本文主要是介绍编写一个Java程序,其中包含三个线程: 厨师(Chef)、服务员(Waiter)和顾客(Customer),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
编写一个Java程序,其中包含三个线程: 厨师(Chef)、服务员(Waiter)和顾客(Customer)。他们的行动如下:
- 厨师准备菜肴,每次准备一个。
- 服务员等待菜肴准备好,然后将其送到顾客那里。
- 顾客等待服务员送来菜看后才开始吃。
- 所有三个角色应该循环进行他们的行为,直到指定数量的菜肴被制作和消费完。
- 使用wait()和notify0)确保线程间正确的通信和同步。
package com;/*** @program: RestaurantDemo* @description: 餐厅类* @author: Casey Hu* @create: 2023-12-18 16:13**/public class Restaurant {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Chef chef = new Chef();Waiter waiter = new Waiter(chef);Customer customer = new Customer(waiter);chef.start();waiter.start();customer.start();chef.join();waiter.join();customer.join();System.out.println("餐厅关闭.");}static class Chef extends Thread {private final int MAX_FOOD = 10;private int foodCount = 0;private boolean isFinished = false;@Overridepublic void run() {while (!isFinished) {try {// 厨师准备菜肴System.out.println("厨师准备菜肴...");Thread.sleep(1000);// 菜肴准备好后唤醒服务员foodCount++;synchronized (this) {this.notify();}if (foodCount >= MAX_FOOD) {isFinished = true;}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}static class Waiter extends Thread {private Chef chef;public Waiter(Chef chef) {this.chef = chef;}@Overridepublic void run() {while (!chef.isFinished) {try {synchronized (chef) {// 等待厨师准备菜肴chef.wait();}// 将菜肴送到顾客那里System.out.println("服务员将菜肴送到顾客那里...");Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}static class Customer extends Thread {private Waiter waiter;public Customer(Waiter waiter) {this.waiter = waiter;}@Overridepublic void run() {while (!waiter.chef.isFinished) {try {// 等待服务员送来菜肴Thread.sleep(1000);// 开始吃菜肴System.out.println("顾客开始吃菜肴...");// 通知服务员可以送下一道菜了synchronized (waiter.chef) {waiter.chef.notify();}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}上述代码中启动了三个子线程:厨师线程、服务员线程和顾客线程。厨师线程使用foodCount计数器来记录制作的菜肴数量,并使用synchronized关键字确保线程安全。每当它制作好一道菜肴后,它唤醒等待的服务员线程。
服务员线程使用synchronized和wait()方法等待厨师线程准备好菜肴。一旦收到通知,它将菜肴送到顾客那里。
顾客线程使用synchronized关键字和notify()方法通知服务员准备下一道菜肴,并在接收到菜肴后开始吃。
主线程使用join()方法等待所有子线程完成。
这个示例使用了Java中的核心多线程机制(Thread、Runnable、synchronized、wait()和notify()等)来模拟餐厅的运作。
运行结果:
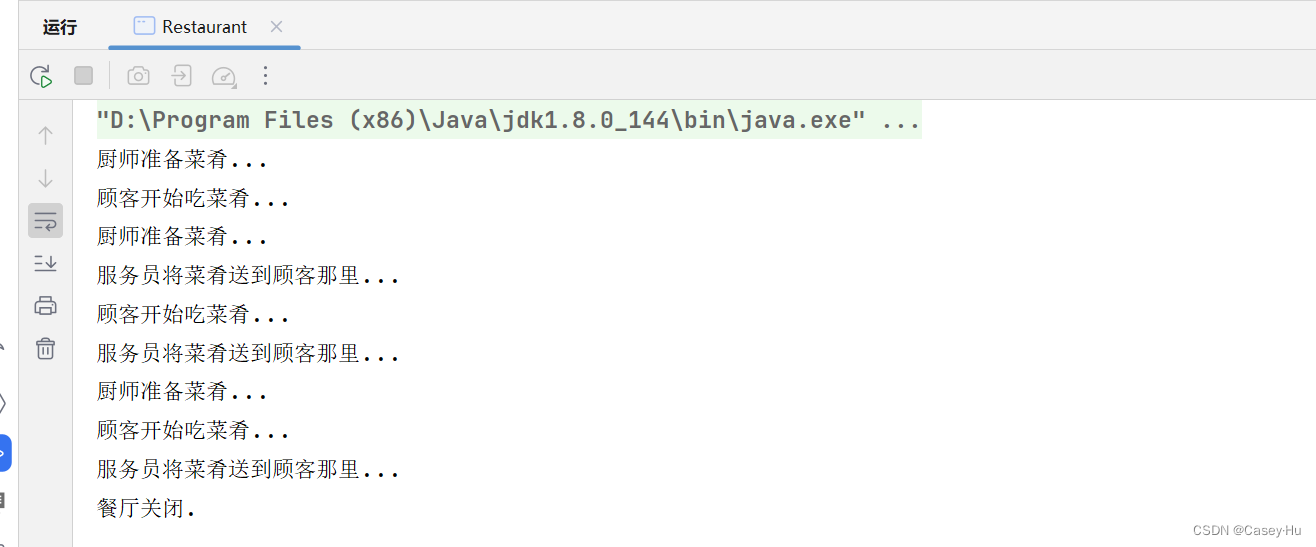
但是有一段代码
public class Restaurant {private static final int MAX_FOOD = 10;private static final Object lock = new Object();private static int foodCount = 0;public static void main(String[] args) {Chef chef = new Chef();Waiter waiter = new Waiter();Customer customer = new Customer();chef.start();waiter.start();customer.start();}static class Chef extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (lock) {while (foodCount < MAX_FOOD) {try {// 厨师准备菜肴System.out.println("厨师准备菜肴...");Thread.sleep(1000);// 菜肴准备好后唤醒服务员foodCount++;lock.notify();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}static class Waiter extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (lock) {while (foodCount < MAX_FOOD) {try {// 等待菜肴准备好lock.wait();// 将菜肴送到顾客那里System.out.println("服务员将菜肴送到顾客那里...");Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}static class Customer extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (lock) {while (foodCount < MAX_FOOD) {try {// 等待菜肴送来lock.wait();// 开始吃菜肴System.out.println("顾客开始吃菜肴...");Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
}运行结果:
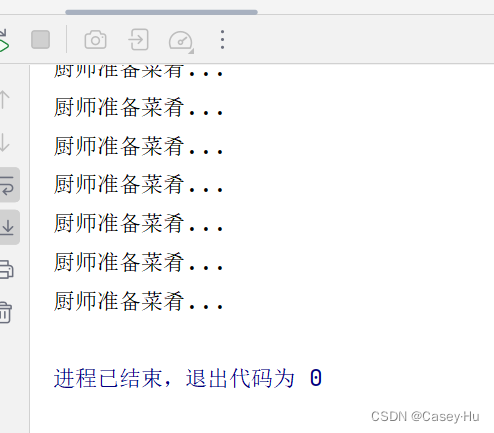
就是厨师准备好菜肴之后,main线程结束
所以才会选择子线程的方式,有大佬知道为啥会出现这样的结果吗?评论区聊聊
这篇关于编写一个Java程序,其中包含三个线程: 厨师(Chef)、服务员(Waiter)和顾客(Customer)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





