本文主要是介绍第 1 场 算法季度赛 蓝桥搜狐畅游(1~5 , 7),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、水题
2、树上dp
3、模拟
4、概率
5、拆位
6、(是没学过的东西了...)
7、组合数学
1. 新年快乐【算法赛】

直接模拟
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{cout <<"2024 AK";return 0;
}2. 蓝桥圣诞树【算法赛】

思路:其实就是连通块大小小于3。定义代表了
的子树中,包含了
这个结点的连通块的大小。 状态转移方程就呼之欲出:
,其中
是
的孩子且跟
颜色相同。在树上跑一边dfs把所有节点的
值求出来即可。然后再看有无大于3的连通块。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){a[i] = 0;}
}
struct HLD {//轻重链剖分int n;std::vector<int> siz, top, dep, parent, in, out, seq , color , dp;//子树大小 所在重链的顶部节点 深度 父亲 子树DFS序的起点 子树DFS序的终点std::vector<std::vector<int>> adj;int cur = 1;HLD() {}HLD(int n) {init(n);}void init(int n) {this->n = n;siz.resize(n);top.resize(n);dep.resize(n);parent.resize(n);in.resize(n);out.resize(n);seq.resize(n);color.resize(n);dp.resize(n);cur = 0;adj.assign(n, {});}void addEdge(int u, int v) {adj[u].push_back(v);adj[v].push_back(u);}void work(int root = 1) {top[root] = root;dep[root] = 0;parent[root] = -1;dfs1(root);dfs2(root);}void dfs1(int u) {if (parent[u] != -1) {adj[u].erase(std::find(adj[u].begin(), adj[u].end(), parent[u]));}siz[u] = 1;for (auto &v : adj[u]) {parent[v] = u;dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;dfs1(v);siz[u] += siz[v];if (siz[v] > siz[adj[u][0]]) {std::swap(v, adj[u][0]);}}}void dfs2(int u) {in[u] = ++cur;seq[in[u]] = u;dp[u] = 1;for (auto v : adj[u]) {top[v] = v == adj[u][0] ? top[u] : v;dfs2(v);if(color[u] == color[v]){dp[u] += dp[v];}}out[u] = cur;}int lca(int u, int v) {while (top[u] != top[v]) {if (dep[top[u]] > dep[top[v]]) {u = parent[top[u]];} else {v = parent[top[v]];}}return dep[u] < dep[v] ? u : v;}int dist(int u, int v) {return dep[u] + dep[v] - 2 * dep[lca(u, v)];}int jump(int u, int k) {if (dep[u] < k) {return -1;}int d = dep[u] - k;while (dep[top[u]] > d) {u = parent[top[u]];}return seq[in[u] - dep[u] + d];}bool isAncester(int u, int v) {//是否为祖先return in[u] <= in[v] && in[v] < out[u];}int rootedParent(int u, int v) {std::swap(u, v);if (u == v) {return u;}if (!isAncester(u, v)) {return parent[u];}auto it = std::upper_bound(adj[u].begin(), adj[u].end(), v, [&](int x, int y) {return in[x] < in[y];}) - 1;return *it;}int rootedSize(int u, int v) {if (u == v) {return n;}if (!isAncester(v, u)) {return siz[v];}return n - siz[rootedParent(u, v)];}int rootedLca(int a, int b, int c) {return lca(a, b) ^ lca(b, c) ^ lca(c, a);}
}hld;
void solve()
{cin >> n;string s;cin >> s;hld.init(n + 5);for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){hld.color[i] = s[i - 1] - '0';}for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){int u , v;cin >> u >> v;hld.addEdge(u , v);}hld.work();for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){if(hld.dp[i] >= 3){cout <<"NO\n";return;}}cout <<"YES\n";
}
int main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);int t=1;cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
3. 空间复杂度【算法赛】

模拟题,注意数据大小。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
vector<int>a(N , 0);
void init(int n){for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){a[i] = 0;}
}
void solve()
{cin >> n;string s;cin >> s;cin >> m;map<string , int> mp;mp["MB"] = 2;mp["KB"] = 1;mp["B"] = 0;int res = n * pow(1024 , mp[s]);cout << res / m << endl;
}
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);int t=1;cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
4. 开关【算法赛】

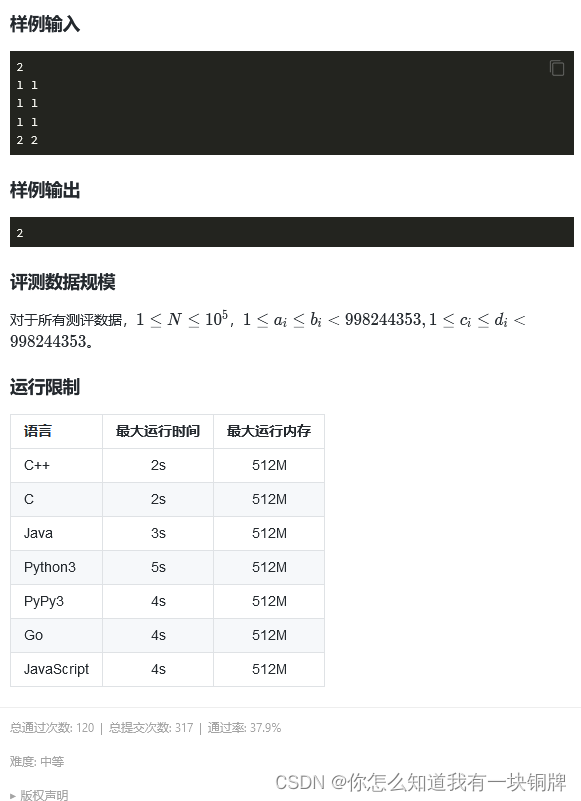
思路:先想最暴力的做法:对于处于坐标的灯而言,会被第
次操作1和第
次操作2所影响。最终该灯亮的情况共有两种:1、触发了操作1且没有触发操作2。2、没触发操作1且触发了操作2。那么它最终亮的概率是
。 对于每个灯都求一遍的话时间复杂度为
。
现考虑如何去优化,可以发现:将所有灯的概率全加起来的式子是可以合并同类项的,即。因此只需要预处理出
和
。然后再遍历所有的
即可。这样做复杂度是
的。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 998244353;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL qpow(LL a , LL b)//快速幂
{LL sum=1;while(b){if(b&1){sum=sum*a%mod;}a=a*a%mod;b>>=1;}return sum;
}
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;n++;vector<int>a(n , 0) , b(n , 0) , c(n , 0) , d(n , 0);for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){cin >> a[i];}for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){cin >> b[i];}for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){cin >> c[i];}for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){cin >> d[i];}vector<int>ab(n , 0) , cd(n , 0) ,ba(n , 0) , dc(n , 0);for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){ab[i] = a[i] * qpow(b[i] , mod - 2);cd[i] = c[i] * qpow(d[i] , mod - 2);ba[i] = (b[i] - a[i]) * qpow(b[i] , mod - 2);dc[i] = (d[i] - c[i]) * qpow(d[i] , mod - 2);ab[i] %= mod;cd[i] %= mod;ba[i] %= mod;dc[i] %= mod;}vector<int>sum1(n , 0) , sum2(n , 0);for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){sum1[i] = sum1[i - 1] + cd[i];sum2[i] = sum2[i - 1] + dc[i];sum1[i] %= mod;sum2[i] %= mod;}//对于第i行的灯而言,有两种方案使得其亮:ab && !cd !ab && cdint ans = 0;for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){ans += ab[i] * sum2[n - 1];ans %= mod;ans += ba[i] * sum1[n - 1];ans %= mod;}cout << ans;
}
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);int t = 1;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
5. 异或与求和【算法赛】

题意:某不知名高手曾经说过,对于所有情况求和,采用定1求1的思考方式,即遍历右端点,考虑如何的去处理每个右端点。
由于与
不存在关联关系,因此此题可以转化为求解
+
。
然后可以先求,再求
,过程是差不多的。
至此,本题其实跟普通的求解 差不多,只不过
这组数对在求和中不止出现了一次,而是总共出现了
所能形成的数对的个数。
然后就是普通的拆位求异或和。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 998244353;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL qpow(LL a , LL b)//快速幂
{LL sum=1;while(b){if(b&1){sum=sum*a%mod;}a=a*a%mod;b>>=1;}return sum;
}
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int dp1[32] , dp0[32];
void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int>a(n , 0);for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){cin >> a[i];}vector<int>dp(n , 0);int cnt0 = 0 , cnt1 = 0;int ans = 0;for(int j = 0 ; j < 32 ; j ++){cnt0 = 0 , cnt1 = 0;for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){if((a[i] >> j) & 1){dp[i] = cnt0; cnt1 ++;}else{dp[i] = cnt1;cnt0 ++;}dp[i] %= mod; int res = n - i - 1;res = res * (res - 1) / 2;res %= mod;ans += ((dp[i] * (1 << j)) % mod) * res;ans %= mod;}}for(int j = 0 ; j < 32 ; j ++){cnt0 = 0 , cnt1 = 0;for(int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i --){if((a[i] >> j) & 1){dp[i] = cnt0; cnt1 ++;}else{dp[i] = cnt1;cnt0 ++;}dp[i] %= mod; int res = i;res = res * (res - 1) / 2;res %= mod;ans += ((dp[i] * (1 << j)) % mod)* res;ans %= mod;}//cout << ans << endl;}
// cout << dp0[1];cout << ans;
}
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);int t = 1;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
7. 集合统计【算法赛】

思路:将有关联的(相互牵制的)数放在到一个集合。然后根据乘法原理,最终方案数为所有集合能够拿出的方案数的乘积,最后再减去空集即最终答案。
直接看例子1 3 2 , 可以发现:(1 , 2)是相互牵制的一组数(有1就不能有2,有2就不能有1)共有3种取数方案,而(3)是单独的数,这个集合共有2种取数方案。因此包含空集的方案共有3 * 2 = 6 个,再减去1就是答案5了。
然后再看(1 4 2)这个例子,可以发现(1 , 2 , 4)这三个数是相互牵制的,但是需要注意的是:1、4是可以同时取到的,因此这个集合共有5种取数方案。1 4 2 最终的答案也就是9。
接下来考虑如果一个集合当中有个数,那么能拿出多少种方案?可以发现,这就是一个简单的dp问题,设
代表了集合中共有
个元素,能够选择的非空方案数。若不能和前一个数同时选
(不选择自己 + 只选择自己)。同时又能和前一个数以外的数同时选,因此
。
解决完一个集合的方案数,接下来考虑总共有多少个集合:之间的数,其都只是一个元素的集合。同理,
之间的数,都是只有两个元素的集合...以此类推。但是需要注意的是:例如题中1 3 2 这个例子,按照上述思路,[2 , 3] 之间的数都是只有一个元素的集合,那么只有一个元素的集合数应该为2,但是事实并非如此,这是因为2这个元素实际上包含在(1,2)这个集合当中了。因此要求真正的集合数量,还需要减去重复的数。
假设一个集合元素为,那么
会出现在集合大小为2的范围内,
会出现在集合大小为1的范围内,这些都是重复的,需要减去的。因此可以得出,假设集合大小为
的集合共有
个,那么所有集合大小小于
的集合数都要减去
,这样才能避免重复。
解决完集合数量之后就是用快速幂快速求解了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 998244353;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL qpow(LL a , LL b)//快速幂
{LL sum=1;while(b){if(b&1){sum=sum*a%mod;}a=a*a%mod;b>>=1;}return sum;
}
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}LL lcm(LL a , LL b){return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int inv[200];
void init(){inv[0] = 1;for(int i = 1 ; i < 200 ; i ++){inv[i] = inv[i - 1] + 1;if(i >= 2){inv[i] += inv[i - 2];}inv[i] %= mod;}
}
void solve()
{int l , r , k;cin >> l >> r >> k;if(k == 1){cout << 0 << endl; }else{int x = r;int pre = r;vector<int>t;while(x >= l){//[x + 1 , pre] 都是处于一个集合的x /= k;t.pb(pre - max(x , l - 1));pre = x;}int len = t.size();for(int i = len - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i --){for(int j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j --){t[j] -= t[i];}}int ans = 1;for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i ++){ans *= qpow(inv[i] + 1 , t[i]);ans %= mod;}cout << (ans - 1 + mod) % mod << endl;}
}
signed main()
{ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cout.precision(10);int t = 1;init();cin >> t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
这篇关于第 1 场 算法季度赛 蓝桥搜狐畅游(1~5 , 7)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









