本文主要是介绍Android开发:使用Fragment改造TabActivity,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
TabActivity在API 13(Android 3.2)被标记为过期,需要使用Fragment来实现,Fragment是Android 3.0引入的一个概念,主要就是为了适应各种不同的屏幕大小(手机、平板电脑)。Android 4.1发布时,google还发布了一个Android Support v4的包,用于Android 1.6以上的系统兼容新的特性,其中包括Fragment。为了在低于Android 3.0的平台上使用Fragment,我们需要在项目的libs中加入android-support-v4.jar这个包,一般现在的开发都需要兼顾3.0以下的平台,所以基本上都是使用这个包里的Fragment,而不是直接使用Android内置的Fragment。
在最新的Android文档里面,关于TabActivity,只讲到了它已经过期,并且贴了两个代码片段,但是点开其中的Sample链接,只是链接到了Sample的首页,还是不能看到完整的代码,要看完整的代码,就要在SDK Manager里面把Sample下载下来,然后用Eclipse打开才能看到。但是,即使看了Sample,要想弄明白怎么把自己的TabActivity转过去,也要耗费不少的功夫,因为那个Sample比较复杂。
我也是搞了两三天才弄明白Fragment的基本概念,实际上就是为了适应不同的屏幕分辨率,有的屏幕在一个Activity中可以包含一个Fragment,有的则可以包含多个,所以需要根据不同的配置调整显示方式,例如在同一个Activity里面显示两个Fragment,或者在一个Activity里面显示其中一个Fragment,另外一个Activity里面显示另外一个Fragment,实际上就是把显示内容划分成多块,每一块都有各自的生命周期,但是每一块又是跟它所在的Activity分不开的,Fragment的生命周期依赖Activity的生命周期而存在。
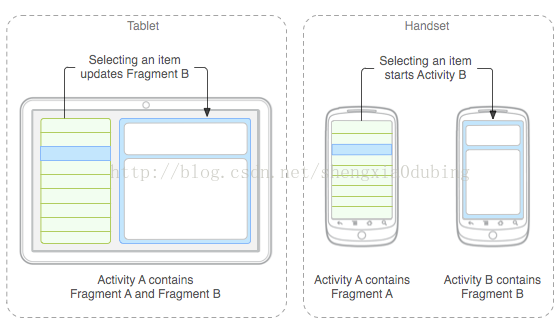
下图是Fragment在不同屏幕上的显示以及Fragment与所在Activity的关系:
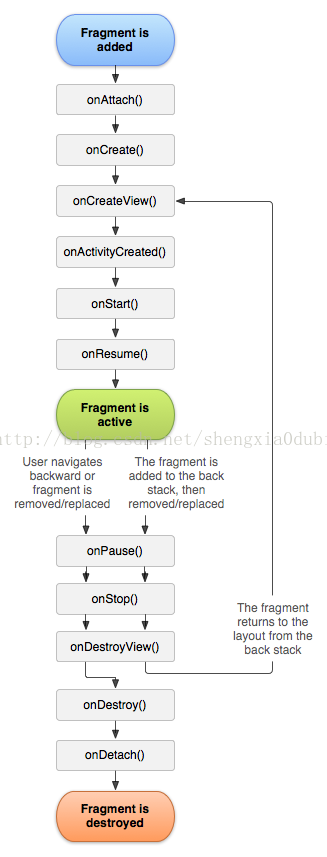
下图是Fragment的生命周期:
下图是Fragment的生命周期与Activity的对应关系:
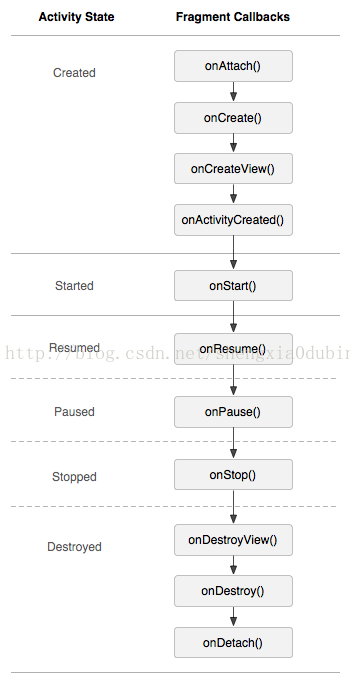
以上图片都来自Android的官方开发指南。
从最后一幅图可以看出,Activity的生命周期中的每个回调函数,在Fragment里都有对应的回调函数,这个在TabActivity的改造中很重要。
好了,这些基本的东西都了解之后,就可以开工了,如果你不打算深入理解Fragment,只是为了去掉横跨在TabActivity上难看的删除线,在你的Activity都是基本的Activity的情况下,那么按照以下的步骤来做就行了:
首先,使用Tab的应用都有一个入口的主Activity,我们把它叫做MainActivity,它包含了多个Tab,每个Tab又对应一个Activity,这个MainActivity的改造如下:
/** Copyright (C) 2011 The Android Open Source Project** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.* You may obtain a copy of the License at** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and* limitations under the License.*//*** Demonstrates combining a TabHost with a ViewPager to implement a tab UI* that switches between tabs and also allows the user to perform horizontal* flicks to move between the tabs.*/
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {TabHost mTabHost;TabManager mTabManager;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.fragment_tabs);Resources res = getResources();mTabHost = (TabHost)findViewById(android.R.id.tabhost);mTabHost.setup();mTabManager = new TabManager(this, mTabHost, R.id.realtabcontent);mTabManager.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("tab1"),Tab1FragmentActivity.Tab1Fragment.class, null);mTabManager.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("tab2").setIndicator("tab2"),Tab1FragmentActivity.Tab2Fragment.class, null);if (savedInstanceState != null) {mTabHost.setCurrentTabByTag(savedInstanceState.getString("tab"));}}@Overrideprotected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);outState.putString("tab", mTabHost.getCurrentTabTag());}/*** This is a helper class that implements a generic mechanism for* associating fragments with the tabs in a tab host. It relies on a* trick. Normally a tab host has a simple API for supplying a View or* Intent that each tab will show. This is not sufficient for switching* between fragments. So instead we make the content part of the tab host* 0dp high (it is not shown) and the TabManager supplies its own dummy* view to show as the tab content. It listens to changes in tabs, and takes* care of switch to the correct fragment shown in a separate content area* whenever the selected tab changes.*/public static class TabManager implements TabHost.OnTabChangeListener {private final FragmentActivity mActivity;private final TabHost mTabHost;private final int mContainerId;private final HashMap<String, TabInfo> mTabs = new HashMap<String, TabInfo>();TabInfo mLastTab;static final class TabInfo {private final String tag;private final Class<?> clss;private final Bundle args;private Fragment fragment;TabInfo(String _tag, Class<?> _class, Bundle _args) {tag = _tag;clss = _class;args = _args;}}static class DummyTabFactory implements TabHost.TabContentFactory {private final Context mContext;public DummyTabFactory(Context context) {mContext = context;}@Overridepublic View createTabContent(String tag) {View v = new View(mContext);v.setMinimumWidth(0);v.setMinimumHeight(0);return v;}}public TabManager(FragmentActivity activity, TabHost tabHost, int containerId) {mActivity = activity;mTabHost = tabHost;mContainerId = containerId;mTabHost.setOnTabChangedListener(this);}public void addTab(TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec, Class<?> clss, Bundle args) {tabSpec.setContent(new DummyTabFactory(mActivity));String tag = tabSpec.getTag();TabInfo info = new TabInfo(tag, clss, args);// Check to see if we already have a fragment for this tab, probably// from a previously saved state. If so, deactivate it, because our// initial state is that a tab isn't shown.info.fragment = mActivity.getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag(tag);if (info.fragment != null && !info.fragment.isDetached()) {FragmentTransaction ft = mActivity.getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction();ft.detach(info.fragment);ft.commit();}mTabs.put(tag, info);mTabHost.addTab(tabSpec);}@Overridepublic void onTabChanged(String tabId) {TabInfo newTab = mTabs.get(tabId);if (mLastTab != newTab) {FragmentTransaction ft = mActivity.getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction();if (mLastTab != null) {if (mLastTab.fragment != null) {ft.detach(mLastTab.fragment);}}if (newTab != null) {if (newTab.fragment == null) {newTab.fragment = Fragment.instantiate(mActivity,newTab.clss.getName(), newTab.args);ft.add(mContainerId, newTab.fragment, newTab.tag);} else {ft.attach(newTab.fragment);}}mLastTab = newTab;ft.commit();mActivity.getSupportFragmentManager().executePendingTransactions();}}}
}
以上代码基本上是从Sample里面copy过来的,但是里面的Tab改成了两个,分别加载Tab1FragmentActivity和Tab2FragmentActivity(实际上是加载依附在这两个Activity上的Fragment),后面讲到。
不要改动TabManager这个静态内部类,只修改OnCreate里面的内容即可,当然,如果你原来的Activity里面的其他回调函数重写了的话,也可以继续保留,这里只是把原来继承Activity改为了继承FragmentActivity。
而OnCreate里面的
这句,表示Activity的布局,这个布局文件fragment_tabs.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--
/* //device/apps/common/assets/res/layout/tab_content.xml
**
** Copyright 2011, The Android Open Source Project
**
** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
** you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
** You may obtain a copy of the License at
**
** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
**
** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
** distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
** WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
** See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
** limitations under the License.
*/
--><TabHostxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:id="@android:id/tabhost"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"><LinearLayoutandroid:orientation="vertical"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"><TabWidgetandroid:id="@android:id/tabs"android:orientation="horizontal"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_weight="0"/><FrameLayoutandroid:id="@android:id/tabcontent"android:layout_width="0dp"android:layout_height="0dp"android:layout_weight="0"/><FrameLayoutandroid:id="@+android:id/realtabcontent"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="0dp"android:layout_weight="1"/></LinearLayout>
</TabHost>
请不要改动这个xml文件。
第二步,把原来包含的两个tab对应的Activity分别改造成FragmentActivity,这个改造起来也很简单,由于Activity生命周期里的Start,Resume,Pause,Stop,Destroy在Fragment中都有对应的生命周期,所以在Activity里的回调函数,直接复制到Fragment里就可以了,而Activity里的OnCreate,则对应Fragment的多个回调函数,但是我们可以把它对应到Fragment里的OnReateView里面,不过需要修改一些东西,先看代码:
public class Tab1FragmentActivity extends FragmentActivity {@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();if (fm.findFragmentById(android.R.id.content) == null) {Tab1Fragment tab1Fragment = new Tab1Fragment();fm.beginTransaction().add(android.R.id.content, tab1Fragment).commit();}}public static class Tab1Fragment extends Fragment {private TextView textView1 = null;private TextView textView2 = null;private tab1BroadcastReceiver receiver;private IntentFilter intentFilter;@Overridepublic void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);}@Overridepublic View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,Bundle savedInstanceState) {View v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.tab1, container, false);textView1 = (TextView) v.findViewById(R.id.textView1);textView1.setText("TextView1");textView2 = (TextView) v.findViewById(R.id.textView2);textView2.setText("TextView2");return v;}@Overridepublic void onPause() {super.onPause();getActivity().unregisterReceiver(receiver);}@Overridepublic void onResume() {super.onResume();receiver = new tab1BroadcastReceiver();getActivity().registerReceiver(receiver, getIntentFilter());}private IntentFilter getIntentFilter() {if (intentFilter == null) {intentFilter = new IntentFilter();intentFilter.addAction("TAB1_ACTION"); }return intentFilter;}class Tab1BroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {@Overridepublic void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {if (intent.getAction().equals("TAB1_ACTION")) { textView1.setText("Received!");}}} }
}
以上代码演示了一个包含两个TextView的Activity,为了演示getActivity()函数,还加了一个BroadcastReceiver。
这个类包含了一个静态内部类,主类继承了FragmentActivity,这是使用Fragment的必要条件,但是这个FragmentActivity的OnCreate回调函数内容非常简单,只有下面几行:
FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();if (fm.findFragmentById(android.R.id.content) == null) {Tab1Fragment tab1Fragment = new Tab1Fragment();fm.beginTransaction().add(android.R.id.content, tab1Fragment).commit();}
一般Activity里面的SetContentView都没有了,也没有了各种控件的成员变量,因为所有这一切,都被包含在静态内部类Tab1Fragment里面,在Activity里,只需要包含上面的代码,这段代码的意思是,如果在这个Activity里面没有Fragment,就新建一个,并加入到后台堆栈中,以便程序控制Fragment的显示顺序。android.R.id.content是个系统自带的常量,这个常量表示“根”内容,也就是说,这个Activity的根内容就是一个Fragment,下面的东西都由Fragment来构造和完成。这里只需要修改Fragment的类名和变量名,其他东西都不要改。
后面的Tab1Fragment静态内部类,OnPause,OnResume等回调函数的内容都直接把原来Activity里面的对应内容复制过来就行了,如果遇到原来使用了this(表示当前Activity,或者所在的Context)的地方,就用getActivity()来代替即可,该函数就是返回Fragment所在的Activity对象。如果原来的控件是Activity的私有成员,就把它们复制到Fragment里面,作为Fragment的私有成员,然后在Fragment的onCreateView回调函数获取,该函数实际对应了Activity的OnCreate回调函数,但是里面的代码要稍作修改。
一般来说,Activity里设置布局的语句是
SetContentView(R.layout.tab1);
在Fragment的OnCreateView里需要改成:
这里获取了根View后,是为了后面获取各控件。
在Activity里的findViewById,需要改成Fragment的
v.findViewById
这个v就是通过上面的语句来取得。这个回调函数的最后就是返回v。其他东西跟Activity的OnCreate基本相同。当然,由于Activity的OnCreate对应了Fragment的多个回调函数,也许有些东西放在其他回调函数里面会更适合。
以下是Tab1对应的布局文件tab1.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><RelativeLayoutxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:id="@+id/tab1_layout"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextViewandroid:id="@+id/textView1"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:gravity="left"/><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/textView2"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:gravity="left"android:layout_below="@id/textView1"/> </RelativeLayout> 第三步,按照第二步的样子修改Tab2,这里省略。
完工之后,你的程序运行起来没有任何改变,唯一的好处就是看不到TabActivity上的删除线了,但是代价却是在libs目录里多了android-support-v4.jar文件,并且代码变得更复杂。另外,假如你用到了地图控件,例如百度地图,你还不能改造,因为百度地图需要放在一个MapActivity里面,这个Activity不能再继承FragmentActivity。Google地图已经在最新的API里解决了这个问题,不过用google地图的风险就是很多行货手机安装不了,因为缺了GMS。
原文地址:http://www.blogjava.net/amplifier/archive/2012/12/27/393409.html
Android 开发文档参考网址:http://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html
直接在Android Developers(developer.android.com)网站右上角查询Fragment即可,其相关内容在Guide,Reference或者Training中都有相关介绍,同时有相应的Sample,大致了解可参考Guide中内容。
这篇关于Android开发:使用Fragment改造TabActivity的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!