本文主要是介绍Servlet,Spring,Spring Boot,Sprint Batch,ThymeLeaf 学习,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
■Spring boot 之 HelloWorld
■Servlet
1.ServletContextListener接口
2.@WebListener
3.@WebServlet
4.xxx
5.xxx
■Spring
1.Spring 中的标注
2.原始的Spring配置 之 web.xml 中的 ContextLoaderListener
3.原始的Spring配置 之 web.xml 中指定 ApplicationContext.xml
4.ApplicationContext.xml
5.pom
6.n年以前,毕业设计的【applicationContext.xml】
7.n年以前,毕业设计的【web.xml】
8.xxx
9.xxx
■Spring全家桶
1.SpringBoot 和 SpringMVC的区别
2.Spring boot 和 Spring MVC 直接有什么关系
3.Spring Boot和Spring MVC 之间, 谁包含谁
4.Spring MVC代码示例
5.xxx
6.xxx
7.xxx
■Spring Boot 学习
1.Spring Boot 介绍1
2.Spring Boot 介绍2
3.yml配置文件1
4.yml配置文件2
5.SpringBoot使用jasypt加解密密码
6. YML 中秘密加密 jasypt
7. YML 中数据库连接配置
8. 启动类
9.配置文件的【加载】与【加载顺序】
■Spring Batch
■Spring 标注
1.@SessionAttributes(names = "user")
2.@ModelAttribute(“user”)
3.@RequestParam
GET请求时
POST请求时
4.pringMVC在调用方法前会创建一个隐含的数据模型
5.标注: @GetMapping("/getuserinfo") @PathVariable
★★★前台 ThymeLeaf
6.接口:Model:从控制层直接返回前端所需的数据
7.检证相关
7.0.需要使用到 @Validated 检证时,Bean对象的定义 使用 @NotNull @Size 等等
7.2.代码示例:@NotNull @Validated BindingResult
7.3.@NotNull @Size @Length @Max 等等
8.标注:@Component @Scope
9.标注:@Repository @Service @Controller
10.标注:@Scope("prototype")
11.标注:@Autowired (Spring) 和、 @Resource 和、 @Inject(JSR330)
13.标注:@Configuration 和 @Bean
14.标注:@ConfigurationProperties
15.@value{“¥{AAA.BBB.CCC}”}
15.1.@Value(“${xxxx}”) 与@Value(“#{}”)
16.@PostConstruct
17.★★★知识点★★★ :在SpringBoot开发中,当一个接口A (IPerson)有多个实现类时,spring会很智能的将bean注入到List<A>或Map<String,A>变量中
18.@Configuration @Bean @Primary @ConfigurationProperties
19.@Transactional @Service
19.1.@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITED) 事务隔离级别
19.2.@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) 事务传播
19.3.@Transactional(readOnly = true)
20.@Component @Value
21.REST 与 RESTful API
21.0.REST
21.1.RESTful API
21.2.URL设计规范
★★★知识点★★★: Spring中的HTTP通信
RestTemplate 代理设置
21.3.RestTemplate (在程序内部发生http请求,访问一些程序提供的WebAPI)
21.4. 使用RestTemplate的exchange()方法时,参数HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, Object>>
22.控制层
22.1.@Controller @ResponseBody @RestController @RequestMapping("/user")
22.2.@Controller @SessionAttributes @PostConstruct @Autowired @Qualifier @GetMapping @ModelAttribute
22.3.@RequestMapping @GetMapping @PostMapping
22.4.@ResponseBody 和 @RequestBody 的使用
23.@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement @MapperScan
24.★★★知识点★★★ :自动装配
为什么SpringBoot中不需要使用@EnableTransactionManagement就能使用事务?
25.@Mapper @MapperScan 和IBatis相关的接口类 @Repository
和IBatis相关的接口类
@Mapper
@Repository
@MapperScan
26.AOP
26.1.@Configuration @ComponentScan @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
26.2@Component @Aspect @Pointcut @Before @After @Around
27.Junit
27.1.@SpringBootTest @DisplayName("Test Junit") @TestExecutionListeners @ActiveProfiles("dev")
27.2.@MockBean @SpyBean @Mock @Spy @BeforeEach @AfterEach
27.3.@Test @DatabaseSetup(value = "/xxx/xxx/input.xml") @ExpectedDatabase(value = "/xxx/xxx/xxx.xml")
28.1.@SpringBootApplication注解背后 @Configuration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan
28.2.Spring 的 @import 和 @ComponentScan 在功能上有什么区别
29.元注解 @Retention @Target @Inherited
30.★★★知识点★★★ :spring.batch.job.enabled 配置用于启动时是否创建JobLauncherCommandLineRunner
@TestPropertySource(properties = { "spring.batch.job.enabled=false" }) 或 -Dspring.batch.job.enabled=false
扩展,SpringBatch的9个Table
扩展,SpringBatch的启动过程
31.@ControllerAdvice @Order(1) 类 ResponseBodyAdvice
@ControllerAdvice
@order
类:ResponseBodyAdvice
32.@Alias // ibatis 的标注
33.@param // ibatis 的标注
为什么要使用@Param
34.★★★ 知识点★★★ :OncePerRequestFilter与Filter的区别
35.XXX
36.XXX
37.xxxx
====
■Spring boot 之 HelloWorld
1. springBoot
SpringBoot之HelloWorld_sun0322-CSDN博客
2. SpringBoot + ThymeLeaf
SpringBoot + Thymeleaf 之 HelloWorld_sun0322-CSDN博客
3. SpringBoot + MyBatis
SpringBoot + MyBatis 之 Hello World_sun0322-CSDN博客
■Servlet
====
1.ServletContextListener接口
创建一个类实现
javax.servlet.ServletContextListener接口并重写contextInitialized方法,该方法会在Web应用启动时被调用。在该方法中,你可以执行你想要在服务启动时加载的逻辑。
比如
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener {@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {// 这里写你想要在服务启动时加载的逻辑}@Overridepublic void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {// 服务关闭时的逻辑}
}====
在web.xml中配置该监听器。找到web.xml文件,添加以下代码:
<listener><listener-class>你的包名.MyServletContextListener</listener-class> <!-- 修改为你的类的全限定名 -->
</listener>2.@WebListener
注意:在最新的Servlet规范和Servlet 3.0之后,你还可以使用注解的方式配置
ServletContextListener。你可以在想要加载的类上添加@WebListener注解,并将其放置在类上方。===
这种方式更简洁,并且不需要在
web.xml中进行配置。无论是使用
web.xml配置还是使用注解配置ServletContextListener,都可以达到在Web服务启动时加载某个类的目的。
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;@WebListener
public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener {@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {// 这里写你想要在服务启动时加载的逻辑}@Overridepublic void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {// 服务关闭时的逻辑}
}xx'x
3.@WebServlet
@WebServlet注解是Servlet 3.0规范引入的一种简化Servlet配置的方式。使用@WebServlet注解,你可以将一个类声明为一个Servlet,并指定它的URL映射和其他配置属性。使用
@WebServlet注解,你无需在web.xml中进行Servlet的配置,可以直接在Servlet类的文件中使用注解进行配置。这样简化了代码结构,并提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。
下面是一个使用@WebServlet注解的示例:
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;@WebServlet(name = "MyServlet", urlPatterns = {"/myservlet"})
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {// 处理GET请求的逻辑}protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {// 处理POST请求的逻辑}
}在上面的示例中,
@WebServlet注解指定了该类为一个Servlet,并用name属性指定了Servlet的名称为"MyServlet",用urlPatterns属性指定了URL映射为"/myservlet"。===
name属性是可选的,可以不指定。但urlPatterns属性是必需的,需要指定至少一个URL映射。===
另外,
@WebServlet注解还可以配置其他属性,如loadOnStartup属性用于指定Servlet的加载顺序、initParams属性用于指定Servlet的初始化参数等。==
使用
@WebServlet注解能够简化Servlet的配置,提高了开发效率,并且更加直观地描述了Servlet的属性和行为。
xxxx
4.xxx
xxx
5.xxx
xxx
===
■Spring
Spring5:@Autowired注解、@Resource注解和@Service注解 - 哈哈呵h - 博客园
Spring的@Service注解的用法_奋斗鱼-CSDN博客
1.Spring 中的标注
https://www.cnblogs.com/smallJunJun/p/11003813.html
=======
1.1.@componet
类定义时,使用此标注(表面,此类的创建等,都交给Spring容器管理)
1.2.
@autowired
引用类时,标注后,无需new,直接使用
=======
1.3.
@ConfigurationProperties
Spring之@ConfigurationProperties注解_明洋的专栏-CSDN博客
springboot中的@mapper标注
1、为了不用再写一次mapper映射文件
2、将mapper交给Spring管理
3、给mapper接口自动生成一个接口实现类和数据库使用相关。
mybatis的xml文件还是要自己定义的。(只是不需要写接口的实现类了)
2.原始的Spring配置 之 web.xml 中的 ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener的作用就是启动Web容器时,自动装配ApplicationContext.xml的配置信息。
在web.xml种这样配置
<listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>因为它实现了ServletContextListener这个接口,在web.xml配置这个监听器,启动容器时,就会默认执行它实现的方法。
ContextLoaderListener是Spring中的核心监听器,当web工程启动时,
该监听器负责创建Spring的IOC容器,存放在ServletContext中;当需要用IOC容器时,就从ServletContext中获取。
好处:
1、不用我们手动创建IOC容器,由监听器负责创建;
2、可以保证整个工程中只有一个IOC容器;
===
====
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-web</artifactId><version>5.2.14.RELEASE</version></dependency>===
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors.package org.springframework.web.context;import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;/*** Bootstrap listener to start up and shut down Spring's root {@link WebApplicationContext}.* Simply delegates to {@link ContextLoader} as well as to {@link ContextCleanupListener}.** <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code ContextLoaderListener} supports injecting the root web* application context via the {@link #ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)}* constructor, allowing for programmatic configuration in Servlet 3.0+ environments.* See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples.** @author Juergen Hoeller* @author Chris Beams* @since 17.02.2003* @see #setContextInitializers* @see org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer*/
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {/*** Create a new {@code ContextLoaderListener} that will create a web application* context based on the "contextClass" and "contextConfigLocation" servlet* context-params. See {@link ContextLoader} superclass documentation for details on* default values for each.* <p>This constructor is typically used when declaring {@code ContextLoaderListener}* as a {@code <listener>} within {@code web.xml}, where a no-arg constructor is* required.* <p>The created application context will be registered into the ServletContext under* the attribute name {@link WebApplicationContext#ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE}* and the Spring application context will be closed when the {@link #contextDestroyed}* lifecycle method is invoked on this listener.* @see ContextLoader* @see #ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)* @see #contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent)* @see #contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent)*/public ContextLoaderListener() {}/*** Create a new {@code ContextLoaderListener} with the given application context. This* constructor is useful in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based* registration of listeners is possible through the {@link javax.servlet.ServletContext#addListener}* API.* <p>The context may or may not yet be {@linkplain* org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() refreshed}. If it* (a) is an implementation of {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} and* (b) has <strong>not</strong> already been refreshed (the recommended approach),* then the following will occur:* <ul>* <li>If the given context has not already been assigned an {@linkplain* org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#setId id}, one will be assigned to it</li>* <li>{@code ServletContext} and {@code ServletConfig} objects will be delegated to* the application context</li>* <li>{@link #customizeContext} will be called</li>* <li>Any {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer ApplicationContextInitializer org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer ApplicationContextInitializers}* specified through the "contextInitializerClasses" init-param will be applied.</li>* <li>{@link org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh refresh()} will be called</li>* </ul>* If the context has already been refreshed or does not implement* {@code ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}, none of the above will occur under the* assumption that the user has performed these actions (or not) per his or her* specific needs.* <p>See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples.* <p>In any case, the given application context will be registered into the* ServletContext under the attribute name {@link* WebApplicationContext#ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE} and the Spring* application context will be closed when the {@link #contextDestroyed} lifecycle* method is invoked on this listener.* @param context the application context to manage* @see #contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent)* @see #contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent)*/public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {super(context);}/*** Initialize the root web application context.*/@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());}/*** Close the root web application context.*/@Overridepublic void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());}}
===
3.原始的Spring配置 之 web.xml 中指定 ApplicationContext.xml
在web.xml种这样配置
<context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
Spring初始化:org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener的作用__大白_的博客-CSDN博客
===
4.ApplicationContext.xml
例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置实例(id:“唯一标识” class="需要被创建的目标对象全限定名") --><bean id="userService" class="com.itranswarp.learnjava.service.UserService"><property name="mailService" ref="mailService" /></bean><bean id="mailService" class="com.itranswarp.learnjava.service.MailService" />
</beans>
===
5.pom
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-web</artifactId><version>5.2.14.RELEASE</version></dependency>====
6.n年以前,毕业设计的【applicationContext.xml】
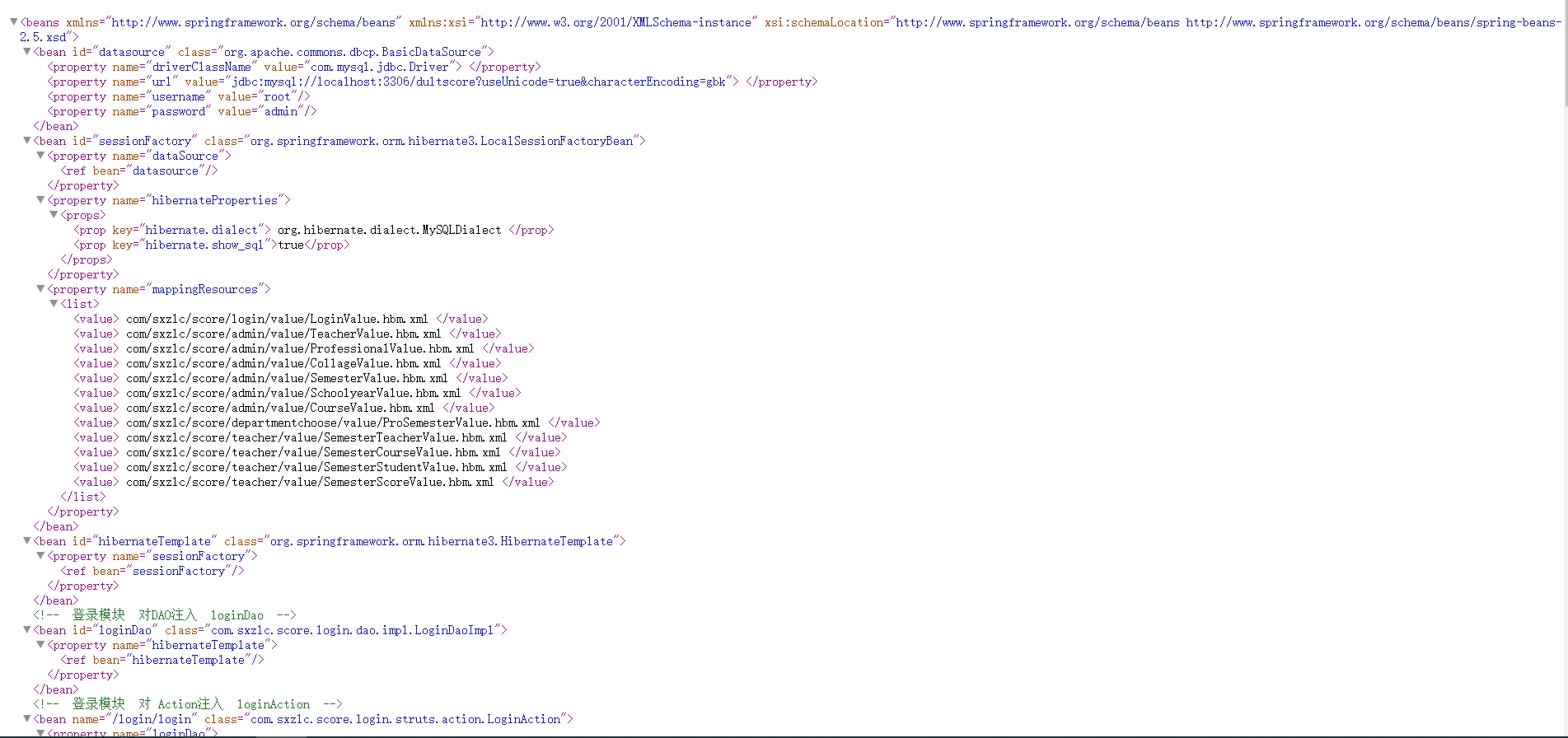
---

---
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"><bean id="datasource"class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"><property name="driverClassName"value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property><property name="url"value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dultscore?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=gbk"></property><property name="username" value="root"></property><property name="password" value="admin"></property></bean><bean id="sessionFactory"class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"><property name="dataSource"><ref bean="datasource" /></property><property name="hibernateProperties"><props><prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop><prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop></props></property><property name="mappingResources"><list><value>com/sxzlc/score/login/value/LoginValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/admin/value/TeacherValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/admin/value/ProfessionalValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/admin/value/CollageValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/admin/value/SemesterValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/admin/value/SchoolyearValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/admin/value/CourseValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/departmentchoose/value/ProSemesterValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/teacher/value/SemesterTeacherValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/teacher/value/SemesterCourseValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/teacher/value/SemesterStudentValue.hbm.xml</value><value>com/sxzlc/score/teacher/value/SemesterScoreValue.hbm.xml</value></list></property></bean><bean id="hibernateTemplate"class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate"><property name="sessionFactory"><ref bean="sessionFactory"/></property></bean><!-- 登录模块 对DAO注入 loginDao --><bean id="loginDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.login.dao.impl.LoginDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 登录模块 对 Action注入 loginAction --><bean name="/login/login" class="com.sxzlc.score.login.struts.action.LoginAction"><property name="loginDao"><ref bean="loginDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对DAO注入 teacherDao --><bean id="teacherDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.dao.impl.TeacherDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 管理员模块 对DAO注入 collageDao --><bean id="collageDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.dao.impl.CollageDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 管理员模块 对DAO注入 professionalDao --><bean id="professionalDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.dao.impl.ProfessionalDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 管理员模块 对DAO注入 semesterDao --><bean id="semesterDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.dao.impl.SemesterDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 管理员模块 对DAO注入 schoolyearDao --><bean id="schoolyearDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.dao.impl.SchoolyearDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 管理员模块 对DAO注入 courseDao --><bean id="courseDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.dao.impl.CourseDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!--======================================================================--><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 teacherAction --><bean name="/admin/registeredteacher" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.TeacherAction"><property name="teacherDao"><ref bean="teacherDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 CollageAction --><bean name="/admin/collage" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.CollageAction"><property name="collageDao"><ref bean="collageDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 ProfessionalAction --><bean name="/admin/professional" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.ProfessionalAction"><property name="professionalDao"><ref bean="professionalDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 SemesterAction --><bean name="/admin/semester" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.SemesterAction"><property name="semesterDao"><ref bean="semesterDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 Schoolyear --><bean name="/admin/schoolyear" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.SchoolyearAction"><property name="schoolyearDao"><ref bean="schoolyearDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 course --><bean name="/admin/course" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.CourseAction"><property name="courseDao"><ref bean="courseDao"/></property></bean><!--======================================================================--> <!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 preTeacherAction --><bean name="/admin/preTeacher" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.PreTeacherAction"><property name="teacherDao"><ref bean="teacherDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 PreDepCollageAction --><bean name="/admin/preDepCollage" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.PreDepCollageAction"><property name="collageDao"><ref bean="collageDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 PreDepProfessionalAction --><bean name="/admin/preDepProfessional" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.PreDepProfessionalAction"><property name="professionalDao"><ref bean="professionalDao"/></property><property name="collageDao"><ref bean="collageDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 preSemesterAction --><bean name="/admin/preSemester" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.PreSemesterAction"><property name="semesterDao"><ref bean="semesterDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 preSchoolyearAction --><bean name="/admin/preSchoolyear" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.PreSchoolyearAction"><property name="schoolyearDao"><ref bean="schoolyearDao"/></property></bean><!-- 管理员模块 对 Action注入 preCourseAction --><bean name="/admin/preCourse" class="com.sxzlc.score.admin.struts.action.PreCourseAction"><property name="courseDao"><ref bean="courseDao"/></property></bean><!--======================================================================--><!-- 院系选择模块 对DAO注入 proSmemesterDao --><bean id="proSmemesterDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.departmentchoose.dao.impl.ProSmemesterDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!--======================================================================--><!-- 院系选择模块 对 Action注入 preActivation0Action --><bean name="/departmentchoose/preActivation1" class=" com.sxzlc.score.departmentchoose.struts.action.PreActivation1Action"><property name="collageDao"><ref bean="collageDao"/></property></bean><!-- 院系选择模块 对 Action注入 Activation1Action --><bean name="/departmentchoose/activation1" class=" com.sxzlc.score.departmentchoose.struts.action.Activation1Action"><property name="semesterDao"><ref bean="semesterDao"/></property><property name="schoolyearDao"><ref bean="schoolyearDao"/></property><property name="professionalDao"><ref bean="professionalDao"/></property></bean><!-- 院系选择模块 对 Action注入Activation2Action --><bean name="/departmentchoose/activation2" class=" com.sxzlc.score.departmentchoose.struts.action.Activation2Action"><property name="proSmemesterDao"><ref bean="proSmemesterDao"/></property><property name="semesterTeacherDao"><ref bean="semesterTeacherDao"/></property></bean><!--======================================================================--><!-- 教师模块 对DAO注入 semesterTeacherDao --><bean id="semesterTeacherDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.teacher.dao.impl.SemesterTeacherDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 教师模块 对DAO注入 semesterCourseDao --><bean id="semesterCourseDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.teacher.dao.impl.SemesterCourseDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 教师模块 对DAO注入 semesterStudentDao --><bean id="semesterStudentDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.teacher.dao.impl.SemesterStudentDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!-- 教师模块 对DAO注入 semesterScoreDao --><bean id="semesterScoreDao" class="com.sxzlc.score.teacher.dao.impl.SemesterScoreDaoImpl"><property name="hibernateTemplate"><ref bean="hibernateTemplate"></ref></property> </bean><!--======================================================================--><!-- 教师模块 对 Buseiness注入 result --><bean name="studentResultDao" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.business.StudentResultDao"><property name="stuDao"><ref bean="semesterStudentDao"/></property><property name="semesterCourseDao"><ref bean="semesterCourseDao"/></property><property name="courseDao"><ref bean="courseDao"/></property><property name="semesterScoreDao"><ref bean="semesterScoreDao"/></property></bean>
<!--======================================================================--><!-- 教师模块 对 Action注入 RegisterAction --><bean name="/teacher/register" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.struts.action.RegisterAction"><property name="registerDao"><ref bean="semesterTeacherDao"/></property></bean><!-- 教师模块 对 Action注入 PreCourseAction --><bean name="/teacher/preCourse" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.struts.action.PreCourseAction"><property name="courseDao"><ref bean="courseDao"/></property></bean><!-- 教师模块 对 Action注入 CourseAction --><bean name="/teacher/course" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.struts.action.CourseAction"><property name="semesterCourseDao"><ref bean="semesterCourseDao"/></property></bean><!-- 教师模块 对 Action注入 StudentAction --><bean name="/teacher/student" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.struts.action.StudentAction"><property name="studentDao"><ref bean="semesterStudentDao"/></property></bean><!-- 教师模块 对 Action注入 PreScoreAction --><bean name="/teacher/preScore" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.struts.action.PreScoreAction"><property name="studentDao"><ref bean="semesterStudentDao"/></property><property name="semesterCourseDao"><ref bean="semesterCourseDao"/></property><property name="courseDao"><ref bean="courseDao"/></property></bean><!-- 教师模块 对 Action注入 ScoreAction --><bean name="/teacher/score" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.struts.action.ScoreAction"><property name="scoreDao"><ref bean="semesterScoreDao"/></property></bean><!-- 教师模块 对 Action注入 PreResultAction --><bean name="/teacher/preResult" class=" com.sxzlc.score.teacher.struts.action.PreResultAction"><property name="studentDao"><ref bean="semesterStudentDao"/></property><property name="semesterCourseDao"><ref bean="semesterCourseDao"/></property><property name="courseDao"><ref bean="courseDao"/></property><property name="studentResultDao"><ref bean="studentResultDao"/></property></bean></beans>====
7.n年以前,毕业设计的【web.xml】
==

===
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" version="2.5" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/classes/applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param><servlet><servlet-name>context</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderServlet</servlet-class><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><!-- 字符转换 过滤器--> <filter><filter-name>CharsetConvertFilter</filter-name><filter-class>com.city.sxzlc.filter.CharsetConvertFilter</filter-class></filter><!-- 字符转换 过滤器 mapping --> <filter-mapping><filter-name>CharsetConvertFilter</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping><!-- 核心控制器 --> <servlet><servlet-name>action</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>config</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>config/login</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config-login.xml</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>config/admin</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config-admin.xml</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>config/teacher</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config-teacher.xml</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>config/departmentchoose</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config-departmentchoose.xml</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>debug</param-name><param-value>3</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>detail</param-name><param-value>3</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup></servlet><!-- 验证码 --> <servlet><description>This is the description of my J2EE component</description><display-name>This is the display name of my J2EE component</display-name><servlet-name>AuthenticationCode</servlet-name><servlet-class>com.city.sxzlc.servlet.AuthenticationCode</servlet-class></servlet><!--成绩录入后的 session释放 --> <servlet><description>This is the description of my J2EE component</description><display-name>This is the display name of my J2EE component</display-name><servlet-name>PreScoreActionSessionDestroy</servlet-name><servlet-class>com.city.sxzlc.servlet.PreScoreActionSessionDestroy</servlet-class></servlet><!--退出登录 session释放 --> <servlet><servlet-name>Logout</servlet-name><servlet-class>com.city.sxzlc.servlet.Logout</servlet-class></servlet> <!-- 核心控制器 apping --> <servlet-mapping><servlet-name>action</servlet-name><url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><!-- 验证码 mapping --> <servlet-mapping><servlet-name>AuthenticationCode</servlet-name><url-pattern>/login/AuthenticationCode</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><!--成绩录入后的 session释放 --> <servlet-mapping><servlet-name>PreScoreActionSessionDestroy</servlet-name><url-pattern>/teacher/PreScoreActionSessionDestroy</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><!--退出登录 session释放 --> <servlet-mapping><servlet-name>Logout</servlet-name><url-pattern>/logout</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><welcome-file-list><welcome-file>main.jsp</welcome-file></welcome-file-list>
</web-app>xx
8.xxx
xxx
9.xxx
xx
■Spring全家桶
1.SpringBoot 和 SpringMVC的区别
Spring Boot和Spring MVC是两个不同的概念和技术。
==
Spring MVC是Spring框架中的一个模块,用于构建Web应用程序。它提供了一套基于MVC模式的架构,可以方便地处理请求和响应,实现Web开发中的控制器、视图和模型的分离。Spring MVC主要关注于处理HTTP请求和响应,包括路由、参数绑定、表单验证、数据转换等功能。通过使用注解或配置文件,开发人员可以灵活地定义URL映射、处理方法、视图解析器等。
===
Spring Boot是在Spring框架的基础上构建的一个快速开发框架,提供了自动化配置和快速启动器等功能,使得开发人员能够更加方便、快速地构建和部署Spring应用程序。Spring Boot可以用来简化Spring MVC应用的配置和部署过程,而且还可以集成其他Spring模块,如Spring Data、Spring Security等。
===
总结来说,Spring Boot是一个快速开发框架,可以用来简化Spring应用程序的开发和部署,而Spring MVC是Spring框架中的一个模块,用于构建Web应用程序。Spring Boot可以集成Spring MVC,简化其配置和部署过程,使得开发人员能够更加方便、快速地开发和部署Web应用程序。
2.Spring boot 和 Spring MVC 直接有什么关系
具体来说,Spring Boot是一个快速开发框架,可以用来简化Spring应用程序的开发和部署过程。它通过自动化配置和快速启动器等功能,可以减少开发人员在配置和部署方面的工作量,使得开发人员能够更加专注于业务逻辑的实现。
===
而Spring MVC是Spring框架中的一个模块,用于构建Web应用程序。它提供了一套基于MVC模式的架构,可以方便地处理请求和响应,实现控制器、视图和模型的分离。Spring MVC主要关注于处理HTTP请求和响应,包括路由、参数绑定、表单验证、数据转换等功能。
===
在实际开发中,Spring Boot可以集成Spring MVC,以简化其配置和部署过程。通过Spring Boot的自动化配置功能,可以减少编写大量的配置代码的工作,而且还可以使用Spring Boot的快速启动器来集成其他Spring模块,如Spring Data、Spring Security等。这样,开发人员可以更加方便、快速地构建和部署基于Spring MVC的Web应用程序。
===
因此,可以说Spring Boot是Spring MVC的一种扩展和简化,可以提供更高效的开发和部署体验。
3.Spring Boot和Spring MVC 之间, 谁包含谁
Spring Boot是一个用于简化Spring应用程序开发和部署的框架,它集成了大量的Spring相关模块,包括Spring MVC。Spring Boot通过自动化配置和快速启动器等功能,使得开发人员可以快速搭建和部署基于Spring MVC的Web应用程序。
===
Spring MVC是Spring框架中的一个模块,用于构建Web应用程序。它提供了一套基于MVC模式的架构,用于处理请求和响应,实现视图、控制器和模型的分离。
===
因此,可以认为Spring Boot是一个更高级的框架,它包含了Spring MVC以及其他Spring模块。通过Spring Boot,开发人员可以更加方便地配置和部署基于Spring MVC的Web应用程序。
4.Spring MVC代码示例
控制层
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Controller
public class HomeController {@GetMapping("/")public String home(Model model) {model.addAttribute("message", "Hello, Spring MVC!");return "home";}
}
这是一个基本的HomeController控制器类,使用
@Controller注解将它标记为Spring MVC的控制器。@GetMapping("/")注解指定了处理根路径"/"的GET请求。===
在
home方法中,我们使用Model参数将一个名为"message"的属性添加到模型中。然后,方法返回一个名为"home"的视图名称,表示将要使用名为"home.html"的视图去渲染响应。
画面
我们需要创建一个名为"home.html"的视图模板,如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>Spring MVC Example</title>
</head>
<body><h1>${message}</h1>
</body>
</html>xxxx
以上就是一个简单的Spring MVC代码示例,它可以处理根路径的GET请求,并在视图模板中显示一条消息。当访问程序的根路径时,将会显示"Hello, Spring MVC!"。
===
5.xxx
6.xxx
7.xxx
■Spring Boot 学习
1.Spring Boot 介绍1
https://qingmiaogu.blog.csdn.net/article/details/106235846
2.Spring Boot 介绍2
整理了八个开源的 Spring Boot 学习资源_江南一点雨的专栏-CSDN博客
3.yml配置文件1
YML简介 - 简书
4.yml配置文件2
yaml文件 .yml_beginya的专栏-CSDN博客_yml和yaml
5.SpringBoot使用jasypt加解密密码
https://blog.csdn.net/sxzlc/article/details/111071591 (本地电脑配置,私密)
SpringBoot使用jasypt加解密密码 - 自行车上的程序员 - 博客园
<dependency><groupId>com.github.ulisesbocchio</groupId><artifactId>jasypt-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>https://www.codeflow.site/ja/article/spring-boot-jasypt
6. YML 中秘密加密 jasypt
■加密
java -cp C:/dev/.m2/repository/org/jasypt/jasypt/1.9.2/jasypt-1.9.2.jar org.jasypt.intf.cli.JasyptPBEStringEncryptionCLI input="test123" password=key123456 algorithm=PBEWithMD5AndDES■解密
java -cp C:/dev/.m2/repository/org/jasypt/jasypt/1.9.2/jasypt-1.9.2.jar org.jasypt.intf.cli.JasyptPBEStringDecryptionCLI input="XXXXXXXXX" password=key123456■加密的值
虽然每次加密后的值都是不相同的,
但是,
都可以正常解密
・YML文件中的使用 ↓ 好用 // ①使用 1.7 版本的 jasypt ② glassfish (glassfish启动不能百分之百成功,1次成功,两次失败)
Spring Boot application.yml 数据源配置密码加密_yz18931904的博客-CSDN博客
【springboot】application.yml配置文件中数据库密码password加密后显示_若水2018的博客-CSDN博客
工作随笔——jasypt-spring-boot使用 - 爱自己 - 博客园
SpringBoot | 第三十七章:集成Jasypt实现配置项加密 - 程序园
每次加密的结果都不一样
jasypt由于其使用的是PBEWithMD5AndDES加密方式,
所以每次加密出来的结果都不一样,所以很适合对数据进行加密jasypt中的加密与解密_我弟是个程序员-CSDN博客_jasypt加密
7. YML 中数据库连接配置
Spring Boot JDBC:加载DataSource过程的源码分析及yml中DataSource的配置 - 坚守梦想 - 博客园
spring:datasource:driver-class-name: com.mysql.XXXXusername: XXXpassword: XXXSpring Boot启动后会调用
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration
(spring-boot-autoconfigure-XXXX.RELEASE.jar)
8. 启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);}
}spring boot启动原理 - 小破天 - 博客园
9.配置文件的【加载】与【加载顺序】
Spring Boot 允许你通过命名约定按照一定的格式 (application-{profile}.properties) 来定义多个配置文件,然后通过在 application.properties 通过 spring.profiles.active 来具体激活一个或者多个配置文件,如果没有指定任何 profile 的配置文件,Spring Boot 默认会启动 application-default.properties。
===
resources
└①application.properties
------------------------
spring.profiles.active=dprod
sever.port=8090
------------------------
└②application-dev.properties
└③application-prod.properties
------------------------ // 这里里面的配置,会覆盖①中的配置
sever.port=8080
------------------------
└④application-test.properties
spring.profiles.active,还可以在启动时指定(优先级最高)
java -Xms3g -Xmx3g -Xmn1g -Xss256k -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:/logdisk/gclog/gctest.log -jar test-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod >/dev/null 2>&1 &
====
■Spring Batch
1.Spring Batch 简介
Spring Batch 批处理框架_不影响全局-CSDN博客
2.TaskLet
介绍Spring Batch 中Tasklet 和 Chunks_neweastsun的专栏-CSDN博客
3.Maven插件系列之spring-boot-maven-plugin
Maven插件系列之spring-boot-maven-plugin - 星朝 - 博客园
4.spring batch教程 之 配置并运行Job
spring batch教程 之 配置并运行Job_回头等终点的博客-CSDN博客
5.spring batch 的jar,调用时,参数 --(双横杠)
・「--XXXX」作为一个整体,作为参数,传递给java程序
・Spring中,SimpleCommandLineArgsParser类的逻辑中,会取出--后面的内容,进行处理
java -jar命令参数的单横杠-和双横杠--用法_s674334235的专栏-CSDN博客
---
■Spring 标注
1.@SessionAttributes(names = "user")
springmvc基础知识(19):@SessionAttributes注解的使用_YellowStar007的博客-CSDN博客_sessionattributes
若希望在多个请求之间共用数据,则可以在控制器类上标注一个 @SessionAttributes,配置需要在session中存放的数据范围,Spring MVC将存放在model中对应的数据暂存到
HttpSession 中。
@SessionAttributes只能使用在类定义上
- 如果在类上面使用了
@SessionAttributes("attributeName")注解,而本类中恰巧存在attributeName,则会将attributeName放入到session作用域。- 如果在类上面使用了
@SessionAttributes("attributeName")注解,SpringMVC会在执行方法之前,自动从session中读取key为attributeName的值, 并注入到Model中。所以我们在方法的参数中使用ModelAttribute("attributeName")就会正常的从Model读取这个值,也就相当于获取了session中的值。- 使用了
@SessionAttributes之后,Spring无法知道什么时候要清掉@SessionAttributes存进去的数据,如果要明确告知,也就是在方法中传入SessionStatus对象参数,并调用status.setComplete就可以了。。
2.@ModelAttribute(“user”)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/0ec4e7afb7ed
从代码中可以看出,使用@ModelAttribute注解的参数,意思是从前面的Model中提取对应名称的属性。
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/modelattribute")
public class ModelAttributeParamController {@ModelAttribute(value = "attributeName")public String myModel(@RequestParam(required = false) String abc) {return abc;}@ModelAttributepublic void myModel3(Model model) {model.addAttribute("name", "zong");model.addAttribute("age", 20);}@RequestMapping(value = "/param")public String param(@ModelAttribute("attributeName") String str,@ModelAttribute("name") String str2,@ModelAttribute("age") int str3) {return "param";}
}3.@RequestParam
GET请求时
@GetMapping("/api/foos")
public String getFoos(@RequestParam String id) {
return "ID: " + id;
}
在上面示例中,使用@RequestParam提取id查询参数。
curl http://localhost:19999/api/foos?id=abc
---
ID: abc
POST请求时
比如传送一个文件过来
@PostMapping("/api/foos")
public String getFoos(@RequestParam MultipartFile csvFile) {...}
===
<from th:action="@{/api/foos}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"><input type="file" id="csvFile" accept=".csv"></from>===
4.pringMVC在调用方法前会创建一个隐含的数据模型
Spring中Model、ModelMap、ModelAndView理解和具体使用总结 - 走看看
SpringMVC在调用方法前会创建一个隐含的数据模型,作为模型数据的存储容器, 成为”隐含模型”。
也就是说在每一次的前后台请求的时候会随带这一个背包,不管你用没有,这个背包确实是存在的,用来盛放我们请求交互传递的值;关于这一点,spring里面有一个注解:
@ModelAttribute :被该注解修饰的方法,会在每一次请求时优先执行,用于接收前台jsp页面传入的参数
@Controller
public class User1Controller{private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(User1Controller.class);// @ModelAttribute修饰的方法会先于login调用,该方法用于接收前台jsp页面传入的参数
@ModelAttribute
public void userModel(String loginname,String password,Model model){logger.info("userModel");// 创建User对象存储jsp页面传入的参数User2 user = new User2();user.setLoginname(loginname);user.setPassword(password);// 将User对象添加到Model当中model.addAttribute("user", user);
}@RequestMapping(value="/login1")public String login(Model model){logger.info("login");// 从Model当中取出之前存入的名为user的对象User2 user = (User2) model.asMap().get("user");System.out.println(user);// 设置user对象的username属性user.setUsername("测试");return "result1";
}5.标注: @GetMapping("/getuserinfo") @PathVariable
★★★前台 ThymeLeaf
<a th:href="@{/getuserinfo/{userId}/{siteId}}">[[${userId}]]</a>URL 使用
@{/AAA/BBB/CCC}
@{htps://aaa.abc.com}
<a th:href="@{htps://aaa.abc.com}">xxxx</a>
URL 使用 ( URL 里面有变量 ) : 通过拼接的方式实现
<a th:href="@{'htps://'+${session.yourPropertity001}+'.abc.com'}">xxxx</a>
变量直接使用 (使用之前,在后台,变量需要被设置到 Model 中)
[[${var1}]]
<div>[[${var1}]]</div>
session中的变量,在标签外面,直接使用
[[${session.yourPropertity001}]]
session中的变量,在标签里面,使用
<div id="yourItemId" hidden="hidden" th:value="${session.yourPropertity001}"></div>
POM变量使用
@sss.bbbb.cccc.var1@
【相关知识 整理】 JS获取div项目的值
=====================
×:var yourVar = document.getElementById("yourItemId").value
↑ alert(yourVar ); 时,得不到你想要的值,显示Undefined
〇:var yourVar = document.getElementById("yourItemId").getAttribute("value")
=====================
★★★后台(ThymeLeaf)
@GetMapping("/getuserinfo/{userId}/{siteId}")
public String getUserInfo(@PathVariable("userId") int userId,@PathVariable("siteId") int siteId, @Validated @ModelAttribute(“user”) User userBindingResult result,Model model) {6.接口:Model:从控制层直接返回前端所需的数据
★★★后台
model.addAttribute("infoList", infoList);★★★前台(ThymeLeaf)
<tbody th:unless="${infoList.isEmpty()}"><tr th:each="info: ${infoList}"><td th:text="${info.xxxxAA}"></td><td th:text="${info.xxxxBB}"></td>7.检证相关
7.0.需要使用到 @Validated 检证时,Bean对象的定义 使用 @NotNull @Size 等等
Spring注解之@validated的使用_屿麟的博客-CSDN博客_validated注解的作用
@data
public class User{@NotNull@Size(max=32, message="userId is null")private String userId;@NotBlank@Size(max=32, message="userName is null")private String userName;
}
7.1.接口:BindingResult 与 @Validated
@RequestMapping(value = "/entry/updateQuantity", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String updateEntryQuantity(@Valid final UpdateQuantityForm form,final BindingResult bindingResult,@RequestParam("pk") final long pk,final Model model) {
}↑ 参数的顺序对于spring来说实际上很重要.BindingResult需要在正在验证的Form之后.同样,[optional] Model参数需要在BindingResult之后.例:
7.2.代码示例:@NotNull @Validated BindingResult
public class ApplyUserInfo extends BaseEntity
{private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;/** 申请人姓名 */@Excel(name = "用户姓名")@NotEmpty(message = "用户姓名不能为空")private String applicantName;/** 申请人性别,0:女士,1:先生 */@Excel(name = "用户性别", readConverterExp = "0=女士,1=先生")@NotNull(message = "用户性别不能为空")private Integer applicantGender;/** 医院名称 */@Excel(name = "医院名称")@NotEmpty(message = "医院名称不能为空")private String hospitalName;
}controller层代码
public AjaxResult save(@Validated @RequestBody ApplyUserInfo applyUserInfo, BindingResult bindingResult){if(bindingResult.hasErrors()) {String errorMsg = bindingResult.getFieldError().getDefaultMessage();return AjaxResult.error(errorMsg);}
}7.3.@NotNull @Size @Length @Max 等等
@NotEmpty:用在集合类上面;不能为null,而且长度必须大于0
@NotBlank:用在String上面;只能作用在String上,不能为null,而且调用trim()后,长度必须大于0
@NotNull:用在基本类型上;不能为null,但可以为empty。
长度检查@Size(min=,max=):验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内 不要错用了异常类型,比如在int上不可用@size
@Length(min=, max=):只适用于String 类型
Booelan检查@AssertTrue:验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse:验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
日期检查@Past:验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future:验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern:验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
其他验证@Vaild 递归验证,用于对象、数组和集合,会对对象的元素、数组的元素进行一一校验
@Email 用于验证一个字符串是否是一个合法的右键地址,空字符串或null算验证通过
@URL(protocol=,host=,port=,regexp=,flags=) 用于校验一个字符串是否是合法URL
数值检查建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上,因为表单值为"" 时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为"",Integer为null
@Min:验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值
@Max:验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值
@DecimalMax:被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@DecimalMin:被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@Digits:验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法
@Digits(integer=,fraction=):验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字,interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。
项目使用中遇到的问题一开始传入的参数没有使用@Validated 修饰,结果绑定不起作用,参数校验不成功,加上此注解即可生效。所以BingdingResult是要与@Validated同时使用的。
===
7.4.@Validated 和 @Valid的区别
别再乱用了,这才是 @Validated 和 @Valid 的真正区别和用法!_Java精选的博客-CSDN博客
java的JSR303声明了@Valid这类接口,而Hibernate-validator对其进行了实现
@Valid是使用Hibernate validation的时候使用
@Validated是只用Spring Validator校验机制使用
注解位置
@Validated:用在类型、方法和方法参数上。但不能用于成员属性(field)
@Valid:可以用在方法、构造函数、方法参数和成员属性(field)上
分组校验
@Validated:提供分组功能,可以在参数验证时,根据不同的分组采用不同的验证机制
@Valid:没有分组功能
8.标注:@Component @Scope
@Component
@Scope("prototype")9.标注:@Repository @Service @Controller
除了@Component以外,Spring提供了3个功能基本和@Component等效的注解
・@Repository:用于对DAO实现类进行标注;
・@Service:用于对Service实现类进行标注;
・@Controller:用于对Controller实现类进行标注
10.标注:@Scope("prototype")
@singleton:容器中创建时只存在一个实例,所有引用此bean都是单一实例
@prototype:spring容器在进行输出prototype的bean对象时,会每次都重新生成一个新的对象给请求方
@request:web程序中应用
@session:web程序中应用
@globalsession:Web全局变量 可以理解为之前的 Application
11.标注:@Autowired (Spring) 和、 @Resource 和、 @Inject(JSR330)
// @Autowired按byType自动注入,而@Resource默认按 byName自动注入12.
@Autowired
public class TestServiceImpl {@Autowired@Qualifier("userDao")private UserDao userDao;
}@Resource
public class TestServiceImpl {// 下面两种@Resource只要使用一种即可@Resource(name="userDao")private UserDao userDao; // 用于字段上@Resource(name="userDao")public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { // 用于属性的setter方法上this.userDao = userDao;}
}
@Inject
@Inject
@Named("namedBean")
private MyClass MyClass;
13.标注:@Configuration 和 @Bean
配置Spring容器管理的对象
14.标注:@ConfigurationProperties
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")//只能从默认的全局文件中获取
public class Person {private String lastName;private Integer age;private Boolean boss;private Date birth;private Map<String,Object> maps;private List<Object> lists;private Dog dog;
properties文件
person:lastName: fang \n xin \n deage: 18boss: falsebirth: 2018/12/10maps: {a1: fang, a2: li,a3: zhang}lists: [cat,pig,dog]dog:name: XXXage: 115.@value{“¥{AAA.BBB.CCC}”}
java -jar XXX.jar --spring.config.location=/Path1/Path2/application.yml
// AAA.BBB.CCC 为yml文件中配置的属性
15.1.@Value(“${xxxx}”) 与@Value(“#{}”)
@Value(“${xxxx}”)注解从配置文件读取值的用法
@Value(“#{}”) 表示SpEl表达式通常用来获取bean的属性,或者调用bean的某个方法。当然还有可以表示常量
@Value("#{1}") private int number; //获取数字 1 @Value("#{'Spring Expression Language'}") //获取字符串常量 private String str; @Value("#{dataSource.url}") //获取bean的属性 private String jdbcUrl; @Value("#{'${user.names}'.split(',')}")private String[] userNameArray;// YML中 // user.name = aaa,bbb,ccc,ddd16.@PostConstruct
//@PostConstruct该注解被用来修饰一个非静态的void()方法。
// 被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在服务器加载Servlet的时候运行,并且只会被服务器执行一次。
// 应用,LogFactory
17.★★★知识点★★★ :在SpringBoot开发中,当一个接口A (IPerson)有多个实现类时,spring会很智能的将bean注入到List<A>或Map<String,A>变量中
@AutowiredMap<String, IPerson> personMap;
personMap中,保存的是,所有实现了IPerson接口的类的实例(Bean)
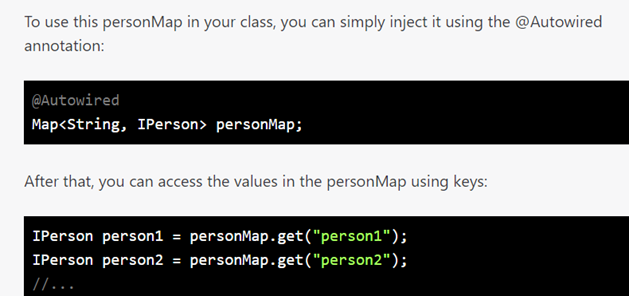
↑:@Autowired is an annotation used in Spring framework to inject dependencies automatically into a class. In this case, it is used to inject a Map with key as String and value as IPerson interface implementation into the class.
The Map<String, IPerson> personMap will be automatically filled with beans that implements the IPerson interface, where the key is the bean name and the value is the bean instance.
===
18.@Configuration @Bean @Primary @ConfigurationProperties
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@MapperScan("aa.bbb.cccc.ddd.repository")
public class XXXXConfiguration@Bean
@primary
@ConfigurationProperties("xxx.xxxx.xxx")
public DataSourceProperties xxxDataSourceProperties() }return new DataSourceProperties();
}@Bean(name = "yourName")
public XXXX xxxxx(){}19.@Transactional @Service
19.1.@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITED) 事务隔离级别
在Service类上添加@Transactional注解的话,那么Service曾的每一个业务方法调用的时候都会打开一个事务。
1.@Transactional 可以作用在类上,当作用在类上的时候,表示所有该类的 public 方法都配置相同的事务属性信息。
2.@Transactional 也可以作用在方法上,当方法上也配置了 @Transactional,方法的事务会覆盖类的事务配置信息
@Service
@Transaction(isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITED)
public class XXXXService====
19.2.@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) 事务传播
1.@Transactional 可以作用在类上,当作用在类上的时候,表示所有该类的 public 方法都配置相同的事务属性信息。
2.@Transactional 也可以作用在方法上,当方法上也配置了 @Transactional,方法的事务会覆盖类的事务配置信息
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA(String name) {。。。methodB(name)
}@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
// @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void methodB(String name){。。。
}===
| 在Service类上添加@Transactional注解的话,那么Service曾的每一个业务方法调用的时候都会打开一个事务。 | |
| 务传播性 | 说明 |
| REQUIRED | 【 默认传播性】 如果当前有事务,就沿用当前事务,如果没有就新建一个事务 |
| 调用MethodA时,环境中没有事务,所以开启一个新的事务。 当在MethodA中调用MethodB时,环境中已经有了一个事务,所以methodB就加入当前事务。 | |
| SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务运行 |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 新建一个事务,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 不支持事务,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 |
| MANDATORY | 强制使用当前事务,如果当前没有事务就抛异常 |
| NEVER | 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常 |
| NESTED | 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作。 |
19.3.@Transactional(readOnly = true)
使用 @Transactional(readOnly = true) 来设置只读事务
使用场景
对于一个函数,如果执行的只是单条查询语句,则没有必要启用事务支持,数据库默认支持SQL执行期间的读一致性;
如果执行多条查询语句,例如统计查询,报表查询等,则多条查询SQL必须保证整体的读一致性;
否则,若在前后两条查询SQL执行的间隙,数据被其他用户改变,则该次整体的统计查询将会出现读数据不一致的情况,
此时,应该启用事务支持。注意,是一次执行多次查询来统计某些信息,这时为了保证数据整体的一致性,要用只读事务。
20.@Component @Value
@Data
@Component
public class XXXXConfig@Value("${xxx.xxx.xxx}")private String myVar;21.REST 与 RESTful API
21.0.REST
Spring REST简介_书香水墨的博客-CSDN博客
表述性(Representational):REST资源实际上可以用各种形式来进行表述,包括XML、JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)甚至HTML——最适合资源使用者的任意形式;
状态(State):当使用REST的时候,我们更关注资源的状态而不是对资源采取的行为;
转移(Transfer):REST涉及到转移资源数据,它以某种表述性形式从一个应用转移到另一个应用。
更简洁地讲,REST就是将资源的状态以最适合客户端或服务端的形式从服务器端转移到客户端(或者反过来)。
21.1.RESTful API
什么是RESTful API?_Evan Wang的博客-CSDN博客_api restful
提到RESTful API 大家势必或多或少听说过。但是什么是RESTful API ?如何理解RESTful API 呢?请大家耐心读完这篇文章,相信您读完后一定会有一个更好的理解。我个人认为,要弄清楚什么是RESTful API,首先要弄清楚什么是REST。REST 全称:REpresentational State Transfer,英文翻译过来就是“表现层状态转化”。如果单看这个概念,估计大家很难理解。那下面就让我来用一句话通俗解释一下。 RESTful:用URL定位资源、用HTTP动词(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)描述操作。只要记住这句话也就不难理解了。
Resource:资源,即数据。
Representational:某种表现形式,比如用JSON,XML,JPEG等;
State Transfer:状态变化。通过HTTP动词实现
到底RESTful长什么样子的呢?下面我们举一些例子。
GET:http://www.xxx.com/source/id 获取指定ID的某一类资源。
GET:http://www.xxx.com/friends/123表示获取ID为123的用户的好友列表。如果不加id就表示获取所有用户的好友列表。
POST:http://www.xxx.com/friends/123表示为指定ID为123的用户新增好友。
21.2.URL设计规范
一文搞懂什么是RESTful API - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
URL为统一资源定位器 ,接口属于服务端资源,首先要通过URL这个定位到资源才能去访问,而通常一个完整的URL组成由以下几个部分构成:
URI = scheme "://" host ":" port "/" path [ "?" query ][ "#" fragment ]
scheme: 指底层用的协议,如http、https、ftp
host: 服务器的IP地址或者域名
port: 端口,http默认为80端口
path: 访问资源的路径,就是各种web 框架中定义的route路由
query: 查询字符串,为发送给服务器的参数,在这里更多发送数据分页、排序等参数。
fragment: 锚点,定位到页面的资源
我们在设计API时URL的path是需要认真考虑的,而RESTful对path的设计做了一些规范,通常一个RESTful API的path组成如下:
/{version}/{resources}/{resource_id}
version:API版本号,有些版本号放置在头信息中也可以,通过控制版本号有利于应用迭代。
resources:资源,RESTful API推荐用小写英文单词的复数形式。
resource_id:资源的id,访问或操作该资源。
当然,有时候可能资源级别较大,其下还可细分很多子资源也可以灵活设计URL的path,例如:
/{version}/{resources}/{resource_id}/{subresources}/{subresource_id}
此外,有时可能增删改查无法满足业务要求,可以在URL末尾加上action,例如
/{version}/{resources}/{resource_id}/action
从大体样式了解URL路径组成之后,对于RESTful API的URL具体设计的规范如下:
不用大写字母,所有单词使用英文且小写。
连字符用中杠"-"而不用下杠"_"
正确使用 "/"表示层级关系,URL的层级不要过深,并且越靠前的层级应该相对越稳定
结尾不要包含正斜杠分隔符"/"
URL中不出现动词,用请求方式表示动作
资源表示用复数不要用单数
不要使用文件扩展名
★★★知识点★★★: Spring中的HTTP通信
RestTemplate 代理设置
方法1:
@Bean(name = "restTemplateWithProxy")
public RestTemplate restTemplateWithProxy() {RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setProxy(new HttpHost("代理主机", 代理端口)).build();HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpClient);restTemplate.setRequestFactory(factory);return restTemplate;}方法2:
@Bean(name = "restTemplateWithProxy")
public RestTemplate restTemplateWithProxy() {CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setProxy(new HttpHost("代理主机", 代理端口)).build();HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpClient);return new RestTemplate(factory);}21.3.RestTemplate (在程序内部发生http请求,访问一些程序提供的WebAPI)
我们经常会使用 RestTemplate 的 exchange方法
// exchange@Overridepublic <T> ResponseEntity<T> exchange(String url, HttpMethod method,@Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity, Class<T> responseType, Object... uriVariables)throws RestClientException {RequestCallback requestCallback = httpEntityCallback(requestEntity, responseType);ResponseExtractor<ResponseEntity<T>> responseExtractor = responseEntityExtractor(responseType);return nonNull(execute(url, method, requestCallback, responseExtractor, uriVariables));}21.4. 使用RestTemplate的exchange()方法时,参数HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, Object>>
Spring RestTemplate为何必须搭配MultiValueMap?_JavaEdge.的博客-CSDN博客
通常使用 HttpEntity 这个参数,其它参数不怎么使用
想要传递的值,保存在 MultiValueMap 中
/*** Create a new {@code HttpEntity} with the given body and headers.* @param body the entity body* @param headers the entity headers*/public HttpEntity(@Nullable T body, @Nullable MultiValueMap<String, String> headers) {this.body = body;HttpHeaders tempHeaders = new HttpHeaders();if (headers != null) {tempHeaders.putAll(headers);}this.headers = HttpHeaders.readOnlyHttpHeaders(tempHeaders);}22.控制层
22.1.@Controller @ResponseBody @RestController @RequestMapping("/user")
@RestController介绍
@RestController是一个组合注解,它包含了@Controller和@ResponseBody两个注解的功能。 只能用在类上。
在类上,使用@RestController可以省去在每个方法上都加@ResponseBody注解的麻烦。
@RestController使用示例
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {@GetMapping("/{id}")public User getUserById(@PathVariable Long id) {// 根据id查询用户信息User user = userService.getUserById(id);return user;}
}其它
在Spring中@RestController的作用等同于@Controller + @ResponseBody。
@ResponseBody表示方法的返回值直接以指定的格式写入Http response body中,而不是解析为跳转路径。
@Controller:在对应的方法上,视图解析器可以解析return 的jsp,html页面,并且跳转到相应页面
若返回json等内容到页面,则需要加@ResponseBody注解
这也就是为什么 ThymeLeaf的模板引擎,不支持@RestController的原因。(Thymeleaf的控制类中,返回值是路径,值都存到了Model中)
package com.sxz.test.one;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;// @RestController // 它是无效的。不支持模板引擎
@Controller // 要使用它配置该类
public class HelloThymeleaf {@Autowiredprivate HttpServletRequest request;@Autowiredprivate HttpServletResponse response;@GetMapping("/hello2")public String hello(ModelMap modelMap) {String agentInfo = request.getHeader("user-agent");String showInfo = agentInfo;LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println("-------------Access Begin----------------");System.out.println(ldt);System.out.println(showInfo);System.out.println("-------------Access End----------------");modelMap.addAttribute("name",showInfo);//return showInfo;return "helloThymeleaf";}}@Controller使用,画面显示(方法的返回值是String)
SpringBoot + Thymeleaf 之 HelloWorld_sun0322的博客-CSDN博客_springboot thymeleaf helloword案例
@RestController使用,画面显示(方法的返回值可以是一个List)
SpringBoot + MyBatis 之 Hello World_sun0322的博客-CSDN博客
22.2.@Controller @SessionAttributes @PostConstruct @Autowired @Qualifier @GetMapping @ModelAttribute
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(name="xxxInfo")
public class XXXXController@Autowiredprivate XXXXConfig xXXXConfig;@Autowired@Qualifier("yourName")private XXXX xxxx;@PostConstructprivate void init(){}@GetMapping("/xxxxxx")public String xxxxxxx(@ModelAttribute("xxxInfo")XxxInfo xxxInfo){return "xxxxxxx"}22.3.@RequestMapping @GetMapping @PostMapping
@RequestMapping:是用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于映射一个请求或一个方法,可以用在类或方法上。
@GetMapping: 是一个组合注解,是@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)的缩写。 用来处理get请求,常用于执行查询操作。
@PostMapping:是一个组合注解,是@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)的缩写。 用来处理post请求,常用于执行添加操作。
22.4.@ResponseBody 和 @RequestBody 的使用
@ResponseBody和@RequestBody的区别_shuxingcq的博客-CSDN博客
1、ResponseBody
@Responsebody 注解表示该方法的返回的结果直接写入 HTTP 响应正文(ResponseBody)中,一般在异步获取数据时使用;
通常是在使用 @RequestMapping 后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,加上 @Responsebody 后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入HTTP 响应正文中。
作用:
该注解用于将Controller的方法返回的对象,通过适当的HttpMessageConverter转换为指定格式后,写入到Response对象的body数据区。
使用时机:
返回的数据不是html标签的页面,而是其他某种格式的数据时(如json、xml等)使用;
2、RequestBody
@RequestBody是作用在形参列表上,用于将前台发送过来固定格式的数据【xml 格式或者 json等】封装为对应的 JavaBean 对象,封装时使用到的一个对象是系统默认配置的 HttpMessageConverter进行解析,然后封装到形参上。
示例代码(两者的区别举一个登陆的例子说明一下):
如果不用RequestBody:
@RequestMapping("/login.do")
@ResponseBody
public Object login(String name, String password, HttpSession session) {user = userService.checkLogin(name, password);session.setAttribute("user", user);return new JsonResult(user);
}使用RequestBody:
@RequestMapping("/login.do")
@ResponseBody
public Object login(@RequestBody User loginUuser, HttpSession session) {user = userService.checkLogin(loginUser);session.setAttribute("user", user);return new JsonResult(user);
}23.@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement @MapperScan
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@MapperScan("aa.bbb.cccc.ddd.repository")
public class XXXXConfiguration24.★★★知识点★★★ :自动装配
为什么SpringBoot中不需要使用@EnableTransactionManagement就能使用事务?
为什么SpringBoot中不需要使用@EnableTransactionManagement就能使用事务?_永寂如孤星的博客-CSDN博客
因为在SpringBoot中自动装配了此注解配置,所以已被默认启用,自然不需要手动加上此注解。
(【spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.x.x.jar】中的【MEAT-INF】中的spring.factories,并在其中搜索Transaction相关的内容)
定位EnableTransactionManagement自动装配
EnableTransactionManagement里面使用了@EnableTransactionManagement
25.@Mapper @MapperScan 和IBatis相关的接口类 @Repository
SpringBoot + MyBatis 之 Hello World_sun0322的博客-CSDN博客
和IBatis相关的接口类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.sxz.test.one.mapper.UserMapper"><select id="findAll" resultType="User">select * from login_user</select>
</mapper>@Mapper
在持久层的接口(和IBatis相关的接口类)上添加@Mapper注解,编译后会生成相应的接口实现类,
package com.sxz.test.one.mapper;import java.util.List;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;import com.sxz.test.one.entity.User;@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {public List<User> findAll();
}@Repository
使用了@Mapper的 类【UserMapper】 的 使用
public class UserRepositoryImpl implements UserRepository {@Autowiredprivate UserMapper userMapper;@Overridepublic List<User> findAll() {return userMapper.findAll();}
}@MapperScan
@MapperScan 是扫描mapper类的注解,在配置类中,使用@MapperScan注解之后,就不用在每个,持久层的接口上添加@Mapper注解
package com.sxz.test.one;import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.sxz.test.one.mapper")
public class HelloWorldMainApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {// Spring应用启动起来SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class,args);}
}
26.AOP
26.1.@Configuration @ComponentScan @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
26.2@Component @Aspect @Pointcut @Before @After @Around
Java学习之「Spring + AspectJ 」_sun0322的博客-CSDN博客
27.Junit
27.1.@SpringBootTest @DisplayName("Test Junit") @TestExecutionListeners @ActiveProfiles("dev")
27.2.@MockBean @SpyBean @Mock @Spy @BeforeEach @AfterEach
27.3.@Test @DatabaseSetup(value = "/xxx/xxx/input.xml") @ExpectedDatabase(value = "/xxx/xxx/xxx.xml")
https://blog.csdn.net/sxzlc/article/details/123195147
28.1.@SpringBootApplication注解背后 @Configuration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan
工作中使用到的单词(软件开发)_sun0322的博客-CSDN博客
@Configuration
作用:指定当前类是一个配置类,在使用spring的时候刚开始都是xml配置,也正是这个注解,开启了类配置方式。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector:导入哪些组件的选择器;
会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration);
(点进去会发现@Import,说白了他就是借助@Import的支持,收集和注册特定场景相关的bean定义。)
@Import作用:用于导入其他的配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration也是借助@Import的帮助,将所有符合自动配置条件的bean定义加载到IoC容器,仅此而已!
★:@EnableAutoConfiguration 会加载 spring.factories 中标记的类
加载原因
在开启@EnableAutoConfiguration标记后,会自动导入AutoConfigurationImportSelector组件,
(@EnableAutoConfiguration中,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class))
该组件内部调用SpringFactoriesLoader
加载autoconfigure.jar包中的spring.factories文件,
根据文件定义列表载入各个配置类
@ComponentScan
作用:用于通过注解指定spring在创建容器时要扫描的包
我们可以通过basePackages等属性来细粒度的定制@ComponentScan自动扫描的范围,
如果不指定,则默认Spring框架实现会从声明@ComponentScan所在类的package进行扫描。
★:这也就是springboot启动类为什么放在包外的原因。
28.2.Spring 的 @import 和 @ComponentScan 在功能上有什么区别
在Spring中,@Import和@ComponentScan注解都用于配置bean的自动装配。它们的区别在于:
===
@Import注解是用来导入其他配置类,可以将多个配置类组合在一起进行配置。例如,可以使用@Import注解将多个@Configuration注解的配置类导入到另一个配置类中,以便在该配置类中使用这些配置类中定义的bean。
====
@ComponentScan注解是用来自动扫描指定包及其子包下的所有类,将其中@Component注解标记的类注册为Spring容器中的bean。可以使用@ComponentScan注解自动注册一些通用的bean,例如@Service、@Controller和@Repository等常用的注解。
===
因此,@Import注解更适合用于组合多个配置类,而@ComponentScan注解更适合用于自动注册通用的bean。但是,在实际使用中,两者都可以用于配置bean的自动装配。
=====
===
29.元注解 @Retention @Target @Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:注解只保留在源文件,当Java文件编译成class文件的时候,注解被遗弃;
RetentionPolicy.CLASS:注解被保留到class文件,但jvm加载class文件时候被遗弃,这是默认的生命周期;
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
CONSTRUCTOR:用于描述构造器
FIELD:用于描述域
LOCAL_VARIABLE:用于描述局部变量
METHOD:用于描述方法
PACKAGE:用于描述包
PARAMETER:用于描述参数
TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
@Inherited (非必要) - 它所标注的注解具有继承性。
30.★★★知识点★★★ :spring.batch.job.enabled 配置用于启动时是否创建JobLauncherCommandLineRunner
@TestPropertySource(properties = { "spring.batch.job.enabled=false" }) 或 -Dspring.batch.job.enabled=false
spring.batch.job.enabled 配置用于启动时是否创建JobLauncherCommandLineRunner,
目的
Spring Batch 的测试类配置@TestPropertySource(properties = { "spring.batch.job.enabled=false" })之后,
测试数据库中,无需有SpringBatch的9个Table
扩展,SpringBatch的9个Table
Eclipse中的,ER图生成工具:【ERMaster】_sun0322的博客-CSDN博客
扩展,SpringBatch的启动过程
使用SpringBoot启动SpringBatch,启动过程源代码分析_sun0322的博客-CSDN博客
31.@ControllerAdvice @Order(1) 类 ResponseBodyAdvice
@ControllerAdvice
@Order(1)@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice 的介绍及三种用法_Ethan.Han的博客-CSDN博客_controlleradvice
@ControllerAdvice学名是Controller增强器,作用是给Controller控制器添加统一的操作或处理。
(Advice 时AOP中的术语,增强)
简单例子1(全局参数绑定
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyGlobalHandler {@ModelAttributepublic void presetParam(Model model){model.addAttribute("globalAttr","this is a global attribute");}
}@order
@order,使用注解方式使bean的加载顺序得到控制,@Order标记定义了组件的加载顺序,值越小拥有越高的优先级,可为负数。
值越小,越先被加载。order如果不标注数字,默认最低优先级,因为其默认值是int最大值
类:ResponseBodyAdvice
SpringBoot使用ResponseBodyAdvice进行统一响应处理_BlueKitty1210的博客-CSDN博客
实现ResponseBodyAdvice接口,其实是对加了@RestController(也就是@Controller+@ResponseBody)注解的处理器将要返回的值进行增强处理。
其实也就是采用了AOP的思想,对返回值进行一次修改。
===
适用场景 , 返回给调用方一个统一的响应对象 , 即Controller中使用了@ResponseBody注解的方法 , 可以随意返回Object , String , List 等 , 在该对象中进行统一处理并返回
package com.xbz.common.web.exception;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseBodyAdvice;/*** @title 全局统一响应处理* @author Xingbz* @createDate 2019-8-2*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalResponseBodyAdvice implements ResponseBodyAdvice {/** 此处如果返回false , 则不执行当前Advice的业务 */@Overridepublic boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class converterType) {return true;}/** 处理响应的具体业务方法 */@Overridepublic Object beforeBodyWrite(Object body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {if(body instanceof JSONModel){return body;}else{if (body instanceof JSONObject){return body;}JSONModel jsonModel = new JSONModel();jsonModel.setCode(JSONModel.CODE_SUCCESS);jsonModel.setMessage(JSONModel.MESSAGE_SUCCESS);jsonModel.setData(body);return jsonModel;}}
}===
32.@Alias // ibatis 的标注
关于mybatis注解之@alias别名用法-蒲公英云
java
import org.apache.ibatis.type.Alias;@Alias(“userInfo”)
public class XXXXXX
sql xml
<select id="findUser" resultType="userInfo">33.@param // ibatis 的标注
@Param主要是用来注解dao类中方法的参数,便于在对应的dao.xml文件中引用
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;@Mapper
public interface UserMapperUser selectByNameAndPwd(@Param("userName") String name,@Param("Password") String );在其对应的dao.xml文件中的查询语句则为:
select username,password from user where username=#{userName} and password=#{Password}为什么要使用@Param
在不使用@Param注解的时候,函数的参数只能为一个,并且在查询语句取值时只能用#{},且其所属的类必须为Javabean(实体类),
而使用@Param注解则可以使用多个参数,在查询语句中使用时可以使用#{}或者${}
public int getUsersDetail(User user);<!--这里直接引用对象属性即可,不需要对象.属性的方式-->
<select id="getUserDetail" statementType="CALLABLE" resultMap="baseMap">Exec WebApi_Get_CustomerList #{userid}
</select>特别说明, $只是字符串拼接,所以要特别小心sql注入问题。 能同时使用#和$的时候,最好用#。
====
34.★★★ 知识点★★★ :OncePerRequestFilter与Filter的区别
Filter 与 OncePerRequestFilter_一棵栗子树的博客-CSDN博客_onceperrequestfilter和filter
OncePerRequestFilter与Filter的区别 - 墨天轮
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
import javax.servlet.Filter@Component
@Order(1)
public class FirstFilter implements Filter {@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain)throws ServletException, IOException {}}// 而doFilterInternal是OncePerRequestFilter 中的一个抽象方法
// 阅读源码可知:
// OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter方法中通过request.getAttribute判断当前过滤器是否已执行
// 若未执行过,则调用doFilterInternal方法,交由其子类实现@Overrideprotected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest servletRequest, HttpServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain)throws ServletException, IOException {
35.XXX
xxx
36.XXX
xxx
37.xxxx
xxx
===
这篇关于Servlet,Spring,Spring Boot,Sprint Batch,ThymeLeaf 学习的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






