本文主要是介绍rsync与 Inotify概述,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、rsync服务器
1、Rsync 介绍
① rsync是一款开源的、快速的、多功能的、可实现全量及增量的本地或远程数据同步备份的优秀工具。并且可以不进行
改变原有数据的属性信息,实现数据的备份迁移特性。
② rsync软件适用于unix/linux/windows等多种操作系统平台
③ rsync是一个快速和非常方便的文件复制工具。它能本地复制,远程复制,或者远程守护进程方式复制,它提供了大量的
参数来控制其行为的各个方面,并且允许非常灵活的方式来实现文件的传输复制
④ 以其delta-transfer算法闻名。
⑤ rsync监听端口:873
⑥ rsync运行模式:C/S
2、同步方式
① 全量备份:
② 原有的数据全部传送
③ 把原来的文件和新的文件一起统一传送
④ 全量复制,效率低
3、增量备份
在传输数据之前通过一些算法通过你有的数据和我有的数据进行对比,把不一样的数据通过网络传输
增量复制,效率高
4、rsync命令
rsync [选项] 原始位置 目标位置
常用选项 说明
-r 递归模式,包含目录及子目录中的所有文件
-l 对于符号链接文件仍然复制为符号链接文件
-v 显示同步过程的详细信息
-z 在传输文件时进行压缩goD
-p 保留文件的权限标记
-a 归档模式,递归并保留对象属性,等同于-rlpt
-t 保留文件的时间标记
-g 保留文件的属组标记(仅超级用户使用)
-o 保留文件的属主标记(仅超级用户使用)
-H 保留硬链接文件
-A 保留ACL属性信息
-D 保留设备文件及其他特殊文件
–delete 删除目标位置有而原始位置没有的文件
–checksum 根据对象的校验和来决定是否跳过文件
二、操作流程(非本人混乱的勿看)
#rsync 本地复制
rsync -avz /abc /opt
rsync -avz /abc/ /opt
区别:
[root@server01 mnt]# mkdir /abc
[root@server01 mnt]# cd /abc/
[root@server01 abc]# touch 1.txt 2.txt
[root@server01 abc]# ls
1.txt 2.txt
[root@server01 /]# rsync -avz /abc /opt/
sending incremental file list
abc/
abc/1.txt
abc/2.txt

sent 165 bytes received 58 bytes 446.00 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
[root@server01 /]# rsync -avz /abc/ /mnt/
sending incremental file list
./
1.txt
2.txt
sent 152 bytes received 57 bytes 418.00 bytes/sec
total size is 0 speedup is 0.00


5、配置源的两种表示方法
① 格式一:
用户名@主机地址::共享模块名
rsync -avz backuper@192.168.10.20::wwwroot /root
② 格式二:
rsync://用户名@主机地址/共享模块名
rsync -avz rsync://backuper@192.168.10.20/wwwroot /root
6、实验:远程复制(下行复制)
主机 IP地址
rsync 192.168.10.20 rsync源服务器
client 192.168.10.21 rsync客户端服务器
#基础环境配置
systemctl stop firewalld.service
setenforce 0
#配置rsync源服务器
rpm -q rsync
yum -y install rsync
#修改/etc/rsyncd.conf配置文件
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf #添加以下配置
uid = nobody #root
gid = nobody #root
use chroot = yes #禁锢在源目录
address = 192.168.226.128 #监听地址
port 873 #监听端口 tcp/udp 873,可通过 cat /etc/services | grep rsync 查看
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #日志文件位置
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid #存放进程ID的文件位置
hosts allow = 192.168.226.0/24 #允许访问的客户机地址 (上行同步中的访问策略)
[wwwroot] ##第一个共享模块
path = /var/www/html #源目录的实际路径
comment = Document Root of www.ljm.com
read only = yes #是否为只读
dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z #同步时不再压缩的文件类型
auth users = backuper #授权账户,多个账号以空格分隔
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db #存放账户信息的数据文件
uid = nobody
gid = nobody
use chroot = yes
address = 192.168.226.128
port 873
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
hosts allow = 192.168.226.0/24
[wwwroot]
path = /var/www/html
comment = Document Root of www.ljm.com
read only = yes
dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z
auth users = backuper
secrets file = /etc/user.db

#如采用匿名的方式,只要将其中的 “auth users” 和 “secrets file”配置项去掉即可
#为备份账户创建数据文件
vim /etc/user.db
backuper:abc123 #无需建立同名系统用户
chmod 600 /etc/user.db

#保证所有用户对源目录 /var/www/html 都有读的权限
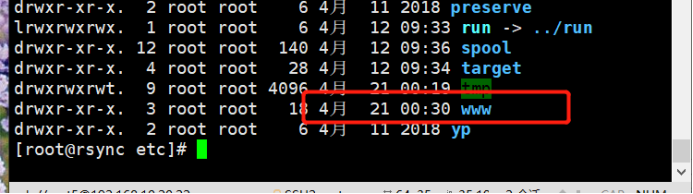
mkdir -p /var/www/html
chmod +r /var/www/html/

ls -ld /var/www/html/
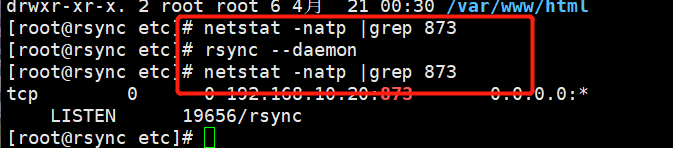
#启动 rsync 服务程序
rsync --daemon
netstat -natp | grep rsync
#关闭 rsync 服务
kill $(cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid)
rm -rf /var/run/rsyncd.pid
#rsync服务端:
cd /var/www/html
echo “hello world” >> 1.txt

#client端:
mkdir /abc
rsync -avz backuper@192.168.10.21::wwwroot /abc/


#查看同步:
cd /abc
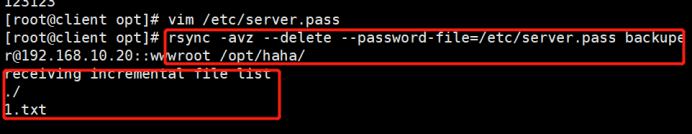
#服务端:免交互格式配置
echo “abc123” > /etc/server.pass
chmod 600 /etc/server.pass
#服务端删除1.txt
rsync -avz --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass backuper@192.168.226.128::wwwroot /abc

1、定义共享模块全局模块配置
2、共享模块(可以为多个) 可以对应不同的“源目录” 和授权账号信息
3、此配置文件是为rsync --daemon模式设置的
Inotify
1、简介
可以监控文件系统的变动情况,并做出通知响应
调整inotify内核参数(优化)
/etc/sysctl.conf(内核参数配置文件)
inotifywait: #用于持续监控,实时输出结果
inotifywatch: #用于短期监控,任务完成后再输出结果
max_queue_events #监控事件队列大小
max_user_instances #最多监控实例数
max_user_watches #每个实例最多监控文件数
2、inotifywait(持续监控并实时输出监控结果的命令)
格式:inotifywait [参数]
常见参数 说明
-m 持续进行监控
-r 递归监控所有子对象
-q 简化输出信息
-e 指定要监控哪些事件类型
3、实验:rsync+inotify
#rsync服务端:修改rsync配置文件
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
uid = root
gid = root
kill cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid
netstat -natp | grep rsync
rsync --daemon
netstat -natp | grep rsync
#服务端:inotify内核参数
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 32768 #监控时间队列,默认为16384
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024 #最多监控实例数,默认为128
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576 #每个实例最多监控文件数,默认为8192
#当要监控的目录、文件数据量较多或者变化频繁时,建议加大参数值
sysctl -p
#服务端安装 inotify-tools
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++
tar zxvf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz -C /opt
cd /opt/inotify-tools-3.14/
./configure
make && make install
#执行“inotifywait”命令,然后在服务端向 /var/www/html 目录下添加文件、移动文件,跟踪屏幕输出结果
inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,move,delete /abc
#服务端编写触发同步脚本
vim /opt/inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
INOTIFY_CMD=“inotifywait -mrq -e create,delete,move,modify,attrib /abc/”
RSYNC_CMD=“rsync -apzH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass backuper@192.168.226.129::wwwroot/ /abc/”
$INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE
do
if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 2 ] ; then
$RSYNC_CMD
fi
done
chmod +x /opt/inotify.sh
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
echo “/opt/inotify.sh” >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
cd /opt
######测试
##客户端/abc创建文件
[root@client abc]# mkdir abc
#服务端查看文件
cd /var/www/html
ls
这篇关于rsync与 Inotify概述的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








