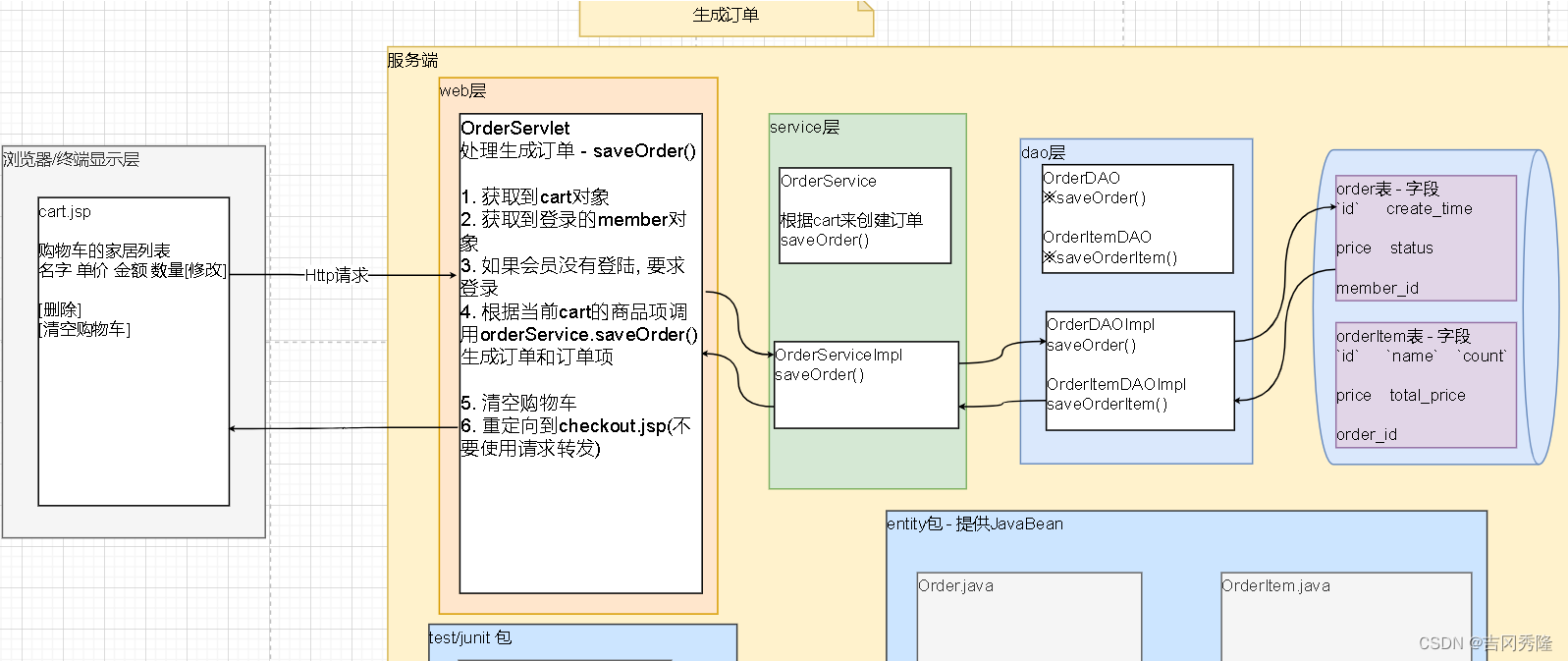
本文主要是介绍C APIs in extension and extensible languages by Roberto 部分翻译,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
C APIs in extension and extensible languages by Roberto 部分翻译Data transfer
The basic set of functions for manipulating data in scripting language APIs is usually
the same: they provide functions for converting values from the language to basic C
types .
A central design issue lies in how to represent a value between
languages.
All values in the Python virtual machine are represented as objects, mapped to the C API as the PyObject structure
More specific types such as PyStringObject, PyBooleanObject and PyListObject are PyObjects by structural equivalence, that is, they can be converted through a C cast.
Similarly, in Ruby, the API defines a C data type called VALUE, which represents a Ruby object.
VALUE may represent both a reference to an object (that is, a pointer to the Ruby heap) as well as an immediate value.
Perl also provides handles to its data in C, but these C values are better understood as containers to Perl values: types of Perl variables are mapped to C structs SV for scalars, AV for arrays, HV for hashes.
Lua, in contrast, employs a different approach for manipulating data in C:
no pointers or handles to Lua objects are ever exposed to C code, and instead,
operations are defined in terms of indices of a virtual stack.
So, data transfer from C to Lua takes place through functions that receive C types, convert them to Lua values and stack them.
在LUA语言中使用一种不同的方法来管理C语言中的数据。
不使用指针和Lua Object 暴露接口给C语言,而是使用虚拟栈在LUA语言和C语言之间交互。
所以,从C语言中把数据传递到Lua语言中,通过函数来接受C语言函数,并把C语言数据类型转换成LUA语言中的数据类型。
All of these languages also offer API functions for manipulating their fundamental structured types .
(tables in Lua, arrays and hashes in Ruby and Perl, lists and dictionaries in Python).
所有语言中同时提供API来操作语言中的基本数据类型。 LUA语言中的Table. Ruby 和Perl语言中的array 和hash table . Python语言中list 和dictionary.
An important task when bridging C code to a scripting language is the creation of data in the scripting language environment containing C structures.
沟通C语言和脚本语言一个重要桥梁就是在脚本语言环境中创建一个包含C语言struct的类型。
Perl, Ruby and Lua provide simple mechanisms for this task.
Perl Ruby 和LUA语言提供一个简单机制来完成这个任务。
Ruby offers the Data_Wrap_Struct macro which receives a C structure and returns a Ruby VALUE.
Ruby语言提供一个Data_Wrap_Struct 宏来接收一个C语言struct 同时返回Ruby Value.
Lua defines a basic type in the language especially for this end, called userdata .
which contains a memory block managed by the Lua VM that is accessible to C code but is an opaque object when accessed from Lua.
在LUA语言中提供一个userdata基本类型来作为LUA语言和C语言沟通的桥梁。
userdata是一个由LUA VM虚拟机管理的原始内存块。userdata可以通过C语言代码来操作,同时对于lua C API也是透明的。
Using the JNI, it is not possible to create new Java types from C; one can only load precompiled classes.
使用JNI不能够通过C 代码创建一个Java类型。只能通过加装预编译的类型。
Another common need when interacting with C is to store pointers in the data space of the scripting language.
Python, Lua and Perl offer features to do this directly.
In Python, a PyCObject is a predefined type that holds a void pointer accessible from C.
另外一个通用需求是在脚本语言中提供保存C语言指针。
Python,Lua 和Perl提供语言特性来直接实现。
在Python语言中,PyCObject是一个预定义好的类型来保存C语言中Void* 类型指针。
Lua offers a built-in type for this end, light userdata.
which differs from userdata in that the memory block it points to is not managed by the virtual machine.
在LUA语言中提供一个light userdata内置类型来保存C语言的指针。
light userdata和userdata的区别是,light userdata执行的内存不通过LUA VM虚拟机管理。
In Ruby and Java, there is no direct way to store pointers. The alternative is to convert pointers and store them as numbers.
在Ruby 和Java语言中,不直接保存C语言的指针,但是可以把指针地址转换成数值保存下来。
Garbage collection
Garbage collection aims to isolate, as much as possible, the programmer from memory management.
This way, ideally an API should also be as independent as possible from the garbage collection algorithm used in the implementation of the virtual machine.
Perl and Python perform garbage collection based on reference counting, and this shows through in the reference increment and decrement operations frequently needed during the use of their APIs.
Ruby uses a mark-and-sweep garbage collector. Its API manages to abstract this
fact well for manipulation of native Ruby objects, but the implementation of the collector
is evident in the creation of Ruby types in C, where we need to declare a mark function
when there are C structures that store reference to Ruby objects.
The Lua API goes further when isolating itself from the implementation of the garbage collector:
the only point of the API where the use of an incremental garbage collection is apparent is in the routine
for direct interaction with the collector, lua_gc, where its parameters can be configured.
Another issue that arises in the communication between C and scripting languages is the management of references.
For manipulating data through the API, Lua and Ruby demand the least concerns from the programmer about managing references.
Lua avoids the problem altogether, by keeping its objects in the virtual stack and not returning references to C code;
accessing data from Lua, thus, always involves function calls for getting the data into the stack.
C语言与脚本语言交互的另外一个问题是对引用的管理。
LUA脚本语言为了避免这个问题,在虚拟栈中保存对象并且在C语言中不返回引用。在LUA语言中获取对象,相当于调用函数把数据压人虚拟栈。
Function calls
In Python, Lua and Perl, functions can be accessed as language objects and invoked.
Python allows any PyObject to be called as a function, as long as they implement the __call__ method, which can be written in either Python or C
(as a function registered in the object’s PyTypeObject struct).
In Lua, there is a built-in primitive type, function, which represents both Lua functions and C functions registered in the Lua VM.
Perl also allows functions to be manipulated as first-class objects using its C API, returning SV structs representing them.
Lua separates the function call routine from argument passing, which is done in a previous step by setting up the contents of the stack.
This is a very simple solution, but the resulting code is less clear than the equivalent calls in languages such as Ruby and Python.
in which arguments to the function call are written in C as arguments to the C API call.
In Lua and Python, the occurrence of errors can be checked through the function’s return value.
Registration of C functions
Python and Ruby offer to the programmer various options for C function signatures that
are recognized by the API, which is practical, given that this way one can choose different
C representations for the input parameters (collected in an array, obtained one by one,
etc.) according to their use in the function.
Lua offers only one possible signature for
C functions to be registered in its virtual machine, as arguments are passed through the
stack and not as arguments to the C function.
在LUA语言中仅仅提供一种签名可以在LUA 虚拟机中注册C语言函数,通过虚拟机来传递参数。
Registration of functions in Ruby and Lua is simple.
In Lua, in particular, it is an assignment (made through API calls), not different from any other object.
在Ruby语言和Lua语言中注册C语言函数非常简单。尤其在LUA语言中,仅仅通过C API来进行赋值。
In Python,there are features for batch registering, using arrays of the PyMethodDef struct .
在Python语言中,提供PyMethodDef Struct特点来批量注册C语言函数。
(Lua offers a similar feature with luaL_register function)
在LUA语言中统一提供luaL_register C API 来提供批量注册C语言函数。
这篇关于C APIs in extension and extensible languages by Roberto 部分翻译的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!