->_IO_write_ptr, s, count);
#elsememcpy (f->_IO_write_ptr, s, count);f->_IO_write_ptr += count;
#endifs += count;to_do -= count;}if (to_do + must_flush > 0) //还有数据没有拷贝到缓冲区或者遇到了行缓冲,这时需要flush缓冲区,{_IO_size_t block_size, do_write;/* Next flush the (full) buffer. */if (_IO_OVERFLOW (f, EOF) == EOF) //flush 缓冲区,并且重置write_base,write_ptr,write_end指针./* If nothing else has to be written we must not signal thecaller that everything has been written. */return to_do == 0 ? EOF : n - to_do;/* Try to maintain alignment: write a whole number of blocks. */block_size = f->_IO_buf_end - f->_IO_buf_base;do_write = to_do - (block_size >= 128 ? to_do % block_size : 0);//block_size = 128;//剩余部分的大小 拆成 block_size * k + r.//do_write = block_size * kif (do_write){count = new_do_write (f, s, do_write); //大块输出,直接sys_write.to_do -= count;if (count < do_write)return n - to_do;}//除去整块大小剩余的部分,调用_IO_default_xsputn if (to_do)to_do -= _IO_default_xsputn (f, s+do_write, to_do); //把剩余的r 输出,(一定是小于 block_size )}return n - to_do;
}
代码逻辑比较简单,这里就不多说明了。
该函数里面调用了三个函数:
_IO_OVERFLOW (f, EOF) == EOFnew_do_write (f, s, do_write);_IO_default_xsputn (f, s+do_write, to_do);
继续分析这三个函数:
_IO_OVERFLOW :
这个实际上是调用了_IO_file_overflow函数,代码里面的名称是_IO_new_file_overflow,
可以由函数名大概猜出,该函数的就是用于当输出缓冲区满了的时候,继续写会溢出,所以要flush输出缓冲区,同样还有_IO_file_underflow函数是read时候缓冲区内容不够,重新往缓冲区读入数据
//溢出.
int _IO_new_file_overflow (_IO_FILE *f, int ch)
{//如果不可写的话直接返回,这个是flag是根据打开文件的方式而设置的if (f->_flags & _IO_NO_WRITES) /* SET ERROR */{f->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN;__set_errno (EBADF);return EOF;}///* If currently reading or no buffer allocated. */if ((f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING) == 0 || f->_IO_write_base == NULL){//这里目前还不太明白什么时候会调用他.........../* Allocate a buffer if needed. */if (f->_IO_write_base == NULL){_IO_doallocbuf (f);_IO_setg (f, f->_IO_buf_base, f->_IO_buf_base, f->_IO_buf_base);}/* Otherwise must be currently reading.If _IO_read_ptr (and hence also _IO_read_end) is at the buffer end,logically slide the buffer forwards one block (by setting theread pointers to all point at the beginning of the block). Thismakes room for subsequent output.Otherwise, set the read pointers to _IO_read_end (leaving thatalone, so it can continue to correspond to the external position). */if (__glibc_unlikely (_IO_in_backup (f))){size_t nbackup = f->_IO_read_end - f->_IO_read_ptr;_IO_free_backup_area (f);f->_IO_read_base -= MIN (nbackup,f->_IO_read_base - f->_IO_buf_base);f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_read_base;}if (f->_IO_read_ptr == f->_IO_buf_end)f->_IO_read_end = f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_buf_base;f->_IO_write_ptr = f->_IO_read_ptr;f->_IO_write_base = f->_IO_write_ptr;f->_IO_write_end = f->_IO_buf_end;f->_IO_read_base = f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_read_end;f->_flags |= _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING;if (f->_mode <= 0 && f->_flags & (_IO_LINE_BUF | _IO_UNBUFFERED))f->_IO_write_end = f->_IO_write_ptr;}if (ch == EOF)return _IO_do_write (f, f->_IO_write_base,f->_IO_write_ptr - f->_IO_write_base);//把缓冲区现有的数据输出.if (f->_IO_write_ptr == f->_IO_buf_end ) /* Buffer is really full */if (_IO_do_flush (f) == EOF)return EOF;*f->_IO_write_ptr++ = ch;if ((f->_flags & _IO_UNBUFFERED)|| ((f->_flags & _IO_LINE_BUF) && ch == '\n'))if (_IO_do_write (f, f->_IO_write_base,f->_IO_write_ptr - f->_IO_write_base) == EOF)return EOF;return (unsigned char) ch;
}
_IO_do_write代码:
int _IO_new_do_write (_IO_FILE *fp, const char *data, _IO_size_t to_do)
{return (to_do == 0|| (_IO_size_t) new_do_write (fp, data, to_do) == to_do) ? 0 : EOF;
}static _IO_size_t new_do_write (_IO_FILE *fp, const char *data, _IO_size_t to_do)
{_IO_size_t count;if (fp->_flags & _IO_IS_APPENDING)fp->_offset = _IO_pos_BAD;else if (fp->_IO_read_end != fp->_IO_write_base){_IO_off64_t new_pos = _IO_SYSSEEK (fp, fp->_IO_write_base - fp->_IO_read_end, 1);if (new_pos == _IO_pos_BAD) return 0;fp->_offset = new_pos;}count = _IO_SYSWRITE (fp, data, to_do);if (fp->_cur_column && count)fp->_cur_column = _IO_adjust_column (fp->_cur_column - 1, data, count) + 1;_IO_setg (fp, fp->_IO_buf_base, fp->_IO_buf_base, fp->_IO_buf_base);fp->_IO_write_base = fp->_IO_write_ptr = fp->_IO_buf_base;fp->_IO_write_end = (fp->_mode <= 0&& (fp->_flags & (_IO_LINE_BUF | _IO_UNBUFFERED))? fp->_IO_buf_base : fp->_IO_buf_end);return count;
}
_IO_default_xsputn 代码 (这个函数会把数据拷贝到缓冲区,然后在缓冲区满的时候flush缓冲区,直到把全部数据拷贝到缓冲区):
_IO_size_t _IO_default_xsputn (_IO_FILE *f, const void *data, _IO_size_t n)
{const char *s = (char *) data;_IO_size_t more = n;if (more <= 0)return 0;for (;;){/* Space available. */if (f->_IO_write_ptr < f->_IO_write_end) {_IO_size_t count = f->_IO_write_end - f->_IO_write_ptr;if (count > more)count = more;//数量不同的时候使用不同的拷贝方式if (count > 20){
#ifdef _LIBCf->_IO_write_ptr = __mempcpy (f->_IO_write_ptr, s, count);
#elsememcpy (f->_IO_write_ptr, s, count);f->_IO_write_ptr += count;
#endifs += count;}else if (count){char *p = f->_IO_write_ptr;_IO_ssize_t i;for (i = count; --i >= 0; )*p++ = *s++;f->_IO_write_ptr = p;}more -= count;}//if (more == 0 || _IO_OVERFLOW (f, (unsigned char) *s++) == EOF)break;more--;}return n - more;
}
emmmmmm貌似只是把代码抄了一次…突然发现C语言的文件操作有很多不明白的地方…还是去看一下的C语言的文件操作,之后应该就能看懂代码为什么要这样写了…
这篇关于glibc-2.23 puts源码分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






