本文主要是介绍08.04有名管道,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1)要求AB进程做通信
-
A进程发送一句话,B进程接收打印
-
然后B进程发送给A进程一句话,A进程接收打印
-
重复1,2步骤,直到A进程或者B进程收到quit,退出AB进程;
A进程:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//管道1if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}//管道2if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");int fd = open("./myfifo",O_WRONLY); //读写if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}int fd1 = open("./fifo",O_RDONLY); //读写if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}ssize_t res = 0;char buf[128];while(1){//输入管道1printf("A-->B:");fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd,buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}if(strcasecmp(buf,"quit") == 0)break;//接收管道2bzero(buf,sizeof(buf)); res = read(fd1,buf,sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}else if(0 == res){printf("接收结束\n");break;}printf("A_get:%ld %s\n",res,buf);if(strcasecmp(buf,"quit") == 0)break;}close(fd);close(fd1);return 0;
}
B进程:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//管道1if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}//管道2if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");int fd = open("./myfifo",O_RDONLY); //读写if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}int fd1 = open("./fifo",O_WRONLY); //读写if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}ssize_t res = 0;char buf[128];while(1){//接收管道1bzero(buf,sizeof(buf)); res = read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return -1;}else if(0 == res){printf("接收结束\n");break;}printf("B get:%ld %s\n",res,buf);if(strcasecmp(buf,"quit") == 0)break;//写入管道2printf("B-->A:");fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd1,buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return -1;}if(strcasecmp(buf,"quit") == 0)break;}close(fd);close(fd1);return 0;
}

图中1代表B进程,2代表A进程
2)在第一题的基础上实现,AB进程能够随时收发数据(附加题)
A进程:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>int fd,fd1;
ssize_t res = 0;
char buf[128];void* putB(void* arg)
{//写入管道2while(1){fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd1,buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return NULL;}}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void* getA(void* arg)
{//接收管道1while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf)); res = read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return NULL;}else if(0 == res){printf("接收结束\n");break;}printf("B get:%ld %s\n",res,buf);}pthread_exit(NULL);}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//管道1if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}//管道2if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");fd = open("./myfifo",O_RDONLY); //读写if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}fd1 = open("./fifo",O_WRONLY); //读写if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}//创建线程pthread_t tid1,tid2;if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,putB,NULL) != 0){perror("pthread_create");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,getA,NULL) != 0){perror("pthread_create");return -1;}pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);close(fd);close(fd1);return 0;
}
B进程:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>int fd,fd1;
ssize_t res = 0;
char buf[128];void* getB(void* arg)
{//接收管道2while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf)); res = read(fd1,buf,sizeof(buf));if(res < 0){perror("read");return NULL;}else if(0 == res){printf("接收结束\n");break;}printf("A_get:%ld %s\n",res,buf);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void* putA(void* arg)
{//输入管道1while(1){fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;if(write(fd,buf,sizeof(buf)) < 0){perror("write");return NULL;}}pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//管道1if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}//管道2if(mkfifo("./fifo",0664) < 0){if(errno != 17){perror("mkfifo");return -1;}}printf("mkfifo success\n");fd = open("./myfifo",O_WRONLY); //读写if(fd < 0){perror("open");return -1;}fd1 = open("./fifo",O_RDONLY); //读写if(fd1 < 0){perror("open");return -1;}//创建线程pthread_t tid1,tid2;if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,putA,NULL) != 0){perror("pthread_create");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,getB,NULL) != 0){perror("pthread_create");return -1;}pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);close(fd);close(fd1);return 0;
}

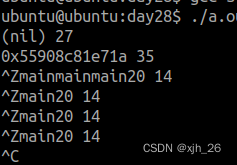
捕获2)3)20)号信号

#include<stdio.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int);void handler1(int sig)
{printf("%d %d\n",sig,__LINE__);
}void handler2(int sig)
{printf("%d %d\n",sig,__LINE__);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//捕获20号信号SIGINTsighandler_t s = signal(20,handler1);if(SIG_ERR == s){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("%p %d\n",s,__LINE__);s = signal(20,handler2);if(SIG_ERR == s){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("%p %d\n",s,__LINE__);while(1){printf("main");sleep(1);}return 0;
}
这篇关于08.04有名管道的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









