本文主要是介绍【Unity SurfaceShader】学习笔记(一)认识结构,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
创建SurfaceShader
1. 新建Unity Project。
2. 在Assets文件夹下新建三个文件夹:Materials、Shaders、Textures。
3. 在Shaders文件夹下右键,Create-Shader-Standard Surface Shader,命名为MySurfaceShader。
4. 在Materials文件夹下新建Material,命名为MySurfaceShader,将它的Shader改为新建的Shader。
5. 新建一个Cube,将新建的材质赋给它。
如果你使用的是低于5.3的版本,你的右键菜单里不会有那么多种Shader,直接创建就好。直接创建的Shader代码和Standard Surface Shader不同,其实就是比Standard Surface Shader更为简化一点,听了解释你就会明白。
右键菜单里总共有四种Shader,分别是Standard Surface Shader、Unlit Shader、ImageEffect Shader、Compute Shader。
Unlit Shader和ImageEffect Shader都是Vertex&Fragment Shader,Compute Shader上一篇文章里讲过。
让我们打开MySurfaceShader看一看。
Shader "Custom/MySurfaceShader" {Properties {_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}_Glossiness ("Smoothness", Range(0,1)) = 0.5_Metallic ("Metallic", Range(0,1)) = 0.0}SubShader {Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }LOD 200CGPROGRAM// Physically based Standard lighting model, and enable shadows on all light types#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows// Use shader model 3.0 target, to get nicer looking lighting#pragma target 3.0sampler2D _MainTex;struct Input {float2 uv_MainTex;};half _Glossiness;half _Metallic;fixed4 _Color;void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {// Albedo comes from a texture tinted by colorfixed4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex) * _Color;o.Albedo = c.rgb;// Metallic and smoothness come from slider variableso.Metallic = _Metallic;o.Smoothness = _Glossiness;o.Alpha = c.a;}ENDCG}FallBack "Diffuse"
}-
第一行代码定义的是Shader在Unity里的路径,在Material的Shader选项的下拉列表里可以看到它,你随时都可以修改它。
-
最后一行表示前面的着色程序显卡不支持的时候就用默认的“Diffuse”。
-
Properties括号里的东西就是Shader的属性,打开Material的Inspector,你可以看见他们。语法就是:
变量名 (“检视面板里显示的名称”, 变量类型)= 默认值
注意啦,没有分号的。
这是Unity官网对Properties的介绍。
Unity支持的Properties类型如下:
Color :颜色 Inspector面板里会有一个选取颜色的picker
Range :某范围内的浮点数 Inspector面板里会出现一个Slider
2D :2D纹理
Rect :创建非2次方边长的纹理
Cube :创建Cube Map,也是一种纹理
Float :浮点数,和Range的区别就是Range是一个范围内的数,Float是单个数
Vector:向量 定义一个四元素的容器
-
SubShader是子着色器。Tags{}是标签。LOD是Level of Detail的缩写。Tag标签里通常可以指定“Queque”和“RenderType”的值。“Queque”指渲染顺序,有一些预定义的值,比如“BackGround”、“Geometry”等,可以自定义。“RenderType”是渲染类型,不透明物体用“Opaque”,透明物体用“Transparent”,还有一些其他的预定义的值,也可以自定义。
-
CGPROGRAM和ENDCG里面是CG程序。
-
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadowssurface说明是surface shader,可以换成Vertex或Fragment,surf是表面处理函数,在代码段的下面就有一个surf函数。Standard fullforwardshadows是光照模型函数。 -
#pragma target 3.0设置编译目标Shader model的版本。
后面surf函数里的东西就是重点啦。
在surf函数的上面,将properties里的变量用相同的名称定义一遍。还有一个Input结构体,这是输入结构。
来看看surf函数里都做了什么吧。
先定义了一个4元的定点数c,tex2D是纹理采样函数,第一个参数是纹理,第二个参数是uv坐标,函数的返回值乘以颜色。o这个变量就是着色器会输出的变量,也就是存储着我们眼睛会看到的效果的变量。后面的语句的意思就是将各个值赋给o里的不同值。rgb就是RGB颜色,Albedo是反射值,Metalic是金属值,Smoothness是光滑值,Alpha是透明通道。其实英语好就能看懂这些变量的意思了。(原谅我的翻译)
如果是低于5.3的版本,o 变量的类型是SurfaceOutPut,这两种类型意思是一样的,只不过是不同的结构体。
如果是Standard fullforwardshadows光照模型,则对应用SurfaceOutputStandard,如果是Lambert光照模型(其他版本Unity默认的光照模型),则对应SurfaceOutput。
这就是一个surface shader程序的基本结构。
两个结构体和CG类型
我们在程序里看到了Sampler2D、float2、half、fixed4几个类型,是不是觉得有些眼熟?C语言里有float这个类型,那这个float2是什么类型?听我详细道来:
CG支持7种数据类型:
float 32位浮点数
half 16位浮点数
int 32位整型数
fixed 12位定点数
bool 布尔数据
sampler 纹理对象的句柄,公有sampler, sampler1D, sampler2D, sampler3D, samplerCUBE, 和 samplerRECT 六种
string 字符,其实没有必要在CG中用到字符
向量类型 float2就是2元的float类型的向量,fixed4就是4元的fixed类型的向量
向量最长不超过4元
此外,CG还支持矩阵数据类型,比如:
float2×4 matrix; // 表示2×4阶矩阵,包含8个float类型数据
那么定义变量的时候怎么知道该用哪种类型呢?有个简单的记忆原则:
-
精度够用就好
-
颜色和单位向量,使用fixed
-
其他情况,尽量使用half(即范围在[-6万, +6万]内、精确到小数点后3.3位);否则才使用float。
下面介绍surface shader的输入输出结构:
输入结构就是存储输入的信息,输出结构就是存储要输出的信息,也就是我们的眼睛会看见的效果。
输入结构通常是这样的:
struct Input
{float2 uv_MainTex;
}
里面保存着纹理坐标。纹理坐标必须命名为“uv”+"纹理名称",uv_MainTex就是名为_MainTex的纹理的uv坐标。
Input中还可以放入额外的变量,比如下面几种:
float3 viewDir - will contain view direction, for computing Parallax effects, rim lighting etc.
为了计算视差、边缘光照等效果,Input需要包含视图方向。float4 screenPos - will contain screen space position for reflection effects. Used by WetStreet shader in Dark Unity for example.
屏幕坐标。 为了获得反射效果,需要包含屏幕坐标。比如在Dark Unity例子中所使用的 WetStreet着色器。float3 worldPos - will contain world space position.
世界坐标。float3 worldRefl - will contain world reflection vector if surface shader does not write to o.Normal. See Reflect-Diffuse shader for example.
世界中的反射向量。如果表面着色不写入o.Normal, 将包含世界反射向量。 float3 worldNormal - will contain world normal vector if surface shader does not write to o.Normal.
世界中的法线向量。如果表面着色器不写入法线(o.Normal)参数,将包含这个参数。float3 worldRefl - will contain world reflection vector if surface shader writes to o.Normal. To get the reflection vector based on per-pixel normal map, use WorldReflectionVector (IN, o.Normal).
世界反射向量。如果表面着色写入到o.Normal,将包含世界反射向量 。为了得到基于每个像素的法线贴图的反射向量, 使用WorldReflectionVector的(IN输入, o.Normal)。float3 worldNormal - will contain world normal vector if surface shader writes to o.Normal. To get the normal vector based on per-pixel normal map, use WorldNormalVector (IN, o.Normal).
世界法线向量。如果表面着色写入到o.Normal, 将包含世界法线向量。为了得到基于每个像素的法线贴图的法线向量,请使用世界法线向量((IN输入, o.Normal)float3 viewDir - will contain view direction, for computing Parallax effects, rim lighting etc. 为了计算视差、边缘光照等效果,Input需要包含视图方向。float4 screenPos - will contain screen space position for reflection effects. Used by WetStreet shader in Dark Unity for example. 屏幕坐标。 为了获得反射效果,需要包含屏幕坐标。比如在Dark Unity例子中所使用的 WetStreet着色器。float3 worldPos - will contain world space position. 世界坐标。float3 worldRefl - will contain world reflection vector if surface shader does not write to o.Normal. See Reflect-Diffuse shader for example. 世界中的反射向量。如果表面着色不写入o.Normal, 将包含世界反射向量。 float3 worldNormal - will contain world normal vector if surface shader does not write to o.Normal. 世界中的法线向量。如果表面着色器不写入法线(o.Normal)参数,将包含这个参数。float3 worldRefl - will contain world reflection vector if surface shader writes to o.Normal. To get the reflection vector based on per-pixel normal map, use WorldReflectionVector (IN, o.Normal). 世界反射向量。如果表面着色写入到o.Normal,将包含世界反射向量 。为了得到基于每个像素的法线贴图的反射向量, 使用WorldReflectionVector的(IN输入, o.Normal)。float3 worldNormal - will contain world normal vector if surface shader writes to o.Normal. To get the normal vector based on per-pixel normal map, use WorldNormalVector (IN, o.Normal). 世界法线向量。如果表面着色写入到o.Normal, 将包含世界法线向量。为了得到基于每个像素的法线贴图的法线向量,请使用世界法线向量((IN输入, o.Normal)
float3 viewDir - will contain view direction, for computing Parallax effects, rim lighting etc.
为了计算视差、边缘光照等效果,Input需要包含视图方向。float4 screenPos - will contain screen space position for reflection effects. Used by WetStreet shader in Dark Unity for example.
屏幕坐标。 为了获得反射效果,需要包含屏幕坐标。比如在Dark Unity例子中所使用的 WetStreet着色器。float3 worldPos - will contain world space position.
世界坐标。float3 worldRefl - will contain world reflection vector if surface shader does not write to o.Normal. See Reflect-Diffuse shader for example.
世界中的反射向量。如果表面着色不写入o.Normal, 将包含世界反射向量。 float3 worldNormal - will contain world normal vector if surface shader does not write to o.Normal.
世界中的法线向量。如果表面着色器不写入法线(o.Normal)参数,将包含这个参数。float3 worldRefl - will contain world reflection vector if surface shader writes to o.Normal. To get the reflection vector based on per-pixel normal map, use WorldReflectionVector (IN, o.Normal).
世界反射向量。如果表面着色写入到o.Normal,将包含世界反射向量 。为了得到基于每个像素的法线贴图的反射向量, 使用WorldReflectionVector的(IN输入, o.Normal)。float3 worldNormal - will contain world normal vector if surface shader writes to o.Normal. To get the normal vector based on per-pixel normal map, use WorldNormalVector (IN, o.Normal).
世界法线向量。如果表面着色写入到o.Normal, 将包含世界法线向量。为了得到基于每个像素的法线贴图的法线向量,请使用世界法线向量((IN输入, o.Normal)surface shader的默认的几种输出结构如下,输出结构也是可以自定义的。
struct SurfaceOutput
{fixed3 Albedo; // 漫反射颜色fixed3 Normal; // 切线空间法线,如果赋值的话fixed3 Emission; // 自发光颜色half Specular; // 高光强度,范围是0-1fixed Gloss; // specular intensityfixed Alpha; // 透明度
};
struct SurfaceOutputStandard
{fixed3 Albedo; // 基础 (漫反射或镜面反射) 颜色fixed3 Normal; // 切线空间法线,如果赋值的话half3 Emission; // 自发光颜色half Metallic; // 0=非金属, 1=金属half Smoothness; // 0=粗糙, 1=光滑half Occlusion; // 遮挡(默认1)fixed Alpha; // 透明度
};
struct SurfaceOutputStandardSpecular
{fixed3 Albedo; // 漫反射颜色fixed3 Specular; // 镜面反射颜色fixed3 Normal; // 切线空间法线,如果赋值的话half3 Emission; // 自发光颜色half Smoothness; // 0=粗糙, 1=光滑half Occlusion; // 遮挡(默认1)fixed Alpha; // 透明度
};
BasicDiffuse和HalfLambert
新建一个Shader,命名为BasicDiffuse。
先将修改Properties里的内容:
Properties {_EmissiveColor ("Emissive Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_AmbientColor ("Ambient Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_MySliderValue ("This is a Slider", Range(0,10)) = 2.5}
将#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows改为:
#pragma surface surf BasicDiffuse
这说明我们要用BasicDiffuse光照模型,这是我们自定义的一个光照模型。
定义在Properties里声明过的变量:
float4 _EmissiveColor;
float4 _AmbientColor;
float _MySliderValue;
修改你的surf函数:
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o){float4 c;c = pow((_EmissiveColor+_AmbientColor), _MySliderValue);o.Albedo = c.rgb;o.Alpha = c.a;
}
注意输出结构的类型,做了修改。
添加下面这个函数,这就是我们自定义的光照模型:
inline float4 LightingBasicDiffuse (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, fixed atten){float difLight = max(0, dot (s.Normal, lightDir));float4 col;col.rgb = s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * (difLight * atten * 2);col.a = s.Alpha;return col;
}
解释
-
在surf函数里,我们将自发光颜色和漫反射颜色相加的和作为底数,然后将_MySliderValue的值作为次幂,进行幂运算得到四元浮点向量c,输出的反射值等于c的RGB颜色,输出的透明通道等于c的透明通道。这其实就是将自发光颜色和漫反射颜色进行了一定的混合。
-
自定义的光照模型的命名规则是“Lighting”+“自定义的光照名称”。这样就定义了一个光照模型。
光照模型有5种原型:half4 LightingName (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, half atten); half4 LightingName (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, fixed3 viewDir, half atten); half4 LightingName_PrePass (SurfaceOutput s, half4 light); half4 LightingName_DirLightmap(SurfaceOutput s, fixed4 color, fixed4 scale, bool surfFuncWritesNormal); half4 LightingName_DirLightmap(SurfaceOutput s, fixed4 color, fixed4 scale, fixed3 viewDir, bool surfFuncWritesNormal,out half3 specColor);这里我们用的就是第一种原型。第一个参数是输出结构,第二个参数是光线方向,也就是光源到物体表面上的点的向量,是单位向量,第三个参数衰减度,attenuation的缩写,因为光线被物体反射之后,会有能量损失,所以会有衰减。我们看到,这个参数没有被赋值,所以它是Unity内置的一个参数,我们知道它表示衰减就可以了。
函数里第一句计算的是漫反射的光强。dot是点乘。将表面的法向量和光线角度点乘,也就是光线和法向量的夹角越大,光线在法向量方向的分量越小,即反射的光越弱。因为夹角超过90度的时候,是负值,所以用max函数使结果大于0。max(x,y)就是取x,y中的最大值。
第三句的意思就是颜色值=反射值×平行光的颜色×漫反射光强×衰减度×2.
_LightColor0也是Unity内置的一个变量,它在不同的render path和pass里的意义不同,在这里就是平行光的颜色。
后面的这个2应该是个经验数值,可以根据自己想要的效果修改。
这就是基本漫反射的计算方法。
我们来看一下它的效果:
新建一个Sphere,将BasicDiffuse材质赋给它。将Slider的数值调为0.不出意外的话,你看到的效果是这样的: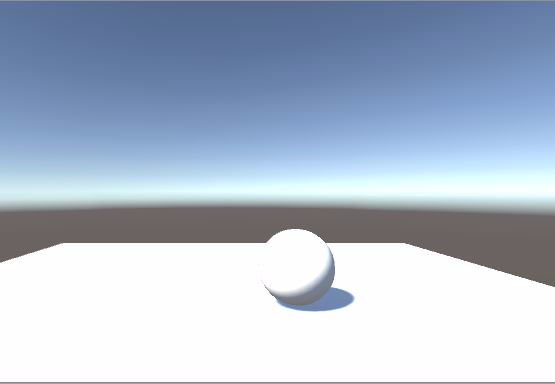
更改自发光的颜色,然后调节Slider,我们发现,Slider数值越大,自发光颜色越明显: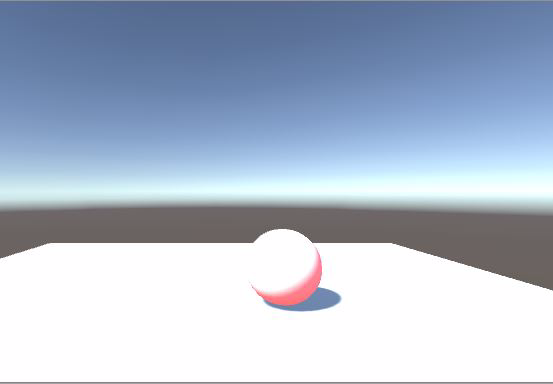
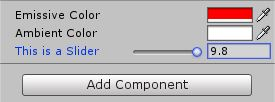
现在将自发光改回白色,更改漫反射的颜色,然后调节Slider:
不出意外的话,看到的效果和自发光一样,Slider=0时,阴影是灰色的,自发光和漫反射的颜色不起作用,数值越大,则自发光和漫反射的颜色越明显。
接下来,同时更改自发光和漫反射的颜色,比如红色和绿色,我们看到球变成了黄色,也就是红光和绿光混合的效果: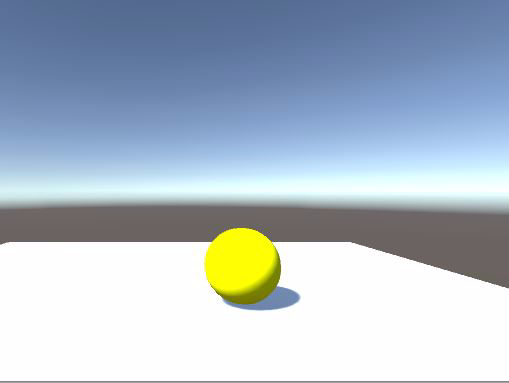
你还可以自己再调节其他颜色试试看,看看都会有些什么效果。
还有那个函数里的数值2,你也可以改改试试看哟~
HalfLambert
接下来再学习一个经典的光照模型——HalfLambert(半兰伯特)。
很简单,我们先把光照模型改名为HalfLambert,也就是修改光照函数和#pragma。
先修改一句:
float difLight = dot (s.Normal, lightDir);
然后添加一句:
float hLambert = 0.5 * difLight + 0.5;
再改一句:
col.rgb = s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * (hLambert * atten * 2);
原先difLight区间[-1,0]的部分变成了[0,0.5],如果直接用max函数使结果大于0的话,小于0的部分都会等于0,也就是背光面都会是黑色。如果用半兰伯特公式的话,小于0的部分就会从0渐变到0.5,颜色的灰度是会有变化。同时,亮部的亮度也提高了。
HalfLambert是由Valve公司提出的技术,是一种用于在低光照区域照亮物体的技术。它用来防止某个物体的背光面丢失形状并且显得太过平面化。这个技术是没有任何物理原理的,是一种感性的视觉增强。
附:代码清单
Shader "Custom/BasicDiffuse" {Properties {_EmissiveColor ("Emissive Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_AmbientColor ("Ambient Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_MySliderValue ("This is a Slider", Range(0,10)) = 2.5}SubShader {Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }LOD 200CGPROGRAM// Physically based Standard lighting model, and enable shadows on all light types#pragma surface surf BasicDiffuse// Use shader model 3.0 target, to get nicer looking lighting#pragma target 3.0float4 _EmissiveColor;float4 _AmbientColor;float _MySliderValue;struct Input{float2 uv_MainTex;};void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o){float4 c;c = pow((_EmissiveColor+_AmbientColor), _MySliderValue);o.Albedo = c.rgb;o.Alpha = c.a;}inline float4 LightingBasicDiffuse (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, fixed atten){float difLight = max(0, dot (s.Normal, lightDir));float4 col;col.rgb = s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * (difLight * atten * 2);col.a = s.Alpha;return col;}ENDCG}FallBack "Diffuse"
}
HalfLambert光照模型函数:
inline float4 LightingHalfLambert (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, fixed atten){float difLight = dot (s.Normal, lightDir);float hLambert = 0.5 * difLight + 0.5;float4 col;col.rgb = s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * (hLambert * atten * 2);col.a = s.Alpha;return col;
}
这篇关于【Unity SurfaceShader】学习笔记(一)认识结构的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







