本文主要是介绍Tensorflow2.0笔记 - where,scatter_nd, meshgrid相关操作,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本笔记记录tf.where进行元素位置查找,scatter_nd用于指派元素到tensor的特定位置,meshgrid用作绘图的相关操作。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plttf.__version__#where操作查找元素位置
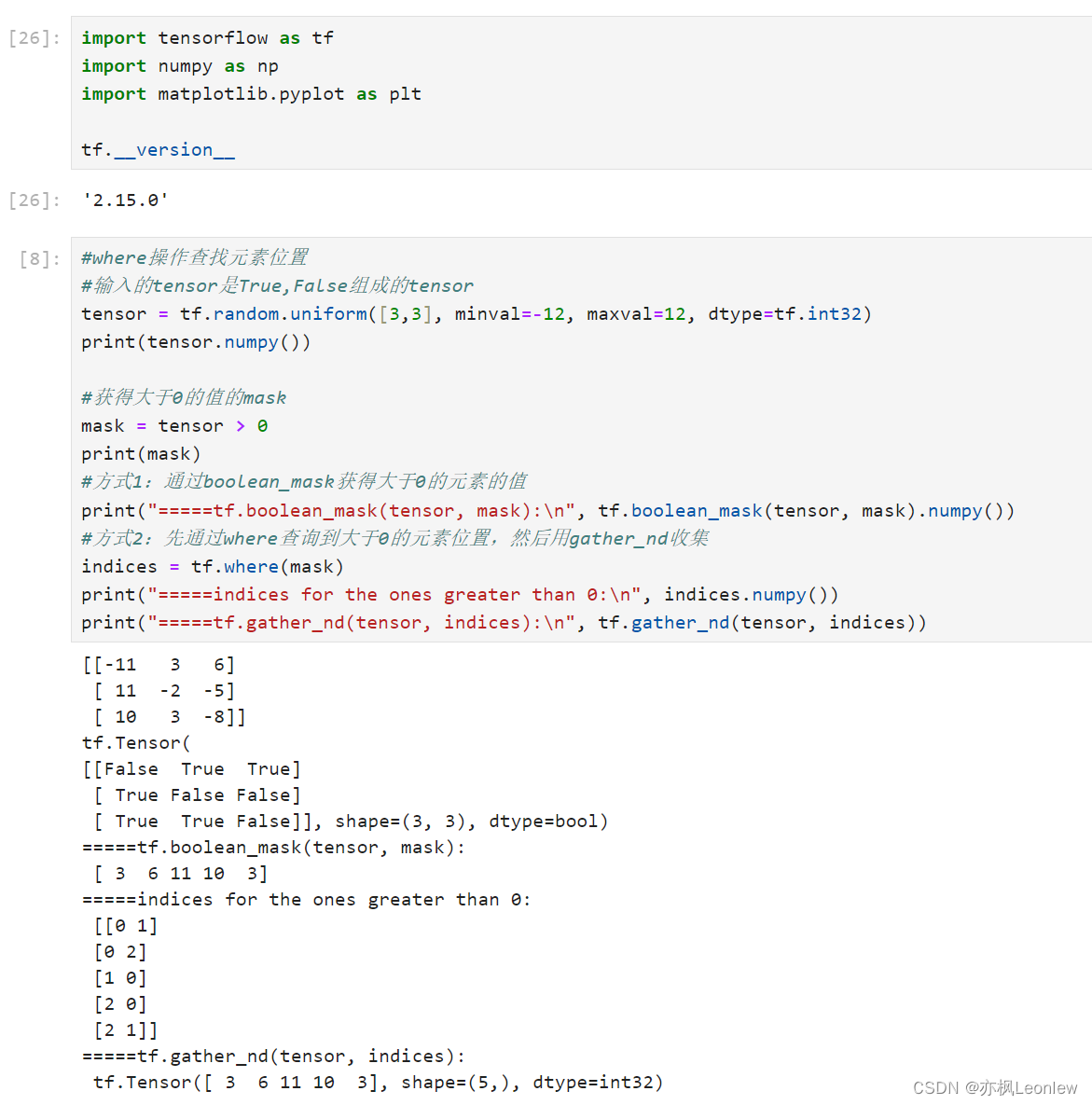
#输入的tensor是True,False组成的tensor
tensor = tf.random.uniform([3,3], minval=-12, maxval=12, dtype=tf.int32)
print(tensor.numpy())#获得大于0的值的mask
mask = tensor > 0
print(mask)
#方式1:通过boolean_mask获得大于0的元素的值
print("=====tf.boolean_mask(tensor, mask):\n", tf.boolean_mask(tensor, mask).numpy())
#方式2:先通过where查询到大于0的元素位置,然后用gather_nd收集
indices = tf.where(mask)
print("=====indices for the ones greater than 0:\n", indices.numpy())
print("=====tf.gather_nd(tensor, indices):\n", tf.gather_nd(tensor, indices))#where带条件选择元素
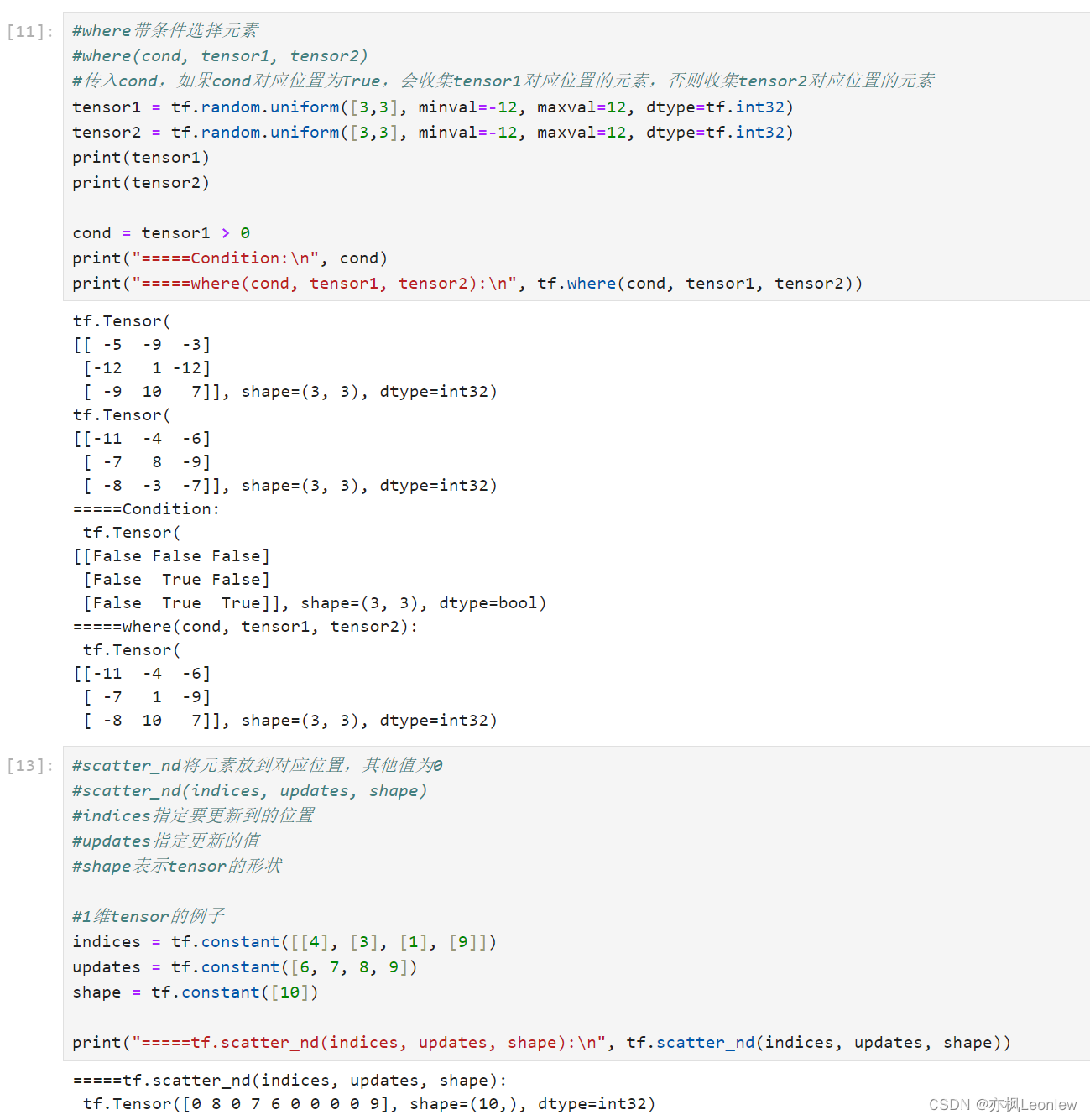
#where(cond, tensor1, tensor2)
#传入cond,如果cond对应位置为True,会收集tensor1对应位置的元素,否则收集tensor2对应位置的元素
tensor1 = tf.random.uniform([3,3], minval=-12, maxval=12, dtype=tf.int32)
tensor2 = tf.random.uniform([3,3], minval=-12, maxval=12, dtype=tf.int32)
print(tensor1)
print(tensor2)cond = tensor1 > 0
print("=====Condition:\n", cond)
print("=====where(cond, tensor1, tensor2):\n", tf.where(cond, tensor1, tensor2))#scatter_nd将元素放到对应位置,其他值为0
#scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape)
#indices指定要更新到的位置
#updates指定更新的值
#shape表示tensor的形状#1维tensor的例子
indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1], [9]])
updates = tf.constant([6, 7, 8, 9])
shape = tf.constant([10])print("=====tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape):\n", tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape))#多维tensor的scatrer_nd
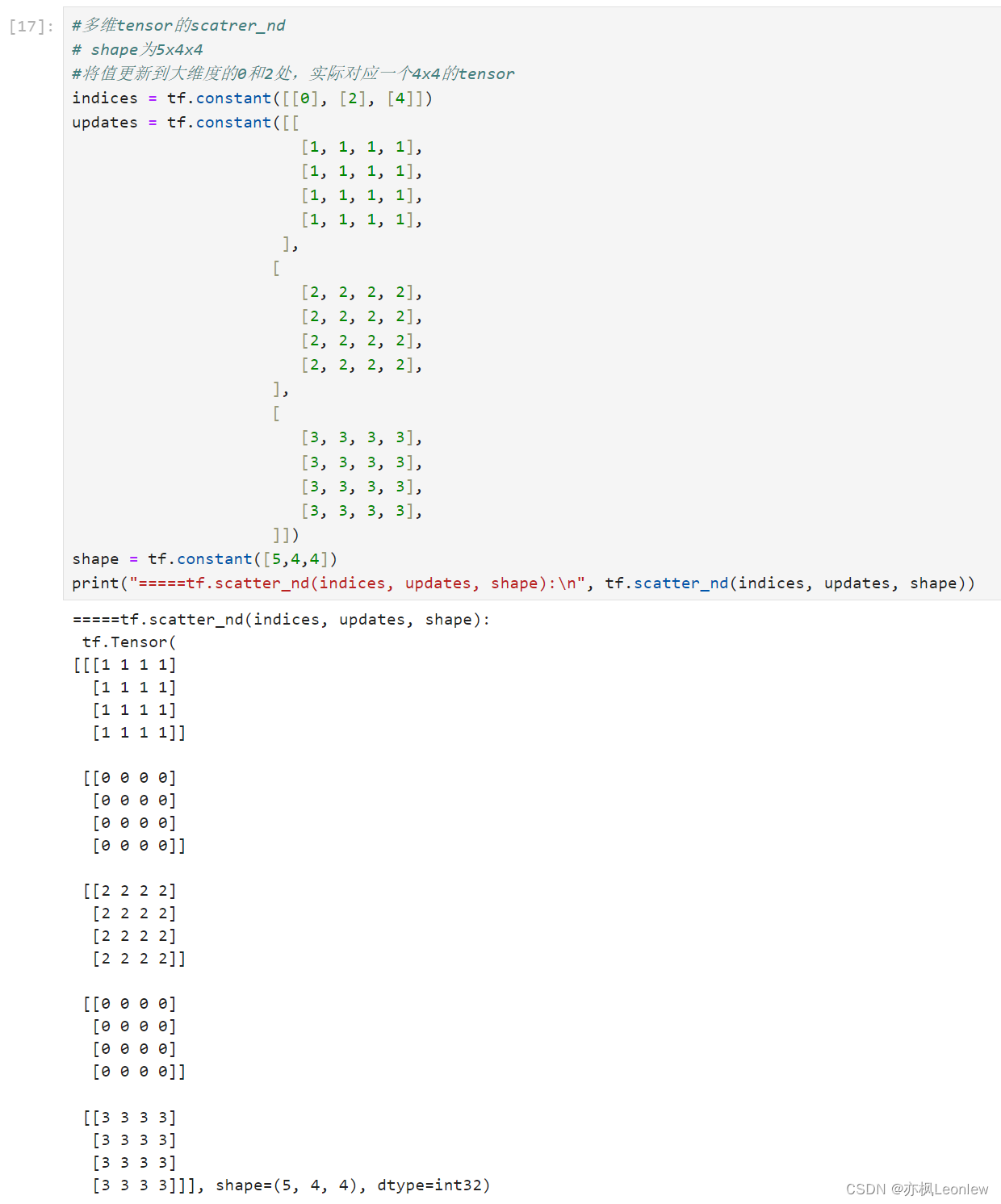
# shape为5x4x4
#将值更新到大维度的0和2处,实际对应一个4x4的tensor
indices = tf.constant([[0], [2], [4]])
updates = tf.constant([[[1, 1, 1, 1],[1, 1, 1, 1],[1, 1, 1, 1],[1, 1, 1, 1],],[[2, 2, 2, 2],[2, 2, 2, 2],[2, 2, 2, 2],[2, 2, 2, 2],],[[3, 3, 3, 3],[3, 3, 3, 3],[3, 3, 3, 3],[3, 3, 3, 3],]])
shape = tf.constant([5,4,4])
print("=====tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape):\n", tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape))#meshgrid绘图
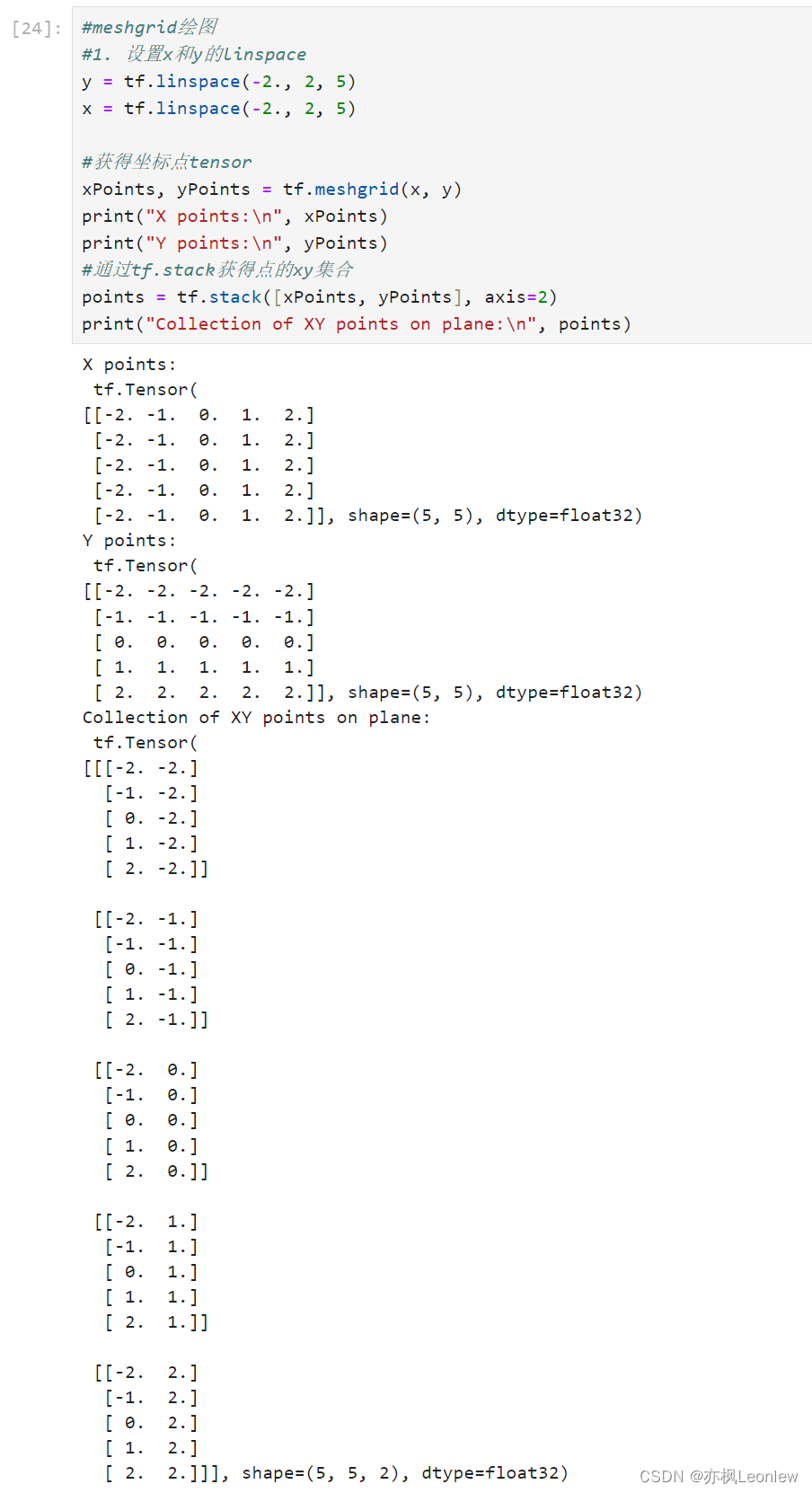
#1. 设置x和y的linspace
y = tf.linspace(-2., 2, 5)
x = tf.linspace(-2., 2, 5)#获得坐标点tensor
xPoints, yPoints = tf.meshgrid(x, y)
print("X points:\n", xPoints)
print("Y points:\n", yPoints)
#通过tf.stack获得点的xy集合
points = tf.stack([xPoints, yPoints], axis=2)
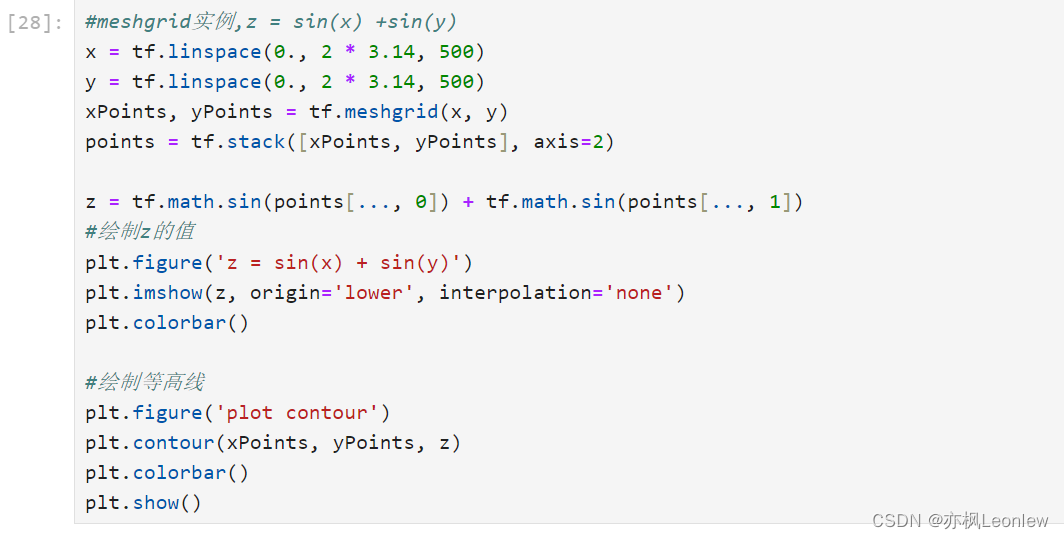
print("Collection of XY points on plane:\n", points)#meshgrid实例,z = sin(x) +sin(y)
x = tf.linspace(0., 2 * 3.14, 500)
y = tf.linspace(0., 2 * 3.14, 500)
xPoints, yPoints = tf.meshgrid(x, y)
points = tf.stack([xPoints, yPoints], axis=2)z = tf.math.sin(points[..., 0]) + tf.math.sin(points[..., 1])
#绘制z的值
plt.figure('z = sin(x) + sin(y)')
plt.imshow(z, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
plt.colorbar()#绘制等高线
plt.figure('plot contour')
plt.contour(xPoints, yPoints, z)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
运行结果:

这篇关于Tensorflow2.0笔记 - where,scatter_nd, meshgrid相关操作的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





