本文主要是介绍bisect_left,bisect_right,bisect的用法,区别以源码分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
bisect_left(*args, **kwargs)
向一个数组插入一个数字,返回应该插入的位置。
如果这个数字不存在于这个数组中,则返回第一个比这个数大的数的索引
如果这个数字存在,则返回数组中这个数的位置的最小值(即最左边那个索引)
案例1:这个数在数组中不存在
arr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置
index = bisect_left(arr, 5.5)print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 4 to maintain sorted order.
我们找到了第一个大于5.5的数字6的位置,输出4
案例2:这个数在数组中存在
我们修改一下代码,寻找6的位置
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_rightarr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置
index = bisect_left(arr, 6)print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 4 to maintain sorted order.
我们发现还是4
bisect_right(*args, **kwargs)
向一个数组插入一个数字,返回应该插入的位置。
作用:返回第一个比这个数大的数的索引
案例1:这个数在数组中不存在
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_rightarr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置index = bisect_right(arr, 6.5)print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
数字7的位置被输出
案例2:这个数在数组中存在
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_rightarr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置index = bisect_right(arr, 6)print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
数字7的位置被输出
对比bisect_left 和 bisect_right
相同点:
当第二个参数数字x不在第一个参数数组arr中时候,二者都会返回arr中第一个比x大的数的位置
不同点:
当arr中存在x,bisect_left会返回arr中x的最小索引,而bisect_right会返回第一个比x大的数的位置
bisect()
我们查看源码发现:
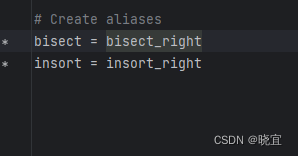
bisect就是bisect_right
完整代码
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_rightarr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置index = bisect_right(arr, 6)print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")index = bisect(arr, 6)print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")index = bisect_left(arr, 6)print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
结果:
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
Insert 6 at index 4 to maintain sorted order.
源码分析
我们先来看 bisect_right 的源码
def bisect_right(a, x, lo=0, hi=None):"""Return the index where to insert item x in list a, assuming a is sorted.The return value i is such that all e in a[:i] have e <= x, and all e ina[i:] have e > x. So if x already appears in the list, a.insert(x) willinsert just after the rightmost x already there.Optional args lo (default 0) and hi (default len(a)) bound theslice of a to be searched."""if lo < 0:raise ValueError('lo must be non-negative')if hi is None:hi = len(a)while lo < hi:mid = (lo+hi)//2# Use __lt__ to match the logic in list.sort() and in heapqif x < a[mid]: hi = midelse: lo = mid+1return lo
bisect_left 的源码
def bisect_left(a, x, lo=0, hi=None):"""Return the index where to insert item x in list a, assuming a is sorted.The return value i is such that all e in a[:i] have e < x, and all e ina[i:] have e >= x. So if x already appears in the list, a.insert(x) willinsert just before the leftmost x already there.Optional args lo (default 0) and hi (default len(a)) bound theslice of a to be searched."""if lo < 0:raise ValueError('lo must be non-negative')if hi is None:hi = len(a)while lo < hi:mid = (lo+hi)//2# Use __lt__ to match the logic in list.sort() and in heapqif a[mid] < x: lo = mid+1else: hi = midreturn lo
我们观察到这两种实现方式主要在于下面两行:
bisect_right:
if x < a[mid]: hi = midelse: lo = mid+1
bisect_left:
if a[mid] < x: lo = mid+1else: hi = mid
我们观察到,两段源码都会返回lo,即左边界,所以我们关注一下这两行代码对于左边界的影响:
在bisect_right中,只有当 x=a[mid] or x>a[mid]时,lo才会更新为mid+1,所以最终的lo只可能是第一个大于x的索引
在bisect_left中,当 a[mid] < x时,lo会更新为mid+1,此时我们想要的索引位置必然在mid右侧,所以lo可以为相同的x的第一次出现的位置;同时我们注意到当 a[mid] >= x时,hi=mid,说明当lo取到了相同的数的最左侧时,hi右端点其实会向左平移的,所以lo既可以是数组中第一个大于x的数的索引,也可以是相同的x的最左侧第一个x的索引
这篇关于bisect_left,bisect_right,bisect的用法,区别以源码分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





