本文主要是介绍NSTimer循环引用分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- NSTimer介绍
- 循环引用问题
- 创建
- 循环引用
- 处理办法
- 方案一:中间代理对象
- 方案一升级版
- 关于NSProxy类的补充
- 方案二:将timer引用改变
- 方案三:使用Category
- 参考文献
NSTimer介绍
官方文档
经过一定时间间隔后将触发的计时器,会将指定的消息发送到目标对象
官方文档中给了三种创建定时器的方法:
- 使用类方法创建计时器,并在默认模式下将其安排在当前运行循环上:
scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:invocation:repeats:
scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:target:selector:userInfo:repeats: - 使用类方法创建计时器对象,而不在RunLoop上安排它(创建计时器后需要手动调用addTimer:forMode: 方法将其添加到RunLoop中)
timerWithTimeInterval:invocation:repeats:
timerWithTimeInterval:target:selector:userInfo:repeats: - 分配计时器并使用方法将其初始化(创建计时器后需要手动调用addTimer:forMode: 方法将其添加到RunLoop中)initWithFireDate:interval:target:selector:userInfo:repeats:
关于销毁,文档的解释如下:
Once scheduled on a run loop, the timer fires at the specified interval until it is invalidated. A nonrepeating timer invalidates itself immediately after it fires. However, for a repeating timer, you must invalidate the timer object yourself by calling its invalidate method. Calling this method requests the removal of the timer from the current run loop; as a result, you should always call the invalidate method from the same thread on which the timer was installed. Invalidating the timer immediately disables it so that it no longer affects the run loop. The run loop then removes the timer (and the strong reference it had to the timer), either just before the invalidate method returns or at some later point. Once invalidated, timer objects cannot be reused.
大致意思是:一旦安排在RunLoop中,计时器就会以指定的时间间隔触发,直到失效为止。非重复计时器在触发后立即失效。而重复计时器需要调用invalidate方法自己使计时器对象无效。调用此方法要求从当前RunLoop中删除计时器。你应该始终从安装计时器的同一线程中调用该方法。使计时器无效就会立即禁用,以使其不再影响RunLoop。然后,RunLoop将删除该计时器(以及该计时器必须具有的强引用),在invalidate方法返回之前或稍后。一旦失效,计时器对象将无法重用。
循环引用问题
创建
从 NSTimer 的官方文档可以得知,RunLoop 对加入其中的 NSTimer 会添加一个强引用。那么我们试试在 NSTimer 创建之后加入 RunLoop 之前,弱引用NSTimer对象是否会释放:
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,weak) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(doSomething) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];if (self.timer == nil) {NSLog(@"timer 被释放了");}}- (void)doSomething {NSLog(@"doSomething");
}

再加入RunLoop看看,因为弱引用会被自动释放,所以需要一个中间变量:
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,weak) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 创建 NSTimerNSTimer *aTimer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(doSomething) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];// 赋值给 weak 变量self.timer = aTimer;// NSTimer 加入 NSRunLoop[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];if (self.timer == nil) {NSLog(@"timer 被释放了");}}- (void)doSomething {NSLog(@"doSomething");
}
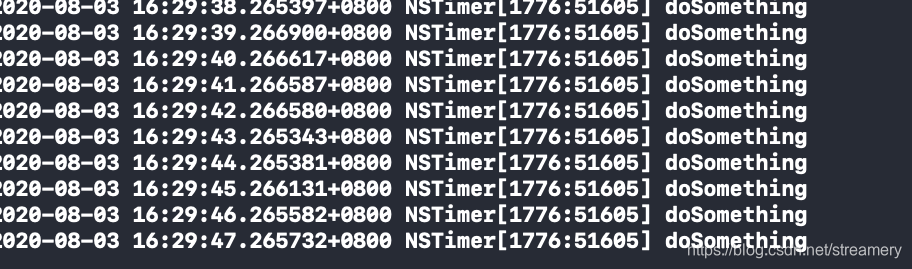
我们就可以看到,timer已经执行了
循环引用
这里我使用跳转的方式结束这个ViewController的的生命
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,weak) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 创建 NSTimerNSTimer *aTimer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(doSomething) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];// 赋值给 weak 变量self.timer = aTimer;// NSTimer 加入 NSRunLoop[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];if (self.timer == nil) {NSLog(@"timer 被释放了");}}- (void)doSomething {NSLog(@"doSomething");
}- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:NO completion:nil];
}- (void)dealloc {NSLog(@"dealloc");// ViewController执行dealloc时timer也销毁[self.timer invalidate];
}
执行后发现,ViewController并没有执行dealloc方法,所以timer也没有销毁,可timer是弱引用,为什么会这样呢,我们分析分析
NSTimer被释放的前提是ViewController被dealloc,而NSTimer一直强引用着ViewController,这就造成了循环引用
处理办法
也就是说,只要NSTimer不强引用ViewController,即target对象不是ViewController,就可以解决
有两个办法处理这个问题:
方案一:中间代理对象
加入一个中间代理对象
@interface TAYProxy : NSObject+ (instancetype) proxyWithTarget:(id)target;
@property (weak, nonatomic) id target;@end@implementation TAYProxy+ (instancetype) proxyWithTarget:(id)target {TAYProxy *proxy = [[TAYProxy alloc] init];proxy.target = target;return proxy;
}- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {return self.target;
}@end
根据上面分析,timer是强引用还是弱引用对结果不造成影响,所以我们直接写成强引用,就不需要创建一个中间变量了
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,strong) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 中间代理对象self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:[TAYProxy proxyWithTarget:self] selector:@selector(doSomething) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];}- (void)doSomething {NSLog(@"doSomething");
}- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:NO completion:nil];
}- (void)dealloc {NSLog(@"dealloc");// ViewController执行dealloc时timer也销毁[self.timer invalidate];
}
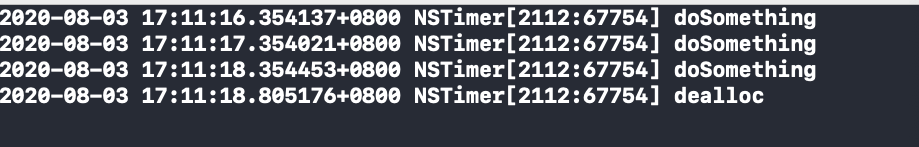
可以看出来是解决了问题的,我们来分析分析原因:
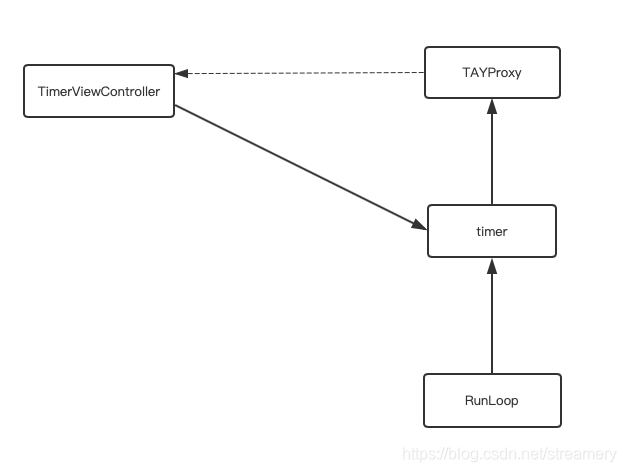
- 当界面dismiss的时候,TimerViewController就没有强指针指向了,可以被销毁
- TimerViewController被销毁的时候会走dealloc,就会调用[self.timer invalidate]; 那么timer会从RunLoop中移除,指向timer的指针被销毁
- TimerViewController销毁了,对应的强指针也就会销毁,即TimerViewController指向timer的指针被销毁
- timer已经没有指针引用了,也会被销毁,那么TAYProxy实例对象也就销毁了
大功告成!
方案一升级版
通过看这篇博客,发现还有一种更高明的写法
思路来源于YYWeakProxy,YYKit 开源项目 ,是一个代理类的实现
有一个NSProxy类,这是一个专门用于做消息转发的类,我们需要通过子类的方式来使用它
创建一个TAYWeakProxy,继承于NSProxy类
@interface TAYWeakProxy : NSProxy+ (instancetype)proxyWithTarget:(id)target;
@property (weak, nonatomic) id target;@end@implementation TAYWeakProxy+ (instancetype)proxyWithTarget:(id)target {TAYWeakProxy *proxy = [TAYWeakProxy alloc];proxy.target = target;return proxy;
}- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)sel {return [self.target methodSignatureForSelector:sel];
}- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation {[invocation invokeWithTarget:self.target];
}
在TimerViewController里操作和上面差不多
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,strong) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 中间代理对象self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:[TAYWeakProxy proxyWithTarget:self] selector:@selector(doSomething) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];}- (void)doSomething {NSLog(@"doSomething");
}- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:NO completion:nil];
}- (void)dealloc {NSLog(@"dealloc");// ViewController执行dealloc时timer也销毁[self.timer invalidate];
}
两者对比:
| TAYProxy | TAYWeakProxy | |
|---|---|---|
| 父类 | NSObject | NSProxy |
| 实现方法 | forwardingTargetForSelector: | methodSignatureForSelector:和forwardInvocation: |
关于NSProxy类的补充
- NSProxy是一个专门用来做消息转发的类
- NSProxy是个抽象类,使用需自己写一个子类继承自NSProxy
- NSProxy的子类需要实现两个方法,就是上面那两个,即:methodSignatureForSelector:和forwardInvocation:
NSProxy类的优点在于直接执行了消息转发机制三次拯救的第三步的调用methodSignatureForSelector:返回方法签名,如果方法签名不为nil,调用forwardInvocation:来执行该方法,会跳过前面的步骤,提高性能
方案二:将timer引用改变
虽然TimerViewController强引用了timer,但是timer可以不强引用TimerViewController,我之前想过使用weakSelf,但是并没有成功,我是这么写的:
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,strong) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 使用weakSelf__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:weakSelf selector:@selector(doSomething) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
}- (void)doSomething {NSLog(@"doSomething");
}- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:NO completion:nil];
}- (void)dealloc {NSLog(@"dealloc");// ViewController执行dealloc时timer也销毁[self.timer invalidate];
}
运行结果显示并没有调用dealloc方法,我便放弃了这个想法,后来在这篇博客中发现将使用的target-action方法改为block方法就可以了
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,strong) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// 使用weakSelf__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
// self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:weakSelf selector:@selector(doSomething) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];self.timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 repeats:YES block:^(NSTimer * _Nonnull timer) {[weakSelf doSomething];}];[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
}- (void)doSomething {NSLog(@"doSomething");
}- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:NO completion:nil];
}- (void)dealloc {NSLog(@"dealloc");// ViewController执行dealloc时timer也销毁[self.timer invalidate];
}
这个原因我还没有探究出来,有知道的朋友麻烦赐教
方案三:使用Category
通过 category 把 NSTimer 的 target 设置为 NSTimer 类,让 NSTimer 自身做为target, 把 selector 通过 block 传入给 NSTimer,在 NSTimer 的 category 里面触发 selector 。这样也可以达到 NSTimer 不直接持有 TimerViewController 的目的,实现更优雅 ( 如果是直接支持 iOS 10 以上的系统版本,那可以使用 iOS 10新增的系统级 block 方案 )
@interface NSTimer (BlocksSupport)
+ (NSTimer *)tay_scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)interval repeats:(BOOL)repeats block: (void(^)())block;@end@implementation NSTimer (BlocksSupport)+ (NSTimer *)tay_scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)interval repeats:(BOOL)repeats block:(void(^)())block {return [self scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:interval target:self selector:@selector(tay_blockInvoke:) userInfo:[block copy] repeats:repeats];
}
+ (void)tay_blockInvoke:(NSTimer *)timer {void (^block)(void) = timer.userInfo;if(block) {block();}
}@end
@interface TimeViewController ()@property (nonatomic,strong) NSTimer *timer;@end@implementation TimeViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];// categoryself.timer =[NSTimer tay_scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1.0 repeats:YES block:^{NSLog(@"doSomething");}];}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {[self dismissViewControllerAnimated:NO completion:nil];
}- (void)dealloc {NSLog(@"dealloc");// ViewController执行dealloc时timer也销毁[self.timer invalidate];
}
参考文献
NSTimer 避坑指南
如何正确的使用NSTimer
这篇关于NSTimer循环引用分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




