本文主要是介绍【Android12】WindowManagerService架构分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Android WindowManagerService架构分析
WindowManagerService(以下简称WMS) 是Android的核心服务。WMS管理所有应用程序窗口(Window)的Create、Display、Update、Destory。
因为Android系统中只有一个WMS(运行在SystemServer进程),可以称其为全局的WMS。其主要的任务有两个:
全局的窗口管理
应用程序的显示(在屏幕上看到应用)在WMS的协助下有序、有层次的输出给底层服务,最终显示到物理屏幕上。
全局的事件管理派发
WMS为Android输入系统(InputManagerService)提供窗口相关信息,让输入事件(比如touch、homekey等等)可派发给适合的应用(窗口)。
触摸屏:主流Android设备都使用了出触控屏,支持手势触控、多指触控。
鼠标:android系统加入鼠标,通过光标触发相应动作。
硬按键:Home、back、menu等等功能按键。
WMS的客户端WindowManager
WindowManager是WMS提供给使用者的API。Manager的命名方式遵循了Android通过的Service/Client框架的命名方法,即
Service端:XXXService
客户端API:XXXManager
WindowManager封装了WMS提供的AIDL对象,主要包括:
- IWindowManager.aidl:官方注释为**“System private interface to the window manager.”**,定义了WMS服务提供的能力接口。
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/IWindowManager.aidl/*
** Copyright 2006, The Android Open Source Project
**
** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
** you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
** You may obtain a copy of the License at
**
** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
**
** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
** distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
** WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
** See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
** limitations under the License.
*/package android.view;import com.android.internal.os.IResultReceiver;
import com.android.internal.policy.IKeyguardDismissCallback;
import com.android.internal.policy.IShortcutService;import android.app.IAssistDataReceiver;
import android.content.res.CompatibilityInfo;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.GraphicBuffer;
import android.graphics.Insets;
import android.graphics.Point;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.Region;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IRemoteCallback;
import android.os.ParcelFileDescriptor;
import android.view.DisplayCutout;
import android.view.IApplicationToken;
import android.view.IAppTransitionAnimationSpecsFuture;
import android.view.ICrossWindowBlurEnabledListener;
import android.view.IDisplayWindowInsetsController;
import android.view.IDisplayWindowListener;
import android.view.IDisplayFoldListener;
import android.view.IDisplayWindowRotationController;
import android.view.IOnKeyguardExitResult;
import android.view.IPinnedTaskListener;
import android.view.IScrollCaptureResponseListener;
import android.view.RemoteAnimationAdapter;
import android.view.IRotationWatcher;
import android.view.ISystemGestureExclusionListener;
import android.view.IWallpaperVisibilityListener;
import android.view.IWindow;
import android.view.IWindowSession;
import android.view.IWindowSessionCallback;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.InputEvent;
import android.view.InsetsState;
import android.view.MagnificationSpec;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.InputChannel;
import android.view.InputDevice;
import android.view.IInputFilter;
import android.view.AppTransitionAnimationSpec;
import android.view.WindowContentFrameStats;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.view.SurfaceControl;
import android.view.displayhash.DisplayHash;
import android.view.displayhash.VerifiedDisplayHash;/*** System private interface to the window manager.** {@hide}*/
interface IWindowManager
{
// 省略
}
- IWindowSession.aidl:官方注释为“System private per-application interface to the window manager.”,同样定义WMS服务提供的能力接口。
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/IWindowSession.aidl
/* //device/java/android/android/view/IWindowSession.aidl
**
** Copyright 2006, The Android Open Source Project
**
** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
** you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
** You may obtain a copy of the License at
**
** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
**
** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
** distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
** WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
** See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
** limitations under the License.
*/package android.view;import android.content.ClipData;
import android.graphics.Point;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.Region;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.RemoteCallback;
import android.util.MergedConfiguration;
import android.view.DisplayCutout;
import android.view.InputChannel;
import android.view.IWindow;
import android.view.IWindowId;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.view.InsetsSourceControl;
import android.view.InsetsState;
import android.view.Surface;
import android.view.SurfaceControl;
import android.view.SurfaceControl.Transaction;
import android.window.ClientWindowFrames;import java.util.List;/**
* System private per-application interface to the window manager.
*
* {@hide}
*/
interface IWindowSession {
// 省略
}
WindowManager常用的方法有三个addView、removeView、updateViewLayout,分别对应添加窗口、移除窗口、更新窗口布局功能。
// 获取WindowManager对象
WindowManager mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
// 构建布局
WindowManager.LayoutParams wmParams = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
wmParams.xxx = xxx;
// 添加窗口到wms
mWindowManager.addView(xxxView,wmParams);
// 更新窗口布局
mWindowManager.updateViewLayout(xxxView, xxxWmParams)
// 从wms中移除窗口
mWindowmanager.remove(xxxView, wmParams);
Android支持多Display(多块物理屏或虚拟屏),在多Display情况下可以指定WindowManager绑定的Display,从而在指定的屏幕上显示内容。默认情况下,WindowManager绑定到DefaultDisplay。
// 获取DisplayManager对象
DisplayManager mDisplayManager;
mDisplayManager = (DisplayManager) context.getSystemService(Context.DISPLAY_SERVICE);// 获取指定DisplayID的Display,可以通过DisplayManager的getDisplays接口取得ID。
// 取得Display对象
Display display = mDisplayManager.getDisplay(displayId);
// 通过特定的Display创建Context
Context displayContext = mContext.createDisplayContext(display);
// 获取特定Display的WindowManager对象
WindowManager displayWindowManager = (WindowManager) displayContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
WMS提供的主要方法源码分析
这里针对WMS提供的主要方法,根据Android12源码进行分析。
获取WindowManager对象
在应用中可通过如下方法获取WindowManager对象。
// 获取WindowManager对象
WindowManager mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
调用context的getSystemService方法,其实现在ContextImpl.java中。
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@Override
public Object getSystemService(String name) {if (vmIncorrectContextUseEnabled()) {// Check incorrect Context usage.// 省略}return SystemServiceRegistry.getSystemService(this, name);
}
调用SystemServiceRegistry对象的getSystemService方法。name为window(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE对应的值)
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/SystemServiceRegistry.java
public static Object getSystemService(ContextImpl ctx, String name) {if (name == null) {return null;}// 从SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS(map)中取的Key为"Window"的valuefinal ServiceFetcher<?> fetcher = SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.get(name);if (fetcher == null) {if (sEnableServiceNotFoundWtf) {Slog.wtf(TAG, "Unknown manager requested: " + name);}return null;}// 调用getService方法// CachedServiceFetcher<T>对应的getServicefinal Object ret = fetcher.getService(ctx);if (sEnableServiceNotFoundWtf && ret == null) {// 省略return null;}return ret;
}/*** Override this class when the system service constructor needs a* ContextImpl and should be cached and retained by that context.*/
static abstract class CachedServiceFetcher<T> implements ServiceFetcher<T> {private final int mCacheIndex;CachedServiceFetcher() {// Note this class must be instantiated only by the static initializer of the// outer class (SystemServiceRegistry), which already does the synchronization,// so bare access to sServiceCacheSize is okay here.mCacheIndex = sServiceCacheSize++;}@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public final T getService(ContextImpl ctx) {final Object[] cache = ctx.mServiceCache;final int[] gates = ctx.mServiceInitializationStateArray;boolean interrupted = false;T ret = null;for (;;) {boolean doInitialize = false;synchronized (cache) {// Return it if we already have a cached instance.// 如果有缓存,从缓存中取出来T service = (T) cache[mCacheIndex];if (service != null) {ret = service;// 跳出循环,直接返回break; // exit the for (;;)}// If we get here, there's no cached instance.// Grr... if gate is STATE_READY, then this means we initialized the service// once but someone cleared it.// We start over from STATE_UNINITIALIZED.// Similarly, if the previous attempt returned null, we'll retry again.if (gates[mCacheIndex] == ContextImpl.STATE_READY|| gates[mCacheIndex] == ContextImpl.STATE_NOT_FOUND) {gates[mCacheIndex] = ContextImpl.STATE_UNINITIALIZED;}// It's possible for multiple threads to get here at the same time, so// use the "gate" to make sure only the first thread will call createService().// At this point, the gate must be either UNINITIALIZED or INITIALIZING.if (gates[mCacheIndex] == ContextImpl.STATE_UNINITIALIZED) {doInitialize = true;gates[mCacheIndex] = ContextImpl.STATE_INITIALIZING;}}if (doInitialize) {// Only the first thread gets here.T service = null;@ServiceInitializationState int newState = ContextImpl.STATE_NOT_FOUND;try {// This thread is the first one to get here. Instantiate the service// *without* the cache lock held.// 创建新的对象。对于Context.WINDOW_SERVICE,创建的是WindowManagerImpl// 在SystemServiceRegistry初始化时,注册了各个服务对应的代理对象,感兴趣的可自行阅读源码。service = createService(ctx);newState = ContextImpl.STATE_READY;} catch (ServiceNotFoundException e) {onServiceNotFound(e);} finally {synchronized (cache) {cache[mCacheIndex] = service;gates[mCacheIndex] = newState;cache.notifyAll();}}ret = service;break; // exit the for (;;)}// 省略}if (interrupted) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}return ret;}public abstract T createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException;
}
上面创建了WindowManagerImpl对象,这个对象实现了 WindowManager接口类,是WMS提供的客户端代理真正实现类。
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerImpl.java
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {@UnsupportedAppUsageprivate final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();@UiContext@VisibleForTestingpublic final Context mContext;private final Window mParentWindow;/*** If {@link LayoutParams#token} is {@code null} and no parent window is specified, the value* of {@link LayoutParams#token} will be overridden to {@code mDefaultToken}.*/private IBinder mDefaultToken;/*** This token will be set to {@link LayoutParams#mWindowContextToken} and used to receive* configuration changes from the server side.*/@Nullableprivate final IBinder mWindowContextToken;public WindowManagerImpl(Context context) {this(context, null /* parentWindow */, null /* clientToken */);}private WindowManagerImpl(Context context, Window parentWindow,@Nullable IBinder windowContextToken) {mContext = context;mParentWindow = parentWindow;mWindowContextToken = windowContextToken;}
}
WindowManagerImpl构造时,会调用WindowManagerGlobal单例类的getInstance方法。WindowManagerGlobal持有IWindowManager对象。所以对应一个进程来讲,默认情况下只需要一个IWindowManager对象。
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerGlobal.javaprivate static IWindowManager sWindowManagerService;// 应用启动加载Activity时就会调用这个初始化。
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static void initialize() {getWindowManagerService();
}@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static WindowManagerGlobal getInstance() {synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {if (sDefaultWindowManager == null) {sDefaultWindowManager = new WindowManagerGlobal();}return sDefaultWindowManager;}
}@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static IWindowManager getWindowManagerService() {synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {if (sWindowManagerService == null) {sWindowManagerService = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService("window"));try {if (sWindowManagerService != null) {ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(sWindowManagerService.getCurrentAnimatorScale());sUseBLASTAdapter = sWindowManagerService.useBLAST();}} catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();}}return sWindowManagerService;}
}
综上,getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)返回的实际上是WindowManagerImpl。WindowManagerImpl通过WindowManagerGlobal这个单例类获取IWindowManager。

WindowManager AddView
通过addView添加窗口到屏幕上,例如:
// 添加窗口到wms
mWindowManager.addView(xxxView,wmParams);
调用WindowManagerImpl的addView方法
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {applyTokens(params);mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplayNoVerify(), mParentWindow,mContext.getUserId());
}
直接调用WindowManagerGlobal的addView方法,在这个方法主要是创建了ViewRootImpl,更新了mViews和mRoots等变量。然后调用了ViewRootImpl的setView方法。
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,Display display, Window parentWindow, int userId) {// 省略ViewRootImpl root;View panelParentView = null;synchronized (mLock) {// 创建ViewRoot// 一个Window对应一个ViewRootroot = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);view.setLayoutParams(wparams);// mDyingViews:进程中所有要销毁的View// mViews:进程中所有View// mRoots:进程中所有ViewRootImplmViews.add(view);mRoots.add(root);mParams.add(wparams);// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing thingstry {root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId);} catch (RuntimeException e) {// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.if (index >= 0) {removeViewLocked(index, true);}throw e;}}
}
ViewRootImpl的setView方法中,通过IWindowSession调用了WMS的addToDisplayAsUser方法,向WMS添加Window。WMS收到请求后,后创建WindowState与客户端的Window 一对一对应。
/*** We have one child*/
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView,int userId) {synchronized (this) {if (mView == null) {mView = view;// 省略try {// 调用IWindowSession,向WMS添加Windowres = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mWindowAttributes,getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId,mInsetsController.getRequestedVisibility(), inputChannel, mTempInsets,mTempControls);} catch (RemoteException e) {mAdded = false;mView = null;mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);unscheduleTraversals();setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);} finally {if (restore) {attrs.restore();}}}
}

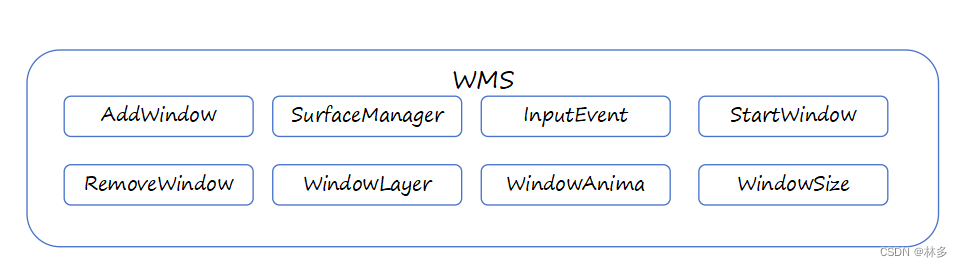
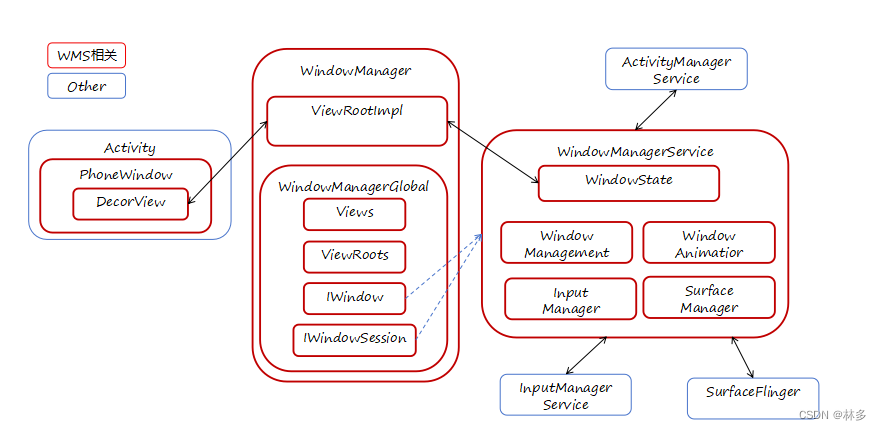
WMS架构
Window
- Window是一个窗口,很多图形系统都会有Window这个概念。比如CEGUI(天龙八部使用的UI系统)将Window作为最小的渲染单位,每个画面都是系列Window组成的二叉树。对于WMS来说,Window是最终呈现给用户的一块显示容器,是一系列View组成的一个画面。
- 实现上Window是一个抽象类,PhoneWindow是它的实现类。PhoneWindow对View进行管理。
- 一个Activity对应一个PhoneWindow,Activity启动时会创建与自身一一对应的PhoneWindow。
- Window是View的容器,View是Window的表现内容。
WindowManager
- WMS的接口类,继承ViewManager。用于给客户端管理窗口,它的实现类是WindowManagerImpl
InputManagerService
- 通过EventHub方式,从系统的输入Device节点中读取Input事件。通过WMS的协助派发给适当的应用。
SurfaceFlinger
- 分配应用程序需要的图形缓冲区,对系统整个图像窗口做Composition,最终图形窗口更新显示到Display。
WMS的主要功能:
- Surface管理:wms会为所有窗口分配Surface(通过surfaceFlinger创建Surface)。客户端向WMS添加窗口(addView)的过程,实质上是WMS为其分配一块Surface的过程。一系列Surface通过WMS进行管理,有序排布(z-order)。所以,View是表象、Window载体、Surface是本质。
- 窗口属性管理:显示层次、size、posotion等等属性管理,这些属性经过WMS的管理后最终反馈到SurfaceFlinger中。
- 窗口动画:进场、退场动画。
- 输入中转:WMS是窗口的管理者,IMS通过EventHub输入的系统Input事件,会经由WMS转发给恰当的应用(窗口)
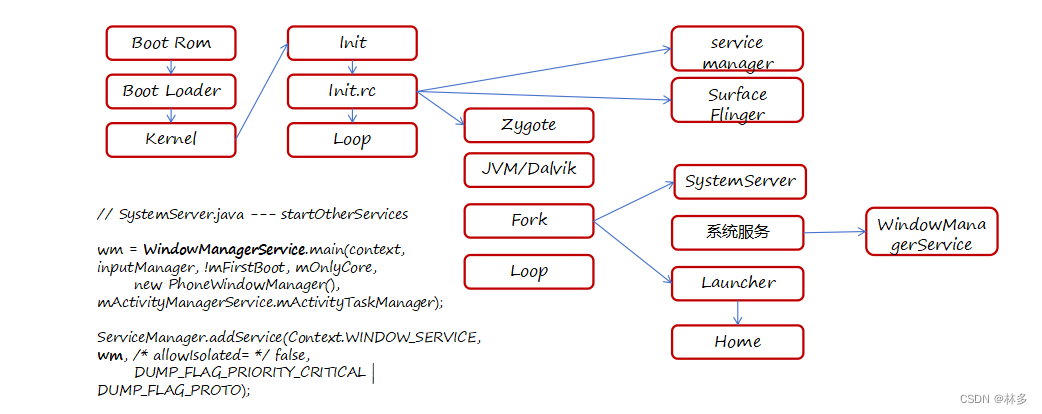
WMS的启动
WMS在SystemServer的startOtherServices阶段启动。
WMS的构造方法
WMS添加窗口
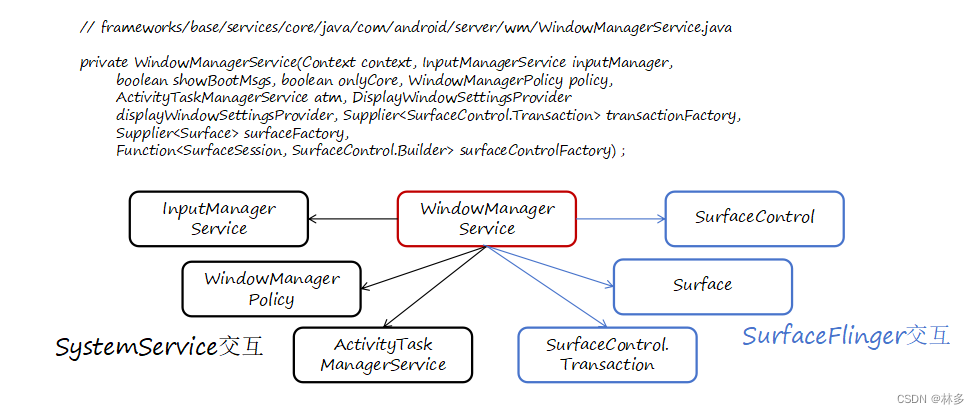
通过调用WMS的addWindow添加窗口,WMS在添加窗口过程中,主要完成了以下内容
- 登记Window:创建WindowState,WindowState与客户端的ViewRoot/View一一对应,通过WindowState对象,WMS可以通知到客户端的ViewRoot。创建完成后,将WindowState加入到WindowMap中进行管理。
- 设置DisplayContent:一个屏幕对应一个DisplayContent,将窗口与对应的DisplayContent进行绑定。
- 申请Surface画布:WMS向SurfaceFligner申请一块Window画布(在SurfaceFlinger中是一个Layer),Surface画布对应着一块内存(fb buffer),Surface画面申请成功后View上的内容才可能显示到屏幕上。
如果View没有通过WindowManager.addView添加到WMS之前,View的onDraw是不会被调用的。View上绘制的内容与WMS无关,应用端可以会用接口直接告知SurfaceFlinger进行重绘。针对描画来讲,WMS只负责窗口的管理。
WMS与SurfaceFlinger的关系
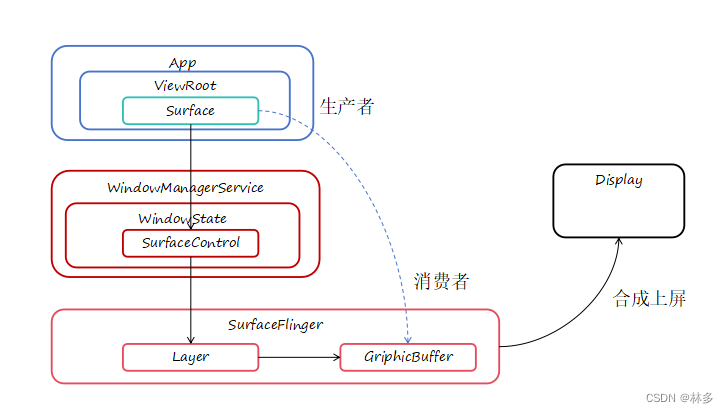
如何调试WMS
可以通过以下几种方法调试WMS
- dumpsys windows: WMS提供了dump方式,可以通过dumpsys查看wms内部状态。对比WMS的实现源码,以进行相关问题调查。
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
private void doDump(FileDescriptor fd, PrintWriter pw, String[] args, boolean useProto){
}
- 使用dumpsys window -h查看支持的命令
- WMS的LogTag:TAG_WITH_CLASS_NAME可以让WMS以统一的Tag”WindowManager”输出。其配置在WindowManagerDebugConfig.java文件中。
// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerDebugConfig.java
/*** Common class for the various debug {@link android.util.Log} output configuration in the window* manager package.*/
public class WindowManagerDebugConfig {// All output logs in the window manager package use the {@link #TAG_WM} string for tagging// their log output. This makes it easy to identify the origin of the log message when sifting// through a large amount of log output from multiple sources. However, it also makes trying// to figure-out the origin of a log message while debugging the window manager a little// painful. By setting this constant to true, log messages from the window manager package// will be tagged with their class names instead fot the generic tag.static final boolean TAG_WITH_CLASS_NAME = false;// Default log tag for the window manager package.static final String TAG_WM = "WindowManager";
}
关于WMS的扩展探讨
大多数系统上WMS都是核心模块之一,拥有良好人机交互是系统流行的基础。WMS虽然与描画系统有关联,但其应属于AppFramework范畴。
考虑WMS,其通用性设计应该包括几个方面:
- 北向:提供稳定的API接口,提供窗口管理、层次管理、动画管理、输入管理等功能。应用通过北向接口,可以申请一块用于上屏的画布。
- 南向:封装并适配底层描画系统。
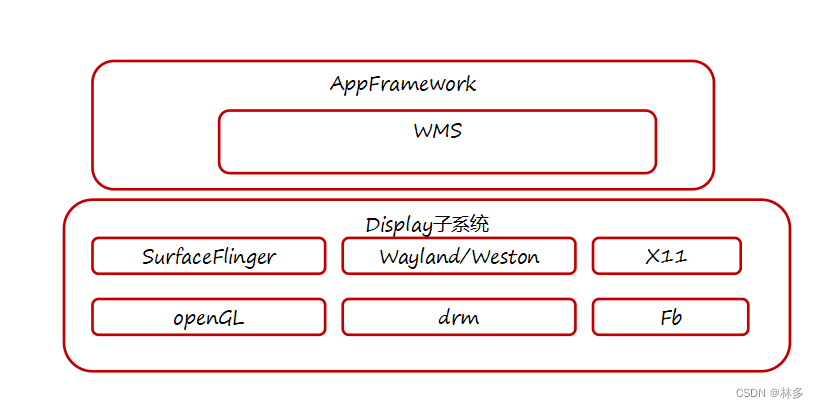
这篇关于【Android12】WindowManagerService架构分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





