国际惯例的题面: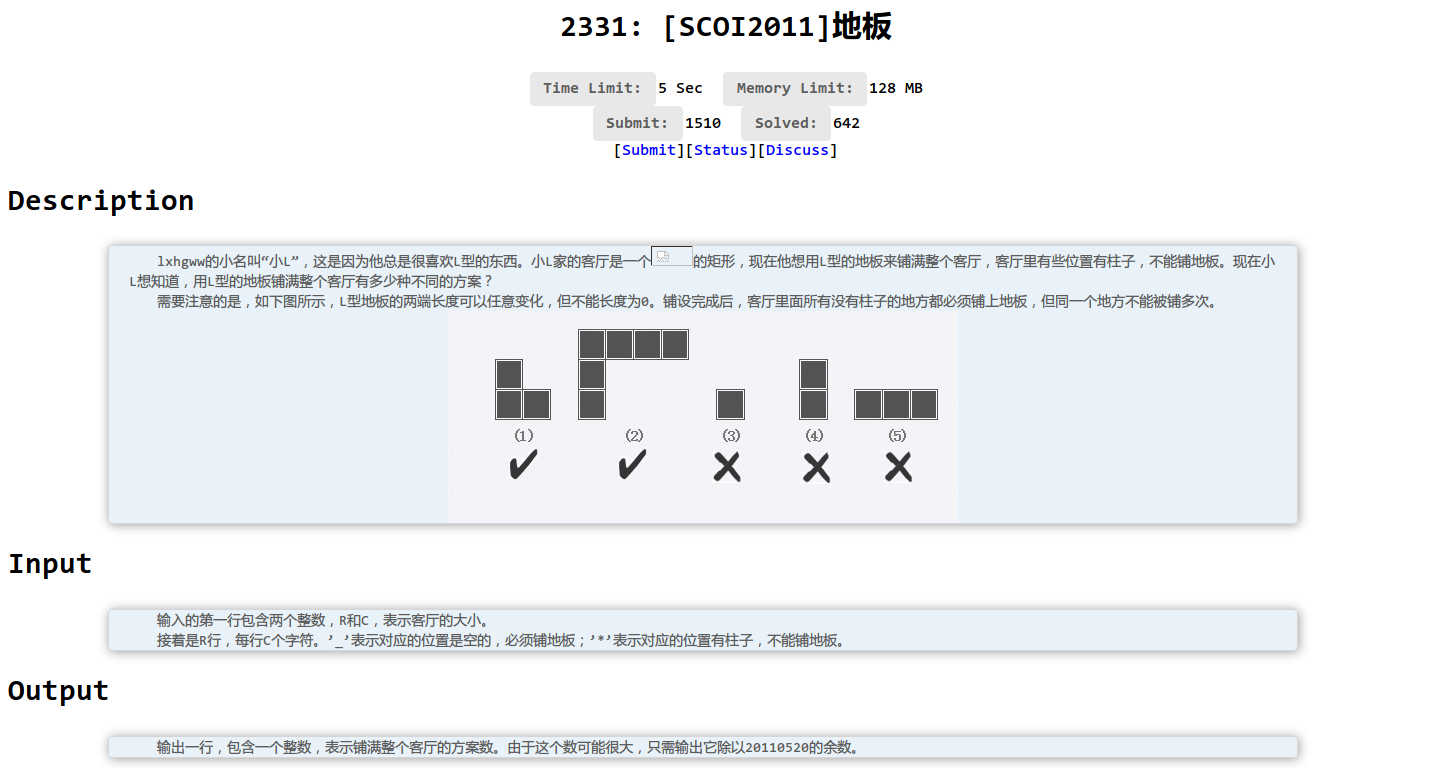
十分显然的插头DP。由于R*C<=100,所以min(R,C)<=10,然后就可以愉悦地状压啦。
我们用三进制状压,0表示没有插头,1表示有一个必须延伸至少一格且拐弯的插头,2表示有一个必须延伸一格且不可以拐弯的插头。
转移的话就十分显然了。
00->22,表示用这个格子作为开始的拐角。
00->10,表示用这个格子向下延伸。
00->01,表示用这个格子向右延伸。
01->10,表示这个格子连接上下。
01->02,表示在这个格子作为中间的拐角。
02->20,表示这个格子连接上下。
02->00,表示这个格子作为某个地板的终点。
10->01,表示这个格子连接左右。
10->20,表示在这个格子作为中间的拐角。
11->00,表示这个格子作为结束的拐角。
20->00,表示这个格子作为某个地板的终点。
20->02,表示这个格子连接左右。
(插头DP的本质就是分类讨论,所以麻烦也没办法,想明白就很容易了)
然后就是实现了。我是用unordered_map存储状态,同时先找到第一个可以放东西的位置开始DP,统计答案的时候统计第n+1行没有插头的状态。
代码:


1 #pragma GCC optimize(2) 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<tr1/unordered_map> 5 using namespace std; 6 using namespace tr1; 7 const int maxn=1e2+1e2; 8 const int mod=20110520; 9 10 int sta[maxn],nxt[maxn]; 11 char in[maxn][maxn]; // in == 1 means empty . 12 int n,m,cur,fx,fy; 13 unordered_map<int,int> f[2]; 14 15 inline void unzip(int* sta,int ss) { 16 for(int i=m+1;i;i--) sta[i] = ss % 3 , ss /= 3; 17 } 18 inline int zip(int* sta) { 19 int ret = 0; 20 for(int i=1;i<=m+1;i++) ret = ret * 3 + sta[i]; 21 return ret; 22 } 23 24 inline void core_trans(unordered_map<int,int> &dst,int x,int y,int add) { 25 memcpy(nxt,sta,sizeof(int)*(m+2)); 26 if( !in[x][y] ) { // not empty . 27 if( sta[y] == 0 && sta[y+1] == 0 ) ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 28 return; 29 } 30 if( sta[y] == 0 ) { 31 if( sta[y+1] == 0 ) { 32 nxt[y] = 2 , nxt[y+1] = 2 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 33 nxt[y] = 1 , nxt[y+1] = 0 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 34 nxt[y] = 0 , nxt[y+1] = 1 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 35 } else if( sta[y+1] == 1 ) { 36 nxt[y] = 1 , nxt[y+1] = 0 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 37 nxt[y] = 0 , nxt[y+1] = 2 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 38 } else if( sta[y+1] == 2 ) { 39 nxt[y] = 2 , nxt[y+1] = 0 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 40 nxt[y] = 0 , nxt[y+1] = 0 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 41 } 42 } else if( sta[y] == 1 ) { 43 if( sta[y+1] == 0 ) { 44 nxt[y] = 0 , nxt[y+1] = 1 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 45 nxt[y] = 2 , nxt[y+1] = 0 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 46 } else if( sta[y+1] == 1 ) nxt[y] = 0 , nxt[y+1] = 0 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 47 } else if( sta[y] == 2 ) { 48 if( sta[y+1] == 0 ) { 49 nxt[y] = 0 , nxt[y+1] = 0 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 50 nxt[y] = 0 , nxt[y+1] = 2 , ( dst[zip(nxt)] += add ) %= mod; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 inline void trans(const unordered_map<int,int> &sou,unordered_map<int,int> &dst,int x,int y) { 55 dst.clear(); 56 for(unordered_map<int,int>::const_iterator it=sou.begin();it!=sou.end();it++) if( it->second ) { 57 unzip(sta,it->first) , core_trans(dst,x,y,it->second); 58 } 59 } 60 inline void transline(const unordered_map<int,int> &sou,unordered_map<int,int> &dst) { 61 dst.clear(); 62 for(unordered_map<int,int>::const_iterator it=sou.begin();it!=sou.end();it++) if( it->second && ! ( it->first % 3 ) ) { 63 dst[it->first/3] = it->second; 64 } 65 } 66 67 inline void revert() { // make m <= n . 68 static char tp[maxn][maxn]; 69 memcpy(tp,in,sizeof(in)) , memset(in,0,sizeof(in)); 70 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) in[j][i] = tp[i][j]; 71 swap(n,m); 72 } 73 74 int main() { 75 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) , fx = -1 , fy = -1; 76 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { 77 scanf("%s",in[i]+1); 78 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) in[i][j] = in[i][j] == '_'; 79 } 80 81 if( n < m ) revert(); 82 for(int i=1;i<=n&&!~fx;i++) for(int j=1;j<=m&&!~fx;j++) if(in[i][j]) fx = i , fy = j; 83 if( !~fx ) return puts("1") , 0; // nothing to do . 84 sta[fy] = 0 , sta[fy+1] = 1 , f[cur][zip(sta)] = 1; 85 sta[fy] = 1 , sta[fy+1] = 0 , f[cur][zip(sta)] = 1; 86 sta[fy] = sta[fy+1] = 2 , f[cur][zip(sta)] = 1; 87 for(int j=fy+1;j<=m;j++) trans(f[cur],f[cur^1],fx,j) , cur ^= 1; 88 transline(f[cur],f[cur^1]) , cur ^= 1; 89 90 for(int i=fx+1;i<=n;i++) { 91 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) 92 trans(f[cur],f[cur^1],i,j) , cur ^= 1; 93 transline(f[cur],f[cur^1]) , cur ^= 1; 94 } 95 96 printf("%d\n",f[cur][0]); 97 98 return 0; 99 }
たいせつなきみのために ぼくにできるいちばんのことは
为了最重要的你 我所能做的最好的事
約束を忘れること君への想い消し去ること
就是忘却与你的约定抹去对你的思念
沈む夕日暮れてく空 夜の帳舞い降りる頃
渐渐归隐大地的夕阳 夜幕降临整个天空 夜的气息轻盈飘落之时
僕は目を閉じて それは闇に溶けるように 滲んで消えた
我闭目去感受 一切就像溶入暗影一样 渗透进去消散无痕了
未来なんていらないよ
未来(明日)什么的已经不需要了吧
君が側にいる過去のままで
因为有你一直陪伴我的往昔(昨日)



