本文主要是介绍【wu-lazy-cloud-network】Java自动化内网穿透架构整理,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
项目介绍
wu-lazy-cloud-network 是一款基于(wu-framework-parent)孵化出的项目,内部使用Lazy ORM操作数据库,主要功能是网络穿透,对于没有公网IP的服务进行公网IP映射
使用环境JDK17 Spring Boot 3.0.2
版本更新
1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT
【fix】修正流量计算保存两位小数
架构图
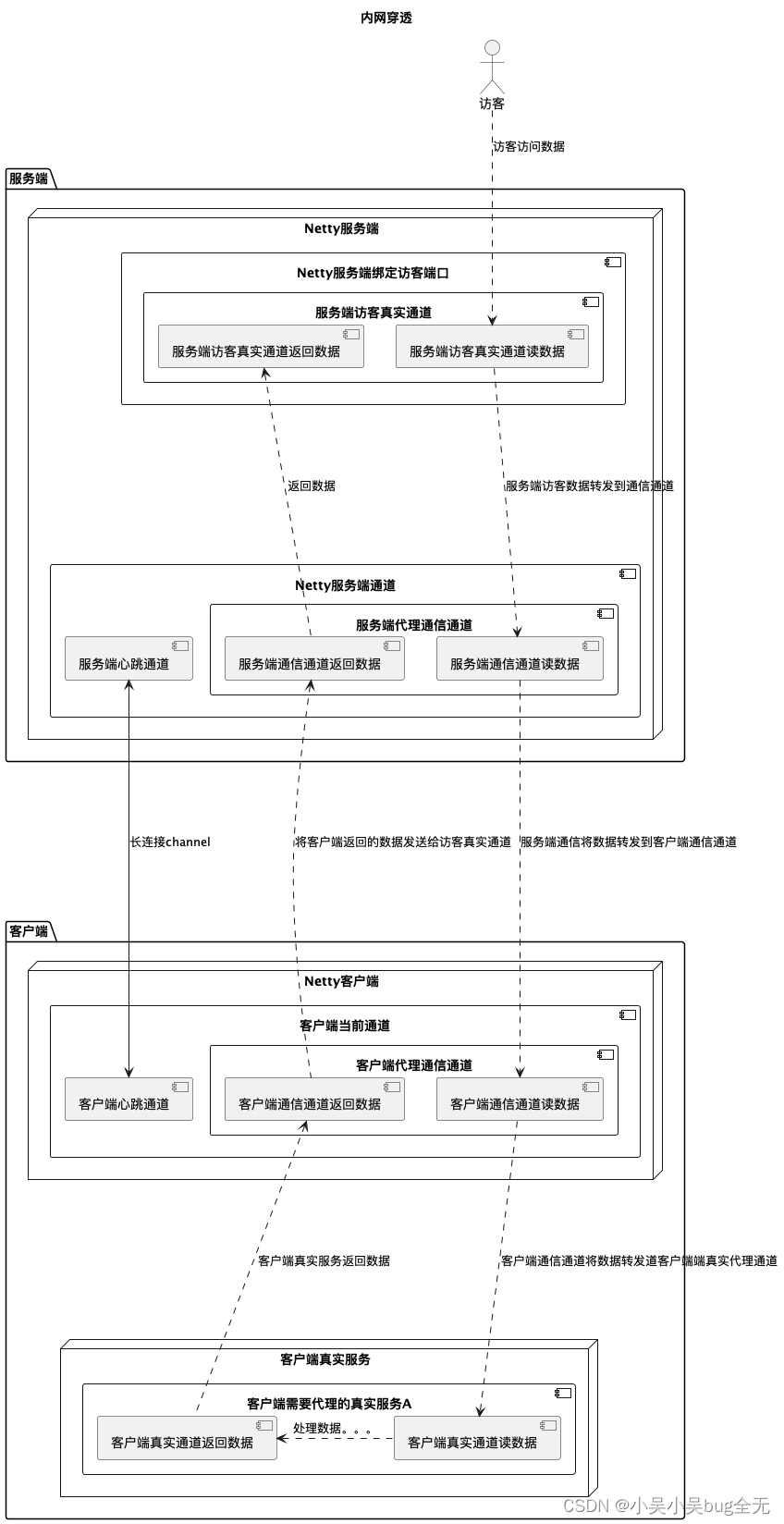
实现原理
服务端创建socket服务端绑定本地端口(用于客户端连接)
package wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.server.netty.socket;import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.server.netty.filter.NettyServerFilter;public class NettyOnCloudNettyServerSocket {private final EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();private final EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();private final NettyServerFilter nettyServerFilter;// 通道业务处理private ChannelFuture channelFuture;public NettyOnCloudNettyServerSocket(NettyServerFilter nettyServerFilter) {this.nettyServerFilter = nettyServerFilter;}/*** 启动服务端** @throws Exception*/public void startServer(int serverPort) throws Exception {try {ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)// 给服务端channel设置属性.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128).childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).childHandler(nettyServerFilter);channelFuture = b.bind(serverPort).sync();channelFuture.addListener((ChannelFutureListener) channelFuture -> {// 服务器已启动});channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {shutdown();// 服务器已关闭}}public void shutdown() {if (channelFuture != null) {channelFuture.channel().close().syncUninterruptibly();}if ((bossGroup != null) && (!bossGroup.isShutdown())) {bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();}if ((workerGroup != null) && (!workerGroup.isShutdown())) {workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}
}
客户端通过class NettyClientSocket 连接服务端
package wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.client.netty.socket;import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.client.application.ClientNettyConfigApplication;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.client.netty.filter.NettyClientFilter;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.common.MessageType;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.common.NettyProxyMsg;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.common.adapter.ChannelTypeAdapter;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.common.advanced.HandleChannelTypeAdvanced;
import wu.framework.lazy.cloud.heartbeat.common.utils.ChannelAttributeKeyUtils;import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** 客户端连接服务端*/
@Slf4j
public class NettyClientSocket {private static final EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();/*** 服务端host*/private final String inetHost;/*** 服务端端口*/private final int inetPort;/*** 当前客户端id*/@Getterprivate final String clientId;/*** nacos配置信息处理应用*/@Getterprivate final ClientNettyConfigApplication clientNettyConfigApplication;private final List<HandleChannelTypeAdvanced> handleChannelTypeAdvancedList; // 处理服务端发送过来的数据类型public NettyClientSocket(String inetHost, int inetPort, String clientId, ClientNettyConfigApplication clientNettyConfigApplication, List<HandleChannelTypeAdvanced> handleChannelTypeAdvancedList) {this.inetHost = inetHost;this.inetPort = inetPort;this.clientId = clientId;this.clientNettyConfigApplication = clientNettyConfigApplication;this.handleChannelTypeAdvancedList = handleChannelTypeAdvancedList;}public void newConnect2Server() throws InterruptedException {newConnect2Server(inetHost, inetPort, clientId, clientNettyConfigApplication);}protected void newConnect2Server(String inetHost, int inetPort, String clientId, ClientNettyConfigApplication clientNettyConfigApplication) throws InterruptedException {Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new NettyClientFilter(new ChannelTypeAdapter(handleChannelTypeAdvancedList), this));log.info("连接服务端IP:{},连接服务端端口:{}", inetHost, inetPort);ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(inetHost, inetPort);Channel channel = future.channel();log.info("使用的客户端ID:" + clientId);future.addListener((ChannelFutureListener) futureListener -> {if (futureListener.isSuccess()) {log.info("连接服务端成功");// 告诉服务端这条连接是client的连接NettyProxyMsg nettyMsg = new NettyProxyMsg();nettyMsg.setType(MessageType.REPORT_CLIENT_CONNECT_SUCCESS);nettyMsg.setClientId(clientId);nettyMsg.setData((clientId).getBytes());ChannelAttributeKeyUtils.buildClientId(channel, clientId);channel.writeAndFlush(nettyMsg);// 在线clientNettyConfigApplication.clientOnLine(clientId);} else {log.info("每隔2s重连....");// 离线clientNettyConfigApplication.clientOffLine(clientId);futureListener.channel().eventLoop().schedule(() -> {try {newConnect2Server(inetHost, inetPort, clientId, clientNettyConfigApplication);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}});}/*** 关闭连接*/public void shutdown() {if ((eventLoopGroup != null) && (!eventLoopGroup.isShutdown())) {eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}}
通过客户端与服务端建立的连接进行访客端口绑定
上述连接会形成一个channel,我们称之为通道(本文中简单叫**心跳通道**)
第一步 页面GUI进行新增访客端口而后将访客端口与客户端绑定(如果客户端已经启动,使用页面客户端下线触发第二步)
第二步 客户端与访客端口绑定后使用**心跳通道** 发送客户端告诉客户端,你帮我绑定你本地真实端口
第三步 访客访问,访客通过访客端口访问数据,此时访客通道打开截取访客发送的数据,然后将数据发送给客户真实通道,数据返回后再返回给访客通道
功能
1.内网穿透
2.服务端自主下发数据到客户端
3.流量监控
项目结构
| 模块 | 版本 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| wu-lazy-cloud-heartbeat-common | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | 内网穿透公共模块(声明接口、枚举、常量、适配器、解析器) |
| wu-lazy-cloud-heartbeat-client | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | 客户端(支持二次开发) |
| wu-lazy-cloud-heartbeat-server | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | 服务端(支持二次开发) |
| wu-lazy-cloud-network-ui | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | 服务端页面 |
| wu-lazy-cloud-heartbeat-client-sample | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | 客户端样例 |
| wu-lazy-cloud-heartbeat-server-sample | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | 服务端样例 |
使用技术
| 框架 | 版本 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| spring-boot | 3.0.7 | springboot框架 |
| wu-framework-web | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | web容器 |
| Lazy -ORM | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | ORM |
| mysql-connector-j | 8.0.33 | mysql驱动 |
| wu-authorization-server-platform-starter | 1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOT | 用户授权体系 |
使用环境
IDEA
Mac、Windows
JAVA >=13
MAVEN
启动
docker启动docker run -d -it -p 18080:18080 --name wu-lazy-cloud-heartbeat-server registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/wu-lazy/wu-lazy-cloud-heartbeat-server:1.2.2-JDK17-SNAPSHOThttp://127.0.0.1:18080/swagger-ui/index.html源码启动
页面操作
启动项目后打开服务端界面
默认账号密码:admin/admin
初始化项目
添加角色
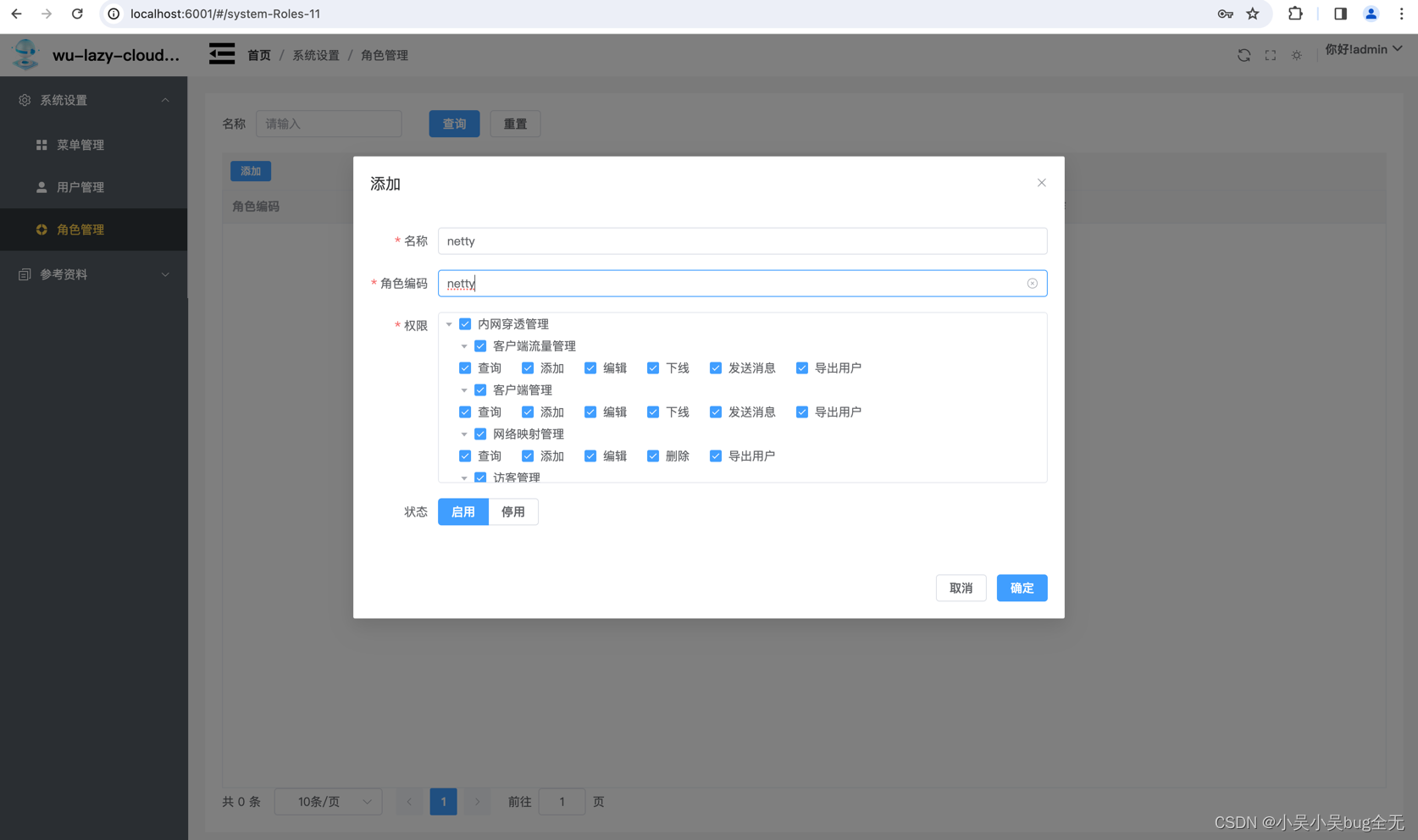
为用户授权
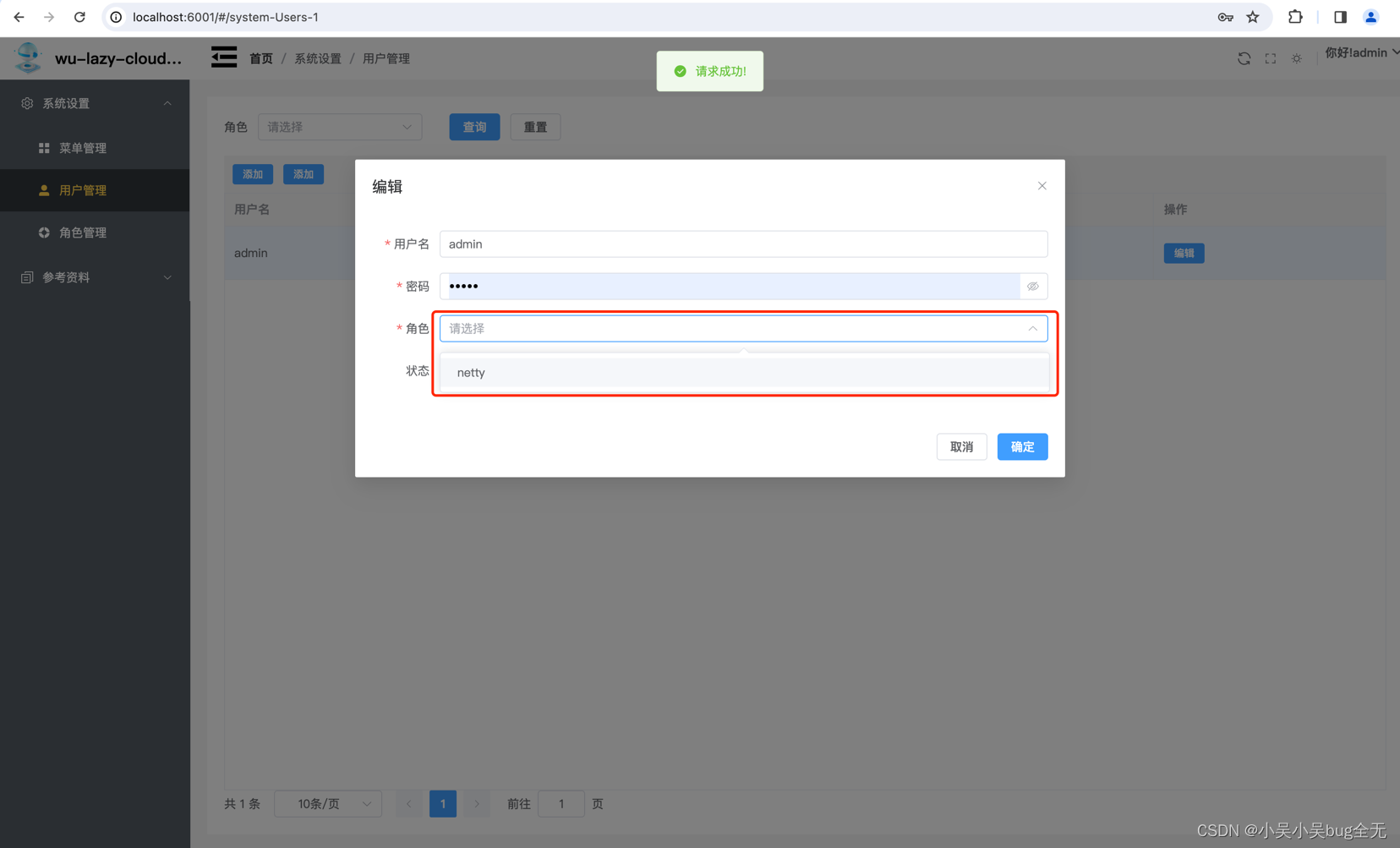
刷新页面
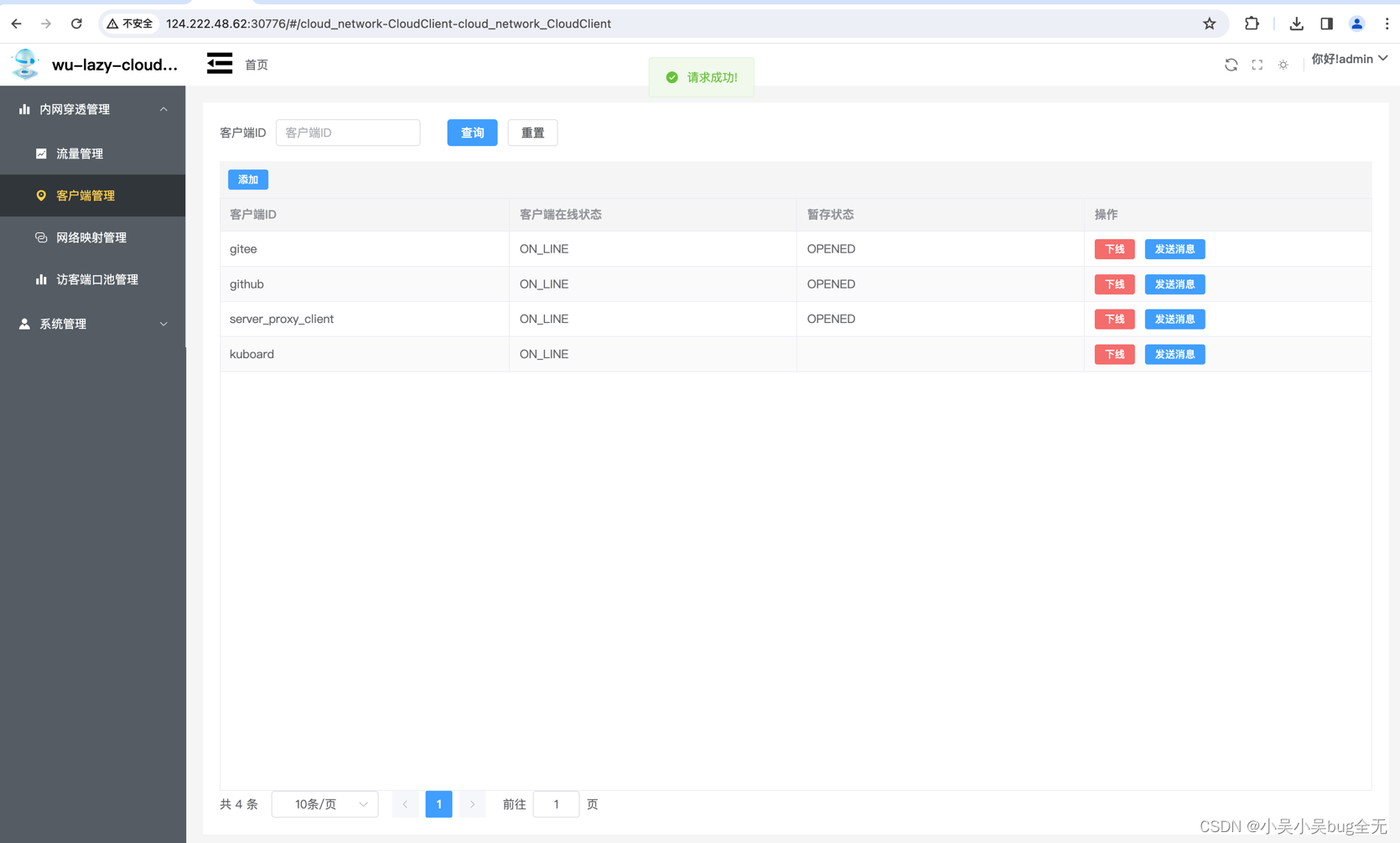
客户端管理(客户端会自动注册)
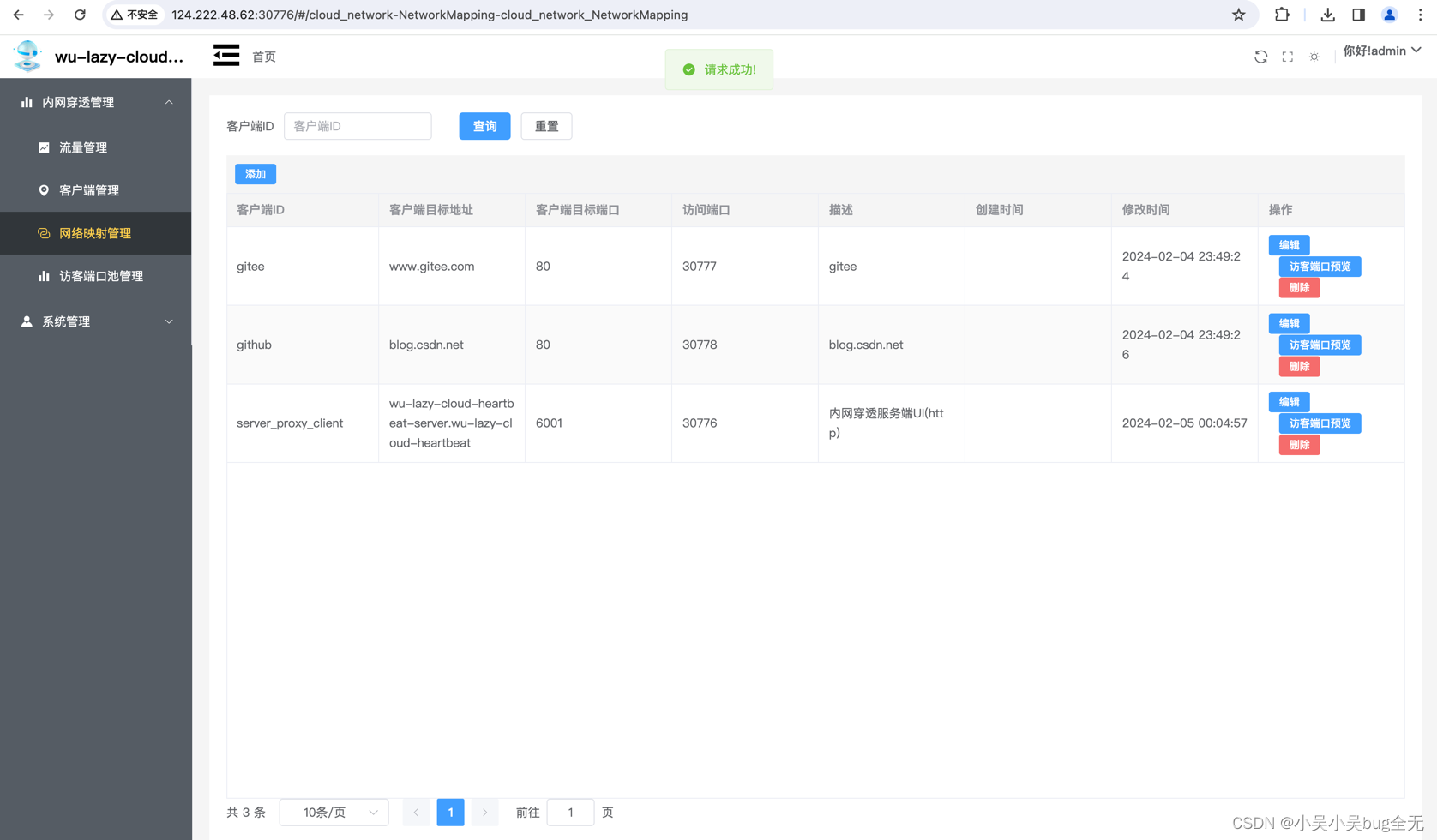
网络映射管理(修改后者新增需要映射的客户端)
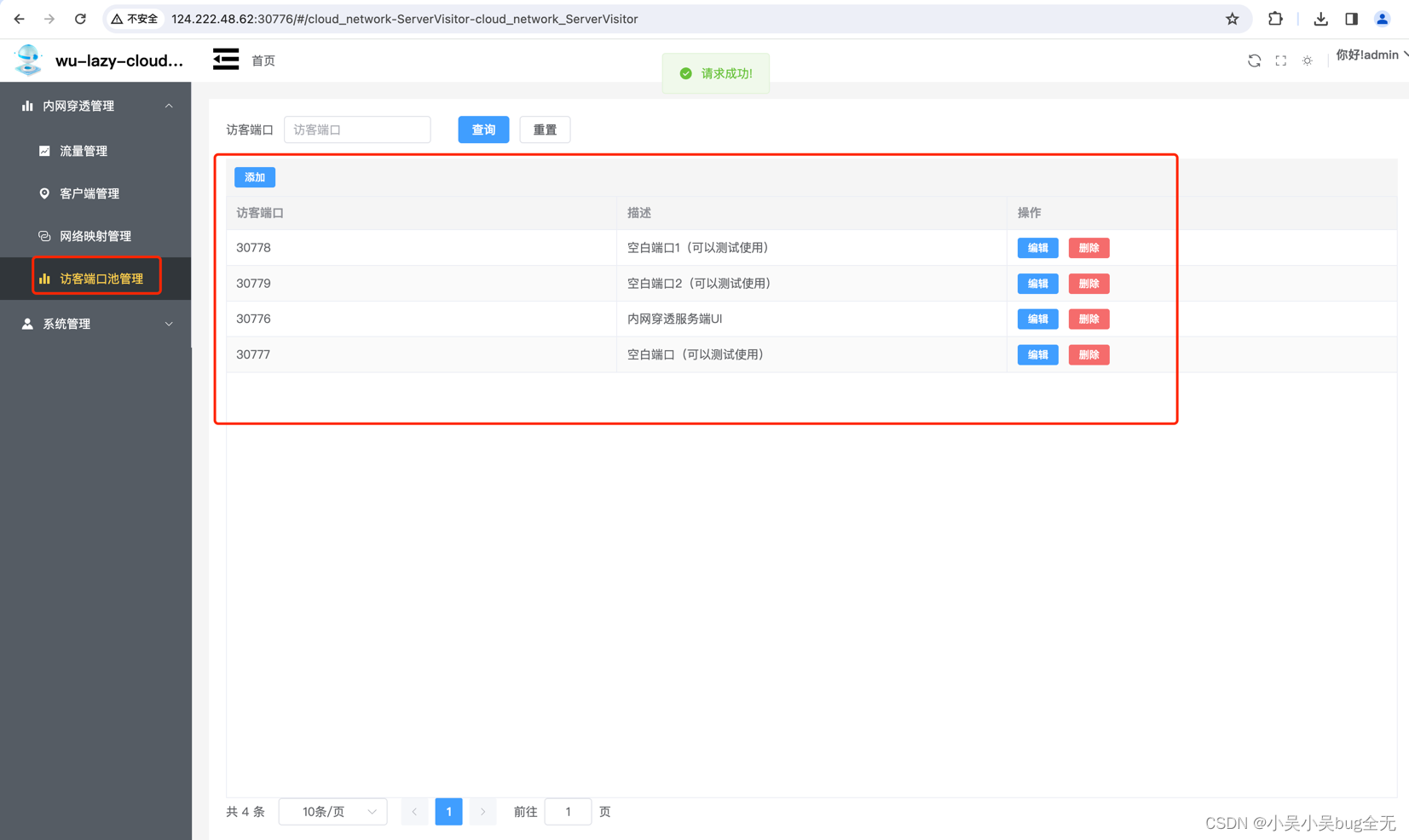
访客端口池管理(服务器端需要开放的端口)
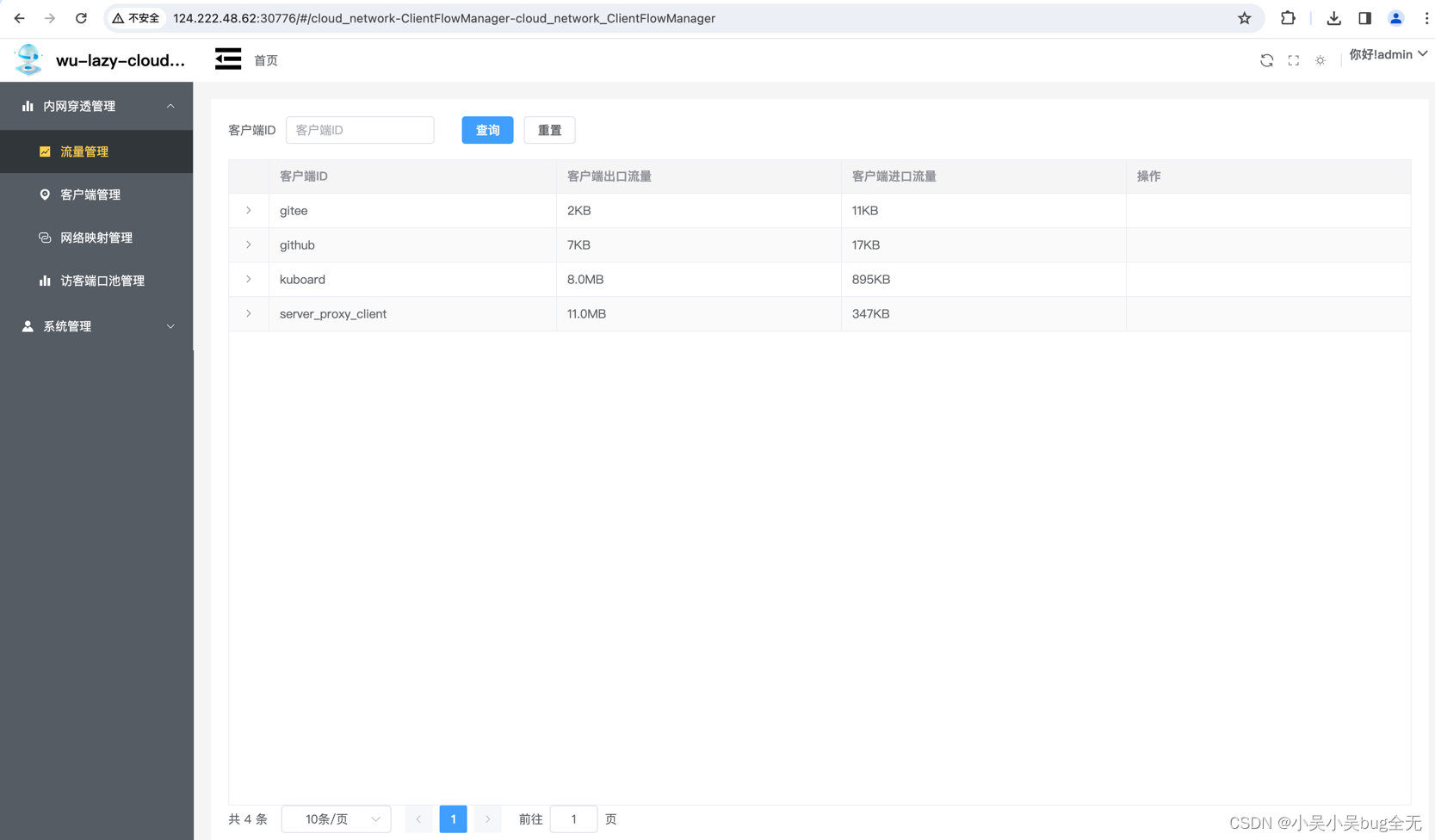
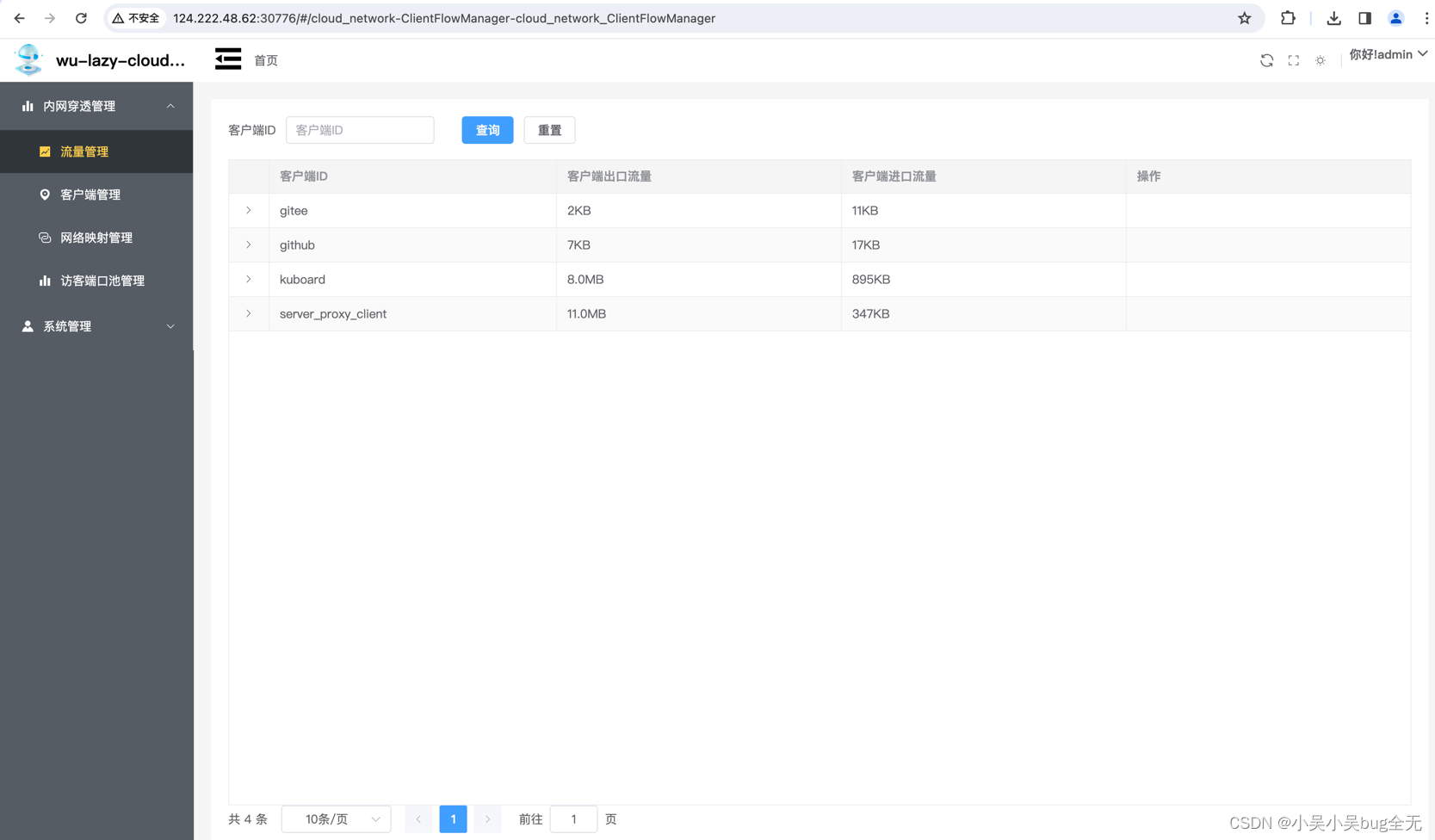
流量管理(每个客户端使用的流量)
这篇关于【wu-lazy-cloud-network】Java自动化内网穿透架构整理的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




