本文主要是介绍西工大计算机学院计算机系统基础实验一(函数编写15~17),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
还是那句话,稳住心态,稳住心态,稳住心态。心里别慌,心里别慌,心里别慌。
第15题,howManyBits,返回用二进制补码形式表示x所需的最小二进制位数。比如howManyBits(12) = 5,12可以被表示为0 1100B,最高位的0为符号位,这样子一共需要5个二进制位来表示x;再比如howManyBits(298) = 10,298可以被表示为01 0010 1010B,最高位的0为符号位,这样子一共需要10个二进制位来表示x;接着比如howManyBits(-5) = 4,-5可以被表示为0xFFFF FFFB,从左到右删除掉连续的1,但最后仍还剩下一个1,即得到了1011B,最高位的1为符号位,这样子一共需要4个二进制位来表示x(1011B各位取反加一可以得到0101B也就是5);接着howManyBits(0) = 1,0可以被表示为0B,符号位为0,一共需要1个二进制位;howManyBits(-1) = 1,-1可以被表示为1B,符号位为1,一共需要1个二进制位;在这里0被当作正的0而不是负的0,就好像int型的0是0x0而不是0x8000 0000一样。最后一个例子howManyBits(0x80000000) = 32,0x8000 0000,从左到右删除掉连续的1,但最后仍还剩下一个1,结果还是0x8000 0000,最高位为符号位,这样子一共需要32个二进制位来表示x。那么我们该怎么写出这个函数呢?
为了便于思考,我们首先先分两类讨论。第一类,当x为正数时,我们可以简单的将x*2,也就是将x左移一位,然后统计x<<1中有几位,比如x=5=101B,x<<1=1010B,这时x<<1中有4位,所以用二进制补码表示x需要4位,而事实也正好是这样;第二类,当x为负数时,就不能简单的统计x<<1中的位数了,比如-5=0xFFFF FFFB,(-5)<<1之后的结果还是0xFFFF FFF6,统计其中的位数,发现还是32位,所以不能简单的统计x<<1中的位数。那么我们该如何去掉从左到右删除掉连续的1,只留下一个1呢?发现可以通过异或的方法,x^(x<<1),这样子就去掉了连续的1,只留下一个1啦!而对于正数来说,x^(x<<1)中的比特位数与x<<1一样。所以综上所述,无论x是正数还是负数,都可以只统计x^(x<<1)中的比特位数。在这里引入变量"int temp=x^(x<<1)"。
接着如何高效的统计temp中的比特位数呐?有这么一种思路,先看能不能用16位表示x,如果16位不够,那么记录下来16位不够,然后让temp=temp>>16,接着看8位够不够表示此时的temp,也就是8位够不够表示x^(x<<1)的高8位,如果能够的话,怀疑8位多了,所以记录下来8位足够,然后temp还是等于temp,接着看4位够不够表示此时的temp... ...下面结合例子来讲讲吧:
假设有一个变量x,其十六进制表示形式为0x0177 7FFF,那么temp为0x0399 8001。先看0x0399 8001可以被用16位非补码表示嘛?(因为temp=x^(x<<1)已经考虑了符号位的问题,所以这里问题只需要简简单单的考虑即可)发现不够,所以记录下来先需要16位,这样子低位的16位已经被记录下来了,把高16位拿到低16位看低16位的情况,也就是看0x0000 0399。0x0000 0399能被8位表示嘛?发现不够,所以记录下来还需要8位,这样子第16到第23位已经被记录下来了,再把8位拿到低位,即得到了0x0000 0003。0x0000 0003能被4位表示嘛?发现绰绰有余,所以记录下来不需要4位,然后不把4位拿到低位,还是0x0000 0003,它能被2位表示嘛?发现刚刚好,但是仍然记录下来不需要2位,然后不把2位拿到低位,还是0x0000 0003,他能被1位表示嘛?发现不够,所以记录下来需要1位。这时还少计算了1位,所以还要加1。
现在结合案例,我们思考该如何编写代码呢?首先如何判断能不能被16、8、4、2、1位表示呢?右移16、8、4、2、1位之后两次逻辑取非即可。那么如何记录下来需要16、8、4、2、1位呢?右移16、8、4、2、1位之后两次逻辑取非的结果,再左移4、3、2、1、0位即可。那么如何判断是否需要把temp的高位移到低位呢?让temp右移“右移16、8、4、2、1位之后两次逻辑取非的结果”即可。如果不能被16、8、4、2、1位表示,那么“右移16、8、4、2、1位之后两次逻辑取非的结果”就会是0;如果能被16、8、4、2、1位表示,那么“右移16、8、4、2、1位之后两次逻辑取非的结果”就会是1。同样也只有不能被16、8、4、2、1位表示的时候,才需要把temp的高位移到低位,此时“右移16、8、4、2、1位之后两次逻辑取非的结果”就会是1,让temp右移“右移16、8、4、2、1位之后两次逻辑取非的结果”,也正好实现了把temp的高位移到低位。代码如 图1:编写第15个函数howManyBits 所示。检查该函数的过程如 图2:检查第15个函数howManyBits 所示。
int temp = x ^ (x << 1);int bit_16,bit_8,bit_4,bit_2,bit_1;bit_16 = !!(temp >> 16) << 4;temp = temp >> bit_16;bit_8 = !!(temp >> 8) << 3;temp = temp >> bit_8;bit_4 = !!(temp >> 4) << 2;temp = temp >> bit_4;bit_2 = !!(temp >> 2) << 1;temp = temp >> bit_2;bit_1 = !!(temp >> 1);return 1 + bit_1 + bit_2 + bit_4 + bit_8 + bit_16;(图1:编写第15个函数howManyBits)

(图2:检查第15个函数howManyBits)
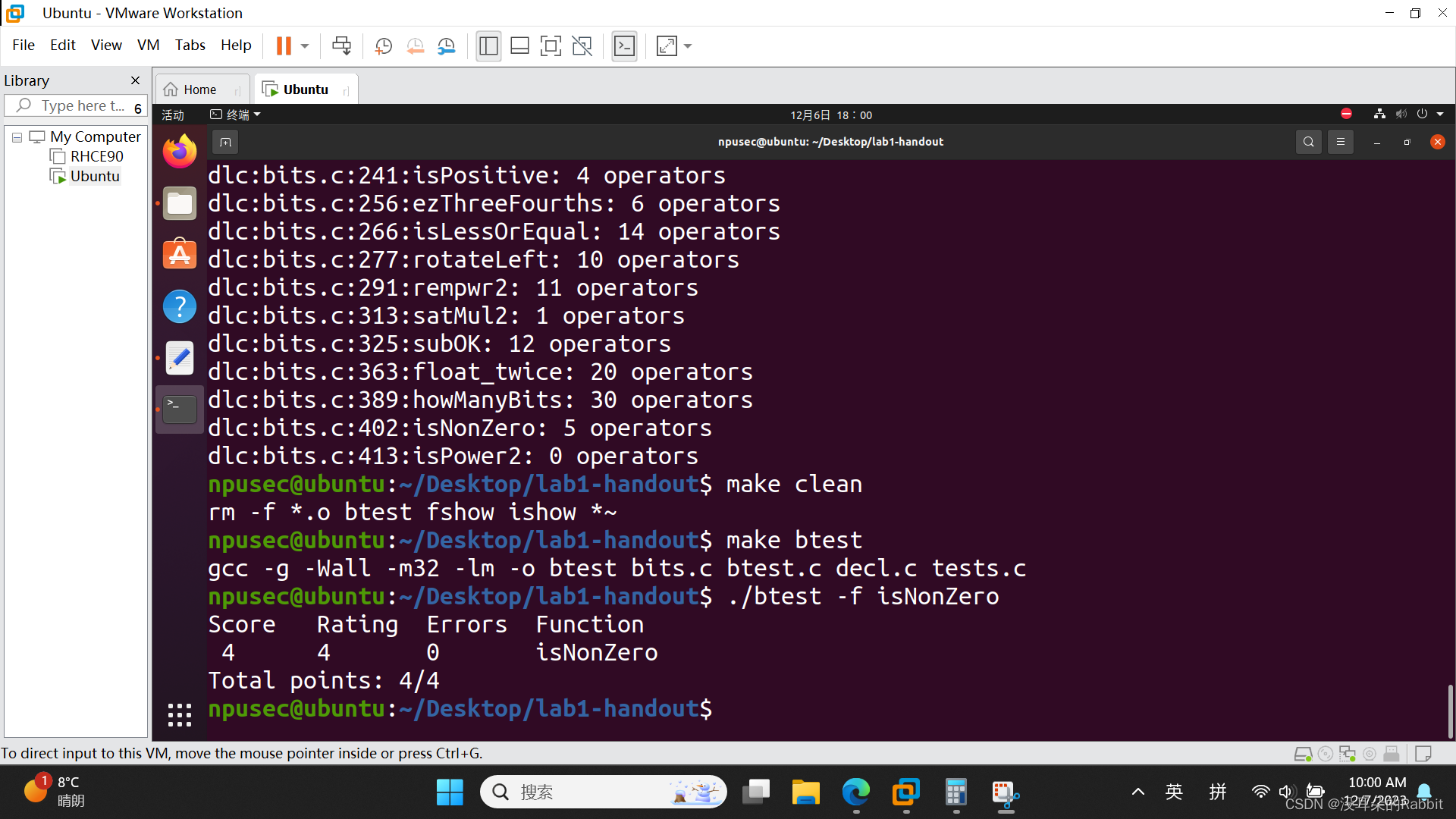
接着第16个函数,isNonZero,不使用逻辑非运算符!,检查x是否非0,比如isNonZero(3) = 1, isNonZero(0) = 0。怎么办呢?想一想发现,除了0之外,+1和-1位或的结果为0xFFFF FFFF,+2与-2位或的结果也是0xFFFF FFFF,+3与-3位或的结果也是0xFFFF FFFF... ...+2147483627与-2147483647位或的结果还是0xFFFF FFFF,甚至-2147483648与+2147483648(虽然不存在)位或的结果也还是0xFFFF FFFF,而+0与-0位或的结果却是0。利用这个性质,我们可以写出如 图3:编写第16个函数isNonZero 所示的代码。检查第16个函数的过程如 图4:检查第16个函数isNonZero 所示。
int ret = ~x + 1; ret = ret | x; return (ret >> 31) & 1;(图3:编写第16个函数isNonZero)
(图4:检查第16个函数isNonZero)
第17个函数,isPower2,判断x是不是2的1、2、3、4... ...次幂,如果是的话,返回1,否则返回0。我们该怎么做这道题呢? 注意没有负数是2的多少次幂。顺着这个思路,我们首先排除0和负数,排除0可以用!!x表示,排除负数可以用!(x>>31)表示。这时如何判断x是不是2的1、2、3、4... ...次幂呢?我们关注这些数的性质,0x0000 8000,0x0000 4000,我们发现其仅有除第一位以外的一位为1,其余位全部为0,这些数加上0xFFFF FFFF之后的结果,与这些本身位与的结果一定为0,而其它数加上0xFFFF FFFF之后再与本身位与的结果必不为0。所以我们可以利用这个性质,写出表达式!(x&(x+~0))。最终的代码如 图5:编写第17个函数isPower2 所示,检查过程如 图6:检查第17个函数isPower2 所示。
int y = x+~0;return !(x&y)&!(x>>31)&!!x;(图5:编写第17个函数isPower2)

(图6:检查第17个函数isPower2)
/* howManyBits - return the minimum number of bits required to represent x in* two's complement* Examples: howManyBits(12) = 5* howManyBits(298) = 10* howManyBits(-5) = 4* howManyBits(0) = 1* howManyBits(-1) = 1* howManyBits(0x80000000) = 32* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 90* Rating: 4*/
int howManyBits(int x) {int temp = x ^ (x << 1);int bit_16,bit_8,bit_4,bit_2,bit_1;bit_16 = !!(temp >> 16) << 4;temp = temp >> bit_16;bit_8 = !!(temp >> 8) << 3;temp = temp >> bit_8;bit_4 = !!(temp >> 4) << 2;temp = temp >> bit_4;bit_2 = !!(temp >> 2) << 1;temp = temp >> bit_2;bit_1 = !!(temp >> 1);return 1 + bit_1 + bit_2 + bit_4 + bit_8 + bit_16;
}
/* * isNonZero - Check whether x is nonzero using* the legal operators except !* Examples: isNonZero(3) = 1, isNonZero(0) = 0* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 10* Rating: 4 */
int isNonZero(int x) {int ret = ~x + 1; ret = ret | x; return (ret >> 31) & 1;
}
/** isPower2 - returns 1 if x is a power of 2, and 0 otherwise* Examples: isPower2(5) = 0, isPower2(8) = 1, isPower2(0) = 0* Note that no negative number is a power of 2.* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 20* Rating: 4*/
int isPower2(int x) {int y = x+(~1)+1;return !(x&y) & !(x>>31) & !!x;
}最后有一份分数很高很高的代码:
/* * CS:APP Data Lab * * <Please put your name and userid here>* * bits.c - Source file with your solutions to the Lab.* This is the file you will hand in to your instructor.** WARNING: Do not include the <stdio.h> header; it confuses the dlc* compiler. You can still use printf for debugging without including* <stdio.h>, although you might get a compiler warning. In general,* it's not good practice to ignore compiler warnings, but in this* case it's OK. */#if 0
/** Instructions to Students:** STEP 1: Read the following instructions carefully.*/You will provide your solution to the Data Lab by
editing the collection of functions in this source file.INTEGER CODING RULES:Replace the "return" statement in each function with oneor more lines of C code that implements the function. Your code must conform to the following style:int Funct(arg1, arg2, ...) {/* brief description of how your implementation works */int var1 = Expr1;...int varM = ExprM;varJ = ExprJ;...varN = ExprN;return ExprR;}Each "Expr" is an expression using ONLY the following:1. Integer constants 0 through 255 (0xFF), inclusive. You arenot allowed to use big constants such as 0xffffffff.2. Function arguments and local variables (no global variables).3. Unary integer operations ! ~4. Binary integer operations & ^ | + << >>Some of the problems restrict the set of allowed operators even further.Each "Expr" may consist of multiple operators. You are not restricted toone operator per line.You are expressly forbidden to:1. Use any control constructs such as if, do, while, for, switch, etc.2. Define or use any macros.3. Define any additional functions in this file.4. Call any functions.5. Use any other operations, such as &&, ||, -, or ?:6. Use any form of casting.7. Use any data type other than int. This implies that youcannot use arrays, structs, or unions.You may assume that your machine:1. Uses 2s complement, 32-bit representations of integers.2. Performs right shifts arithmetically.3. Has unpredictable behavior when shifting an integer by morethan the word size.EXAMPLES OF ACCEPTABLE CODING STYLE:/** pow2plus1 - returns 2^x + 1, where 0 <= x <= 31*/int pow2plus1(int x) {/* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */return (1 << x) + 1;}/** pow2plus4 - returns 2^x + 4, where 0 <= x <= 31*/int pow2plus4(int x) {/* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */int result = (1 << x);result += 4;return result;}FLOATING POINT CODING RULESFor the problems that require you to implent floating-point operations,
the coding rules are less strict. You are allowed to use looping and
conditional control. You are allowed to use both ints and unsigneds.
You can use arbitrary integer and unsigned constants.You are expressly forbidden to:1. Define or use any macros.2. Define any additional functions in this file.3. Call any functions.4. Use any form of casting.5. Use any data type other than int or unsigned. This means that youcannot use arrays, structs, or unions.6. Use any floating point data types, operations, or constants.NOTES:1. Use the dlc (data lab checker) compiler (described in the handout) to check the legality of your solutions.2. Each function has a maximum number of operators (! ~ & ^ | + << >>)that you are allowed to use for your implementation of the function. The max operator count is checked by dlc. Note that '=' is not counted; you may use as many of these as you want without penalty.3. Use the btest test harness to check your functions for correctness.4. Use the BDD checker to formally verify your functions5. The maximum number of ops for each function is given in theheader comment for each function. If there are any inconsistencies between the maximum ops in the writeup and in this file, considerthis file the authoritative source./** STEP 2: Modify the following functions according the coding rules.* * IMPORTANT. TO AVOID GRADING SURPRISES:* 1. Use the dlc compiler to check that your solutions conform* to the coding rules.* 2. Use the BDD checker to formally verify that your solutions produce * the correct answers.*/#endif
/* Copyright (C) 1991-2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc.This file is part of the GNU C Library.The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/ormodify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General PublicLicense as published by the Free Software Foundation; eitherversion 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty ofMERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNULesser General Public License for more details.You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General PublicLicense along with the GNU C Library; if not, see<http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */
/* This header is separate from features.h so that the compiler caninclude it implicitly at the start of every compilation. It mustnot itself include <features.h> or any other header that includes<features.h> because the implicit include comes before any featuretest macros that may be defined in a source file before it firstexplicitly includes a system header. GCC knows the name of thisheader in order to preinclude it. */
/* glibc's intent is to support the IEC 559 math functionality, realand complex. If the GCC (4.9 and later) predefined macrosspecifying compiler intent are available, use them to determinewhether the overall intent is to support these features; otherwise,presume an older compiler has intent to support these features anddefine these macros by default. */
/* wchar_t uses Unicode 8.0.0. Version 8.0 of the Unicode Standard issynchronized with ISO/IEC 10646:2014, plus Amendment 1 (published2015-05-15). */
/* We do not support C11 <threads.h>. */
/* * bitXor - x^y using only ~ and & * Example: bitXor(4, 5) = 1* Legal ops: ~ &* Max ops: 14* Rating: 1*/
int bitXor(int x, int y) {return ~(x&y)&~(~x&~y);
}
/** isZero - returns 1 if x == 0, and 0 otherwise * Examples: isZero(5) = 0, isZero(0) = 1* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 2* Rating: 1*/
int isZero(int x) {return !x;
}
/* * thirdBits - return word with every third bit (starting from the LSB) set to 1* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 8* Rating: 1*/
int thirdBits(void) {int t=0x49+(0x49<<9);return t+(t<<18);
}
/* * anyOddBit - return 1 if any odd-numbered bit in word set to 1* Examples anyOddBit(0x5) = 0, anyOddBit(0x7) = 1* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 12* Rating: 2*/
int anyOddBit(int x) {int a=0xAA;int b=a<<8;int c=a+b;int d=c+(c<<16);return !!(x&d);
}
/* * isEqual - return 1 if x == y, and 0 otherwise * Examples: isEqual(5,5) = 1, isEqual(4,5) = 0* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 5* Rating: 2*/
int isEqual(int x, int y) {return !(x^y);
}
/* * leastBitPos - return a mask that marks the position of the* least significant 1 bit. If x == 0, return 0* Example: leastBitPos(96) = 0x20* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 6* Rating: 2 */
int leastBitPos(int x) {return ((~x)+1)&x;
}
/* * isPositive - return 1 if x > 0, return 0 otherwise * Example: isPositive(-1) = 0.* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 8* Rating: 2*/
int isPositive(int x) {return !(x>>31|!x);
}
/** ezThreeFourths - multiplies by 3/4 rounding toward 0,* Should exactly duplicate effect of C expression (x*3/4),* including overflow behavior.* Examples: ezThreeFourths(11) = 8* ezThreeFourths(-9) = -6* ezThreeFourths(1073741824) = -268435456 (overflow)* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 12* Rating: 3*/
int ezThreeFourths(int x) {int a=(x<<1)+x;return (a+((a>>31)&0x3))>>2;
}
/* * isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0 * Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5) = 1.* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 24* Rating: 3*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {return ((x + ~(((x^y)>>31)|y))>>31)&1;// return ((((((x+~y+1)&(x^~y))|(x&~y))>>0x1f))&1)|!(x^y);
}
/* * rotateLeft - Rotate x to the left by n* Can assume that 0 <= n <= 31* Examples: rotateLeft(0x87654321,4) = 0x76543218* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >> !* Max ops: 25* Rating: 3 */
int rotateLeft(int x, int n) {return (x<<n)|((x>>(32+~n+1))&(~0+(1<<n)));
}
/* * rempwr2 - Compute x%(2^n), for 0 <= n <= 30* Negative arguments should yield negative remainders* Examples: rempwr2(15,2) = 3, rempwr2(-35,3) = -3* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 20* Rating: 3*/
int rempwr2(int x, int n) {int s = x>>31;x = (x+s)^s;x &= ((~0)+(1<<n));return (x^s)+~s+1;
}
/** satMul2 - multiplies by 2, saturating to Tmin or Tmax if overflow* Examples: satMul2(0x30000000) = 0x60000000* satMul2(0x40000000) = 0x7FFFFFFF (saturate to TMax)* satMul2(0x80034000) = 0x80000000 (saturate to TMin)* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 20* Rating: 3*/
int satMul2(int x) {// int x2=x<<1;// int sx2=x2>>31;// int flag=(x^x2)>>31;// int tmin=1<<31;return x<<1;// return ((~flag&x2)+(flag&(~(!!x2)+1)&(sx2+tmin)));// int isx2zero=!x2;// int x2notzero=!isx2zero;// return ((~flag&x2)+(flag&(~(!!x2)+1)&(~x2notzero&(sx2+tmin))));// int istmin=!(x^tmin);// return ((istmin<<31)|((~istmin)&((~flag&x2)|(flag&(sx2+tmin)))));
}
/* * subOK - Determine if can compute x-y without overflow* Example: subOK(0x80000000,0x80000000) = 1,* subOK(0x80000000,0x70000000) = 0, * Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 20* Rating: 3*/
int subOK(int x, int y) {
/*int flag=x^~y;return ((flag|(~flag&(~(x^(x+~y+1)))))>>31)&1;
*/int rlt = x + (~y + 1);int mid = (x ^ y) & (x ^ rlt);return !(mid >> 31);
}
/* * float_twice - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for* floating point argument f.* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of* single-precision floating point values.* When argument is NaN, return argument* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while* Max ops: 30* Rating: 4*/
unsigned float_twice(unsigned uf) {unsigned result = uf;if ((uf & 0x7f800000) == 0) {result = ((uf & 0x007fffff) << 1) | (uf & 0x80000000);}else if((uf & 0x7f800000) != 0x7f800000) {result = uf + 0x00800000;}return result;/*
unsigned exp = (uf&0x7f800000) >> 23;//取出exp,即阶数,也可以<< 1 >> 24的方法取出unsigned sign = uf & (1<<31); //取出符号位//阶数为零if(exp==0) return uf<<1 | sign; //相当于原数乘2//阶数为255 ,即无穷大或NaNif(exp==255) return uf;//阶数正常时,乘2等价于阶数加1exp++;if(exp==255) return 0x7f800000 | sign; //溢出return exp<<23 | (uf&0x007fffff) | sign;
*//*unsigned sign = 0, enow = 0, fnow = 0;unsigned pos = 1 << 31;unsigned frule = (1 << 23) - 1;if (uf == 0) {return 0;}if (uf == pos) {return uf;}sign = uf & pos;enow = (uf >> 23) & 0xff;if (enow == 0xff) {return uf;}fnow = uf & frule;if (enow == 0) {fnow = fnow << 1;if (fnow & (1 << 23)) {fnow = fnow & frule;enow += 1;}}else{enow += 1;}return sign | (enow << 23) | fnow;*/
}
/* howManyBits - return the minimum number of bits required to represent x in* two's complement* Examples: howManyBits(12) = 5* howManyBits(298) = 10* howManyBits(-5) = 4* howManyBits(0) = 1* howManyBits(-1) = 1* howManyBits(0x80000000) = 32* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 90* Rating: 4*/
int howManyBits(int x) {int temp = x ^ (x << 1);int bit_16,bit_8,bit_4,bit_2,bit_1;bit_16 = !!(temp >> 16) << 4;temp = temp >> bit_16;bit_8 = !!(temp >> 8) << 3;temp = temp >> bit_8;bit_4 = !!(temp >> 4) << 2;temp = temp >> bit_4;bit_2 = !!(temp >> 2) << 1;temp = temp >> bit_2;bit_1 = !!(temp >> 1);return 1 + bit_1 + bit_2 + bit_4 + bit_8 + bit_16;
}
/* * isNonZero - Check whether x is nonzero using* the legal operators except !* Examples: isNonZero(3) = 1, isNonZero(0) = 0* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 10* Rating: 4 */
int isNonZero(int x) {int ret = ~x + 1; ret = ret | x; return (ret >> 31) & 1;
}
/** isPower2 - returns 1 if x is a power of 2, and 0 otherwise* Examples: isPower2(5) = 0, isPower2(8) = 1, isPower2(0) = 0* Note that no negative number is a power of 2.* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 20* Rating: 4*/
int isPower2(int x) {int y = x+~0;return !(x&y) & !(x>>31) & !!x;
}这篇关于西工大计算机学院计算机系统基础实验一(函数编写15~17)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




