本文主要是介绍Ubantu基础设置以及多网卡绑定,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
更改主机名称
~$ sudo -i
~# vim /etc/hostname
hosname
~# reboot
更改网卡名称为eth*
~$ sudo vim /etc/default/grub
GRUB_DEFAULT=0
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=hidden
GRUB_TIMEOUT=2
GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR=`lsb_release -i -s 2> /dev/null || echo Debian`
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=""
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0" #只要修改此项即可~$ sudo update-grub #重新更新加载Grub
Sourcing file `/etc/default/grub'
Generating grub configuration file ...
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-4.15.0-55-generic
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-4.15.0-55-generic
done
~$ sudo reboot #重启
配置root远程登录
~$ sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
32 #PermitRootLogin prohibit-password #默认为禁⽌登录
33 PermitRootLogin yes #改为允许登录57 #PasswordAuthentication yes
58 PasswordAuthentication yes #打开密码认证,其实默认就是允许通过密码认证登录~$ sudo su - root #切换到root⽤⼾环境
~# passwd #设置root账号密码
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
~# systemctl restart sshd #重启ssh服务并测试root⽤⼾远程ssh连接
查看ubantu版本
root@ubuntu1-server:~# cat /etc/issue
Ubuntu 18.04.3 LTS \n \lroot@ubuntu1-server:~# cat /proc/version
Linux version 4.15.0-55-generic (buildd@lcy01-amd64-029) (gcc version 7.4.0
(Ubuntu 7.4.0-1ubuntu1~18.04.1))
#60-Ubuntu SMP Tue Jul 2 18:22:20 UTC 2019root@ubuntu1-server:~# uname -a
Linux ubuntu1-server 4.15.0-55-generic #60-Ubuntu SMP Tue Jul 2 18:22:20 UTC 2019
x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linuxroot@ubuntu1-server:~# lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 18.04.3 LTS
Release: 18.04
Codename: bionic
root@ubuntu1-server:~#
Ubuntu 18.04网络配置
Ubuntu 从 17.10 开始,已放弃在 /etc/network/interfaces ⾥固定IP的配置,⽽是改成 netplan ⽅式,
配置⽂件是:/etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
ubuntu 17.04及之前的静态IP配置⽅式
~# cat /etc/network/interfaces
root@ubantu:~# cat /etc/network/interfaces
# interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8)
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0 #⽹卡⾃启动,写⾃⼰要配置IP的实际⽹卡名称
iface eth0 inet static #配置静态IP,写⾃⼰要配置IP的实际⽹卡名称
address 172.20.32.100 #IP地址
netmask 255.255.0.0 #掩码
gateway 172.20.0.1 #⽹关
dns-nameservers 223.6.6.6 #DNS
dns-nameservers 223.5.5.5
#重启⽹络服务
~# /etc/init.d/networking restart
~# systemctl restart networking.service
单网卡静态IP地址:
~#sudo vim /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6]
# sudo netplan apply
配置多网卡静态IP
~# sudo vim /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6]eth1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [10.20.3.18/16]routes:- to: 172.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.2.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.8.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1
~# sudo netplan apply
单网卡桥接
~# sudo cat /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: nobridges:br0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6]interfaces: #桥接在哪一个网卡 把br0桥接到eth0- eth0
多网卡桥接
ubuntu 18.04多⽹卡的桥接配置,将br0和br1分别桥接到eth0和eth1
~# sudo cat /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: nobridges:br0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6]interfaces:- eth0- br1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [10.20.3.18/16]routes:- to: 172.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.2.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.8.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1interfaces:- eth1
双网卡绑定
七种bond模式说明
第⼀种模式:mod=0,即:(balance-rr) Round-robin policy(平衡抡循环策略)
特点:传输数据包顺序是依次传输(即:第1个包⾛eth0,下⼀个包就⾛eth1….⼀直循环下去,直到最后⼀个传输完
毕),此模式提供负载平衡和容错能⼒。第⼆种模式:mod=1,即: (active-backup) Active-backup policy(主-备份策略)
特点:只有⼀个设备处于活动状态,当⼀个宕掉另⼀个⻢上由备份转换为主设备。mac地址是外部可⻅得,从外⾯看
来,bond的MAC地址是唯⼀的,以避免switch(交换机)发⽣混乱。此模式只提供了容错能⼒;由此可⻅此算法的优点
是可以提供⾼⽹络连接的可⽤性,但是它的资源利⽤率较低,只有⼀个接⼝处于⼯作状态,在有 N 个⽹络接⼝的情况
下,资源利⽤率为1/N。第三种模式:mod=2,即:(balance-xor) XOR policy(平衡策略)
特点:基于指定的传输HASH策略传输数据包。缺省的策略是:(源MAC地址 XOR ⽬标MAC地址) % slave数量。其他
的传输策略可以通过xmit_hash_policy选项指定,此模式提供负载平衡和容错能⼒。第四种模式:mod=3,即:broadcast(⼴播策略)
特点:在每个slave接⼝上传输每个数据包,此模式提供了容错能⼒。第五种模式:mod=4,即:(802.3ad) IEEE 802.3adDynamic link aggregation(IEEE 802.3ad 动态链接
聚合)
特点:创建⼀个聚合组,它们共享同样的速率和双⼯设定。根据802.3ad规范将多个slave⼯作在同⼀个激活的聚合体
下。
必要条件:
条件1:ethtool⽀持获取每个slave的速率和双⼯设定。
条件2:switch(交换机)⽀持IEEE 802.3ad Dynamic link aggregation。
条件3:⼤多数switch(交换机)需要经过特定配置才能⽀持802.3ad模式。第六种模式:mod=5,即:(balance-tlb) Adaptive transmit load balancing(适配器传输负载均衡)
特点:不需要任何特别的switch(交换机)⽀持的通道bonding。在每个slave上根据当前的负载(根据速度计算)分
配外出流量。如果正在接受数据的slave出故障了,另⼀个slave接管失败的slave的MAC地址。
该模式的必要条件:
ethtool⽀持获取每个slave的速率
第七种模式:mod=6,即:(balance-alb) Adaptive load balancing(适配器适应性负载均衡)特点:该模式包含了balance-tlb模式,同时加上针对IPV4流量的接收负载均衡(receive load balance,rlb),⽽且不需要任何switch(交换机)的⽀持。
ubuntu 18.04的双网卡绑定配置
需要提前安装好bridge命令
~# sudo vim /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: nobonds:bond0:interfaces:- eth0- eth1addresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6,223.5.5.5] #2个阿里的DNSparameters:mode: active-backup #modemii-monitor-interval: 100
~# sudo netplan apply
双网卡绑定需要同一种类型的网卡类型。不能是仅主机和桥接混着使用。这里全部都是桥接网卡
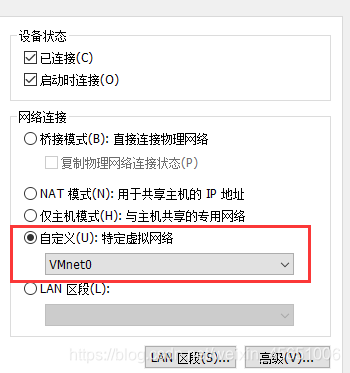
可能需要自定义虚拟网络接口,2个都band的网卡需要统一。
ping不通网关bug:重启虚拟机即可。
双网卡绑定+桥接
⽹卡绑定⽤于提供⽹卡接⼝冗余以及⾼可⽤和端⼝聚合功能,桥接⽹卡再给需要桥接设备的服务使⽤。
~# sudo cat /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: nobonds:bond0: #绑定eth0和eth1interfaces:- eth0- eth1
#addresses: [172.18.3.18/16] #地址、网关、DNS不需要配置在band0上面直接配置在br0中即可
#gateway4: 172.18.0.1
#nameservers:
# addresses: [223.6.6.6,223.5.5.5]parameters:mode: active-backup #MODEmii-monitor-interval: 100bridges:br0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6,223.5.5.5]interfaces:- bond0 #调用的下一级接口 下一层bond0接口调用eth0和eth1
~#netplay apply
~#reboot
内外多网卡绑定+桥接
多⽹络情况下实现⽹卡绑定。
~# sudo cat /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth2:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth3:dhcp4: nodhcp6: nobonds:bond0:interfaces:- eth0- eth1addresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6,223.5.5.5]parameters:mode: active-backupmii-monitor-interval: 100bond1:interfaces:- eth2- eth3addresses: [10.20.3.18/16]parameters:mode: active-backupmii-monitor-interval: 100routes:- to: 172.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.2.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.8.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1
~#reboot
内网多网卡绑定+桥接
~# sudo cat /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:version: 2renderer: networkdethernets:eth0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth2:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noeth3:dhcp4: nodhcp6: nobonds:bond0:interfaces:- eth0- eth1parameters:mode: active-backupmii-monitor-interval: 100bond1:interfaces:- eth2- eth3parameters:mode: active-backupmii-monitor-interval: 100bridges:br0:dhcp4: nodhcp6: noaddresses: [172.18.3.18/16]gateway4: 172.18.0.1nameservers:addresses: [223.6.6.6,223.5.5.5]interfaces:- bond0br1:dhcp4: nodhcp6: nointerfaces:- bond1addresses: [10.20.3.18/16]routes:- to: 172.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.20.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.2.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1- to: 10.8.0.0/16via: 10.20.0.1
~#reboot
修改软件仓库
阿⾥云仓库地址:https://opsx.alibaba.com/mirror
中科⼤:http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/help/ubuntu.html
清华⼤学:https://mirror.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/ubuntu/
华为:https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/
apt/apt-get
# apt list #apt列出仓库软件包,等于yum list
# apt search NAME #搜索安装包
# apt show apache2 #查看某个安装包的详细信息
# apt install apache2 #在线安装软件包
# apt remove apache2 #卸载单个软件包但是保留配置⽂件
# apt autoremove apache2 #删除安装包并解决依赖关系
# apt update #更新本地软件包列表索引,修改了apt仓库后必须执⾏
# apt purge apache2 #卸载单个软件包删除配置⽂件
# apt upgrade #升级所有已安装且可升级到新版本的软件包
# apt full-upgrade #升级整个系统,必要时可以移除旧软件包。
# apt edit-sources #编辑source源⽂件
# apt-cache madison nginx #查看仓库中软件包有哪些版本可以安装
# apt install nginx=1.14.0-0ubuntu1.6 #安装软件包的时候指定安装具体的版本
安装常用系统命令
root@ubuntu1-server:~# apt purge ufw lxd lxd-client lxcfs lxc-common -y #卸载不必要的系统命令root@ubuntu1-server:~# apt install iproute2 ntpdate tcpdump telnet traceroute nfs-kernel-server nfs-common \
lrzsz tree openssl libssl-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev zlib1g-dev ntpdate tcpdump telnet traceroute gcc openssh-\
server lrzsz tree openssl libssl-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev zlib1g-dev ntpdate tcpdump telnet traceroute iotop\unzip zip -y #安装常用系统命令
系统资源限制优化
实际生产环境中工作中的经验值
root@ubuntu1-server:~# ulimit -n
1024
经过测试最大 ulimit -n 的最大值为1048576
#cat /etc/security/limits.conf
#root账⼾的资源软限制和硬限制
root soft core unlimited
root hard core unlimited
root soft nproc 1000000
root hard nproc 1000000
root soft nofile 1000000
root hard nofile 1000000
root soft memlock 32000
root hard memlock 32000
root soft msgqueue 8192000
root hard msgqueue 8192000#其他账⼾的资源软限制和硬限制 #在centos中下面这些即可,在ubantu中root需要单独配置
* soft core unlimited
* hard core unlimited
* soft nproc 1000000
* hard nproc 1000000
* soft nofile 1000000
* hard nofile 1000000
* soft memlock 32000
* hard memlock 32000
* soft msgqueue 8192000
* hard msgqueue 8192000
内核参数优化
实际生产环境中工作中的经验值
root@ubuntu1-server:~# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
# Controls source route verification
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1
net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
# Do not accept source routing
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0
# Controls the System Request debugging functionality of the kernel
kernel.sysrq = 0
# Controls whether core dumps will append the PID to the core filename.
# Useful for debugging multi-threaded applications.
kernel.core_uses_pid = 1
# Controls the use of TCP syncookies
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
# Disable netfilter on bridges.
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 0
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 0
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables = 0
# Controls the default maxmimum size of a mesage queue
kernel.msgmnb = 65536
# # Controls the maximum size of a message, in bytes
kernel.msgmax = 65536
# Controls the maximum shared segment size, in bytes
kernel.shmmax = 68719476736
# # Controls the maximum number of shared memory segments, in pages
kernel.shmall = 4294967296
# TCP kernel paramater
net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 786432 1048576 1572864
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 4194304
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 16384 4194304
net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1
# socket buffer
net.core.wmem_default = 8388608
net.core.rmem_default = 8388608
net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 262144
net.core.somaxconn = 20480
net.core.optmem_max = 81920
# TCP conn
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 262144
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 3
net.ipv4.tcp_retries1 = 3
net.ipv4.tcp_retries2 = 15
# tcp conn reuse
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 20000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 3276800
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
# keepalive conn
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 300
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 30
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 3
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 10001 65000
# swap
vm.overcommit_memory = 0
vm.swappiness = 10
#net.ipv4.conf.eth1.rp_filter = 0
#net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1
#net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
#net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
#net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2root@ubuntu1-server:~# sysctl -p #加载
dpkg安装包管理
rpm:RPM(Red Hat Package Manager),是基于Red hat的Linux Distribution的包管理系统,同时也指rpm包本⾝,RPM⽤于rpm包的管理(诸如安装、卸载、升级等)
"dpkg "是"Debian Packager "的简写,为 "Debian"专⻔开发的套件管理系统,⽅便软件的安装、更新及移除。所有源⾃“Debian”的“Linux ”发⾏版都使⽤ “dpkg”,例如 “Ubuntu”、“Knoppix ”等。
# dpkg -i gitlab-ce_11.9.8-ce.0_amd64.deb #安装某个软件包 后缀叫做deb i:install
# dpkg -r gitlab-ce #删除某个软件包保留配置⽂件
# dpkg -r -P gitlab-ce #删除某个软件包不保留配置⽂件
# dpkg -I gitlab-ce_11.9.8-ce.0_amd64.deb #查看软件包信息
# dpkg -c gitlab-ce_11.9.8-ce.0_amd64.deb #查看软件包内的⽂件及⽬录内容 查看里面内容
# dpkg -l #列出本机已经安装的所有软件这篇关于Ubantu基础设置以及多网卡绑定的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



