本文主要是介绍Mask augmentation for segmentation,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
For instance and semantic 语义的 segmentation tasks, you need to augment both the input image and one or more output masks.
- You import the required libraries.
- You define an augmentation pipeline.
- You read images and masks from the disk.
- You pass an image and one or more masks to the augmentation pipeline and receive augmented images and masks.
Steps 1 and 2. Import the required libraries and define an augmentation pipeline.
import albumentations as A
import cv2transform = A.Compose([A.RandomCrop(width=256, height=256),A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.2),
])Step 3. Read images and masks from the disk.¶
- Reading an image
image = cv2.imread("/path/to/image.jpg")
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)- For semantic segmentation, you usually read one mask per image. Albumentations expects the mask to be a NumPy array. The height and width of the mask should have the same values as the height and width of the image.
mask = cv2.imread("/path/to/mask.png")- For instance segmentation, you sometimes need to read multiple masks per image. Then you create a list that contains all the masks.
mask_1 = cv2.imread("/path/to/mask_1.png")
mask_2 = cv2.imread("/path/to/mask_2.png")
mask_3 = cv2.imread("/path/to/mask_3.png")
masks = [mask_1, mask_2, mask_3]Step 4. Pass image and masks to the augmentation pipeline and receive augmented images and masks.¶
If the image has one associated mask, you need to call transform with two arguments: image and mask. In image you should pass the input image, in mask you should pass the output mask. transform will return a dictionary with two keys: image will contain the augmented image, and mask will contain the augmented mask.
transformed = transform(image=image, mask=mask)
transformed_image = transformed['image']
transformed_mask = transformed['mask']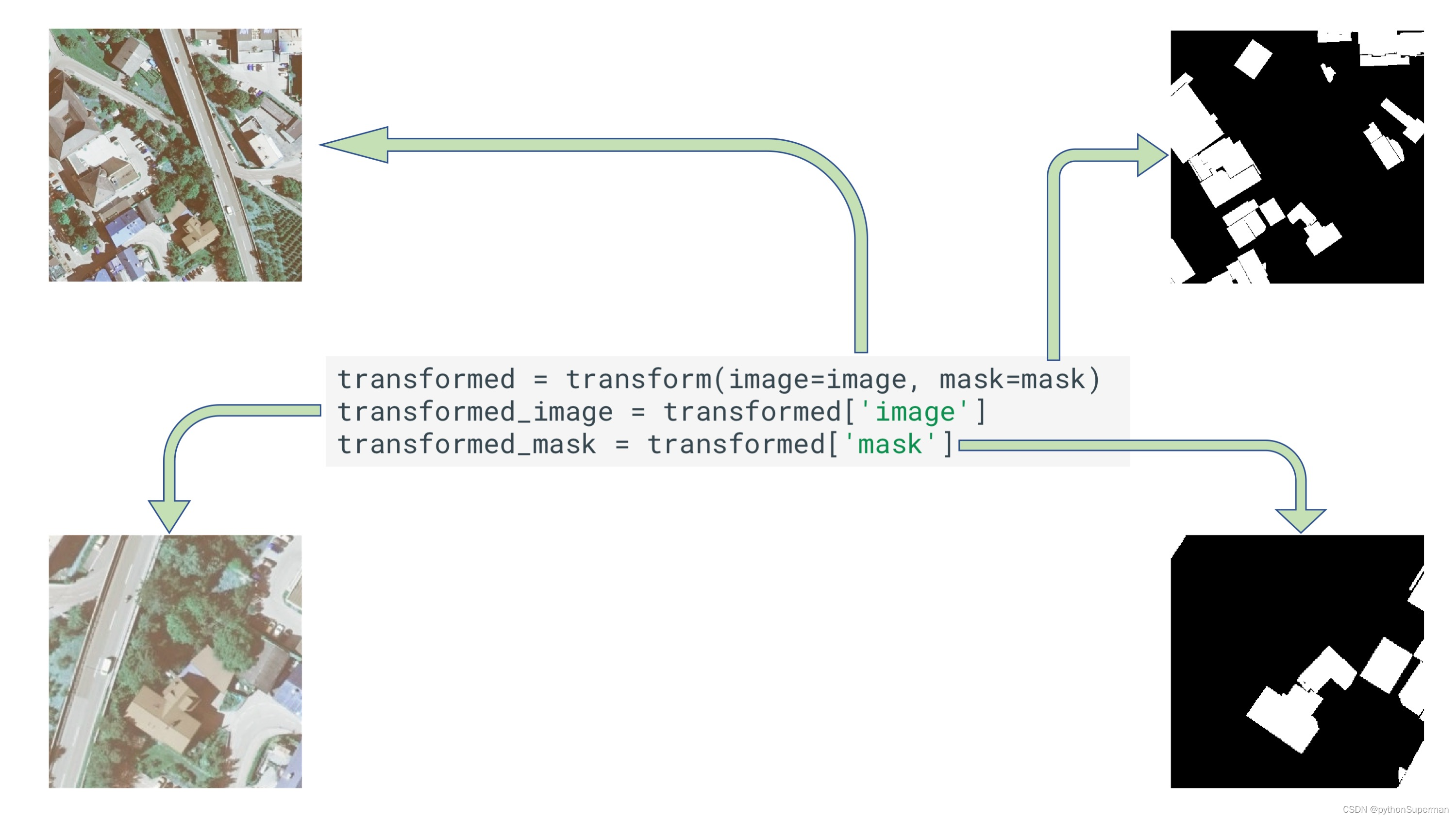
An image and a mask before and after augmentation. Inria Aerial Image Labeling dataset Inria航空图像标签数据集 contains aerial photos as well as their segmentation masks. Each pixel of the mask is marked as 1 if the pixel belongs to the class building and 0 otherwise.
If the image has multiple associated masks, you should use the masks argument instead of mask. In masks you should pass a list of masks.
transformed = transform(image=image, masks=masks)
transformed_image = transformed['image']
transformed_masks = transformed['masks']这篇关于Mask augmentation for segmentation的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







