本文主要是介绍2.4 AWS EC2 Pricing options,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Overview
Amazon EC2 provides the following purchasing options to enable you to optimize your costs based on your needs:
-
On-Demand Instances – Pay, by the second, for the instances that you launch.
-
Savings Plans – Reduce your Amazon EC2 costs by making a commitment to a consistent amount of usage, in USD per hour, for a term of 1 or 3 years.
-
Reserved Instances – Reduce your Amazon EC2 costs by making a commitment to a consistent instance configuration, including instance type and Region, for a term of 1 or 3 years.
-
Spot Instances – Request unused EC2 instances, which can reduce your Amazon EC2 costs significantly.
-
Dedicated Hosts – Pay for a physical host that is fully dedicated to running your instances, and bring your existing per-socket, per-core, or per-VM software licenses to reduce costs.
-
Dedicated Instances – Pay, by the hour, for instances that run on single-tenant hardware.
-
Capacity Reservations – Reserve capacity for your EC2 instances in a specific Availability Zone for any duration.
On-Demand Instances
- With On-Demand Instances, you pay for compute capacity by the second with no long-term commitments. You have full control over its lifecycle—you decide when to launch, stop, hibernate, start, reboot, or terminate it.
- On-Demand instances are recommended for:
- Users that prefer the low cost and flexibility of Amazon EC2 without any up-front payment or long-term commitment
- Applications with short-term, spiky, or unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted
- Applications being developed or tested on Amazon EC2 for the first time
Limitation
- There is a limit on the number of running On-Demand Instances per AWS account per Region. On-Demand Instance limits are managed in terms of the number of virtual central processing units (vCPUs) that your running On-Demand Instances are using, regardless of the instance type.
- You can launch any combination of instance types that meet your changing application needs, as long as the number of vCPUs does not exceed your account limit.
Reserved Instances
- Reserved Instances provide you with a significant discount (up to 75%) compared to On-Demand instance pricing.
- Reserved Instances are not physical instances, but rather a billing discount applied to the use of On-Demand Instances in your account.
- These On-Demand Instances must match certain attributes, such as instance type and Region, in order to benefit from the billing discount.
- The following diagram shows a basic overview of purchasing and using Reserved Instances.
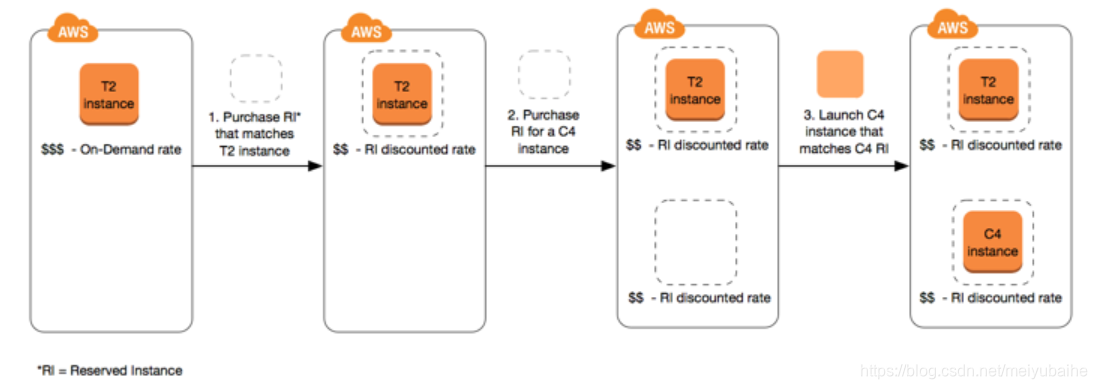
- Reserved Instances are recommended for:
- Applications with steady state usage
- Applications that may require reserved capacity
- Customers that can commit to using EC2 over a 1 or 3 year term to reduce their total computing costs
Key variables that determine Reserved Instance pricing
Instance attributes
A Reserved Instance has four instance attributes that determine its price.
-
Instance type: For example,
m4.large. This is composed of the instance family (for example,m4) and the instance size (for example,large). -
Region: The Region in which the Reserved Instance is purchased.
-
Tenancy: Whether your instance runs on shared (default) or single-tenant (dedicated) hardware.
-
Platform: The operating system; for example, Windows or Linux/Unix
Term commitment
You can purchase a Reserved Instance for a one-year or three-year commitment, with the three-year commitment offering a bigger discount.
-
One-year: A year is defined as 31536000 seconds (365 days).
-
Three-year: Three years is defined as 94608000 seconds (1095 days).
Reserved Instances do not renew automatically; when they expire, you can continue using the EC2 instance without interruption, but you are charged On-Demand rates.
Payment options
The following payment options are available for Reserved Instances:
-
All Upfront: Full payment is made at the start of the term, with no other costs or additional hourly charges incurred for the remainder of the term, regardless of hours used.
-
Partial Upfront: A portion of the cost must be paid upfront and the remaining hours in the term are billed at a discounted hourly rate, regardless of whether the Reserved Instance is being used.
-
No Upfront: You are billed a discounted hourly rate for every hour within the term, regardless of whether the Reserved Instance is being used. No upfront payment is required.
Generally speaking, you can save more money making a higher upfront payment for Reserved Instances. You can also find Reserved Instances offered by third-party sellers at lower prices and shorter term lengths on the Reserved Instance Marketplace.
Offering class
If your computing needs change, you might be able to modify or exchange your Reserved Instance, depending on the offering class.
-
Standard: These provide the most significant discount, but can only be modified. Standard Reserved Instances can't be exchanged.
-
Convertible: These provide a lower discount than Standard Reserved Instances, but can be exchanged for another Convertible Reserved Instance with different instance attributes. Convertible Reserved Instances can also be modified.
After you purchase a Reserved Instance, you cannot cancel your purchase. However, you might be able to modify, exchange, or sell your Reserved Instance if your needs change.
Regional and zonal Reserved Instances (scope)
- When you purchase a Reserved Instance, you determine the scope of the Reserved Instance. The scope is either regional or zonal.
- Regional: When you purchase a Reserved Instance for a Region, it's referred to as a regional Reserved Instance.
- A regional Reserved Instance applies a discount to a running On-Demand Instance.
- The default On-Demand Instance limit is 20.
- You cannot exceed your running On-Demand Instance limit by purchasing regional Reserved Instances.
- For example, if you already have 20 running On-Demand Instances, and you purchase 20 regional Reserved Instances, the 20 regional Reserved Instances are used to apply a discount to the 20 running On-Demand Instances. If you purchase more regional Reserved Instances, you will not be able to launch more instances because you have reached your On-Demand Instance limit.
- Before purchasing regional Reserved Instances, make sure your On-Demand Instance limit matches or exceeds the number of regional Reserved Instances you intend to own. If required, make sure you request an increase to your On-Demand Instance limit before purchasing more regional Reserved Instances.
- Zonal: When you purchase a Reserved Instance for a specific Availability Zone, it's referred to as a zonal Reserved Instance.
- provides capacity reservation as well as a discount.
- You can exceed your running On-Demand Instance limit by purchasing zonal Reserved Instances.
- For example, if you already have 20 running On-Demand Instances, and you purchase 20 zonal Reserved Instances, you can launch a further 20 On-Demand Instances that match the specifications of your zonal Reserved Instances, giving you a total of 40
- Regional: When you purchase a Reserved Instance for a Region, it's referred to as a regional Reserved Instance.
- The scope does not affect the price. You pay the same price for a regional or zonal Reserved Instance.
-
Differences between regional and zonal Reserved Instances:
-
Regional Reserved Instances Zonal Reserved Instances Ability to reserve capacity A regional Reserved Instance does not reserve capacity. A zonal Reserved Instance reserves capacity in the specified Availability Zone. Availability Zone flexibility The Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage in any Availability Zone in the specified Region. No Availability Zone flexibility—the Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage in the specified Availability Zone only. Instance size flexibility The Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage within the instance family, regardless of size. Only supported on Amazon Linux/Unix Reserved Instances with default tenancy. No instance size flexibility—the Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage for the specified instance type and size only. Queuing a purchase You can queue purchases for regional Reserved Instances.
You can't queue purchases for zonal Reserved Instances.
Types of Reserved Instances (offering classes)
The following are the differences between Standard and Convertible Reserved Instances.
| Standard Reserved Instance | Convertible Reserved Instance | |
|---|---|---|
| Modifying Reserved Instances | Some attributes can be modified | Some attributes can be modified |
| Exchanging Reserved Instances | Can't be exchanged. | Can be exchanged during the term for another Convertible Reserved Instance with new attributes, including instance family, instance type, platform, scope, or tenancy. |
| Selling in the Reserved Instance Marketplace | Can be sold in the Reserved Instance Marketplace. | Can't be sold in the Reserved Instance Marketplace. |
| Buying in the Reserved Instance Marketplace | Can be bought in the Reserved Instance Marketplace. | Can't be bought in the Reserved Instance Marketplace. |
How Reserved Instances are applied
- Zonal
- Reserved Instances assigned to a specific Availability Zone provide the Reserved Instance discount to matching instance usage in that Availability Zone.
- The attributes (tenancy, platform, Availability Zone, instance type, and instance size) of the running instances must match that of the Reserved Instances.
- Regional
- Regional Reserved Instances are purchased for a Region and provide Availability Zone flexibility.
- The Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage in any Availability Zone in that Region.
- Regional Reserved Instances also provide instance size flexibility where the Reserved Instance discount applies to instance usage within the instance family, regardless of size.
- The only attributes that must be matched are the instance family, tenancy, and platform
- Instance size flexibility is determined by the normalization factor of the instance size. The discount applies either fully or partially to running instances of the same instance family, depending on the instance size of the reservation, in any Availability Zone in the Region.
Use your Reserved Instances
If you're launching an instance to take advantage of the billing benefit of a Reserved Instance, ensure that you specify the following information during launch:
- Platform: You must choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) that matches the platform (product description) of your Reserved Instance.
- Instance type: Specify the same instance type as your Reserved Instance
- Availability Zone
- If you purchased a zonal Reserved Instance for a specific Availability Zone, you must launch the instance into the same Availability Zone.
- If you purchased a regional Reserved Instance, you can launch your instance into any Availability Zone.
- Tenancy: The tenancy of your instance must match the tenancy of the Reserved Instance
How you are billed
- With Reserved Instances, you pay for the entire term regardless of actual use.
- When Reserved Instances expire, you are charged On-Demand rates for EC2 instance usage.
Renew a Reserved Instance
- You can renew a Reserved Instance before it is scheduled to expire.
- Renewing a Reserved Instance queues the purchase of a Reserved Instance with the same configuration until the current Reserved Instance expires.
Modify Reserved Instances
- When your needs change, you can modify your Standard or Convertible Reserved Instances and continue to benefit from the billing benefit.
- You can modify all or a subset of your Reserved Instances, in one or more of the following ways:
- Switch Availability Zones within the same region.
- Change between EC2-VPC and EC2-Classic.
- Change the instance type within the same instance family (Linux instances only)
- You can separate your original Reserved Instances into two or more new Reserved Instances.
- You can also merge two or more Reserved Instances into a single Reserved Instance.
- Modification does not change the remaining term of your Reserved Instances; their end dates remain the same. There is no fee, and you do notreceive any new bills or invoices.
- The platform is Linux/UNIX.
- The original and new Reserved Instance must have the same instance size footprint.
- Each Reserved Instance has an instance size footprint, which is determined by the normalization factor of the instance size and the number of instances in the reservation.
- To calculate the instance size footprint of a Reserved Instance, multiply the number of instances by the normalization factor.
Exchange Convertible Reserved Instances
- You can exchange one or more Convertible Reserved Instances for another Convertible Reserved Instance with a different configuration, including instance family, operating system, and tenancy.
- You can't exchange Standard Reserved Instances, but you can modify them.
- Convertible Reserved Instances are associated with a specific Region, which is fixed for the duration of the reservation's term. You cannot exchange a Convertible Reserved Instance for a Convertible Reserved Instance in a different Region.
- You can exchange one or more Convertible Reserved Instances at a time for one Convertible Reserved Instance only.
- To exchange a portion of a Convertible Reserved Instance, you can modify it into two or more reservations, and then exchange one or more of the reservations for a new Convertible Reserved Instance.
- All Upfront Convertible Reserved Instances can be exchanged for Partial Upfront Convertible Reserved Instances, and vice versa.
- To benefit from better pricing, you can exchange a No Upfront Convertible Reserved Instance for an All Upfront or Partial Upfront Convertible Reserved Instance.
- You cannot exchange All Upfront and Partial Upfront Convertible Reserved Instances for No Upfront Convertible Reserved Instances.
- You can exchange a No Upfront Convertible Reserved Instance for another No Upfront Convertible Reserved Instance only if the new Convertible Reserved Instance's hourly price is the same or higher than the exchanged Convertible Reserved Instance's hourly price.
- If you exchange multiple Convertible Reserved Instances that have different expiration dates, the expiration date for the new Convertible Reserved Instance is the date that's furthest in the future.
- If you exchange a single Convertible Reserved Instance, it must have the same term (1-year or 3-years) as the new Convertible Reserved Instance. If you merge multiple Convertible Reserved Instances with different term lengths, the new Convertible Reserved Instance has a 3-year term.
- After you exchange a Convertible Reserved Instance, the original reservation is retired. Its end date is the start date of the new reservation, and the end date of the new reservation is the same as the end date of the original Convertible Reserved Instance
Spot Instances
- Amazon EC2 Spot instances allow you to request spare Amazon EC2 computing capacity for up to 90% off the On-Demand price.
- Spot instances are recommended for:
- Applications that have flexible start and end times
- Applications that are only feasible at very low compute prices
- Users with urgent computing needs for large amounts of additional capacity
- For workloads that are not time critical and are tolerant of interruption
- The instances will run until:
- The customer terminates them.
- The Spot price goes above the customer’s bid price.
- There is not enough unused capacity to meet the demand for Spot Instances.
Concepts
- Spot capacity pool – A set of unused EC2 instances with the same instance type and Availability Zone.
- Spot price – The current price of a Spot Instance per hour.
- Spot Instance request – Requests a Spot Instance. The request provides the maximum price per hour that you are willing to pay for a Spot Instance.
- EC2 instance rebalance recommendation - Amazon EC2 emits an instance rebalance recommendation signal to notify you that a Spot Instance is at an elevated risk of interruption. This signal gives you the opportunity to proactively rebalance your workloads across existing or new Spot Instances without having to wait for the two-minute Spot Instance interruption notice.
- Spot Instance interruption – Amazon EC2 terminates, stops, or hibernates your Spot Instance when capacity is no longer available or the Spot price exceeds the maximum price for your request. Amazon EC2 provides a Spot Instance interruption notice, which gives the instance a two-minute warning before it is interrupted.
Strategies for using Spot Instances
- One strategy is to maintain a minimum level of guaranteed compute resources for your applications by launching a core group of On-Demand Instances, and supplementing them with Spot Instances when the opportunity arises.
- Another strategy is to launch Spot Instances with a specified duration (also known as Spot blocks), which are designed not to be interrupted and will run continuously for the duration you select
Best practices for EC2 Spot
- Spot Instances are recommended for stateless, fault-tolerant, flexible applications.
- Prepare individual instances for interruptions: We recommend that you create a rule in Amazon EventBridge that captures the rebalance recommendations and interruption notifications, and then triggers a checkpoint for the progress of your workload or gracefully handles the interruption.
-
Be flexible about instance types and Availability Zones
- gives Spot a better chance to find and allocate your required amount of compute capacity
- A good rule of thumb is to be flexible across at least 10 instance types for each workload.
- In addition, make sure that all Availability Zones are configured for use in your VPC and selected for your workload.
- Use EC2 Auto Scaling groups or Spot Fleet to manage your aggregate capacity: Auto Scaling groups and Spot Fleet enable you to launch and maintain a target capacity, and to automatically request resources to replace any that are disrupted or manually terminated.
- Use the capacity optimized allocation strategy: Allocation strategies in Auto Scaling groups help you to provision your target capacity without the need to manually look for the Spot capacity pools with spare capacity
- Use proactive capacity rebalancing:When Capacity Rebalancing is enabled, Auto Scaling or Spot Fleet attempts to proactively replace Spot Instances that have received a rebalance recommendation, providing the opportunity to rebalance your workload to new Spot Instances that are not at elevated risk of interruption. Spot Instances with a defined duration (also known as Spot blocks) do not receive rebalance recommendations.
- Use integrated AWS services to manage your Spot Instances:Amazon EMR, Amazon ECS, AWS Batch, Amazon EKS, SageMaker, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Amazon GameLift.
Spot Instance requests
- To use Spot Instances, you create a Spot Instance request that includes the desired number of instances, the instance type, the Availability Zone, and the maximum price that you are willing to pay per instance hour.
- Notice that the request type (one-time or persistent) determines whether the request is opened again when Amazon EC2 interrupts a Spot Instance or if you stop a Spot Instance.
- If the request is persistent, the request is opened again after your Spot Instance is interrupted.
- If the request is persistent and you stop your Spot Instance, the request only opens after you start your Spot Instance.
- Spot Instances with a defined duration (also known as Spot blocks) are designed not to be interrupted and will run continuously for the duration you select. You can use a duration of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 hours. The price that you pay depends on the specified duration
- Interruption behaviors
- Stop interrupted Spot Instances
- Hibernate interrupted Spot Instances
- Terminate interrupted Spot Instances (this is the default behavior)
Savings Plans
Savings Plans are a flexible pricing model that offer low prices on EC2 and Fargate usage, in exchange for a commitment to a consistent amount of usage (measured in $/hour) for a 1 or 3 year term.
Dedicated Hosts
A Dedicated Host is a physical EC2 server dedicated for your use. Dedicated Hosts can help you reduce costs by allowing you to use your existing server-bound software licenses, including Windows Server, SQL Server, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (subject to your license terms), and can also help you meet compliance requirements.
- Can be purchased On-Demand (hourly).
- Can be purchased as a Reservation for up to 70% off the On-Demand price.
The following table highlights some of the key differences between Dedicated Hosts and Dedicated Instances:
| Dedicated Host | Dedicated Instance | |
|---|---|---|
| Billing | Per-host billing | Per-instance billing |
| Visibility of sockets, cores, and host ID | Provides visibility of the number of sockets and physical cores | No visibility |
| Host and instance affinity | Allows you to consistently deploy your instances to the same physical server over time | Not supported |
| Targeted instance placement | Provides additional visibility and control over how instances are placed on a physical server | Not supported |
| Automatic instance recovery | Supported | Supported |
| Bring Your Own License (BYOL) | Supported | Not supported |
Dedicated Hosts restrictions
- To run RHEL, SUSE Linux, and SQL Server on Dedicated Hosts, you must bring your own AMIs.
- Up to two On-Demand Dedicated Hosts per instance family, per Region can be allocated.
- The instances that run on a Dedicated Host can only be launched in a VPC.
- Auto Scaling groups are supported when using a launch template that specifies a host resource group.
- Amazon RDS instances are not supported.
- The AWS Free Usage tier is not available for Dedicated Hosts.
- Instance placement control refers to managing instance launches onto Dedicated Hosts. You cannot launch Dedicated Hosts into placement groups.
Allocate Dedicated Hosts
- To begin using Dedicated Hosts, you must allocate Dedicated Hosts in your account using the Amazon EC2 console or the command line tools. After you allocate the Dedicated Host, the Dedicated Host capacity is made available in your account immediately and you can start launching instances onto the Dedicated Host.
Launch instances onto a Dedicated Host
- After you have allocated a Dedicated Host, you can launch instances onto it.
- You can't launch instances with
hosttenancy if you do not have active Dedicated Hosts with enough available capacity for the instance type that you are launching.
Launch instances into a host resource group
- When you launch an instance into a host resource group that has a Dedicated Host with available instance capacity, Amazon EC2 launches the instance onto that host.
- If the host resource group does not have a host with available instance capacity, Amazon EC2 automatically allocates a new host in the host resource group, and then launches the instance onto that host.
Auto-placement
- Auto-placement is configured at the host level.
- It allows you to manage whether instances that you launch are launched onto a specific host, or onto any available host that has matching configurations.
- When the auto-placement of a Dedicated Host is disabled, it only accepts Host tenancy instance launches that specify its unique host ID. This is the default setting for new Dedicated Hosts.
- When the auto-placement of a Dedicated Host is enabled, it accepts any untargeted instance launches that match its instance type configuration.
- Launching an instance onto a Dedicated Host without providing a specific
HostIdenables it to launch on any Dedicated Host that has auto-placement enabled and that matches its instance type.
Host affinity
- Host affinity is configured at the instance level. It establishes a launch relationship between an instance and a Dedicated Host.
- When affinity is set to
Host, an instance launched onto a specific host always restarts on the same host if stopped. This applies to both targeted and untargeted launches. - When affinity is set to
Off, and you stop and restart the instance, it can be restarted on any available host.
Work with shared Dedicated Hosts
- Dedicated Host sharing enables Dedicated Host owners to share their Dedicated Hosts with other AWS accounts or within an AWS organization,A Dedicated Host owner can share a Dedicated Host with:
- Specific AWS accounts inside or outside of its AWS organization
- An organizational unit inside its AWS organization
- Its entire AWS organization
Host recovery
- Host recovery automatically restarts your instances on to a new replacement host if failures are detected on your Dedicated Host.
- When a system failure is detected on your Dedicated Host, host recovery is initiated and Amazon EC2 automatically allocates a replacement Dedicated Host., The replacement Dedicated Host receives a new host ID, but retains the same attributes as the original Dedicated Host, including:
- Availability Zone
- Instance type
- Tags
- Auto placement settings
- After the replacement Dedicated Host is allocated, the instances are recovered on to the replacement Dedicated Host. The recovered instances retain the same attributes as the original instances, including:
- Instance ID
- Private IP addresses
- Elastic IP addresses
- EBS volume attachments
- All instance metadata
- Stopped instances are not recovered on to the replacement Dedicated Host.
- Instances with instance storage are not recovered on to the replacement Dedicated Host.
Dedicated Instances
- Dedicated Instances are Amazon EC2 instances that run in a virtual private cloud (VPC) on hardware that's dedicated to a single customer.
- Dedicated Instances that belong to different AWS accounts are physically isolated at a hardware level, even if those accounts are linked to a single payer account.
- However, Dedicated Instances may share hardware with other instances from the same AWS account that are not Dedicated Instances.
Dedicated Instance basics
- Each instance that you launch into a VPC has a tenancy attribute. This attribute has the following values.
default: Your instance runs on shared hardware.dedicated: Your instance runs on single-tenant hardware.host: Your instance runs on a Dedicated Host, which is an isolated server with configurations that you can control.
- After you launch an instance, there are some limitations to changing its tenancy.
-
You cannot change the tenancy of an instance from
defaulttodedicatedorhostafter you've launched it. -
You cannot change the tenancy of an instance from
dedicatedorhosttodefaultafter you've launched it. - You can change the tenancy of an instance from
dedicatedtohost, or fromhosttodedicatedafter you've launched it.
-
- Each VPC has a related instance tenancy attribute. This attribute has the following values.
default: An instance launched into the VPC runs on shared hardware by default, unless you explicitly specify a different tenancy during instance launch.dedicated:An instance launched into the VPC is a Dedicated Instance by default, unless you explicitly specify a tenancy ofhostduring instance launch. You cannot specify a tenancy ofdefaultduring instance launch.- You can change the instance tenancy of a VPC from
dedicatedtodefaultafter you create it. You cannot change the instance tenancy of a VPC fromdefaulttodedicatedafter it is created.
- You can use Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to launch Dedicated Instances
- You can run a Dedicated Spot Instance by specifying a tenancy of
dedicatedwhen you create a Spot Instance request.
On-Demand Capacity Reservations
- On-Demand Capacity Reservations enable you to reserve compute capacity for your Amazon EC2 instances in a specific Availability Zone for any duration.
- When you create a Capacity Reservation, you specify:
- The Availability Zone in which to reserve the capacity
- The number of instances for which to reserve capacity
- The instance attributes, including the instance type, tenancy, and platform/OS
-
Differences between Capacity Reservations, Reserved Instances, and Savings Plans
Capacity Reservations Zonal Reserved Instances Regional Reserved Instances Savings Plans Term No commitment required. Can be created and canceled as needed. Requires a fixed one-year or three-year commitment Capacity benefit Capacity reserved in a specific Availability Zone. No capacity reserved. Billing discount No billing discount. † Provides a billing discount. Instance Limits Your On-Demand Instance limits per Region apply. Default is 20 per Availability Zone. You can request a limit increase. Default is 20 per Region. You can request a limit increase. No limit. - Capacity Reservation limits
- The number of instances for which you are allowed to reserve capacity is based on your account's On-Demand Instance limit.
- Active and unused Capacity Reservations count toward your On-Demand Instance limits.
- Capacity Reservations are not transferable from one AWS account to another.
- Zonal Reserved Instance billing discounts do not apply to Capacity Reservations.
- Capacity Reservations can't be created in placement groups.
- Capacity Reservations can't be used with Dedicated Hosts.
- Capacity Reservations do not ensure that a hibernated instance can resume after you try to start it.
Reference
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/concepts.html
https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/?ec2-whats-new.sort-by=item.additionalFields.postDateTime&ec2-whats-new.sort-order=desc
AWS Certified Solutions Architect Official Study Guide - Associate
AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide- Associate 2nd Edition
这篇关于2.4 AWS EC2 Pricing options的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








