本文主要是介绍JAVA读取文件单词出现次数_用javaIO流读取文本中英文字母和英文单词的出现次数及频率...,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、读取文本中英文字母出现的次数并降序输出英文字母的百分比
源码;
package total;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Statistics_letter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileReader fr=new FileReader("a.txt");
BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader(fr);
StringBuffer str=new StringBuffer();
String Line=null;
while((Line=bufr.readLine())!=null) {
str.append(Line);
}
bufr.close();
double capitalletter[]=new double[26];
double lowercaseletter[]=new double[26];
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i
char ch=str.charAt(i);
if(ch>='A'&&ch<='Z'||ch>='a'&&ch<='z') {
for(int j=0;j<26;j++) {
if(ch=='A'+j)
capitalletter[j]++;
}
for(int k=0;k<26;k++) {
if(ch=='a'+k)
lowercaseletter[k]++;
}
count++;
}
}
double percentage1[]=new double[52];
double percentage2[]=new double[52];
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
percentage1[i]=capitalletter[i]/count;
percentage2[i]=percentage1[i];
}
for(int i=26;i<52;i++) {
percentage1[i]=lowercaseletter[i-26]/count;
percentage2[i]=percentage1[i];
}
Arrays.sort(percentage1);
for(int i=51;i>=0;i--) {
int max=0;
for(int j=0;j<52;j++) {
if(percentage2[j]==percentage1[i])
max=j;
}
if(max>=26)
System.out.print(((char)('a'+max-26))+":");
else
System.out.print(((char)('A'+max))+":");
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",percentage1[i]*100)+'%');
}
System.out.println("英文字母总数为:"+count);
}
}
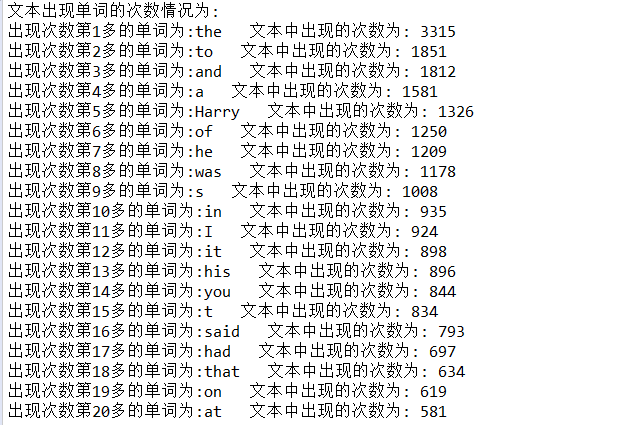
运行结果截图:

二、读取文本中的英文单词并按出现次数降序输出结果
源码:
package total;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Statistics_words {
public Map map1 = new HashMap();
public static void main(String arg[]) throws IOException {
String sz[];
Integer num[];
final int MAXNUM = 20;
sz = new String[MAXNUM + 1];
num = new Integer[MAXNUM + 1];
Statistics_words Statistics_words = new Statistics_words();
int account = 1;
// Vector ve1=new Vector();
Statistics_words.textImport();
System.out.println("文本出现单词的次数情况为:");
int g_run = 0;
for (g_run = 0; g_run < MAXNUM + 1; g_run++) {
account = 1;
for (Map.Entry it : Statistics_words.map1.entrySet()) {
if (account == 1) {
sz[g_run] = it.getKey();
num[g_run] = it.getValue();
account = 2;
}
if (account == 0) {
account = 1;
continue;
}
if (num[g_run] < it.getValue()) {
sz[g_run] = it.getKey();
num[g_run] = it.getValue();
}
// System.out.println("英文单词: "+it.getKey()+" 该英文单词出现次数: "+it.getValue());
}
Statistics_words.map1.remove(sz[g_run]);
}
int g_count = 1;
String tx1 = new String();
for (int i = 0; i < g_run; i++) {
if (sz[i] == null)
continue;
if (sz[i].equals(""))
continue;
tx1 += "出现次数第" + (g_count) + "多的单词为:" + sz[i] + "\t\t\t出现次数: " + num[i] + "\r\n";
System.out.println("出现次数第" + (g_count) + "多的单词为:" + sz[i] + "\t\t\t出现次数: " + num[i]);
g_count++;
}
Statistics_words.textExport(tx1);
}
public void textImport() throws IOException {
File a = new File("C:\\Users\\22400\\Desktop\\a.txt");
FileInputStream b = new FileInputStream(a);
InputStreamReader c = new InputStreamReader(b, "UTF-8");
String string2 = new String();
while (c.ready()) {
char string1 = (char) c.read();
if (!isWord(string1)) {
if (map1.containsKey(string2)) {
Integer num1 = map1.get(string2) + 1;
map1.put(string2, num1);
} else {
Integer num1 = 1;
map1.put(string2, num1);
}
string2 = "";
} else {
string2 += string1;
}
}
if (!string2.isEmpty()) {
if (map1.containsKey(string2)) {
Integer num1 = map1.get(string2) + 1;
map1.put(string2, num1);
} else {
Integer num1 = 1;
map1.put(string2, num1);
}
string2 = "";
}
c.close();
b.close();
}
public void textExport(String txt) throws IOException {
File fi = new File("StatisticsWord.txt");
FileOutputStream fop = new FileOutputStream(fi);
OutputStreamWriter ops = new OutputStreamWriter(fop, "UTF-8");
ops.append(txt);
ops.close();
fop.close();
}
public boolean isWord(char a) {
if (a <= 'z' && a >= 'a' || a <= 'Z' && a >= 'A')
return true;
return false;
}
}
标签:java,String,英文字母,javaIO,英文单词,run,import,new,string2
来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/weixiao1717/p/12151740.html
这篇关于JAVA读取文件单词出现次数_用javaIO流读取文本中英文字母和英文单词的出现次数及频率...的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






