本文主要是介绍Python测试开发预习课6/18,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
注意:
切片是可以越界的
遍历不要改原字符串
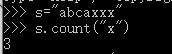
1、abcxxx,请统计一下x有多少个?用函数实现
知识点:
>>> s="abcaxxx"
>>> s.count("x")
3
count函数的算法
算法:
1 定义一个函数,参数传递一个字符串
2 声明一个变量letter_count存储某个字符出现的个数
3 遍历字符串,逐一拿出来,判断是否是你想要统计的那个
4 如果是,则letter_count+1
5 如果不是,则什么都不做
6 把函数中的统计结果变量返回回来 return letter_count
def count(s,target_letter):letter_count = 0for i in s:if i == target_letter:letter_count+=1return letter_countprint(count("abcxxx","x"))
2、abcxabcyabc,请统计一下abc有多少个?用函数实现
算法:
例如:0位置的s[0:3]==“xxx” 当前i是0,
满足的条件下1和2不需要做if判断了,直接跳过去
把当前的i+1,i+2这两个位置,放入到filter_position
代码:
def count(s,target_letters):string_count = 0length=len(target_letters)filter_position = []for i in range(len(s)):if i in filter_position:continueif s[i:i+length] == target_letters:string_count+=1for j in range(1,length):filter_position.append(i+j)return string_countprint(count("xxxxabcxxxx","xxx"))
3、列表的增删改查
>>> arr=[]
>>> type(arr)
<class 'list'>
>>> arr.append(1)
>>> arr.append("1")
>>> arr.append([])
>>> arr.append((1,2))
>>> arr.append(1.24)
>>> arr
[1, '1', [], (1, 2), 1.24]
>>> len(arr)
5
>>> arr.insert(0,"xyz")
>>> arr[0]
'xyz'
>>> arr[2]#列表是一个序列,基于坐标查看
'1'
>>> for i in range(10):
... arr.append(i)
...
>>> arr
['xyz', 1, '1', [], (1, 2), 1.24, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> del arr[0]
>>> del arr[0]
>>> arr
['1', [], (1, 2), 1.24, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> del arr[2:5]
>>> arr
['1', [], 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> a[0]="aaa"
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'a' is not defined
>>> arr[0]="xxx"
>>> arr
['xxx', [], 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> arr[0:4]="111"
>>> arr
['1', '1', '1', 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> for i in arr:
... print(i)
...
1
1
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
>>> for i in range(len(arr)):
... print(arr[i])
...
1
1
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
>>> a=[1,2,3]
>>> arr=["a","b"]
>>> arr.extend(a)
>>> arr
['a', 'b', 1, 2, 3]


4、元组的增删改查–元组:它所有子元素的地址,是不能改变的
>>> a=()
>>> type(a)
<class 'tuple'>
>>> a=(1)
>>> type(a)
<class 'int'>
>>> a=(1,)
>>> type(a)
<class 'tuple'>
>>> a=(1,"a",[],{})
>>> a[0]="x"
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
>>> del a[0]
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'tuple' object doesn't support item deletion
>>> a[0]
1
>>> a[1]
'a'
>>> a[2]
[]
>>> a[3]
{}
>>> a[4]
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: tuple index out of range
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>> a
(1, 'a', [], {})
>>> a[2]
[]
>>> a[2].append(100)
>>> a[2].append(233)
>>> a
(1, 'a', [100, 233], {})
>>> a
(1, 'a', [100, 233], {})

5、字典的增删改查–字典的key不能重复,如果赋值重复了,会把value替换掉
>>> d={}
>>> type(d)
<class 'dict'>
>>> d["1"]=100
>>> d
{'1': 100}
>>> d[[1]]=100
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
>>> d
{'1': 100}
>>> d[1]
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: 1
>>> d["1"]
100
>>> d[10000]
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: 10000
>>> d["2"]=9000
>>> d["2"]=9000
>>> d
{'1': 100, '2': 9000}
>>> del d["2"]
>>> d
{'1': 100}
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>> d={1:2,3:4,5:6}
>>> d
{1: 2, 3: 4, 5: 6}
>>> d.keys()
dict_keys([1, 3, 5])
>>> list(d.keys())
[1, 3, 5]
>>> for i in d.keys():
... print(i)
...
1
3
5
>>> for i in d.values():
... print(i)
...
2
4
6
>>> for k,v in d.items():
... print(k,"=",value)
...
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 2, in <module>
NameError: name 'value' is not defined
>>> for k,v in d.items():
... print(k,"=",v)
...
1 = 2
3 = 4
5 = 6
>>> d
{1: 2, 3: 4, 5: 6}
>>> d.clear()
>>> d
{}
>>> d={1:2,3:4,5:6}
>>> for i in d.keys():
... d[i]=1190
...
>>> d
{1: 1190, 3: 1190, 5: 1190}
>>> new_d={}
>>> for i in d.keys():
... if i%2==1:
... continue
... new_d[i]=d[i]
...
>>> new_d[i]
Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: 5
>>> new_d
{}

这篇关于Python测试开发预习课6/18的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





