本文主要是介绍回溯法解决地图填色问题,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
回溯法
最大度优先
最少可选颜色优先
向前探测
随机产生不同规模的图,分析算法效率与图规模的关系(四色)
回溯法
回溯法的基本思想是采用递归和深度优先搜索的方法,尝试在一组可能的解中搜索出符合要求的解,在搜索过程中,若发现当前所选的方案不能得到正解,就回溯到前面的某一步(即撤销上一次的选择),换一种可能性继续尝试,直到找到符合要求的解或者所有的可能性都已尝试完毕。
在地图填色中,回溯法从某一区域开始,如图4所示,尝试使用不同的颜色进行填充,然后递归地尝试填充相邻的区域,如果发现当前填充颜色与相邻区域的颜色冲突,则回溯到之前的状态重新选择一种颜色进行填充,如此往复直到所有的区域都被填充上颜色或者无解。
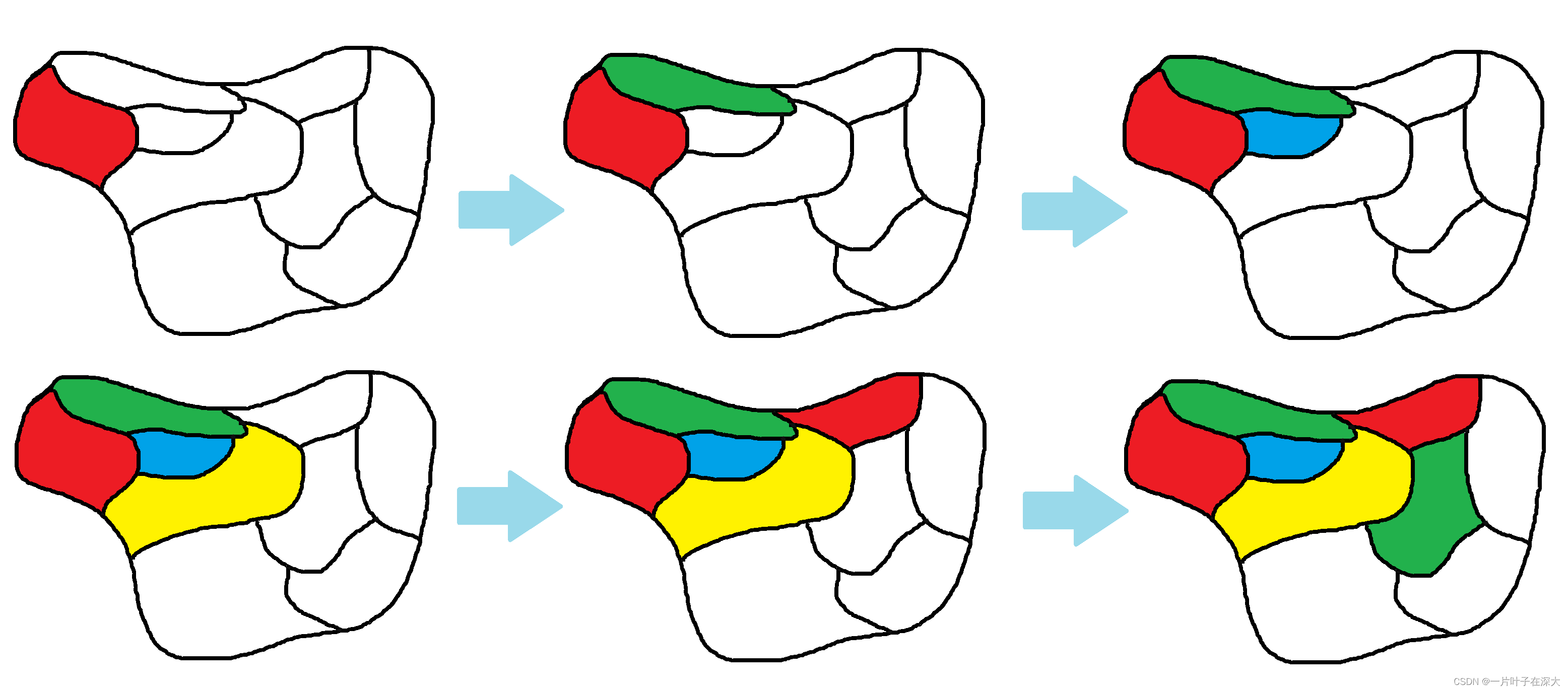
图4 回溯法地图填色示例
伪代码

C++代码
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<chrono>
#include<sstream>using namespace std;
void fillColor(const int);
int map[450][450] = {0};
int color[450] = {0};
const int colorNumber = 4;
int vertexNumber = 0;
int edgeNumber = 0;
int solution = 0;
int done=0;
fstream file("C:\\Users\\Yezi\\Desktop\\C++\\MapColoring\\Map\\le9_4.txt");
string line, word;int main() {if (!file.is_open()) {cout << "File error.\n";return 1;}getline(file, line);istringstream iss(line);iss >> word >> word >> vertexNumber >> edgeNumber;int head, tail;for (int i = 0; i < edgeNumber; i++) {getline(file, line);istringstream ISS(line);ISS >> word >> head >> tail;map[tail - 1][head - 1] = map[head - 1][tail - 1] = 1;}auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();fillColor(0);auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();auto consume = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end - start);cout << "There is " << solution << " solutions.\n" << "The time consumed is " << consume.count()<< " ms.\n";return 0;
}bool conflict(const int &vertex) {for (int i = 0; i < vertexNumber; i++) {if (map[vertex][i] && color[vertex] == color[i])return true;}return false;
}void fillColor(const int vertex) {if(done==vertexNumber){solution++;for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++)cout<<color[i]<<' ';cout<<endl;return;}for(int i=1;i<=colorNumber;i++){color[vertex]=i;if(!conflict(vertex)){done++;fillColor(vertex + 1);done--;}color[vertex]=0;}
}
运行结果
如图5所示,对于小规模地图,回溯法成功在323毫秒内找出480个解,并将每个解打印出来,验证了算法的正确性。

图5 回溯法小规模地图填色
对附件中给定的地图数据填涂;
首先还是用经典回溯法试跑一下,只找一个解的情况,如表1所示。

表1 经典回溯法大规模地图填色
由结果可以看出,当规模大时,回溯法的搜索空间会变得非常庞大,从而需要耗费大量的时间和内存资源来完成搜索过程,这将导致算法的运行时间呈指数级增长,短时间内无法求解。因此,我们需要对回溯法进行优化。
最大度优先
经典回溯法的问题在于解的空间太大,回溯次数太多,而优先选择邻边个数最多的顶点进行填色则会对剩下未填色的顶点产生更多的限制,从而减少回溯的次数,如图6所示,每次填色,我们都优先填度最大的区域。

图6 最大度优先地图填色示例
伪代码

C++代码
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<chrono>
#include<sstream>using namespace std;
struct Vertex{int degree=0;int place;
}vertex[450];
void fillColor(const int);
int map[450][450] = {0};
int color[450] = {0};
const int colorNumber = 15;
int vertexNumber = 0;
int edgeNumber = 0;
int solution = 0;
int done=0;
fstream file("C:\\Users\\Yezi\\Desktop\\C++\\MapColoring\\Map\\le450_15b.txt");
string line, word;int main() {if (!file.is_open()) {cout << "File error.\n";return 1;}getline(file, line);istringstream iss(line);iss >> word >> word >> vertexNumber >> edgeNumber;int head, tail;for (int i = 0; i < edgeNumber; i++) {getline(file, line);istringstream ISS(line);ISS >> word >> head >> tail;map[tail - 1][head - 1] = map[head - 1][tail - 1] = 1;}for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++){vertex[i].place=i;for(int j=0;j<vertexNumber;j++){vertex[i].degree+=map[i][j];}}sort(vertex,vertex+vertexNumber,[](const Vertex&a,const Vertex&b){return a.degree>b.degree;});auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();fillColor(0);auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();auto consume = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end - start);cout << "We had found " << solution << " solutions.\n" << "The time consumed is " << consume.count()<< " ms.\n";return 0;
}bool conflict(const int &vertexIndex) {for (int i = 0; i < vertexNumber; i++) {if (map[vertexIndex][i] && color[vertexIndex] == color[i])return true;}return false;
}void fillColor(const int vertexIndex) {if(done==vertexNumber){solution++;return;}for(int i=1;i<=colorNumber;i++){color[vertex[vertexIndex].place]=i;if(!conflict(vertex[vertexIndex].place)){done++;fillColor(vertexIndex + 1);if(solution>0)return;done--;}color[vertex[vertexIndex].place]=0;}
}
运行结果
先在小规模地图上验证算法的正确性,如图7所示,最大度优先可以在325毫秒内找出480个解。

图7 最大度优先小规模地图填色
然后尝试填涂三个大规模地图,只找一个解的情况,如表2所示。

表2 最大度优先大规模地图填色
由结果可知,我们的最大度优先优化策略略显成效,但是第一个和第二个地图还是无法在短时间内找到解,我们需要继续努力。
最少可选颜色优先
每次选择区域进行填色时优先选择剩余可用颜色最少的区域进行填色,这样可以减少剩余可用颜色最多的地区需要尝试不同颜色的次数,如图8所示,每填完一个区域就更新邻近区域的可选颜色,然后优先选择可选颜色最少的区域进行填色。

图8 最少可选颜色优先地图填色示例
伪代码

C++代码
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<chrono>
#include<sstream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void fillColor(const int);
int map[450][450] = {0};
int color[450] = {0};
const int colorNumber = 25;
bool colorAccess[450][colorNumber+1];
int degree[450]={0};
int colorAccessNumber[450];
int vertexNumber = 0;
int edgeNumber = 0;
int solution = 0;
int done=0;
fstream file("C:\\Users\\Yezi\\Desktop\\C++\\MapColoring\\Map\\le450_25a.txt");
string line, word;int main() {if (!file.is_open()) {cout << "File error.\n";return 1;}getline(file, line);istringstream iss(line);iss >> word >> word >> vertexNumber >> edgeNumber;int head, tail;for (int i = 0; i < edgeNumber; i++) {getline(file, line);istringstream ISS(line);ISS >> word >> head >> tail;map[tail - 1][head - 1] = map[head - 1][tail - 1] = 1;}for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++){for(int j=1;j<=colorNumber;j++)colorAccess[i][j]= true;for(int j=0;j<vertexNumber;j++)degree[i]+=map[i][j];}auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();fillColor(0);auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();auto consume = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end - start);cout << "There is " << solution << " solutions.\n" << "The time consumed is " << consume.count()<< " ms.\n";return 0;
}bool conflict(const int &vertex) {for (int i = 0; i < vertexNumber; i++) {if (map[vertex][i] && color[vertex] == color[i])return true;}return false;
}
int MRV(const int vertex,vector<int>&MRVRecover){for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++){if(map[vertex][i]){if(colorAccess[i][color[vertex]]){MRVRecover.push_back(i);colorAccess[i][color[vertex]]= false;}}}int next=0;int minColor=colorNumber;for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++){colorAccessNumber[i]=0;for(int j=1;j<=colorNumber;j++){if(colorAccess[i][j])colorAccessNumber[i]++;}if(minColor>colorAccessNumber[i]&&color[i]==0){minColor=colorAccessNumber[i];next=i;}}return next;
}
void MRV_Recover(const int vertex,vector<int>&MRVRecover){for(auto&it:MRVRecover){colorAccess[it][color[vertex]]= true;}
}
void fillColor(const int vertex) {if(done==vertexNumber){solution++;
// for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++)
// cout<<color[i]<<' ';
// cout<<endl;return;}for(int i=1;i<=colorNumber;i++){color[vertex]=i;if(!conflict(vertex)){done++;vector<int>MRVRecover;int next= MRV(vertex,MRVRecover);fillColor(next);if(solution>0)return;MRV_Recover(vertex,MRVRecover);done--;}color[vertex]=0;}
}
运行结果
先在小规模地图上验证算法的正确性,如图9所示,可以在321毫秒内找出480个解。
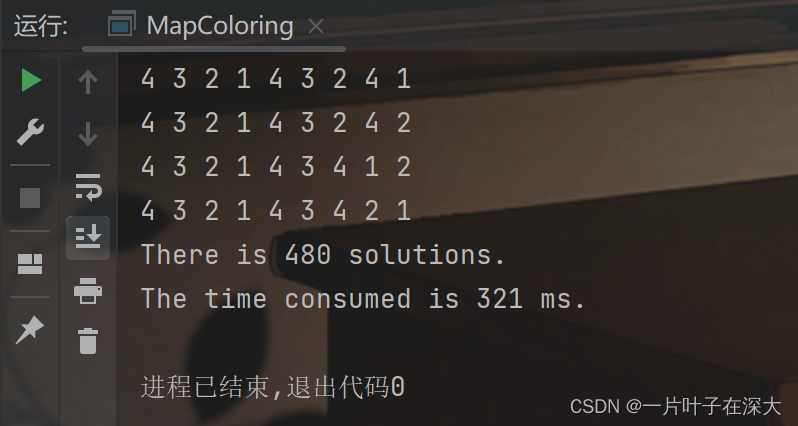
图9 最少可选颜色小规模地图填色
然后尝试填涂三个大规模地图,结果如表3所示
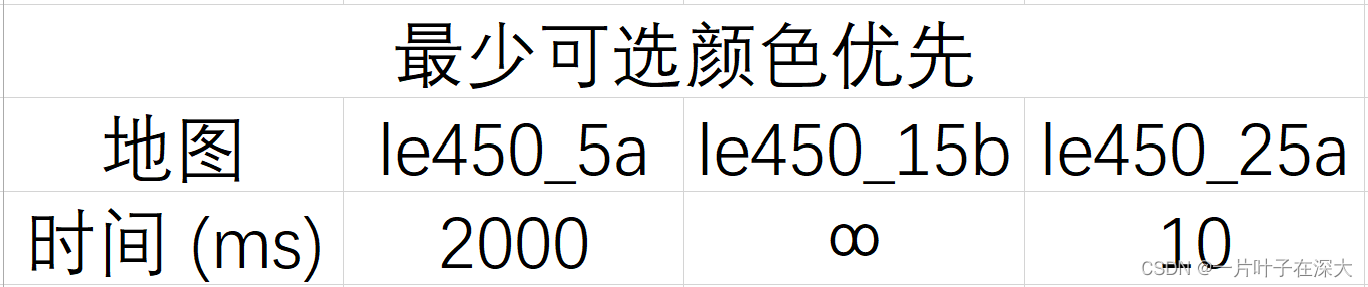
表3 最少可选颜色优先大规模地图填色
由结果可知,最少可选颜色优先的优化策略使得第一个图也可以在2秒内找到解了,通过算法的优化,原本短时间内无解的问题可以迅速解决。
然后我们尝试将最大度优先和最少可选颜色优先结合去填涂三个大规模地图,结果如表4所示。

表4 最少可选颜色+最大度地图填色
由结果可知,将最少可选颜色优先和最大度优先相结合后,三个地图均可以迅速找到解,其中第一个地图需要600毫秒,而第二个地图在3秒内终于找到了一个解。
继续测试,对第一个地图找全部解,对第二个和第三个地图找10万个解,结果如表5所示,可知该优化策略可以迅速找解。
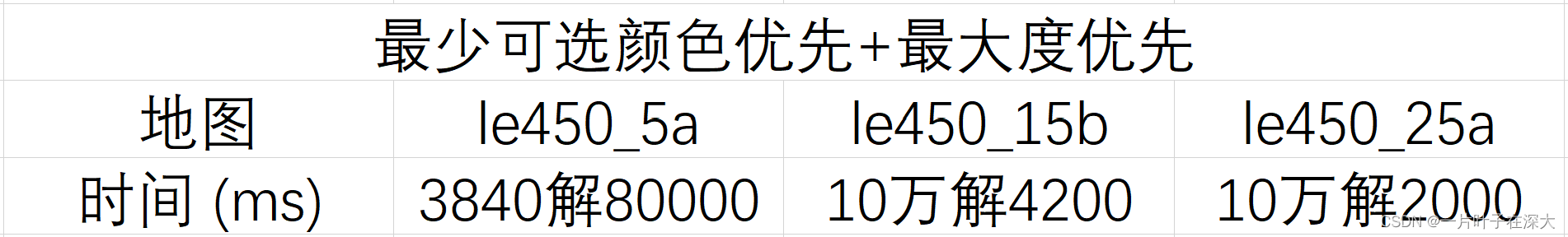
表5 最少可选颜色+最大度找多解
向前探测
每次选择区域进行填色的时候,先判断该填涂的颜色是否会导致邻近的区域无色可填,如果导致了邻近区域无色可填则直接换一种颜色填涂,如图10所示,每填一个区域就更新邻近区域的可用颜色,如果可用颜色为0则说明此处不能填这个颜色,进行剪枝。

图10 向前探测地图填色示例
伪代码

C++代码
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<chrono>
#include<sstream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void fillColor(const int);
int map[450][450] = {0};
int color[450] = {0};
const int colorNumber = 5;
bool colorAccess[450][colorNumber+1];
int colorAccessNumber[450];
int vertexNumber = 0;
int edgeNumber = 0;
int solution = 0;
int done=0;
fstream file("C:\\Users\\Yezi\\Desktop\\C++\\MapColoring\\Map\\le450_5a.txt");
string line, word;int main() {if (!file.is_open()) {cout << "File error.\n";return 1;}getline(file, line);istringstream iss(line);iss >> word >> word >> vertexNumber >> edgeNumber;int head, tail;for (int i = 0; i < edgeNumber; i++) {getline(file, line);istringstream ISS(line);ISS >> word >> head >> tail;map[tail - 1][head - 1] = map[head - 1][tail - 1] = 1;}for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++){for(int j=1;j<=colorNumber;j++)colorAccess[i][j]= true;}auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();fillColor(0);auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();auto consume = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(end - start);cout << "There is " << solution << " solutions.\n" << "The time consumed is " << consume.count()<< " ms.\n";return 0;
}bool conflict(const int &vertex) {for (int i = 0; i < vertexNumber; i++) {if (map[vertex][i] && color[vertex] == color[i])return true;}return false;
}void FC_Recover(const int vertex,vector<int>&FCRecover){for(auto&it:FCRecover){colorAccess[it][color[vertex]]= true;}
}
bool FC(const int vertex,vector<int>&FCRecover){for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++){if(map[vertex][i]){if(colorAccess[i][color[vertex]]){FCRecover.push_back(i);colorAccess[i][color[vertex]]= false;}}}for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++){colorAccessNumber[i]=0;for(int j=1;j<=colorNumber;j++){if(colorAccess[i][j])colorAccessNumber[i]++;}if(colorAccessNumber[i]==0&&color[i]==0){FC_Recover(vertex,FCRecover);return false;}}return true;
}
void fillColor(const int vertex) {if(done==vertexNumber){solution++;
// for(int i=0;i<vertexNumber;i++)
// cout<<color[i]<<' ';
// cout<<endl;return;}for(int i=1;i<=colorNumber;i++){color[vertex]=i;vector<int>FCRecover;if(!conflict(vertex)&&FC(vertex,FCRecover)){done++;fillColor(vertex+1);if(solution>0)return;done--;FC_Recover(vertex,FCRecover);}color[vertex]=0;}
}
运行结果
先在小规模地图上验证算法的正确性,如图11所示,可以在412毫秒内找出480个解。
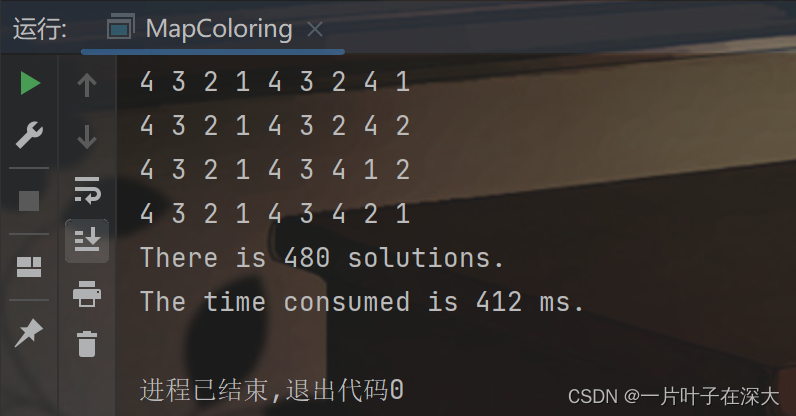
图11 向前探测小规模地图填色
然后尝试填涂三个大规模地图,结果如表6所示。

表6 向前探测大规模地图填色
由结果可知,单纯的向前探测无法在短时间内找出三个地图的解,下面我们将向前探测和最大度优先结合起来,填涂三个大规模地图,结果如表7所示。

表7 向前探测+最大度地图填色
再加上最少可选颜色优先,填涂三个大地图,结果如表8所示。

表8 向前探测+最少可选颜色+最大度地图填色
对第一个地图找全部解,对第二个和第三个地图找10万个解,结果如表9所示。
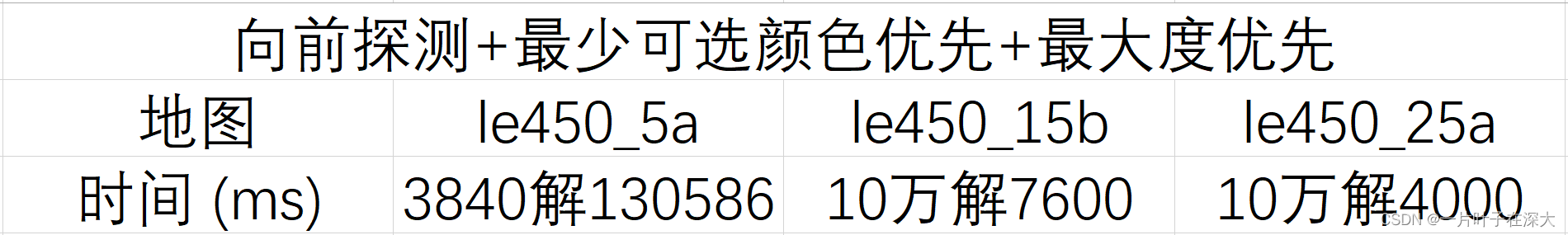
表9 向前探测+最少可选颜色+最大度找多解
由此可知,与最大度优先和最少可选颜色优先相比,向前探测的优化效果不是特别明显。
随机产生不同规模的图,分析算法效率与图规模的关系(四色)
(1)固定边
固定图的边数为1000条边,然后随机生成顶点数为100到1000的平面图,测试多组数据取众数,结果如图12所示。

图12 固定边为1000不同顶点数的地图填色
具体数据如表10所示。

表10 固定边为1000不同顶点数的地图填色
由结果可知,边数固定的情况,顶点数越多,消耗的时间和资源也更多,解的搜索空间变大,搜索时间更长。
(2)固定点
固定图的顶点数为100,随机生成边数为100到1000的平面图,测试多组数据取众数,结果如图13所示。

图13 固定点为100不同边数的地图填色
具体数据如表10所示。

表10 固定点为100不同边数的地图填色
由结果分析,算法执行的时间先是随着边数的增加而增加,这是因为解的搜索空间增加了,而后当边数达到一定程度,边密度越大,图变得更加复杂,可选的颜色减少,算法剪枝的效率更高,所以搜索效率会更高。
这篇关于回溯法解决地图填色问题的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





