本文主要是介绍【React系列】受控非受控组件,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本文来自#React系列教程:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/mp/appmsgalbum?__biz=Mzg5MDAzNzkwNA==&action=getalbum&album_id=1566025152667107329)
一. refs 的使用
在React的开发模式中,通常情况下不需要、也不建议直接操作DOM原生,但是某些特殊的情况,确实需要获取到DOM进行某些操作:
- 管理焦点,文本选择或媒体播放。
- 触发强制动画。
- 集成第三方 DOM 库。
1.1. 创建 ref 的方式
如何创建refs来获取对应的DOM呢?目前有三种方式:
- 方式一:传入字符串
- 使用时通过
this.refs.传入的字符串格式获取对应的元素;
- 使用时通过
- 方式二:传入一个对象
- 对象是通过
React.createRef()方式创建出来的; - 使用时获取到创建的对象其中有一个
current属性就是对应的元素;
- 对象是通过
- 方式三:传入一个函数
- 该函数会在DOM被挂载时进行回调,这个函数会传入一个 元素对象,我们可以自己保存;
- 使用时,直接拿到之前保存的元素对象即可;
代码演练:
import React, { PureComponent, createRef } from 'react'export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.titleRef = createRef();this.titleEl = null;}render() {return (<div><h2 ref="title">String Ref</h2><h2 ref={this.titleRef}>Hello Create Ref</h2><h2 ref={element => this.titleEl = element}>Callback Ref</h2><button onClick={e => this.changeText()}>改变文本</button></div>)}changeText() {this.refs.title.innerHTML = "你好啊,李银河";this.titleRef.current.innerHTML = "你好啊,李银河";this.titleEl.innerHTML = "你好啊,李银河";}
}
1.2. ref 节点的类型
ref 的值根据节点的类型而有所不同:
- 当
ref属性用于 HTML 元素时,构造函数中使用React.createRef()创建的ref接收底层 DOM 元素作为其current属性; - 当
ref属性用于自定义class组件时,ref对象接收组件的挂载实例作为其current属性; - 你不能在函数组件上使用
ref属性,因为他们没有实例;
这里我们演示一下ref引用一个class组件对象:

import React, { PureComponent, createRef } from 'react';class Counter extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {counter: 0}}render() {return (<div><h2>当前计数: {this.state.counter}</h2><button onClick={e => this.increment()}>+1</button></div>)}increment() {this.setState({counter: this.state.counter + 1})}
}export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.counterRef = createRef();}render() {return (<div><Counter ref={this.counterRef}/><button onClick={e => this.increment()}>app +1</button></div>)}increment() {this.counterRef.current.increment();}
}
函数式组件是没有实例的,所以无法通过ref获取他们的实例:
- 但是某些时候,我们可能想要获取函数式组件中的某个DOM元素;
- 这个时候我们可以通过
React.forwardRef,后面我们也会学习hooks中如何使用ref;
1.3 ref 转发
import React, { PureComponent, createRef } from 'react';function Home(props) {return (<div><h2 ref={props.ref}>Home</h2><button>按钮</button></div>)
}export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.homeTitleRef = createRef();}render() {return (<div><Home ref={this.homeTitleRef}/><button onClick={e => this.printInfo()}>打印ref</button></div>)}printInfo() {console.log(this.homeTitleRef);}
}
使用forwardRef
import React, { PureComponent, createRef, forwardRef } from 'react';const Home = forwardRef(function(props, ref) {return (<div><h2 ref={ref}>Home</h2><button>按钮</button></div>)
})export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.homeTitleRef = createRef();}render() {return (<div><Home ref={this.homeTitleRef}/><button onClick={e => this.printInfo()}>打印ref</button></div>)}printInfo() {console.log(this.homeTitleRef.current);}
}
二. 受控组件
2.1. 认识受控组件
2.1.1. 默认提交表单方式
在React中,HTML表单的处理方式和普通的DOM元素不太一样:表单元素通常会保存在一些内部的state。
比如下面的HTML表单元素:
<form><label>名字:<input type="text" name="name" /></label><input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>
- 这个处理方式是DOM默认处理HTML表单的行为,在用户点击提交时会提交到某个服务器中,并且刷新页面;
- 在React中,并没有禁止这个行为,它依然是有效的;
- 但是通常情况下会使用JavaScript函数来方便的处理表单提交,同时还可以访问用户填写的表单数据;
- 实现这种效果的标准方式是使用“受控组件”;
2.1.2. 受控组件提交表单
在 HTML 中,表单元素(如<input>、 <textarea> 和 <select>)之类的表单元素通常自己维护 state,并根据用户输入进行更新。
而在 React 中,可变状态(mutable state)通常保存在组件的 state 属性中,并且只能通过使用 setState()来更新。
- 我们将两者结合起来,使React的
state成为“唯一数据源”; - 渲染表单的 React 组件还控制着用户输入过程中表单发生的操作;
- 被 React 以这种方式控制取值的表单输入元素就叫做“受控组件”;
例如,如果我们想让前一个示例在提交时打印出名称,我们可以将表单写为受控组件:
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {username: ""}}render() {const {username} = this.state;return (<div><form onSubmit={e => this.handleSubmit(e)}><label htmlFor="username">用户名: <input type="text" id="username" onChange={e => this.handleUsernameChange(e)} value={username}/></label><input type="submit" value="提交"/></form></div>)}handleUsernameChange(event) {this.setState({username: event.target.value})}handleSubmit(event) {console.log(this.state.username);event.preventDefault();}
}
由于在表单元素上设置了 value 属性,因此显示的值将始终为 this.state.value,这使得 React 的 state 成为唯一数据源。
由于 handleUsernameChange 在每次按键时都会执行并更新 React 的 state,因此显示的值将随着用户输入而更新。
2.2. 常见表单的处理
刚才我们演示的是一个input表单的处理,这里我们再演示一下其他的情况。
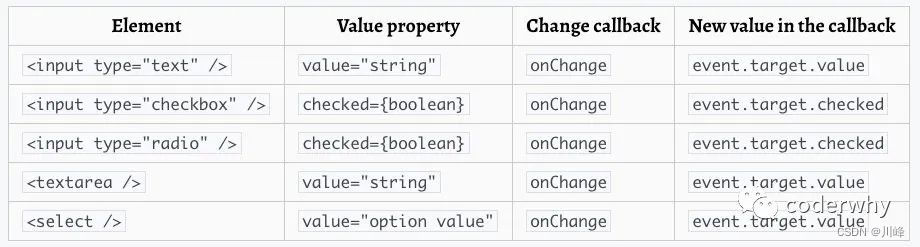
2.2.1. textarea标签
texteare标签和input比较相似:
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {article: "请编写你喜欢的文章"}}render() {return (<div><form onSubmit={e => this.handleSubmit(e)}><label htmlFor="article"><textarea id="article" cols="30" rows="10"value={this.state.article}onChange={e => this.handleArticelChange(e)}/></label><div><input type="submit" value="发布文章"/></div></form></div>)}handleArticelChange(event) {this.setState({article: event.target.value})}handleSubmit(event) {console.log(this.state.article);event.preventDefault();}
}
2.2.2. select标签
select标签的使用也非常简单,只是它不需要通过selected属性来控制哪一个被选中,它可以匹配state的value来选中。
我们来进行一个简单的演示:
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {fruits: "orange"}}render() {return (<div><form onSubmit={e => this.handleSubmit(e)}><label htmlFor="fruits"><select id="fruits" value={this.state.fruits}onChange={e => this.handleFruitsChange(e)}><option value="apple">苹果</option><option value="orange">橘子</option><option value="banana">香蕉</option></select></label><div><input type="submit" value="提交"/></div></form></div>)}handleFruitsChange(event) {this.setState({fruits: event.target.value})}handleSubmit(event) {console.log(this.state.article);event.preventDefault();}
}
2.2.3. 处理多个输入
多处理方式可以像单处理方式那样进行操作,但是需要多个监听方法:
- 这里我们可以使用ES6的一个语法:计算属性名(Computed property names)
let i = 0
let a = {['foo' + ++i]: i,['foo' + ++i]: i,['foo' + ++i]: i
}console.log(a.foo1) // 1
console.log(a.foo2) // 2
console.log(a.foo3) // 3let param = 'size'
let config = {[param]: 12,['mobile' + param.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + param.slice(1)]: 4
}console.log(config) // {size: 12, mobileSize: 4}
我们进行对应的代码演练:
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {username: "",password: ""}}render() {const {username, password} = this.state;return (<div><form onSubmit={e => this.handleSubmit(e)}><label htmlFor="username">用户: <input type="text" id="username" name="username"onChange={e => this.handleChange(e)} value={username}/></label><label htmlFor="password">密码: <input type="text" id="password" name="password"onChange={e => this.handleChange(e)} value={password}/></label><input type="submit" value="提交"/></form></div>)}handleChange(event) {this.setState({[event.target.name]: event.target.value})}handleSubmit(event) {console.log(this.state.username, this.state.password);event.preventDefault();}
}
三. 非受控组件
React推荐大多数情况下使用 受控组件 来处理表单数据:
- 一个受控组件中,表单数据是由 React 组件来管理的;
- 另一种替代方案是使用非受控组件,这时表单数据将交由 DOM 节点来处理;
如果要使用非受控组件中的数据,那么我们需要使用 ref 来从DOM节点中获取表单数据。
我们来进行一个简单的演练:
- 使用
ref来获取input元素; - 在非受控组件中通常使用
defaultValue来设置默认值;
import React, { PureComponent, createRef } from 'react'export default class App extends PureComponent {constructor(props) {super(props);this.usernameRef = createRef();}render() {return (<div><form onSubmit={e => this.handleSubmit(e)}><label htmlFor="">用户:<input defaultValue="username" type="text" name="username" ref={this.usernameRef}/></label><input type="submit" value="提交"/></form></div>)}handleSubmit(event) {event.preventDefault();console.log(this.usernameRef.current.value);}
}
同样,<input type="checkbox"> 和 <input type="radio"> 支持 defaultChecked,<select> 和 <textarea> 支持 defaultValue。
这篇关于【React系列】受控非受控组件的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








