本文主要是介绍【学网攻】 第(11)节 -- 静态路由及默认路由,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
系列文章目录
提示:这里可以添加系列文章的所有文章的目录,目录需要自己手动添加
例如:第一章 Python 机器学习入门之pandas的使用
提示:写完文章后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 【学网攻】 第(1)节 -- 认识网络
- 【学网攻】 第(2)节 -- 交换机认识及使用
- 【学网攻】 第(3)节 -- 交换机配置聚合端口
- 【学网攻】 第(4)节 -- 交换机划分Vlan
- 【学网攻】 第(5)节 -- Cisco VTP的使用
- 【学网攻】 第(6)节 -- 三层交换机实现VLAN间路由
- 【学网攻】 第(7)节 -- 生成树配置
- 【学网攻】 第(8)节 -- 端口安全
- 【学网攻】 第(9)节 -- 路由器使用以及原理
- 【学网攻】 第(10)节 -- 路由器单臂路由配置
前言
网络已经成为了我们生活中不可或缺的一部分,它连接了世界各地的人们,让信息和资源得以自由流动。随着互联网的发展,我们可以通过网络学习、工作、娱乐,甚至是社交。因此,学习网络知识和技能已经成为了每个人都需要掌握的重要能力。
本课程博主将带领读者深入了解网络的基本原理、结构和运作方式,帮助读者建立起对网络的全面理解。我们将介绍网络的发展历程、网络的分类和组成、网络的安全和隐私保护等内容,帮助读者掌握网络知识,提高网络素养。
通过学习本书,读者将能够更好地利用网络资源,提高工作效率,拓展人际关系,甚至是保护自己的网络安全。网络世界充满了无限的可能,希望本课程能够帮助读者更好地驾驭网络,享受网络带来的便利和乐趣。
一、静态路由是什么?
静态路由(英语:Static routing)是一种路由的方式,路由项(routing entry)由手动配置,而非动态决定。与动态路由不同,静态路由是固定的,不会改变,即使网络状况已经改变或是重新被组态。一般来说,静态路由是由网络管理员逐项加入路由表。
二、实验
1.引入
实验目标
- 掌握静态路由的配置方法和技巧;
- 掌握通过静态路由方式实现网络的连通性;
- 熟悉广域网线缆的链接方式;
实验背景
学校有新旧两个校区,每个校区是一个独立的局域网,为了使新旧校区能够正常相互通讯,共享资源。每个校区出口利用一台路由器进行连接,两台路由器间学校申请了一条2M的DDN专线进行相连,要求做适当配置实现两个校区的正常相互访问。
技术原理
- 路由器属于网络层设备,能够根据IP包头的信息,选择一条最佳路径,将数据包转发出去。实现不同网段的主机之间的互相访问。路由器是根据路由表进行选路和转发的。而路由表里就是由一条条路由信息组成。
- 生成路由表主要有两种方法:手工配置和动态配置,即静态路由协议配置和动态路由协议配置。
- 静态路由是指有网络管理员手工配置的路由信息。
- 静态路由除了具有简单、高效、可靠的优点外,它的另一个好处是网络安全保密性高。
- 缺省路由可以看做是静态路由的一种特殊情况。当数据在查找路由表时,没有找到和目标相匹配的路由表项时,为数据指定路由。
实验步骤
- 新建packet tracer拓扑图
- 在路由器R1、R2上配置接口的IP地址和R1串口上的时钟频率;
- 查看路由器生成的直连路由;
- 在路由器R1、R2上配置静态路由;
- 验证R1、R2上的静态路由配置;
- 将PC1、PC2主机默认网关分别设置为路由器接口fa 1/0的IP地址;
- PC1、PC2主机之间可以相互通信;
实验设备
Routers-2811(3台),PC(2台)
实验拓扑图

两根串口线(NM-4A/S),两根交叉线

实验配置
PC配置
PC0:
IP 地址:192.168.10.1
子网掩码:255.255.255.0
网 关:192.168.10.254
PC1:
IP 地址:192.168.20.1
子网掩码:255.255.255.0
网 关:192.168.20.254Routers路由器的线路配置(1-3)
R1:
Router>
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#h R1
R1(config)#int f0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.10.254 255.255.255.0 //配置接口网关
R1(config-if)#no shut
R1(config)#int s1/0
R1(config-if)#no shut
R1(config-if)#ip add 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 //配置出接口IP
R2:
Router>
Router>en
Router#conf
Router(config)#h R2
R2(config)#int s1/0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#ip add 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config)#int s1/1
R2(config-if)#ip add 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R3:
Router>
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#h R3
R3(config)#int s1/0
R3(config-if)#ip add 10.0.2.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shut
R3(config)#int f0/0
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.20.254 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shut
静态路由
R1:
R1(config)#ip route 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.2 //目标IP 子网掩码 下一跳IP
R1(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGPD - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter areaN1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGPi - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODRP - periodic downloaded static routeGateway of last resort is not set10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
L 10.0.1.1/32 is directly connected, Serial1/0192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
L 192.168.10.254/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 192.168.20.0/24 [1/0] via 10.0.1.2 //主要是这一条,一定要有
R2:
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.1 //静态路由
R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.2 //默认路由
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGPD - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter areaN1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGPi - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODRP - periodic downloaded static routeGateway of last resort is 10.0.2.2 to network 0.0.0.010.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
L 10.0.1.2/32 is directly connected, Serial1/0
C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/1
L 10.0.2.1/32 is directly connected, Serial1/1
S 192.168.10.0/24 [1/0] via 10.0.1.1
S* 0.0.0.0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.2R3:
R3(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.1
R3(config)#do show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGPD - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter areaN1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGPi - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODRP - periodic downloaded static routeGateway of last resort is 10.0.2.1 to network 0.0.0.010.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
L 10.0.2.2/32 is directly connected, Serial1/0192.168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
L 192.168.20.254/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S* 0.0.0.0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.1实验验证
PC0 PING PC1 :
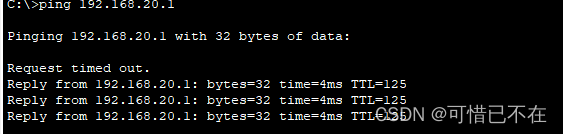
| PC0 PING PC1 | 通 |
总结
默认路由与静态路由在公司中经常使用,因为后者的安全系数更高,所以基本都是工程师手动的去配置,
这篇关于【学网攻】 第(11)节 -- 静态路由及默认路由的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





