本文主要是介绍Open CASCADE学习|扫掠,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
1、BRepPrimAPI_MakePrism
Draw Test Harness:
C++:
2、BRepPrimAPI_MakeRevol
Draw Test Harness:
C++:
3、BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell
Draw Test Harness:
C++:
Draw Test Harness:
C++:
Draw Test Harness:
C++:
锥度弯曲管
参考文献:
1、BRepPrimAPI_MakePrism
生成线性扫掠
Draw Test Harness:
polyline p 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 0prism r p 0 0 1vdisplay p r
C++:
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon.hxx>#include <BRepPrimAPI_MakePrism.hxx>#include"Viewer.h"int main(int argc, char* argv[]){BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon p;p.Add(gp_Pnt(0,0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 1, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0));TopoDS_Shape r=BRepPrimAPI_MakePrism(p,gp_Vec(0,0,1));Viewer vout(50, 50, 500, 500);vout << r;vout.StartMessageLoop();return 0;}
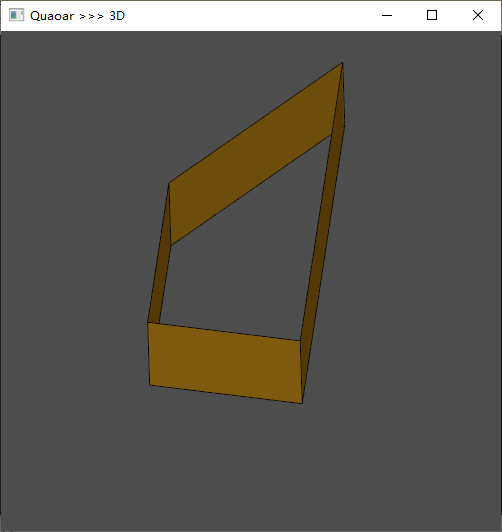

2、BRepPrimAPI_MakeRevol
生成旋转扫掠
Draw Test Harness:
polyline p 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 0revol r p 3 0 0 0 1 0 280vdisplay p r
C++:
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon.hxx>
#include <BRepPrimAPI_MakeRevol.hxx>
#include"Viewer.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon p;p.Add(gp_Pnt(0,0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 1, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0));TopoDS_Shape r= BRepPrimAPI_MakeRevol(p, gp_Ax1(gp_Pnt(3,0,0), gp_Dir(0,1,0)),280*M_PI/180);Viewer vout(50, 50, 500, 500);vout << r;vout.StartMessageLoop();return 0;
}


3、BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell
生成通用的扫掠。该类提供了一个框架,沿着脊柱的导线构建一个shell或者solid。构造solid,初始线框必须闭合的。
在Draw Test Harness中使用如下命令:
mksweep
addsweep
deletesweep
sestsweep
sestsweep有以下选项
-FR选项:切矢和法向由Frenet标架确定;
-CF选项:切矢由Frenet标架指定,法向通过计算最小扭转来确定;
-DT选项:切矢和法向由Darboux标架确定;
-CN选项:副法向由指定的dx, dy, dz确定;
-FT:切矢和法向是固定的;
buildsweep
buildsweep有指定不连续的处理方式及是否生成实体。其中
-C:将路径Path中不连续的地方通过延长和相交进行处理;
-R:将路径Path中不连续的地方通过相交和填充进行处理;
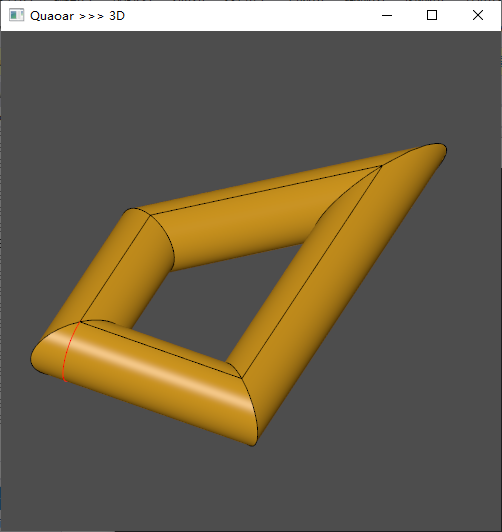
Draw Test Harness:
polyline p 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0circle c 0 0 0 1 0 0 0.2mkedge e cwire w emksweep paddsweep wsetsweep -FX 1 0 0buildsweep r -Cvdisplay p w r
C++:
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon.hxx>
#include <Geom_Circle.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire.hxx>
#include <BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell.hxx>
#include <TopoDS.hxx>
#include"Viewer.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon p;p.Add(gp_Pnt(0,0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 1, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0));Handle(Geom_Circle) c = new Geom_Circle(gp_Ax2(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0), gp_Dir(1, 0, 0)), 0.2);TopoDS_Edge e = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(c);BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire w;w.Add(e);BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell* Sweep = new BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell(TopoDS::Wire(p));gp_Dir D(1, 0, 0);gp_Ax2 Axe(gp_Pnt(0., 0., 0.), D);Sweep->SetMode(Axe);BRepBuilderAPI_TransitionMode Transition = BRepBuilderAPI_Transformed;Transition = BRepBuilderAPI_RightCorner;Sweep->SetTransitionMode(Transition);Sweep->Add(w, Standard_False, Standard_False);Sweep->Build();TopoDS_Shape r = Sweep->Shape();Viewer vout(50, 50, 500, 500);vout << p;vout << w;vout << r;vout.StartMessageLoop();return 0;
}

Draw Test Harness:
mksweep paddsweep wsetsweep -FRbuildsweep r -Cvdisplay p w r
C++:
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon.hxx>
#include <Geom_Circle.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire.hxx>
#include <BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell.hxx>
#include <TopoDS.hxx>
#include"Viewer.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon p;p.Add(gp_Pnt(0,0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 1, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0));Handle(Geom_Circle) c = new Geom_Circle(gp_Ax2(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0), gp_Dir(1, 0, 0)), 0.2);TopoDS_Edge e = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(c);BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire w;w.Add(e);BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell* Sweep = new BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell(TopoDS::Wire(p));Sweep->SetMode(Standard_True);BRepBuilderAPI_TransitionMode Transition = BRepBuilderAPI_Transformed;Transition = BRepBuilderAPI_RightCorner;Sweep->SetTransitionMode(Transition);Sweep->Add(w, Standard_False, Standard_False);Sweep->Build();TopoDS_Shape r = Sweep->Shape();Viewer vout(50, 50, 500, 500);vout << p;vout << w;vout << r;vout.StartMessageLoop();return 0;
}
Draw Test Harness:
polyline p 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 0circle c 0 0 0 1 0 0 0.2mkedge e cwire w emksweep paddsweep wbuildsweep r -Rvdisplay p w r
C++:
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon.hxx>
#include <Geom_Circle.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire.hxx>
#include <BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell.hxx>
#include <TopoDS.hxx>
#include"Viewer.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{BRepBuilderAPI_MakePolygon p;p.Add(gp_Pnt(0,0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 0, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 1, 0));p.Add(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0));Handle(Geom_Circle) c = new Geom_Circle(gp_Ax2(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 0), gp_Dir(1, 0, 0)), 0.2);TopoDS_Edge e = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(c);BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire w;w.Add(e);BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell* Sweep = new BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell(TopoDS::Wire(p));Sweep->Add(w, Standard_False, Standard_False);Sweep->SetMode(Standard_True);BRepBuilderAPI_TransitionMode Transition = BRepBuilderAPI_Transformed;Transition = BRepBuilderAPI_RoundCorner;Sweep->SetTransitionMode(Transition);Sweep->Build();TopoDS_Shape r = Sweep->Shape();Viewer vout(50, 50, 500, 500);vout << p;vout << w;vout << r;vout.StartMessageLoop();return 0;
}

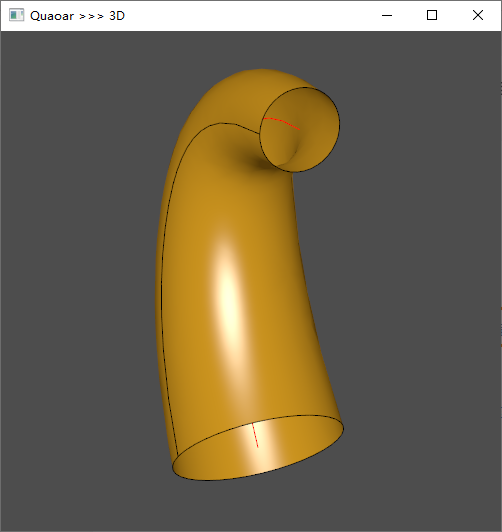
锥度弯曲管
#include <Geom_BezierCurve.hxx>
#include <BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell.hxx>
#include <Law_Linear.hxx>
#include <BRepAdaptor_Curve.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge.hxx>
#include <Geom2d_TrimmedCurve.hxx>
#include <GCE2d_MakeSegment.hxx>
#include <GeomAPI_PointsToBSpline.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace.hxx>
#include <GC_MakeCircle.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire.hxx>
#include <BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipe.hxx>
#include <GC_MakeArcOfCircle.hxx>
#include <BRepAlgoAPI_Fuse.hxx>
#include <GCPnts_QuasiUniformDeflection.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeVertex.hxx>
#include"Viewer.h"
#include <GProp_GProps.hxx>
#include <BRepGProp.hxx>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{//Creation of points for the spineTColgp_Array1OfPnt array = TColgp_Array1OfPnt(1, 5);array.SetValue(1, gp_Pnt(1, 4, 0));array.SetValue(2, gp_Pnt(2, 2, 0));array.SetValue(3, gp_Pnt(3, 3, 0));array.SetValue(4, gp_Pnt(4, 3, 0));array.SetValue(5, gp_Pnt(5, 5, 0));
//Creation of a Bezier Curve as the spine #创建贝塞尔曲线作为主干Geom_BezierCurve* bz_curv = new Geom_BezierCurve(array);TopoDS_Edge bz_curv_edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(bz_curv);TopoDS_Wire bz_curv_wire = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire(bz_curv_edge);
//Creation of profile to sweep along the spine #创建沿脊柱扫描的轮廓gp_Circ circle = gp_Circ(gp::ZOX(), 1);circle.SetLocation(array[1]);TopoDS_Edge circle_edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(circle);TopoDS_Wire circle_wire = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire(circle_edge);//Creation of the law to dictate the evolution of the profile#规定轮廓的演变BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell* brep1 = new BRepOffsetAPI_MakePipeShell(bz_curv_wire);Handle(Law_Linear) law_f =new Law_Linear();law_f->Set(0, 0.5, 1, 1);brep1->SetLaw(circle_wire, law_f, Standard_False,Standard_True);Viewer vout(50, 50, 500, 500);vout << bz_curv_wire;vout << brep1->Shape();vout.StartMessageLoop();return 0;
}
参考文献:
1、https://dev.opencascade.org/doc/occt-7.0.0/refman/html/class_b_rep_offset_a_p_i___make_pipe_shell.html#details
2、https://www.cnblogs.com/opencascade/p/OpenCASCADE_Sweep_Algorithm.html
3、https://blog.csdn.net/ydk001001/article/details/121210419
这篇关于Open CASCADE学习|扫掠的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






