本文主要是介绍Codeforces Round 930 (Div. 2 ABCDEF题) 视频讲解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
A. Shuffle Party
Problem Statement
You are given an array a 1 , a 2 , … , a n a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n a1,a2,…,an. Initially, a i = i a_i=i ai=i for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n 1 \le i \le n 1≤i≤n.
The operation swap ( k ) \texttt{swap}(k) swap(k) for an integer k ≥ 2 k \ge 2 k≥2 is defined as follows:
- Let d d d be the largest divisor † ^\dagger † of k k k which is not equal to k k k itself. Then swap the elements a d a_d ad and a k a_k ak.
Suppose you perform swap ( i ) \texttt{swap}(i) swap(i) for each i = 2 , 3 , … , n i=2,3,\ldots, n i=2,3,…,n in this exact order. Find the position of 1 1 1 in the resulting array. In other words, find such j j j that a j = 1 a_j = 1 aj=1 after performing these operations.
† ^\dagger † An integer x x x is a divisor of y y y if there exists an integer z z z such that y = x ⋅ z y = x \cdot z y=x⋅z.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104). The description of the test cases follows.
The only line of each test case contains one integer n n n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le n \le 10^9 1≤n≤109) — the length of the array a a a.
Output
For each test case, output the position of 1 1 1 in the resulting array.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 4 |
| 1 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 120240229 |
| output |
|---|
| 1 |
| 4 |
| 4 |
| 67108864 |
Note
In the first test case, the array is [ 1 ] [1] [1] and there are no operations performed.
In the second test case, a a a changes as follows:
- Initially, a a a is [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ] [1,2,3,4] [1,2,3,4].
- After performing swap ( 2 ) \texttt{swap}(2) swap(2), a a a changes to [ 2 ‾ , 1 ‾ , 3 , 4 ] [\underline{2},\underline{1},3,4] [2,1,3,4] (the elements being swapped are underlined).
- After performing swap ( 3 ) \texttt{swap}(3) swap(3), a a a changes to [ 3 ‾ , 1 , 2 ‾ , 4 ] [\underline{3},1,\underline{2},4] [3,1,2,4].
- After performing swap ( 4 ) \texttt{swap}(4) swap(4), a a a changes to [ 3 , 4 ‾ , 2 , 1 ‾ ] [3,\underline{4},2,\underline{1}] [3,4,2,1].
Finally, the element 1 1 1 lies on index 4 4 4 (that is, a 4 = 1 a_4 = 1 a4=1). Thus, the answer is 4 4 4.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;int i = 1;while (i * 2 <= n) i *= 2;cout << i << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int Data;cin >> Data;while (Data --)solve();return 0;
}
B. Binary Path
Problem Statement
You are given a 2 × n 2 \times n 2×n grid filled with zeros and ones. Let the number at the intersection of the i i i-th row and the j j j-th column be a i j a_{ij} aij.
There is a grasshopper at the top-left cell ( 1 , 1 ) (1, 1) (1,1) that can only jump one cell right or downwards. It wants to reach the bottom-right cell ( 2 , n ) (2, n) (2,n). Consider the binary string of length n + 1 n+1 n+1 consisting of numbers written in cells of the path without changing their order.
Your goal is to:
- Find the lexicographically smallest † ^\dagger † string you can attain by choosing any available path;
- Find the number of paths that yield this lexicographically smallest string.
† ^\dagger † If two strings s s s and t t t have the same length, then s s s is lexicographically smaller than t t t if and only if in the first position where s s s and t t t differ, the string s s s has a smaller element than the corresponding element in t t t.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 2≤n≤2⋅105).
The second line of each test case contains a binary string a 11 a 12 … a 1 n a_{11} a_{12} \ldots a_{1n} a11a12…a1n ( a 1 i a_{1i} a1i is either 0 0 0 or 1 1 1).
The third line of each test case contains a binary string a 21 a 22 … a 2 n a_{21} a_{22} \ldots a_{2n} a21a22…a2n ( a 2 i a_{2i} a2i is either 0 0 0 or 1 1 1).
It is guaranteed that the sum of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output two lines:
- The lexicographically smallest string you can attain by choosing any available path;
- The number of paths that yield this string.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 3 |
| 2 |
| 00 |
| 00 |
| 4 |
| 1101 |
| 1100 |
| 8 |
| 00100111 |
| 11101101 |
| output |
|---|
| 000 |
| 2 |
| 11000 |
| 1 |
| 001001101 |
| 4 |
Note
In the first test case, the lexicographically smallest string is 000 \mathtt{000} 000. There are two paths that yield this string:
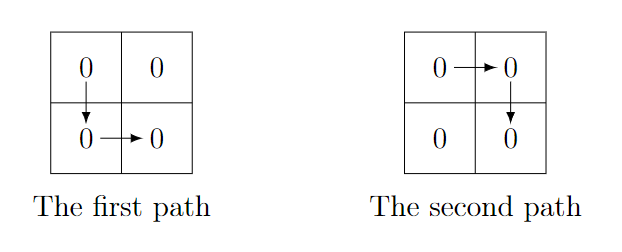
In the second test case, the lexicographically smallest string is 11000 \mathtt{11000} 11000. There is only one path that yields this string:
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;void solve()
{int n;string s[2];cin >> n >> s[0] >> s[1];int p = n - 1;for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++)if (s[0][i] != '0' && s[1][i - 1] == '0'){p = i - 1;break;}string res;for (int i = 0; i <= p; i ++)res += s[0][i];res += s[1][p];for (int i = p + 1; i < n; i ++)res += s[1][i];int lst = 0;for (int i = n - 1, j = n; i >= 0; i --, j --)if (res[j] != s[1][i]){lst = i + 1;break;}cout << res << endl;cout << p - lst + 1 << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int Data;cin >> Data;while (Data --)solve();return 0;
}
C. Bitwise Operation Wizard
Problem Statement
There is a secret sequence p 0 , p 1 , … , p n − 1 p_0, p_1, \ldots, p_{n-1} p0,p1,…,pn−1, which is a permutation of { 0 , 1 , … , n − 1 } \{0,1,\ldots,n-1\} {0,1,…,n−1}.
You need to find any two indices i i i and j j j such that p i ⊕ p j p_i \oplus p_j pi⊕pj is maximized, where ⊕ \oplus ⊕ denotes the bitwise XOR operation.
To do this, you can ask queries. Each query has the following form: you pick arbitrary indices a a a, b b b, c c c, and d d d ( 0 ≤ a , b , c , d < n 0 \le a,b,c,d < n 0≤a,b,c,d<n). Next, the jury calculates x = ( p a ∣ p b ) x = (p_a \mid p_b) x=(pa∣pb) and y = ( p c ∣ p d ) y = (p_c \mid p_d) y=(pc∣pd), where ∣ | ∣ denotes the bitwise OR operation. Finally, you receive the result of comparison between x x x and y y y. In other words, you are told if x < y x < y x<y, x > y x > y x>y, or x = y x = y x=y.
Please find any two indices i i i and j j j ( 0 ≤ i , j < n 0 \le i,j < n 0≤i,j<n) such that p i ⊕ p j p_i \oplus p_j pi⊕pj is maximum among all such pairs, using at most 3 n 3n 3n queries. If there are multiple pairs of indices satisfying the condition, you may output any one of them.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 3 1 \le t \le 10^3 1≤t≤103). The description of the test cases follows.
Interaction
The first line of each test case contains one integer n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 4 2 \le n \le 10^4 2≤n≤104). At this moment, the permutation p 0 , p 1 , … , p n − 1 p_0, p_1, \ldots, p_{n-1} p0,p1,…,pn−1 is chosen. The interactor in this task is not adaptive. In other words, the sequence p p p is fixed in every test case and does not change during the interaction.
To ask a query, you need to pick four indices a a a, b b b, c c c, and d d d ( 0 ≤ a , b , c , d < n 0 \le a,b,c,d < n 0≤a,b,c,d<n) and print the line of the following form:
- “? a b c d”
After that, you receive:
- “<” if ( p a ∣ p b ) < ( p c ∣ p d ) (p_a \mid p_b) < (p_c \mid p_d) (pa∣pb)<(pc∣pd);
- “=” if ( p a ∣ p b ) = ( p c ∣ p d ) (p_a \mid p_b) = (p_c \mid p_d) (pa∣pb)=(pc∣pd);
- “>” if ( p a ∣ p b ) > ( p c ∣ p d ) (p_a \mid p_b) > (p_c \mid p_d) (pa∣pb)>(pc∣pd).
You can make at most 3 n 3n 3n queries of this form.
Next, if your program has found a pair of indices i i i and j j j ( 0 ≤ i , j < n 0 \le i, j < n 0≤i,j<n) such that p i ⊕ p j p_i \oplus p_j pi⊕pj is maximized, print the line of the following form:
- “! i j”
Note that this line is not considered a query and is not taken into account when counting the number of queries asked.
After this, proceed to the next test case.
If you make more than 3 n 3n 3n queries during an interaction, your program must terminate immediately, and you will receive the Wrong Answer verdict. Otherwise, you can get an arbitrary verdict because your solution will continue to read from a closed stream.
After printing a query or the answer for a test case, do not forget to output the end of line and flush the output. Otherwise, you will get the verdict Idleness Limit Exceeded. To do this, use:
- fflush(stdout) or cout.flush() in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- see the documentation for other languages.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 1 0 4 10^4 104.
Hacks
To hack, follow the test format below.
The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 3 1 \le t \le 10^3 1≤t≤103). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains one integer n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 4 2 \le n \le 10^4 2≤n≤104).
The second line of each test case contains n n n integers p 0 , p 1 , … , p n − 1 p_0,p_1,\ldots,p_{n-1} p0,p1,…,pn−1, which represent a permutation of integers from 0 0 0 to n − 1 n - 1 n−1.
The sum of n n n over all test cases should not exceed 1 0 4 10^4 104.
Example
| input |
|---|
| 2 |
| 4 |
| < |
| = |
| > |
2
| output |
|---|
| ? 0 2 3 1 |
| ? 1 1 2 3 |
| ? 1 2 0 3 |
| ! 3 2 |
| ! 0 1 |
Note
In the first test case, the hidden permutation is p = [ 0 , 3 , 1 , 2 ] p=[0,3,1,2] p=[0,3,1,2].
For the query “? 0 2 3 1”, the jury return “<” because ( p 0 ∣ p 2 ) = ( 0 ∣ 1 ) = 1 < ( p 3 ∣ p 1 ) = ( 2 ∣ 3 ) = 3 (p_0 \mid p_2) = (0 \mid 1) =1 < (p_3 \mid p_1) = (2 \mid 3) = 3 (p0∣p2)=(0∣1)=1<(p3∣p1)=(2∣3)=3.
For the query “? 1 1 2 3”, the jury return “=” because ( p 1 ∣ p 1 ) = ( 3 ∣ 3 ) = 3 = ( p 2 ∣ p 3 ) = ( 1 ∣ 2 ) = 3 (p_1 \mid p_1) = (3\mid 3)= 3 = (p_2 \mid p_3) = (1 \mid 2)=3 (p1∣p1)=(3∣3)=3=(p2∣p3)=(1∣2)=3.
For the query “? 1 2 0 3”, the jury return “>” because ( p 1 ∣ p 2 ) = ( 3 ∣ 1 ) = 3 > ( p 0 ∣ p 3 ) = ( 0 ∣ 2 ) = 2 (p_1 \mid p_2) = (3 \mid 1) = 3 > (p_0 \mid p_3) = (0\mid 2)=2 (p1∣p2)=(3∣1)=3>(p0∣p3)=(0∣2)=2.
The answer i = 3 i = 3 i=3 and j = 2 j = 2 j=2 is valid: ( p 3 ⊕ p 2 ) = ( 2 ⊕ 1 ) = 3 (p_3 \oplus p_2) = (2 \oplus 1) = 3 (p3⊕p2)=(2⊕1)=3 is indeed equal to the maximum possible value of p i ⊕ p j p_i \oplus p_j pi⊕pj. Another valid answer would be i = 0 i=0 i=0 and j = 1 j=1 j=1. As the number of queries does not exceed 3 n = 12 3n=12 3n=12, the answer is considered correct.
In the second test case, n = 2 n = 2 n=2, so p p p is either [ 0 , 1 ] [0, 1] [0,1] or [ 1 , 0 ] [1, 0] [1,0]. In any case, p 0 ⊕ p 1 = 1 p_0 \oplus p_1 = 1 p0⊕p1=1 is maximum possible.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;int ask(int a, int b, int c, int d)
{cout << "? " << a << " " << b << " " << c << " " << d << endl;char t;cin >> t;if (t == '=') return 0;else if (t == '<') return 1;else return 2;
}void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;int mx = 0;for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++)if (ask(mx, mx, i, i) == 1)mx = i;std::vector<int> best;best.push_back(0);for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++){int j = *best.begin(), v = ask(i, mx, j, mx);if (v == 2)best.clear(), best.push_back(i);else if (v == 0)best.push_back(i);}int mn = *best.begin();for (int i = 1; i < best.size(); i ++)if (ask(mn, mn, best[i], best[i]) == 2)mn = best[i];cout << "! " << mx << " " << mn << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int Data;cin >> Data;while (Data --)solve();return 0;
}
D. Pinball
Problem Statement
There is a one-dimensional grid of length n n n. The i i i-th cell of the grid contains a character s i s_i si, which is either ‘<’ or ‘>’.
When a pinball is placed on one of the cells, it moves according to the following rules:
- If the pinball is on the i i i-th cell and s i s_i si is ‘<’, the pinball moves one cell to the left in the next second. If s i s_i si is ‘>’, it moves one cell to the right.
- After the pinball has moved, the character s i s_i si is inverted (i. e. if s i s_i si used to be ‘<’, it becomes ‘>’, and vice versa).
- The pinball stops moving when it leaves the grid: either from the left border or from the right one.
You need to answer n n n independent queries. In the i i i-th query, a pinball will be placed on the i i i-th cell. Note that we always place a pinball on the initial grid.
For each query, calculate how many seconds it takes the pinball to leave the grid. It can be shown that the pinball will always leave the grid within a finite number of steps.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 5 1 \le t \le 10^5 1≤t≤105). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains an integer n n n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 5 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le n \le 5 \cdot 10^5 1≤n≤5⋅105).
The second line of each test case contains a string s 1 s 2 … s n s_1s_2 \ldots s_{n} s1s2…sn of length n n n consisting of characters ‘<’ and ‘>’.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 5 ⋅ 1 0 5 5 \cdot 10^5 5⋅105.
Output
For each test case, for each i i i ( 1 ≤ i ≤ n 1 \le i \le n 1≤i≤n) output the answer if a pinball is initially placed on the i i i-th cell.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 3 |
| 3 |
| ><< |
| 4 |
| <<<< |
| 6 |
| <><<<> |
| output |
|---|
| 3 6 5 |
| 1 2 3 4 |
| 1 4 7 10 8 1 |
Note
In the first test case, the movement of the pinball for i = 1 i=1 i=1 is shown in the following pictures. It takes the pinball 3 3 3 seconds to leave the grid.

The movement of the pinball for i = 2 i=2 i=2 is shown in the following pictures. It takes the pinball 6 6 6 seconds to leave the grid.

Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;void solve()
{int n;string s;cin >> n >> s;s = '>' + s + '<';int lst = 0;std::vector<int> pre(n + 2, 0), suf(n + 2, 0), less(n + 2, 0), grt(n + 2, 0);std::vector<int> cnt1(n + 2, 0), cnt2(n + 2, 0), pos1, pos2;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){cnt1[i] = cnt1[i - 1] + (s[i] == '>');pre[i] = pre[i - 1] + (s[i] == '>') * i;if (s[i] == '<' && lst) less[i] = less[i - 1] + i - lst, lst = i;else if (s[i] == '<') less[i] = less[i - 1], lst = i;else less[i] = less[i - 1];}lst = 0;for (int i = n; i >= 1; i --){suf[i] = suf[i + 1] + (s[i] == '<') * i, cnt2[i] = cnt2[i + 1] + (s[i] == '<');if (s[i] == '<') pos1.push_back(i);else pos2.push_back(i);if (s[i] == '>' && lst) grt[i] = grt[i + 1] + lst - i, lst = i;else if (s[i] == '>') grt[i] = grt[i + 1], lst = i;else grt[i] = grt[i + 1];}pos1.push_back(n + 1), pos2.push_back(0);sort(pos1.begin(), pos1.end());sort(pos2.begin(), pos2.end());for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){// cerr << i << ":";if (cnt1[i] > cnt2[i] || (cnt1[i] == cnt2[i] && s[i] == '<')){int tot = min(cnt1[i], cnt2[i]);if (!cnt2[i]){cout << n - i + 1 << " ";continue;}if (s[i] == '<'){auto it = lower_bound(pos1.begin(), pos1.end(), i), it2 = lower_bound(pos2.begin(), pos2.end(), i);int l1 = it - pos1.begin();int r1 = l1 + tot - 1;int r2 = ( -- it2) - pos2.begin();int l2 = r2 - tot + 1;cout << ((suf[pos1[l1]] - suf[pos1[r1] + 1]) - (pre[pos2[r2]] - pre[pos2[l2] - 1])) * 2 + less[pos1[r1]] - less[pos1[l1]] + (n - pos1[r1] + 1) << " ";}else{auto it = lower_bound(pos2.begin(), pos2.end(), i), it2 = lower_bound(pos1.begin(), pos1.end(), i);auto r1 = it - pos2.begin();int l1 = r1 - tot + 1;auto l2 = it2 - pos1.begin();int r2 = l2 + tot - 1;int v = ((suf[pos1[l2]] - suf[pos1[r2] + 1]) - (pre[pos2[r1]] - pre[pos2[l1] - 1])) * 2 + grt[pos2[l1 - 1]] - grt[pos2[r1]];cout << v + n - pos2[l1 - 1] + 1 << " ";}}else{int tot = min(cnt1[i], cnt2[i]);if (!cnt1[i]){cout << i << " ";continue;}if (s[i] == '<'){auto it = lower_bound(pos1.begin(), pos1.end(), i), it2 = lower_bound(pos2.begin(), pos2.end(), i);auto l1 = it - pos1.begin();int r1 = l1 + tot - 1;auto r2 = ( -- it2) - pos2.begin();int l2 = r2 - tot + 1;int v = ((suf[pos1[l1]] - suf[pos1[r1] + 1]) - (pre[pos2[r2]] - pre[pos2[l2] - 1])) * 2 + less[pos1[r1 + 1]] - less[pos1[l1]];cout << v + pos1[r1 + 1] << " ";}else{auto it = lower_bound(pos2.begin(), pos2.end(), i), it2 = lower_bound(pos1.begin(), pos1.end(), i);auto r1 = it - pos2.begin();int l1 = r1 - tot + 1;auto l2 = it2 - pos1.begin();int r2 = l2 + tot - 1;// cerr << l2 << " " << r2 << " " << l1 << " " << r1 << endl;int v = ((suf[pos1[l2]] - suf[pos1[r2] + 1]) - (pre[pos2[r1]] - pre[pos2[l1] - 1])) * 2 + grt[pos2[l1]] - grt[pos2[r1]];cout << v + pos2[l1] << " ";}}}cout << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int Data;cin >> Data;while (Data --)solve();return 0;
}
E. Pokémon Arena
Problem Statement
You are at a dueling arena. You also possess n n n Pokémons. Initially, only the 1 1 1-st Pokémon is standing in the arena.
Each Pokémon has m m m attributes. The j j j-th attribute of the i i i-th Pokémon is a i , j a_{i,j} ai,j. Each Pokémon also has a cost to be hired: the i i i-th Pokémon’s cost is c i c_i ci.
You want to have the n n n-th Pokémon stand in the arena. To do that, you can perform the following two types of operations any number of times in any order:
- Choose three integers i i i, j j j, k k k ( 1 ≤ i ≤ n 1 \le i \le n 1≤i≤n, 1 ≤ j ≤ m 1 \le j \le m 1≤j≤m, k > 0 k > 0 k>0), increase a i , j a_{i,j} ai,j by k k k permanently. The cost of this operation is k k k.
- Choose two integers i i i, j j j ( 1 ≤ i ≤ n 1 \le i \le n 1≤i≤n, 1 ≤ j ≤ m 1 \le j \le m 1≤j≤m) and hire the i i i-th Pokémon to duel with the current Pokémon in the arena based on the j j j-th attribute. The i i i-th Pokémon will win if a i , j a_{i,j} ai,j is greater than or equal to the j j j-th attribute of the current Pokémon in the arena (otherwise, it will lose). After the duel, only the winner will stand in the arena. The cost of this operation is c i c_i ci.
Find the minimum cost you need to pay to have the n n n-th Pokémon stand in the arena.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 5 1 \le t \le 10^5 1≤t≤105). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n n n and m m m ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 4 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \le n \le 4 \cdot 10^5 2≤n≤4⋅105, 1 ≤ m ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le m \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤m≤2⋅105, 2 ≤ n ⋅ m ≤ 4 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \leq n \cdot m \leq 4 \cdot 10^5 2≤n⋅m≤4⋅105).
The second line of each test case contains n n n integers c 1 , c 2 , … , c n c_1, c_2, \ldots, c_n c1,c2,…,cn ( 1 ≤ c i ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le c_i \le 10^9 1≤ci≤109).
The i i i-th of the following n n n lines contains m m m integers a i , 1 , a i , 2 , … , a i , m a_{i,1}, a_{i,2}, \ldots, a_{i,m} ai,1,ai,2,…,ai,m ( 1 ≤ a i , j ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le a_{i,j} \le 10^9 1≤ai,j≤109).
It is guaranteed that the sum of n ⋅ m n \cdot m n⋅m over all test cases does not exceed 4 ⋅ 1 0 5 4 \cdot 10^5 4⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output the minimum cost to make the n n n-th Pokémon stand in the arena.
Example
| input |
|---|
| 4 |
| 3 3 |
| 2 3 1 |
| 2 9 9 |
| 6 1 7 |
| 1 2 1 |
| 3 3 |
| 2 3 1 |
| 9 9 9 |
| 6 1 7 |
| 1 2 1 |
| 4 2 |
| 2 8 3 5 |
| 18 24 |
| 17 10 |
| 1 10 |
| 1 1 |
| 6 3 |
| 21412674 3212925 172015806 250849370 306960171 333018900 |
| 950000001 950000001 950000001 |
| 821757276 783362401 760000001 |
| 570000001 700246226 600757652 |
| 380000001 423513575 474035234 |
| 315201473 300580025 287023445 |
| 1 1 1 |
| output |
|---|
| 2 |
| 6 |
| 17 |
| 1224474550 |
Note
In the first test case, the attribute array of the 1 1 1-st Pokémon (which is standing in the arena initially) is [ 2 , 9 , 9 ] [2,9,9] [2,9,9].
In the first operation, you can choose i = 3 i=3 i=3, j = 1 j=1 j=1, k = 1 k=1 k=1, and increase a 3 , 1 a_{3,1} a3,1 by 1 1 1 permanently. Now the attribute array of the 3 3 3-rd Pokémon is [ 2 , 2 , 1 ] [2,2,1] [2,2,1]. The cost of this operation is k = 1 k = 1 k=1.
In the second operation, you can choose i = 3 i=3 i=3, j = 1 j=1 j=1, and hire the 3 3 3-rd Pokémon to duel with the current Pokémon in the arena based on the 1 1 1-st attribute. Since a i , j = a 3 , 1 = 2 ≥ 2 = a 1 , 1 a_{i,j}=a_{3,1}=2 \ge 2=a_{1,1} ai,j=a3,1=2≥2=a1,1, the 3 3 3-rd Pokémon will win. The cost of this operation is c 3 = 1 c_3 = 1 c3=1.
Thus, we have made the 3 3 3-rd Pokémon stand in the arena within the cost of 2 2 2. It can be proven that 2 2 2 is minimum possible.
In the second test case, the attribute array of the 1 1 1-st Pokémon in the arena is [ 9 , 9 , 9 ] [9,9,9] [9,9,9].
In the first operation, you can choose i = 2 i=2 i=2, j = 3 j=3 j=3, k = 2 k=2 k=2, and increase a 2 , 3 a_{2,3} a2,3 by 2 2 2 permanently. Now the attribute array of the 2 2 2-nd Pokémon is [ 6 , 1 , 9 ] [6,1,9] [6,1,9]. The cost of this operation is k = 2 k = 2 k=2.
In the second operation, you can choose i = 2 i=2 i=2, j = 3 j=3 j=3, and hire the 2 2 2-nd Pokémon to duel with the current Pokémon in the arena based on the 3 3 3-rd attribute. Since a i , j = a 2 , 3 = 9 ≥ 9 = a 1 , 3 a_{i,j}=a_{2,3}=9 \ge 9=a_{1,3} ai,j=a2,3=9≥9=a1,3, the 2 2 2-nd Pokémon will win. The cost of this operation is c 2 = 3 c_2 = 3 c2=3.
In the third operation, you can choose i = 3 i=3 i=3, j = 2 j=2 j=2, and hire the 3 3 3-rd Pokémon to duel with the current Pokémon in the arena based on the 2 2 2-nd attribute. Since a i , j = a 1 , 2 = 2 ≥ 1 = a 2 , 2 a_{i,j}=a_{1,2}=2 \ge 1=a_{2,2} ai,j=a1,2=2≥1=a2,2, the 3 3 3-rd Pokémon can win. The cost of this operation is c 3 = 1 c_3 = 1 c3=1.
Thus, we have made the 3 3 3-rd Pokémon stand in the arena within the cost of 6 6 6. It can be proven that 6 6 6 is minimum possible.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 4e6 + 10;int h[N], e[N], ne[N], w[N], idx, id, dist[N], Vis[N];void add(int a, int b, int c)
{e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
}void solve()
{int n, m;cin >> n >> m;for (int i = 1; i <= 3 * n * m; i ++)h[i] = -1;idx = 0;std::vector<int> c(n + 1);std::vector<vector<int>> a(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cin >> c[i];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++)cin >> a[i][j];id = n;for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++){std::vector<PII> v;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)v.emplace_back(a[i][j], i);sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<>());int source = id + 1;for (auto i : v)add(i.second, ++ id, c[i.second]), add( ++ id, i.second, 0);//, cout << id << " " << i.second << " " << 0 << endl;for (int i = source; i <= id; i += 2)add(i, i + 1, 0);//, cerr << i << " " << i + 1 << " " << 0 << endl;for (int i = source, k = 1; i + 2 <= id; i += 2, k ++)add(i + 2, i, v[k - 1].first - v[k].first);//, cerr << i + 2 << " " << i << " " << v[k - 1].first - v[k].first << endl;for (int i = source + 1; i + 2 <= id; i += 2)add(i, i + 2, 0);//, cerr << i << " " << i + 2 << " " << 0 << endl;}for (int i = 1; i <= id; i ++) dist[i] = 1e18, Vis[i] = 0;priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> Heap;Heap.emplace(0, n), dist[n] = 0;while (Heap.size()){auto Tmp = Heap.top();Heap.pop();int u = Tmp.second;if (Vis[u]) continue;Vis[u] = 1;for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]){int j = e[i];if (dist[j] > dist[u] + w[i]){dist[j] = dist[u] + w[i];Heap.emplace(dist[j], j);}}}cout << dist[1] << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int Data;cin >> Data;while (Data --)solve();return 0;
}
F. Bitwise Paradox
Problem Statement
You are given two arrays a a a and b b b of size n n n along with a fixed integer v v v.
An interval [ l , r ] [l, r] [l,r] is called a good interval if ( b l ∣ b l + 1 ∣ … ∣ b r ) ≥ v (b_l \mid b_{l+1} \mid \ldots \mid b_r) \ge v (bl∣bl+1∣…∣br)≥v, where ∣ | ∣ denotes the bitwise OR operation. The beauty of a good interval is defined as max ( a l , a l + 1 , … , a r ) \max(a_l, a_{l+1}, \ldots, a_r) max(al,al+1,…,ar).
You are given q q q queries of two types:
- “1 i x”: assign b i : = x b_i := x bi:=x;
- “2 l r”: find the minimum beauty among all good intervals [ l 0 , r 0 ] [l_0,r_0] [l0,r0] satisfying l ≤ l 0 ≤ r 0 ≤ r l \le l_0 \le r_0 \le r l≤l0≤r0≤r. If there is no suitable good interval, output − 1 -1 −1 instead.
Please process all queries.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 5 1 \le t \le 10^5 1≤t≤105). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n n n and v v v ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤n≤2⋅105, 1 ≤ v ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le v \le 10^9 1≤v≤109).
The second line of each testcase contains n n n integers a 1 , a 2 , … , a n a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n a1,a2,…,an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le a_i \le 10^9 1≤ai≤109).
The third line of each testcase contains n n n integers b 1 , b 2 , … , b n b_1, b_2, \ldots, b_n b1,b2,…,bn ( 1 ≤ b i ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le b_i \le 10^9 1≤bi≤109).
The fourth line of each testcase contains one integer q q q ( 1 ≤ q ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le q \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤q≤2⋅105).
The i i i-th of the following q q q lines contains the description of queries. Each line is of one of two types:
- “1 i x” ( 1 ≤ i ≤ n 1 \le i \le n 1≤i≤n, 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 0 9 ) 1 \le x \le 10^9) 1≤x≤109);
- “2 l r” ( 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n 1 \le l \le r \le n 1≤l≤r≤n).
It is guaranteed that both the sum of n n n and the sum of q q q over all test cases do not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output the answers for all queries of the second type.
Example
| input |
|---|
| 3 |
| 3 7 |
| 2 1 3 |
| 2 2 3 |
| 4 |
| 2 1 3 |
| 1 2 5 |
| 2 2 3 |
| 2 1 3 |
| 4 5 |
| 5 1 2 4 |
| 4 2 3 3 |
| 6 |
| 2 1 4 |
| 1 3 15 |
| 2 3 4 |
| 2 2 4 |
| 1 2 13 |
| 2 1 4 |
| 1 5 |
| 6 |
| 4 |
| 1 |
| 2 1 1 |
| output |
|---|
| -1 3 2 |
| 5 2 2 1 |
| -1 |
Note
In the first test case, a = [ 2 , 1 , 3 ] a = [2, 1, 3] a=[2,1,3], b = [ 2 , 2 , 3 ] b = [2, 2, 3] b=[2,2,3], and v = 7 v = 7 v=7.
The first query is of the second type and has l = 1 l = 1 l=1 and r = 3 r = 3 r=3. The largest interval available is [ 1 , 3 ] [1, 3] [1,3], and its bitwise OR is b 1 ∣ b 2 ∣ b 3 = 3 b_1 \mid b_2 \mid b_3 = 3 b1∣b2∣b3=3 which is less than v v v. Thus, no good interval exists.
The second query asks to change b 2 b_2 b2 to 5 5 5, so b b b becomes [ 2 , 5 , 3 ] [2, 5, 3] [2,5,3].
The third query is of the second type and has l = 2 l = 2 l=2 and r = 3 r = 3 r=3. There are three possible intervals: [ 2 , 2 ] [2, 2] [2,2], [ 3 , 3 ] [3, 3] [3,3], and [ 2 , 3 ] [2, 3] [2,3]. However, b 2 = 5 < v b_2 = 5 < v b2=5<v, b 3 = 3 < v b_3 = 3 < v b3=3<v. So only the last interval is good: it has b 2 ∣ b 3 = 7 b_2 \mid b_3 = 7 b2∣b3=7. The answer is thus max ( a 2 , a 3 ) = 3 \max(a_2, a_3) = 3 max(a2,a3)=3.
The fourth query is of the second type and has l = 1 l = 1 l=1 and r = 3 r = 3 r=3. There are three good intervals: [ 1 , 2 ] [1, 2] [1,2], [ 2 , 3 ] [2, 3] [2,3], and [ 1 , 3 ] [1, 3] [1,3]. Their beauty is 2 2 2, 3 3 3, 3 3 3 correspondingly. The answer is thus 2 2 2.
In the second test case, a = [ 5 , 1 , 2 , 4 ] a = [5, 1, 2, 4] a=[5,1,2,4], b = [ 4 , 2 , 3 , 3 ] b = [4, 2, 3, 3] b=[4,2,3,3], and v = 5 v = 5 v=5.
The first query has l = 1 l = 1 l=1 and r = 4 r = 4 r=4. The only good intervals are: [ 1 , 2 ] [1, 2] [1,2], [ 1 , 3 ] [1, 3] [1,3], [ 1 , 4 ] [1, 4] [1,4]. Their beauty is 5 5 5, 5 5 5, 5 5 5 correspondingly. The answer is thus 5 5 5.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10, INF = 2e9;int n, q, v;
int a[N], b[N];
int F1[N][32], lg[N];
struct Segment
{int l, r;int pre[32], suf[32], res;
}Tree[N << 2];void Init()
{int m = log2(n) + 1;for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )for (int i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n; i ++ )if (!j) F1[i][j] = a[i];else F1[i][j] = max(F1[i][j - 1], F1[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]);
}inline int Max(int l, int r)
{int len = r - l + 1;int k = lg[len];return max(F1[l][k], F1[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]);
}void Pushup(Segment &rt, Segment L, Segment R)
{rt.l = L.l, rt.r = R.r;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i --)rt.pre[i] = L.pre[i] ? L.pre[i] : R.pre[i], rt.suf[i] = R.suf[i] ? R.suf[i] : L.suf[i];int pl = L.r, pr = R.l;rt.res = min(L.res, R.res);for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i --){int p = L.suf[i], q = R.pre[i];if (p) p = min(p, pl);if (q) q = max(q, pr);int lr = p ? Max(p, pr) : INF, rr = q ? Max(pl, q) : INF;if (lr < rr){if (v >> i & 1){if (lr < rt.res)pl = p;else break;}elsert.res = min(rt.res, lr);}else{if (v >> i & 1){if (rr < rt.res)pr = q;else break;}elsert.res = min(rt.res, rr);}}
}void Build(int u, int l, int r)
{Tree[u] = {l, r};if (l == r){if (b[l] > v) Tree[u].res = a[l];else Tree[u].res = INF;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i --)if (b[l] >> i & 1)Tree[u].pre[i] = Tree[u].suf[i] = l;return;}int mid = l + r >> 1;Build(u << 1, l, mid), Build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);Pushup(Tree[u], Tree[u << 1], Tree[u << 1 | 1]);
}void Modify(int u, int x, int d)
{if (Tree[u].l == Tree[u].r){if (d > v) Tree[u].res = a[x];else Tree[u].res = INF;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i --)if (d >> i & 1)Tree[u].pre[i] = Tree[u].suf[i] = x;elseTree[u].pre[i] = Tree[u].suf[i] = 0;return;}int mid = Tree[u].l + Tree[u].r >> 1;if (mid >= x) Modify(u << 1, x, d);else Modify(u << 1 | 1, x, d);Pushup(Tree[u], Tree[u << 1], Tree[u << 1 | 1]);
}Segment Query(int u, int l, int r)
{if (Tree[u].l >= l && Tree[u].r <= r)return Tree[u];int mid = Tree[u].l + Tree[u].r >> 1;if (mid >= l && mid < r){Segment res;Pushup(res, Query(u << 1, l, r), Query(u << 1 | 1, l, r));return res;}else if (mid >= l) return Query(u << 1, l, r);else return Query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
}void solve()
{cin >> n >> v;v --;for (int i = 1, j = 1, k = 0; i <= n; i ++){if (j * 2 <= i) k ++, j *= 2;lg[i] = k;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cin >> a[i];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cin >> b[i];Init(), Build(1, 1, n);cin >> q;while (q --){int op, l, r;cin >> op >> l >> r;if (op == 1)Modify(1, l, r);else{int v = Query(1, l, r).res;if (v == INF) printf("-1 ");else printf("%d ", v);}}printf("\n");
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int Data;cin >> Data;while (Data --)solve();return 0;
}
视频讲解
Codeforces Round 930 (Div. 2)(A ~ F 题讲解)
最后祝大家早日
这篇关于Codeforces Round 930 (Div. 2 ABCDEF题) 视频讲解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







