本文主要是介绍两种尺度的图像滑窗效果,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、简单示例
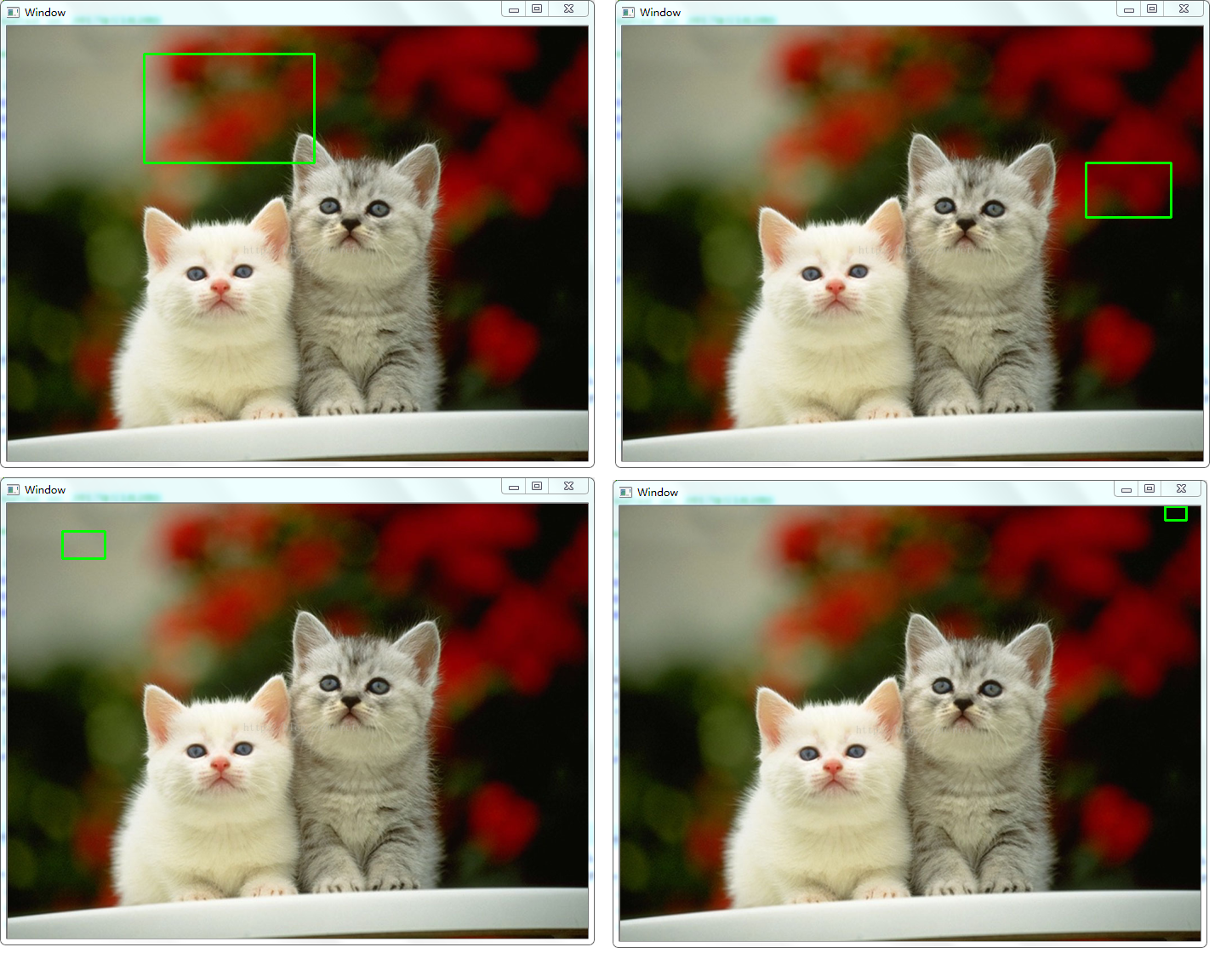
当给你一张随机大小的图片时,用固定的矩形框框住目标,有些目标可能很大,有些目标也可能很小,比如从下面的目标找出猫眼,如果采用固定大小的矩形框,会出现漏检的情况:
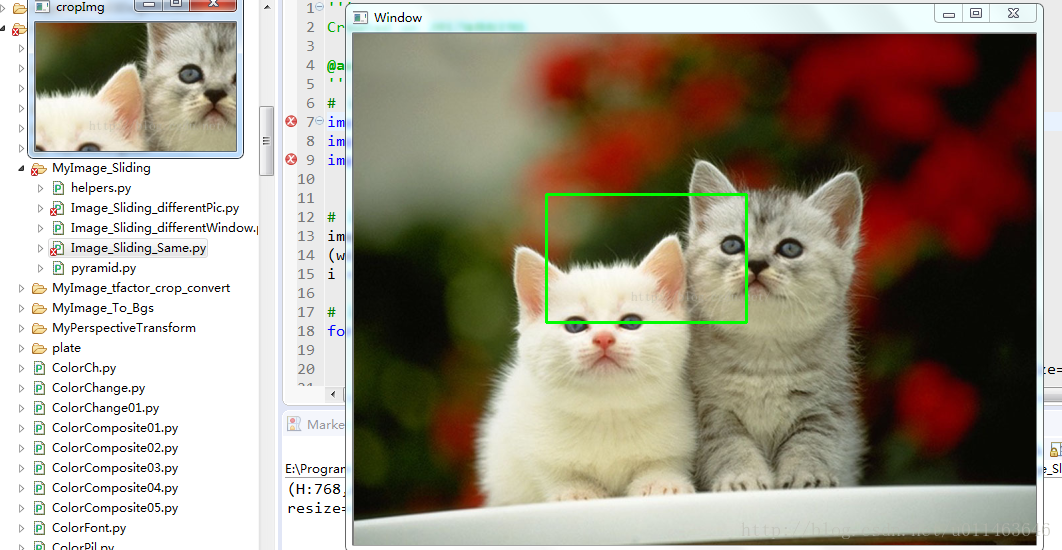
这里的固定框、固定大小图片代码为:
'''
Created on 2017年8月19日@author: XuTing
'''
# import the necessary packages
import helpers
import time
import cv2# load the image and define the window width and height
image = cv2.imread('../image/cat2.jpg')
(winW, winH) = (200, 128)
i = 0# loop over the image pyramid
for resized in helpers.pyramid(image, scale=1.5,minSize=(winW, winH)):# loop over the sliding window for each layer of the pyramidfor (x, y, window) in helpers.sliding_window(resized, stepSize=32, windowSize=(winW, winH)):# if the window does not meet our desired window size, ignore itif window.shape[0] != winH or window.shape[1] != winW:continue# THIS IS WHERE YOU WOULD PROCESS YOUR WINDOW, SUCH AS APPLYING A# MACHINE LEARNING CLASSIFIER TO CLASSIFY THE CONTENTS OF THE# WINDOW# since we do not have a classifier, we'll just draw the windowclone = resized.copy()cropImg_clone = resized.copy()cv2.rectangle(clone, (x, y), (x + winW, y + winH), (0, 255, 0), 2)cropImg = cropImg_clone[y: (y + winH),x:(x + winW)]#H,Wcv2.imshow("Window", clone)cv2.imshow("cropImg", cropImg)cv2.waitKey(1)#write
# WinName = "Layer {}".format(i + 1)
# cv2.imwrite('./'+WinName+'.jpg',clone)
# i += 1time.sleep(0.025)helpers:
'''
Created on 2017年8月19日@author: XuTing
'''
# import the necessary packages
import imutils
from skimage.transform import pyramid_gaussian
import cv2def pyramid(image, scale=1.5, minSize=(30, 30)):# yield the original imageprint('(H:{},W:{})'.format(image.shape[0], image.shape[1]))
# yield image# compute the new dimensions of the image and resize itw = int(image.shape[1] / scale)image = imutils.resize(image, width=w)print('resize=(H:{},W:{})'.format(image.shape[0], image.shape[1]))# if the resized image does not meet the supplied minimum# size, then stop constructing the pyramidif image.shape[0] < minSize[1] or image.shape[1] < minSize[0]:print("Out of size!")else:yield imagedef pyramid2(image, scale=1.5, minSize=(30, 30)):# yield the original imageyield image# keep looping over the pyramidwhile True:# compute the new dimensions of the image and resize itw = int(image.shape[1] / scale)image = imutils.resize(image, width=w)print('(H:{},W:{})'.format(image.shape[0], image.shape[1]))# if the resized image does not meet the supplied minimum# size, then stop constructing the pyramidif image.shape[0] < minSize[1] or image.shape[1] < minSize[0]:print("Out of size!")break# yield the next image in the pyramidyield image
def sliding_window(image, stepSize, windowSize):# slide a window across the imagefor y in range(0, image.shape[0], stepSize):for x in range(0, image.shape[1], stepSize):# yield the current windowyield (x, y, image[y:y + windowSize[1], x:x + windowSize[0]])if __name__ == '__main__':image = cv2.imread('../image/cat2.jpg') # METHOD #2: Resizing + Gaussian smoothing.for (i, resized) in enumerate(pyramid_gaussian(image, downscale=2)):# if the image is too small, break from the loopif resized.shape[0] < 30 or resized.shape[1] < 30:break# show the resized imageWinName = "Layer {}".format(i + 1)cv2.imshow(WinName, resized)cv2.waitKey(0)resized = resized*255cv2.imwrite('./'+WinName+'.jpg',resized)
为此采用了两种策略:
1)基于多尺度图片的定位;
固定的滑动窗口大小,而图像的尺寸按照一定比例缩放,而不是压缩,类似于金字塔的形状。
2)基于多尺寸滑动窗口的定位;
固定的图片大小,而滑动窗口尺寸会按照一定比例缩小,当小于设定的最小尺寸时,程序结束。
2、基于多尺度图片的定位
参考多尺度图片滑动窗口输出 - Alex_XT的博客 - CSDN博客
http://blog.csdn.net/u011463646/article/details/77417049
其实现的效果为:
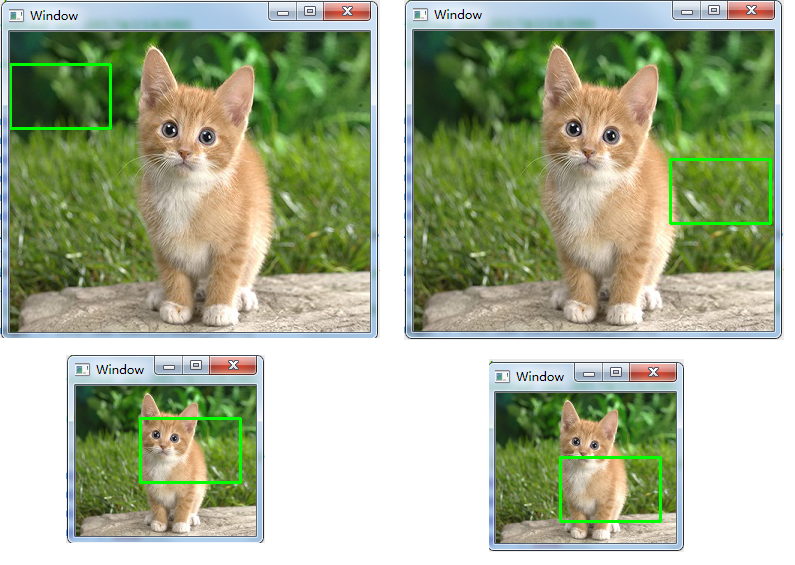
代码:
'''
Created on 2017年11月20日@author: XuTing
'''
# import the necessary packages
import helpers
import argparse
import time
import cv2
import os
import sys
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)
IMAGE_PATH=os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'image','cat.jpg')
print(IMAGE_PATH)
# load the image and define the window width and height
image = cv2.imread(IMAGE_PATH)
(winW, winH) = (100, 64)
i = 0# loop over the image pyramid
for resized in helpers.pyramid2(image, scale=2):# loop over the sliding window for each layer of the pyramidfor (x, y, window) in helpers.sliding_window(resized, stepSize=32, windowSize=(winW, winH)):# if the window does not meet our desired window size, ignore itif window.shape[0] != winH or window.shape[1] != winW:continue# THIS IS WHERE YOU WOULD PROCESS YOUR WINDOW, SUCH AS APPLYING A# MACHINE LEARNING CLASSIFIER TO CLASSIFY THE CONTENTS OF THE# WINDOW# since we do not have a classifier, we'll just draw the windowclone = resized.copy()cv2.rectangle(clone, (x, y), (x + winW, y + winH), (0, 255, 0), 2)cv2.imshow("Window", clone)cv2.waitKey(100)#write
# WinName = "Layer {}".format(i + 1)
# cv2.imwrite('./'+WinName+'.jpg',clone)
# i += 1
# time.sleep(0.025)3、基于多尺寸滑动窗口的定位
在固定的图片大小中,使用不同大小的滑动窗口来实现目标的定位与检验:
(H:768,W:1024)
resize=(H:511,W:682)
minSize=windowList[-1]= (25, 16)
(winW, winH)=(200,128)
(winW, winH)=(100,64)
(winW, winH)=(50,32)
(winW, winH)=(25,16)
代码下载:http://download.csdn.net/download/u011463646/10126421
'''
Created on 2017年11月20日@author: XuTing
'''
# import the necessary packages
import helpers
import time
import cv2# load the image and define the window width and height
image = cv2.imread('../image/cat2.jpg')
windowList = [(200, 128),(100,64),(50,32),(25,16)]# 使用了元组
i = 0# loop over the image pyramid
for resized in helpers.pyramid(image, scale=1.5,minSize=windowList[-1]):print("minSize=windowList[-1]=",windowList[-1])# loop over the sliding window for each layer of the pyramidfor winSize in windowList:winW=winSize[0]winH=winSize[1]print("(winW, winH)=({},{})".format(winW,winH))for (x, y, window) in helpers.sliding_window(resized, stepSize=32, windowSize=(winW, winH)):# if the window does not meet our desired window size, ignore itif window.shape[0] != winH or window.shape[1] != winW:continue# THIS IS WHERE YOU WOULD PROCESS YOUR WINDOW, SUCH AS APPLYING A# MACHINE LEARNING CLASSIFIER TO CLASSIFY THE CONTENTS OF THE# WINDOW# since we do not have a classifier, we'll just draw the windowclone = resized.copy()cropImg_clone = resized.copy()cv2.rectangle(clone, (x, y), (x + winW, y + winH), (0, 255, 0), 2)cropImg = cropImg_clone[y: (y + winH),x:(x + winW)]#H,Wcv2.imshow("Window", clone)cv2.imshow("cropImg", cropImg)cv2.waitKey(1)#write#WinName = "Layer {}".format(i + 1)#cv2.imwrite('./'+WinName+'.jpg',clone)#i += 1time.sleep(0.025)
这篇关于两种尺度的图像滑窗效果的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






