本文主要是介绍多任务并行处理相关面试题,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
我自己面试时被问过两次多任务并行相关的问题:
假设现在有10个任务,要求同时处理,并且必须所有任务全部完成才返回结果
这个面试题的难点是:
- 既然要同时处理,那么肯定要用多线程。怎么设计多线程同时处理任务呢?
- 要求返回结果,那么就不能用简单的Thread+Runnable了,这个是无返回结果的
- 最难的是,这些任务彼此间还有关系:任务全部结束才算完成
下面3个Demo,CountDownLatch的结果处理交给大家自行完成。
FutureTask
/*** @author mx*/
public class FutureTaskDemo {private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 准备10个线程ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);// 收集每个任务的结果List<Future<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 并行处理10个任务for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {// 准备任务Callable<Integer> task = () -> {// 模拟任务耗时 0~4秒int seconds = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);System.out.println("task is completed! cost:" + seconds + "s left: " + count.decrementAndGet());// 模拟返回结果return 1;};// 提交任务Future<Integer> partResult = executorService.submit(task);// 收集结果resultList.add(partResult);}int result = 0;// 阻塞获取并累加结果for (Future<Integer> future : resultList) {result += future.get();}// 最终全部任务完成,总耗时取决于最耗时的任务时长System.out.println("all task is completed! result=" + result + " cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");}
}结果展示
task is completed! cost:0s left: 9
task is completed! cost:1s left: 8
task is completed! cost:1s left: 7
task is completed! cost:2s left: 6
task is completed! cost:3s left: 4
task is completed! cost:3s left: 5
task is completed! cost:3s left: 3
task is completed! cost:3s left: 1
task is completed! cost:3s left: 2
task is completed! cost:4s left: 0
all task is completed! result=10 cost: 4110ms
我原先还写过另一个复杂版本:
/*** @author mx*/
public class FutureTaskDemo {private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 准备10个线程ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);// 收集任务List<Callable<Integer>> taskList = new ArrayList<>();// 收集结果List<Future<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 先准备10个任务for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Callable<Integer> task = () -> {// 模拟任务耗时 0~4秒int seconds = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);System.out.println("task is completed! cost:" + seconds + "s left: " + count.decrementAndGet());// 模拟返回结果return 1;};// 收集任务taskList.add(task);}// 10个任务并行执行for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {// 从任务列表取出任务,丢到线程池执行Future<Integer> partResult = executorService.submit(taskList.get(i));// 收集异步结果resultList.add(partResult);}// 最终结果,用于累加int result = 0;// 是否全部结束,否则一直循环等待while (notFinished(resultList)) {// wait for all task to be completed...}// 主线程执行到这,肯定全部任务已经结束,所以get()会立即返回结果,不会再阻塞等待for (Future<Integer> future : resultList) {result += future.get();}// 最终全部任务完成,总耗时取决于最耗时的任务时长System.out.println("all task is completed! result=" + result + " cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");}/*** 是否全部完成** @param list* @return*/private static boolean notFinished(List<Future<Integer>> list) {for (Future<Integer> future : list) {if (!future.isDone()) {return true;}}return false;}
}结果展示
task is completed! cost:0s left: 9
task is completed! cost:0s left: 8
task is completed! cost:2s left: 7
task is completed! cost:3s left: 6
task is completed! cost:3s left: 3
task is completed! cost:3s left: 4
task is completed! cost:3s left: 5
task is completed! cost:4s left: 2
task is completed! cost:4s left: 1
task is completed! cost:4s left: 0
all task is completed! result=10 cost: 4051ms
在当前场景下,其实没必要。
有些人可能觉得第一个版本会出现以下问题:
假设总共就2个任务,但是第一个任务耗时3秒,第二个任务耗时1秒。第二个任务的1秒是建立在第一个任务的3秒后,所以总耗时就变成了4秒。
实际上并不会。当future1#get()阻塞获取第一个任务结果的过程中,第二个任务已经完成,所以future2.get()不会再阻塞,而是直接返回结果。
CountDownLatch
CountDownLatch是什么?学名叫闭锁,俗名叫门栓。
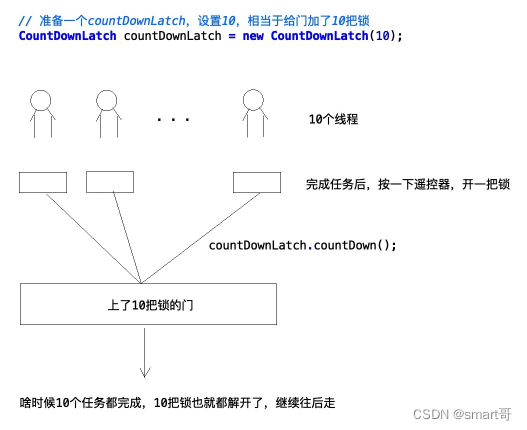
/*** @author mx*/
public class CountDownLatchDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 1.先看简单demo,了解下CountDownLatchmainThreadAndAsyncThread();// 2.尝试使用CountDownLatch解决任务并行问题(不处理结果)
// multiThreadTask();}/*** CountDownLatch简单demo** @throws InterruptedException*/private static void mainThreadAndAsyncThread() throws InterruptedException {// 准备一个countDownLatch,设置10,相当于给门加了10把锁CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 副线程去处理任务,每个任务耗时1秒,每处理完1个任务就解开一把锁new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000L);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}countDownAndPrint(countDownLatch, 1);}}).start();// 一夫当关,万夫莫开。只要门上10把锁没有全部解开,任何线程都别想想往下走countDownLatch.await();System.out.println("all task is completed! cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");}/*** CountDownLatch应用:演示10个任务并行执行,全部完成后返回结果** @throws InterruptedException*/private static void multiThreadTask() throws InterruptedException {// 准备一个countDownLatch,设置10,相当于给门加了10把锁CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 启动10个线程执行任务for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {new Thread(() -> {try {// 线程进来执行任务,随机睡0~4秒int seconds = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);// 每完成一个任务,解开一把锁countDownAndPrint(countDownLatch, seconds);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();}// 一夫当关,万夫莫开。只要门上10把锁没有全部解开,任何线程都别想想往下走countDownLatch.await();System.out.println("all task is completed! cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");}/*** countDown()并且打印,其实是不需要加synchronized的,这里只是为了多线程环境下正确打印** @param countDownLatch* @param seconds*/private static synchronized void countDownAndPrint(CountDownLatch countDownLatch, int seconds) {countDownLatch.countDown();System.out.println("task completed, cost: " + seconds + "s left: " + countDownLatch.getCount());}
}结果展示
task is completed! cost:0s left: 9
task is completed! cost:0s left: 8
task is completed! cost:0s left: 7
task is completed! cost:2s left: 6
task is completed! cost:2s left: 5
task is completed! cost:2s left: 3
task is completed! cost:2s left: 4
task is completed! cost:3s left: 2
task is completed! cost:4s left: 1
task is completed! cost:4s left: 0
all task is completed! result=10 cost: 4049ms
CompletableFuture
顺便说一句,上面的两个Demo都是闹着玩呢,实际开发别傻不拉几地自己写哈...会被打,而且是背身单打颜扣的那种。
/*** @author mx*/
public class CompletableFutureDemo {private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {// 准备10个线程ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);// 收集结果List<CompletableFuture<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 任务并行for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟任务耗时 0~4秒try {int seconds = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);System.out.println("task is completed! cost:" + seconds + "s left: " + count.decrementAndGet());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 模拟返回结果return 1;}, executorService);resultList.add(completableFuture);}// 处理结果int result = 0;for (CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture : resultList) {result += completableFuture.get();}// 最终全部任务完成,总耗时取决于最耗时的任务时长System.out.println("all task is completed! result=" + result + " cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");}
}结果展示
task is completed! cost:0s left: 9
task is completed! cost:0s left: 8
task is completed! cost:0s left: 7
task is completed! cost:0s left: 6
task is completed! cost:2s left: 5
task is completed! cost:3s left: 4
task is completed! cost:3s left: 3
task is completed! cost:3s left: 2
task is completed! cost:4s left: 1
task is completed! cost:4s left: 0
all task is completed! result=10 cost: 4051ms
实际开发案例
public class CompletableFutureDemo {private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(2);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {// 准备10个线程ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 模拟处理订单CompletableFuture<Void> dealOrder = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {// 模拟任务耗时 0~4秒try {int seconds = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);System.out.println("task is completed! cost:" + seconds + "s left: " + count.decrementAndGet());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, executorService);// 模拟处理库存CompletableFuture<Void> dealStock = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {// 模拟任务耗时 0~4秒try {int seconds = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);System.out.println("task is completed! cost:" + seconds + "s left: " + count.decrementAndGet());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, executorService);// 可变参数,可以传任意个CompletableFuture,阻塞等待所有任务完成CompletableFuture.allOf(dealOrder, dealStock).get();// 最终全部任务完成,总耗时取决于最耗时的任务时长System.out.println("all task is completed! cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");}
}结果展示
task is completed! cost:2s left: 1
task is completed! cost:3s left: 0
all task is completed! cost: 3058ms
这篇关于多任务并行处理相关面试题的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





