本文主要是介绍哈工大李治军操作系统--操作系统基础(操作系统启动),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
打开电源,计算机执行的第一句指令是什么?
(1) x86PC刚开机时CPU处于实模式;
(2) 开机时, CS=0xFFFF, IP=0x0000;
(3) 寻址0xFFFF0(ROM BIOS映射区);
(4) 检查RAM, 键盘, 显示器, 软硬磁盘;
(5) 将软盘0面0道1扇区(主引导扇区, 对应操作系统第一段代码,即主引导程序.Linux 0.11源码对应文件为boot/bootsect.s)读入0x7c00处;
(6) 设置cs=0x07c0, ip=0x0000.

bootsect.s
bootsect.s (1个扇区)把自身从0x7c000处搬到0x90000处,再把setup.s(4个扇区)搬到0x90200处,然后调用0x13号中断在屏幕上打印“Loading system…”,再把system模块加载到0x10000处。之后确定根文件系统的设备号,若没指定,则根据所保存的引导盘的每磁道扇区数判定盘的类型(是1.44M A盘吗?)并保存其设备号于root_dev。最后139行跳转到setup.s执行。




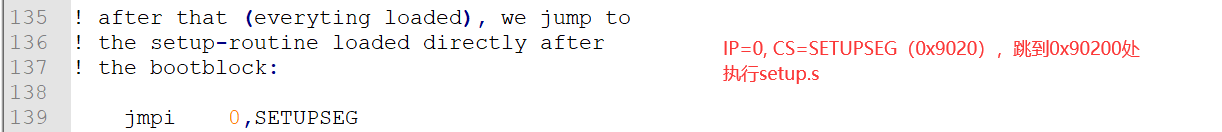
140行~227行代码用来加载system模块,由于采用比较原始的CHS模式读取软盘比较复杂,不再细看,暂且当成一个黑箱吧,日后若研究细节再做分析。


setup.s
代码105行之前,利用 ROM BIOS 中断例程获取系统参数(如光标位置、内存大小等),并写入 0x900000-x901FF 处(覆盖原来的 bootsect.s 区域)。然后把 system 模块从 0x10000-0x8ffff (当时认为 system 模块不会超过512K)搬到 0x0000 处(0x00000-0x003ff 的256个中断号的中断向量表被覆盖,之后再用int就不再是查0x00000处的中断向量表了,而是查IDT)。然后开启 A20 地址线并设置 8259A 中断控制芯片,再设置 CR0 的 PE 位,进入 32 位保护模式,转到 system 模块的第一个代码 head.s 执行。

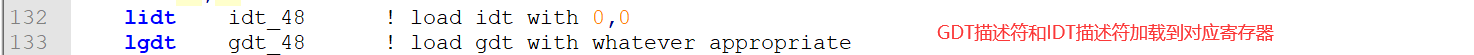





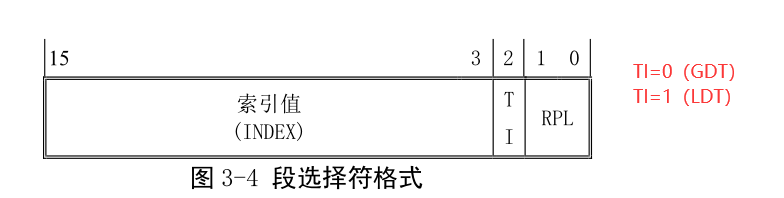
执行191行之后,跳到0x00000000。那么该处对应哪个代码文件呢?
Makefile
要让操作系统正常运行,必须通过Makefile控制各个代码文件加载顺序、如何组合等工作。Makefile是make工具的配置文件,相当于批处理文件,在含有Makefile的当前目录里执行make命令,就会根据Makefile中的信息对源代码进行编译、链接等工作。
根据Makefile的配置要求,0x00000000处就是system模块的head.s,下面要进入head.s执行。

head.s
本程序重新设置GDT和IDT,并做一些校验工作(如A20地址线是否启动等),然后设置并开启分页(分页相关的内容在内存管理再说),然后跳入main函数执行。



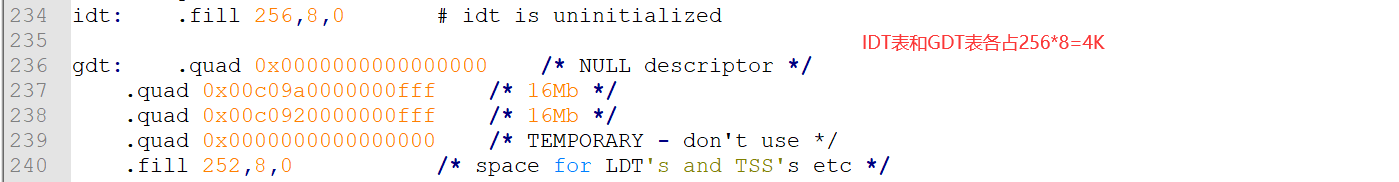


源代码(个人适当增加注释)
bootsect.s
!
! SYS_SIZE is the number of clicks (16 bytes) to be loaded.
! 0x3000 is 0x30000 bytes = 196kB, more than enough for current
! versions of linux
!
SYSSIZE = 0x3000
!
! bootsect.s (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
!
! bootsect.s is loaded at 0x7c00 by the bios-startup routines, and moves
! iself out of the way to address 0x90000, and jumps there.
!
! It then loads 'setup' directly after itself (0x90200), and the system
! at 0x10000, using BIOS interrupts.
!
! NOTE! currently system is at most 8*65536 bytes long. This should be no
! problem, even in the future. I want to keep it simple. This 512 kB
! kernel size should be enough, especially as this doesn't contain the
! buffer cache as in minix
!
! The loader has been made as simple as possible, and continuos
! read errors will result in a unbreakable loop. Reboot by hand. It
! loads pretty fast by getting whole sectors at a time whenever possible..globl begtext, begdata, begbss, endtext, enddata, endbss
.text
begtext:
.data
begdata:
.bss
begbss:
.textSETUPLEN = 4 ! nr of setup-sectors
BOOTSEG = 0x07c0 ! original address of boot-sector
INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way
SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! setup starts here
SYSSEG = 0x1000 ! system loaded at 0x10000 (65536).
ENDSEG = SYSSEG + SYSSIZE ! where to stop loading! ROOT_DEV: 0x000 - same type of floppy as boot.
! 0x301 - first partition on first drive etc
ROOT_DEV = 0x306 ! 设备号=主设备*256+次设备号,指定根文件系统是第2个硬盘的第1个分区! (主设备号:1-内存/2-软盘/3-硬盘/4-ttyx/5-tty/6-并行口/7-非命名管道)
entry _start
_start:mov ax,#BOOTSEGmov ds,axmov ax,#INITSEGmov es,axmov cx,#256sub si,sisub di,direpmovwjmpi go,INITSEG
go: mov ax,csmov ds,axmov es,ax
! put stack at 0x9ff00.mov ss,axmov sp,#0xFF00 ! arbitrary value >>512,从0x90000开始的5个扇区是bootsect.s和setup.s,! sp > 5*0x200 + 堆栈大小
! load the setup-sectors directly after the bootblock.
! Note that 'es' is already set up.load_setup:mov dx,#0x0000 ! drive 0, head 0mov cx,#0x0002 ! sector 2, track 0mov bx,#0x0200 ! address = 512, in INITSEGmov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN ! service 2, nr of sectorsint 0x13 ! read it,参考BIOS中断手册,查看0x13号详情对比阅读jnc ok_load_setup ! ok - continuemov dx,#0x0000 mov ax,#0x0000 ! reset the disketteint 0x13 j load_setup ! 加载不成功,重新加载ok_load_setup:! Get disk drive parameters, specifically nr of sectors/trackmov dl,#0x00mov ax,#0x0800 ! AH=8 is get drive parametersint 0x13mov ch,#0x00seg cs ! 87行只影响下一行即88行,87和88行等价于mov cs:[sectors],cxmov sectors,cx ! 每道的扇区数mov ax,#INITSEGmov es,ax! Print some inane messagemov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor posxor bh,bhint 0x10mov cx,#24 ! 打印到屏幕的字节数mov bx,#0x0007 ! page 0, attribute 7 (normal)mov bp,#msg1 ! 加载完setup.s,就打印msg1处的信息到屏幕mov ax,#0x1301 ! write string, move cursorint 0x10! ok, we've written the message, now
! we want to load the system (at 0x10000)mov ax,#SYSSEGmov es,ax ! segment of 0x010000call read_itcall kill_motor ! 关闭驱动马达,这样就可以获取驱动器的状态信息了! After that we check which root-device to use. If the device is
! defined (!= 0), nothing is done and the given device is used.
! Otherwise, either /dev/PS0 (2,28) or /dev/at0 (2,8), depending
! on the number of sectors that the BIOS reports currently.! 软驱主设备号是2,次设备号是type*4+nr,nr为0-3对应软驱A/B/C/Dseg cs ! type是软驱类型,2-1.2M,7-1.44M,7*4+0=28(/dev/PS0,设备号0x021c)mov ax,root_dev ! ax = ROOT_DEVcmp ax,#0jne root_definedseg csmov bx,sectorsmov ax,#0x0208 ! /dev/ps0 - 1.2Mbcmp bx,#15je root_definedmov ax,#0x021c ! /dev/PS0 - 1.44Mbcmp bx,#18je root_defined
undef_root:jmp undef_root
root_defined:seg csmov root_dev,ax! after that (everyting loaded), we jump to
! the setup-routine loaded directly after
! the bootblock:jmpi 0,SETUPSEG! This routine loads the system at address 0x10000, making sure
! no 64kB boundaries are crossed. We try to load it as fast as
! possible, loading whole tracks whenever we can.
!
! in: es - starting address segment (normally 0x1000)
!
sread: .word 1+SETUPLEN ! sectors read of current track
head: .word 0 ! current head
track: .word 0 ! current trackread_it:mov ax,estest ax,#0x0fff
die: jne die ! es must be at 64kB boundaryxor bx,bx ! bx is starting address within segment
rp_read:mov ax,escmp ax,#ENDSEG ! have we loaded all yet?jb ok1_readret
ok1_read:seg csmov ax,sectorssub ax,sreadmov cx,axshl cx,#9add cx,bxjnc ok2_readje ok2_readxor ax,axsub ax,bxshr ax,#9
ok2_read:call read_trackmov cx,axadd ax,sreadseg cscmp ax,sectorsjne ok3_readmov ax,#1sub ax,headjne ok4_readinc track
ok4_read:mov head,axxor ax,ax
ok3_read:mov sread,axshl cx,#9add bx,cxjnc rp_readmov ax,esadd ax,#0x1000mov es,axxor bx,bxjmp rp_readread_track:push axpush bxpush cxpush dxmov dx,trackmov cx,sreadinc cxmov ch,dlmov dx,headmov dh,dlmov dl,#0and dx,#0x0100mov ah,#2int 0x13jc bad_rtpop dxpop cxpop bxpop axret
bad_rt: mov ax,#0mov dx,#0int 0x13pop dxpop cxpop bxpop axjmp read_track!/*
! * This procedure turns off the floppy drive motor, so
! * that we enter the kernel in a known state, and
! * don't have to worry about it later.
! */
kill_motor:push dxmov dx,#0x3f2mov al,#0outbpop dxretsectors:.word 0msg1:.byte 13,10.ascii "Loading system ...".byte 13,10,13,10.org 508
root_dev:.word ROOT_DEV
boot_flag:.word 0xAA55.text
endtext:
.data
enddata:
.bss
endbss:setup.s
!
! setup.s (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
!
! setup.s is responsible for getting the system data from the BIOS,
! and putting them into the appropriate places in system memory.
! both setup.s and system has been loaded by the bootblock.
!
! This code asks the bios for memory/disk/other parameters, and
! puts them in a "safe" place: 0x90000-0x901FF, ie where the
! boot-block used to be. It is then up to the protected mode
! system to read them from there before the area is overwritten
! for buffer-blocks.
!! NOTE! These had better be the same as in bootsect.s!INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way
SYSSEG = 0x1000 ! system loaded at 0x10000 (65536).
SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! this is the current segment.globl begtext, begdata, begbss, endtext, enddata, endbss
.text
begtext:
.data
begdata:
.bss
begbss:
.textentry start
start:! ok, the read went well so we get current cursor position and save it for
! posterity.mov ax,#INITSEG ! this is done in bootsect already, but...mov ds,axmov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor posxor bh,bhint 0x10 ! save it in known place, con_init fetchesmov [0],dx ! it from 0x90000.
! Get memory size (extended mem, kB)mov ah,#0x88int 0x15mov [2],ax! Get video-card data:mov ah,#0x0fint 0x10mov [4],bx ! bh = display pagemov [6],ax ! al = video mode, ah = window width! check for EGA/VGA and some config parametersmov ah,#0x12mov bl,#0x10int 0x10mov [8],axmov [10],bxmov [12],cx! Get hd0 datamov ax,#0x0000mov ds,axlds si,[4*0x41] ! lds reg,操作数,操作数高16位给ds,低16位给regmov ax,#INITSEGmov es,axmov di,#0x0080mov cx,#0x10repmovsb! Get hd1 datamov ax,#0x0000mov ds,axlds si,[4*0x46]mov ax,#INITSEGmov es,axmov di,#0x0090mov cx,#0x10repmovsb! Check that there IS a hd1 :-)mov ax,#0x01500mov dl,#0x81int 0x13jc no_disk1cmp ah,#3je is_disk1
no_disk1:mov ax,#INITSEGmov es,axmov di,#0x0090mov cx,#0x10mov ax,#0x00repstosb
is_disk1:! now we want to move to protected mode ...cli ! no interrupts allowed !! first we move the system to it's rightful placemov ax,#0x0000cld ! 'direction'=0, movs moves forward
do_move:mov es,ax ! destination segmentadd ax,#0x1000cmp ax,#0x9000jz end_movemov ds,ax ! source segmentsub di,disub si,simov cx,#0x8000repmovswjmp do_move! then we load the segment descriptorsend_move:mov ax,#SETUPSEG ! right, forgot this at first. didn't work :-)mov ds,axlidt idt_48 ! load idt with 0,0lgdt gdt_48 ! load gdt with whatever appropriate! that was painless, now we enable A20call empty_8042mov al,#0xD1 ! command writeout #0x64,alcall empty_8042mov al,#0xDF ! A20 onout #0x60,alcall empty_8042! well, that went ok, I hope. Now we have to reprogram the interrupts :-(
! we put them right after the intel-reserved hardware interrupts, at
! int 0x20-0x2F. There they won't mess up anything. Sadly IBM really
! messed this up with the original PC, and they haven't been able to
! rectify it afterwards. Thus the bios puts interrupts at 0x08-0x0f,
! which is used for the internal hardware interrupts as well. We just
! have to reprogram the 8259's, and it isn't fun.mov al,#0x11 ! initialization sequenceout #0x20,al ! send it to 8259A-1.word 0x00eb,0x00eb ! jmp $+2, jmp $+2out #0xA0,al ! and to 8259A-2.word 0x00eb,0x00ebmov al,#0x20 ! start of hardware int's (0x20)out #0x21,al.word 0x00eb,0x00ebmov al,#0x28 ! start of hardware int's 2 (0x28)out #0xA1,al.word 0x00eb,0x00ebmov al,#0x04 ! 8259-1 is masterout #0x21,al.word 0x00eb,0x00ebmov al,#0x02 ! 8259-2 is slaveout #0xA1,al.word 0x00eb,0x00ebmov al,#0x01 ! 8086 mode for bothout #0x21,al.word 0x00eb,0x00ebout #0xA1,al.word 0x00eb,0x00ebmov al,#0xFF ! mask off all interrupts for nowout #0x21,al.word 0x00eb,0x00ebout #0xA1,al! well, that certainly wasn't fun :-(. Hopefully it works, and we don't
! need no steenking BIOS anyway (except for the initial loading :-).
! The BIOS-routine wants lots of unnecessary data, and it's less
! "interesting" anyway. This is how REAL programmers do it.
!
! Well, now's the time to actually move into protected mode. To make
! things as simple as possible, we do no register set-up or anything,
! we let the gnu-compiled 32-bit programs do that. We just jump to
! absolute address 0x00000, in 32-bit protected mode.mov ax,#0x0001 ! protected mode (PE) bitlmsw ax ! This is it! 加载机器状态字jmpi 0,8 ! jmp offset 0 of segment 8 (cs)! This routine checks that the keyboard command queue is empty
! No timeout is used - if this hangs there is something wrong with
! the machine, and we probably couldn't proceed anyway.
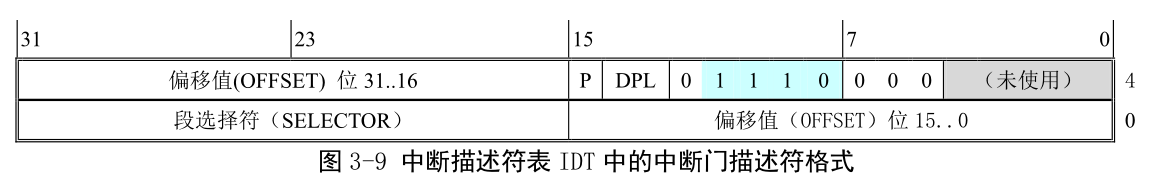
empty_8042:.word 0x00eb,0x00ebin al,#0x64 ! 8042 status porttest al,#2 ! is input buffer full?jnz empty_8042 ! yes - loopretgdt:.word 0,0,0,0 ! dummy.word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb).word 0x0000 ! base address=0.word 0x9A00 ! code read/exec.word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386.word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb).word 0x0000 ! base address=0.word 0x9200 ! data read/write.word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386idt_48:.word 0 ! idt limit=0.word 0,0 ! idt base=0Lgdt_48:.word 0x800 ! gdt limit=2048, 256 GDT entries.word 512+gdt,0x9 ! gdt base = 0X9xxxx 32位线性基地址高16位是0x0009,! 低16位是512+gdt,对应绝对地址就是0x0009xxxx,更
.text ! 准确的就是0x0009020+gdt,正好就是本代码标号gdt处
endtext:
.data
enddata:
.bss
endbss:参考资料
[1] 中国大学MOOC《操作系统》李治军 哈尔滨工业大学
[2] 《Linux内核完全注释》赵炯
[3] BIOS中断大全
[4] 汇编语言最全指令表
[5] 《x86汇编语言:从实模式到保护模式》李忠 著
[6] https://blog.csdn.net/ccnuacmhdu/article/details/104946213
这篇关于哈工大李治军操作系统--操作系统基础(操作系统启动)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







