本文主要是介绍探索Pyecharts之美-绘制多彩旭日图的艺术与技巧【第37篇—python:旭日图】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 引言
- 准备工作
- 绘制基本旭日图
- 调整颜色和样式
- 添加交互功能
- 定制标签和标签格式
- 嵌套层级数据
- 高级样式与自定义
- 进阶主题:动态旭日图
- 数据源扩展:外部JSON文件
- 总结
引言
数据可视化在现代编程中扮演着重要的角色,而Pyecharts是Python中一个强大的图表库,可以轻松实现各种炫酷的数据可视化效果。其中,旭日图是一种展示层次结构数据的理想选择,通过不同的颜色和半径呈现数据的层级和关系。在本篇技术博客中,我们将深入探讨Pyecharts中绘制旭日图的多种参数,同时提供实用的代码示例,帮助你更好地利用这一功能。
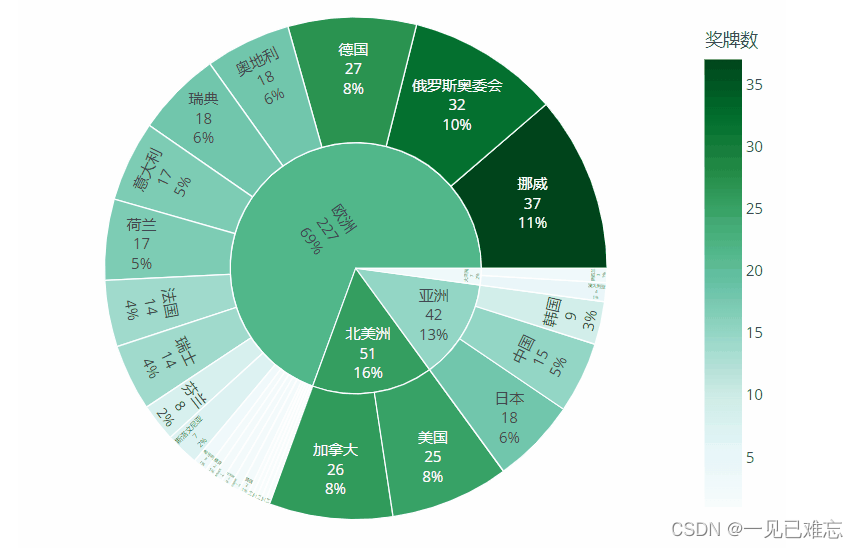
准备工作
在开始之前,请确保你已经安装了Pyecharts库。如果没有安装,可以使用以下命令进行安装:
pip install pyecharts
绘制基本旭日图
首先,我们从最基本的旭日图开始,使用Pyecharts的Sunburst类。
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburstdata = {"name": "root","children": [{"name": "A", "value": 10},{"name": "B", "value": 20},{"name": "C", "value": 15},{"name": "D", "value": 25},],
}sunburst = Sunburst()
sunburst.add("", data['children'], radius=[0, "90%"])
sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="基本旭日图"))
sunburst.render("basic_sunburst.html")
在上述代码中,我们定义了一个简单的层级结构数据,然后使用Sunburst类绘制了基本的旭日图。radius参数用于设置旭日图的半径范围。
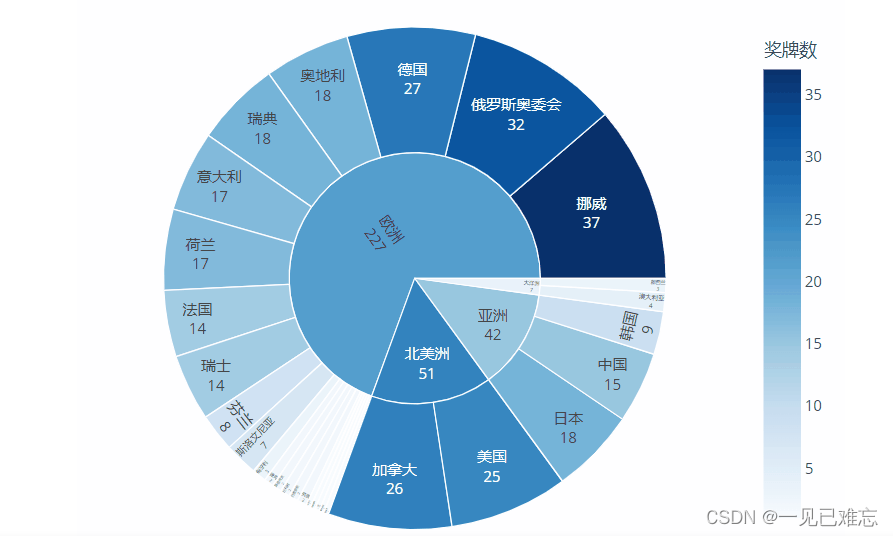
调整颜色和样式
为了让旭日图更具吸引力,我们可以调整颜色和样式。
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburstdata = {"name": "root","children": [{"name": "A", "value": 10},{"name": "B", "value": 20},{"name": "C", "value": 15},{"name": "D", "value": 25},],
}sunburst = Sunburst()
sunburst.add("", data['children'], radius=[0, "90%"], color_scheme="purple")
sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="调整颜色和样式"),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
)
sunburst.render("styled_sunburst.html")
在这个例子中,我们使用了color_scheme参数来指定颜色方案,并通过legend_opts隐藏了图例。
添加交互功能
为了增强用户体验,我们可以添加一些交互功能,如数据提示和缩放。
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburstdata = {"name": "root","children": [{"name": "A", "value": 10},{"name": "B", "value": 20},{"name": "C", "value": 15},{"name": "D", "value": 25},],
}sunburst = Sunburst()
sunburst.add("", data['children'], radius=[0, "90%"], color_scheme="purple")
sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="添加交互功能"),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(trigger="item", formatter="{b}: {c}"),toolbox_opts=opts.ToolboxOpts(is_show=True, feature={"saveAsImage": {}}),
)
sunburst.render("interactive_sunburst.html")
在这个例子中,我们通过tooltip_opts添加了数据提示,toolbox_opts增加了保存为图片的功能。
定制标签和标签格式
在旭日图中,标签对于传达信息非常重要。我们可以通过label_opts参数来定制标签的样式和格式。
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburstdata = {"name": "root","children": [{"name": "A", "value": 10},{"name": "B", "value": 20},{"name": "C", "value": 15},{"name": "D", "value": 25},],
}sunburst = Sunburst()
sunburst.add("",data['children'],radius=[0, "90%"],color_scheme="purple",label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}", position="inside"),
)
sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="定制标签和标签格式"),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
)
sunburst.render("custom_label_sunburst.html")
在上述代码中,我们使用了label_opts参数来设置标签的格式和位置,通过formatter来自定义标签的显示内容。
嵌套层级数据
如果你的数据包含多个层级,你可以通过嵌套的方式表示。
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburstdata = {"name": "root","children": [{"name": "A","children": [{"name": "A1", "value": 10},{"name": "A2", "value": 20},],},{"name": "B","children": [{"name": "B1", "value": 15},{"name": "B2", "value": 25},],},],
}sunburst = Sunburst()
sunburst.add("", data['children'], radius=[0, "90%"], color_scheme="purple")
sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="嵌套层级数据"),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
)
sunburst.render("nested_sunburst.html")
在这个例子中,我们通过嵌套层级的方式,更好地表达了数据之间的关系。

高级样式与自定义
如果你需要更高级的样式和自定义,可以进一步使用Pyecharts提供的丰富功能,如渐变色、阴影效果等。
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburstdata = {"name": "root","children": [{"name": "A", "value": 10},{"name": "B", "value": 20},{"name": "C", "value": 15},{"name": "D", "value": 25},],
}sunburst = Sunburst()
sunburst.add("",data['children'],radius=[0, "90%"],color_scheme="purple",label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}", position="inside"),itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(border_color="white",border_width=1,opacity=0.7,shadow_blur=10,shadow_color="rgba(120, 36, 50, 0.5)",),
)
sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="高级样式与自定义"))
sunburst.render("advanced_sunburst.html")
在这个例子中,我们通过itemstyle_opts参数实现了边框、透明度和阴影效果的自定义。
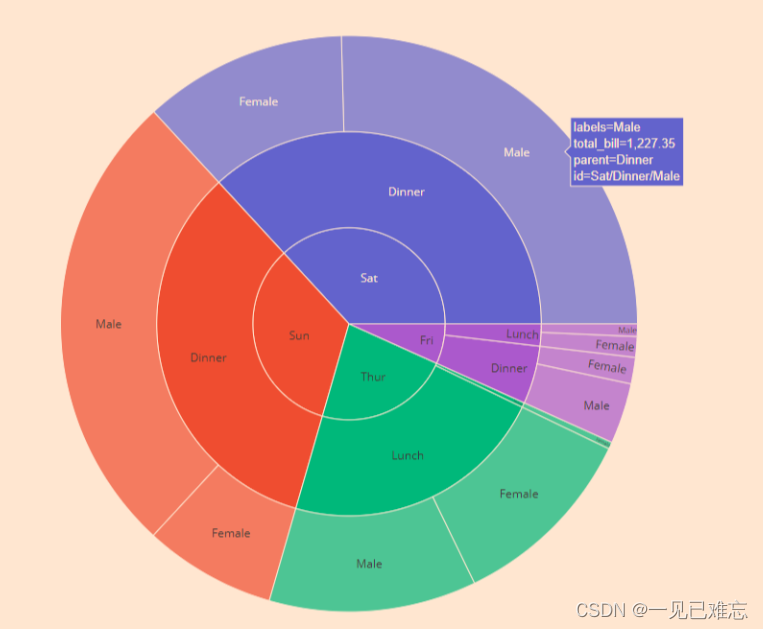
进阶主题:动态旭日图
在一些场景下,我们希望展示数据的动态变化,这时候可以借助Pyecharts的Timeline组件,创建一个动态的旭日图。
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburst, Timeline# 模拟多个时间点的数据
data_timeline = [{"time": "2023-01-01","data": {"name": "root","children": [{"name": "A", "value": 15},{"name": "B", "value": 25},{"name": "C", "value": 20},{"name": "D", "value": 30},],},},# 添加更多时间点的数据...
]timeline = Timeline()for time_data in data_timeline:sunburst = Sunburst()sunburst.add("",time_data['data']['children'],radius=[0, "90%"],color_scheme="purple",label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}", position="inside"),)sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=f"动态旭日图 - {time_data['time']}"),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),)timeline.add(sunburst, time_data['time'])timeline.render("dynamic_sunburst.html")
在这个例子中,我们使用了Timeline组件,根据不同时间点的数据绘制了一系列动态的旭日图。这是一个强大的工具,使得你可以清晰地展示数据在时间轴上的演变过程。
数据源扩展:外部JSON文件
当数据较为庞大或需要动态加载时,可以将数据存储在外部JSON文件中,并通过读取文件的方式进行数据绑定。
import json
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Sunburst# 从外部JSON文件读取数据
with open("data.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:external_data = json.load(f)sunburst = Sunburst()
sunburst.add("",external_data['children'],radius=[0, "90%"],color_scheme="purple",label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}", position="inside"),
)
sunburst.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="外部JSON文件数据展示"),legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
)
sunburst.render("external_data_sunburst.html")
在上述代码中,我们通过json.load方法读取了外部JSON文件中的数据,然后将其传递给Sunburst图表进行绘制。
总结
通过本文,你学会了如何使用Pyecharts绘制多种炫酷的旭日图,并深入了解了各种参数的用法。无论是基本的图形绘制,还是高级的样式定制,Pyecharts都提供了强大而灵活的工具,助力你创建令人印象深刻的数据可视化图表。希望这篇文章对你在数据可视化的学习和实践中有所帮助。
这篇关于探索Pyecharts之美-绘制多彩旭日图的艺术与技巧【第37篇—python:旭日图】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








