本文主要是介绍【高级网络程序设计】Week3-2 Servlet,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、 What are servlets?

1. 定义
(1)Servlets are Java’s answer to CGI:
| programs that run on a web server acting as middle layer between HTTP request and databases or other applications. |
| Used for client requests that cannot be satisfied using pre-built (static) documents. |
| Used to generate dynamic web pages in response to client. |
(2)图解
| Web Browser | Sending Requests to a Web Server |
| Web Server | hold/return static web pages – e.g. index.html does not respond to user input. |
| Server Side Programs | different technologies written in various languages – e.g. CGI scripts, Java Servlets (and JSPs – later), PHP scripts – Call to http://localhost:8080/servlet/myhelloservlet.HelloServlet – Not web-browsing but executing program (servlet) |
| Dynamic response | – database lookup, calculation etc. |
| We’ll look at the Java solution | how to write servlets; how the container (Tomcat) works. |
2. A general purpose Web Server
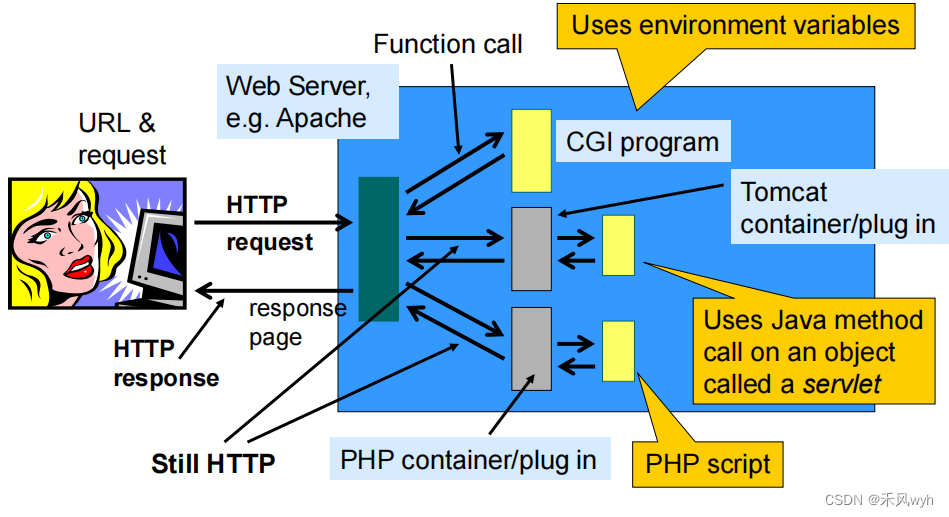
二、Simple Example
<form action=“http://server.com/ExecuteServlet”>
<input type=“submit” value = “press for servlet”>
</form>1. A Basic Servlet
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
//import jakarta.servlet.*:imports classes in this directory, but not in sub-directories
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {response.setContentType("text/html");//设置响应文件类型、响应式的编码形式PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();//获取字符输出流out.println(“<html><body>Hello!</body></html>”);out.close();}
}2. Echo Servlet
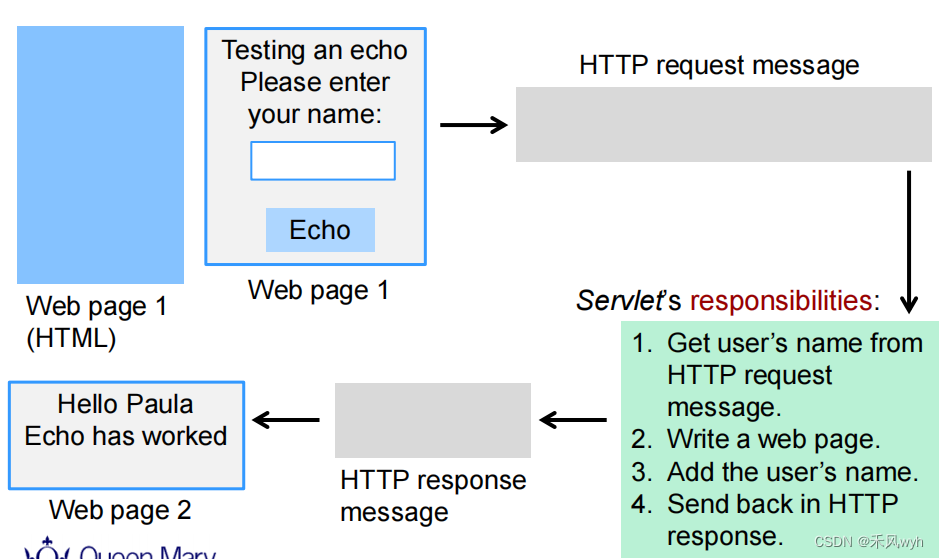
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class GetEchoServlet extends HttpServlet {public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)throws IOException, ServletException {String userName = request.getParameter(“fname”);//获取form中输入的参数response.setContentType("text/html");//设置响应文件类型、响应式编码格式PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();//获取字符输出流out.println(“<html><body>Hello”);if (userName != null) out.println(userName);else out.println(“mystery person”);out.println(“</body></html>”);out.close();}
}3. BMI Servlet
//Page that asks for weight (kg) and height (cm) :Write the HTML and the HTTP Request (GET)
<form method=“GET”action=“http://server.com/BMIServlet”>
<input type=“text” name=“weight”/>weight<br>
<input type=“text” name=“height”/>height<br>
<input type=“submit” value=“send”>
</form>- Servlet
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class BMIServlet extends HttpServlet {public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException,ServletException {String ht = request.getParameter(“height”);int height = Integer.parseInt(ht);double weight = Double.parseDouble(request.getParameter(“weight”));double ht_squared = (height/100.0)*(height/100.0);response.setContentType("text/html");PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();out.println(“<html><body><br>”);out.println(“Your BMI is: ” + weight/ht_squared + “<body></html>”);out.close();}
}4. Name-salary Servlet
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
import java.io.*;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {String name = request.getParameter("name");int salary = Integer.parseInt(salary);response.setContentType("text/html");PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();out.println("<html><body><br>");out.println("Hello,"+name);out.println("Your salary is"+salary);out.println("<body><html>");out.close();} // end of method
} // end of class三、Servlet Key Points
1. Servlets: Key points
| NO main method | public static void main(String[] args) |
| NO constructor | There is one (default) constructor but the developer should never write an explicit constructor – Why——servlet lifecycle |
| Two key (service) methods | doGet(); doPost() |
2. Finding things
| Tracing the user data | – e.g. name attribute inside an HTML element – name in HTTP request message – argument in request.getParameter(...) |
| String(int/double required) | then have to use appropriate method on this String to convert - Integer.parseInt(); - Double.parseDouble(); |
| Finding the servlet | – <form> tag action attribute e.g. <FORM action=“servlet/myServlet” ...> – Used by deployment descriptor, web.xml (see later), to map to the corresponding servlet class. |
3. JavaBeans, JSPs and Servlets
| Although a servlet can be a completely self-contained program, to ease server-side programming, generating content should be split into | The business logic (content generation), which governs the relationship between input, processing, and output. |
| The presentation logic (content presentation, or graphic design rules), which determines how information is presented to the user. | |
| controller | the servlet handles the HTTP protocol and coordination of which other servlets and auxiliary class methods to call |
| model | Java classes/JavaBeans handle the business logic |
| view | Java Server Pages handle presentation logic |
4. Advantages of Servlets over CGI
| Efficient | – Servlets run in the JVM. Each request is serviced using a thread rather than a new process (so lower overhead). - Though some scripting languages, e.g. perl on certain web servers do this now. |
| Convenient | – Provides infrastructure that parses and decodes HTML forms. |
| Powerful | – Can communicate directly with web server. – Multiple servlets can share database connections. – Simplifies session tracking. |
| Portable | – Written in Java and follows standard API. |
| Secure | – CGI often executed using O/S shells, which can cause many security breaches. – Array checking & exception handling is automatic in Java. |
| Inexpensive | – Many Java web servers are freely available. |
四、Servlets in Detail
1. A general purpose Web Server
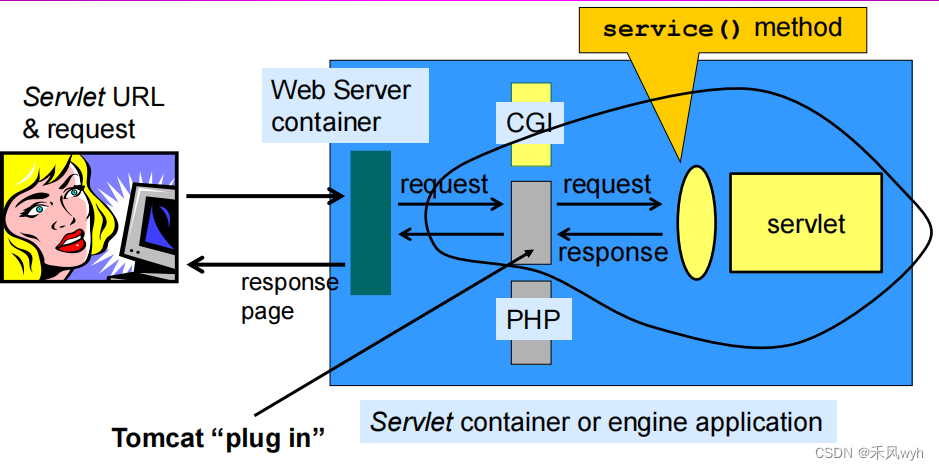
2. What servlets do
| request | Read any data sent by the user |
| Look up information embedded in HTTP request | |
| Generate results. | |
| response | Format results inside a document (e.g. HTML, XML, GIF, EXCEL). |
| Set appropriate HTTP response parameters. | |
| Send the document back to the client. |
3. Typical generic servlet code
import java.io.*;
import jakarta.servlet.*;
public class AnyServlet extends GenericServlet {public AnyServlet() {} // constructor – BUT USE THE DEFAULT// NEVER ANY NEED TO WRITE ONE//ONLY creates an object, becomes a “proper” servlet after init().public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;// The method is actually called by container when servlet is// first created or loaded.public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)throws ServletException, IOException;// Called by a new thread (in the container) each time a// request is received.public void destroy();// Called when servlet is destroyed or removed.
}4. A Servlet is “deployed” in a container
5. Dissecting the Container’s actions
GET /myServlet/BMIInfo height=156&name=paula+fonseca HTTP/1.1
public class BMIServlet extends HttpServlet {public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throwsIOException, ServletException {// ...String ht = request.getParameter(“height”);// ...}}
6. The servlet life cycle
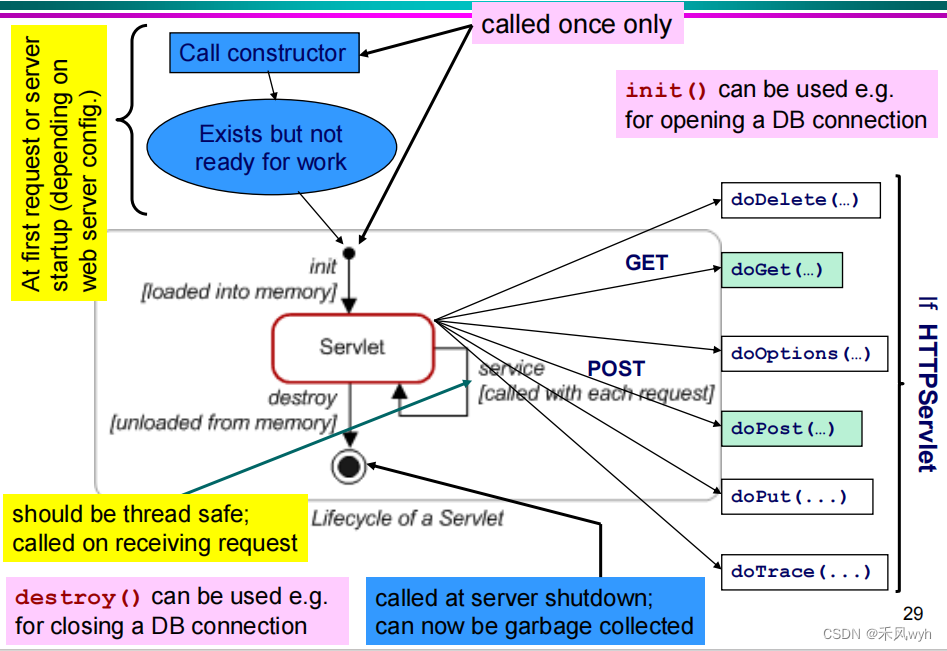
7. methods & inheritance
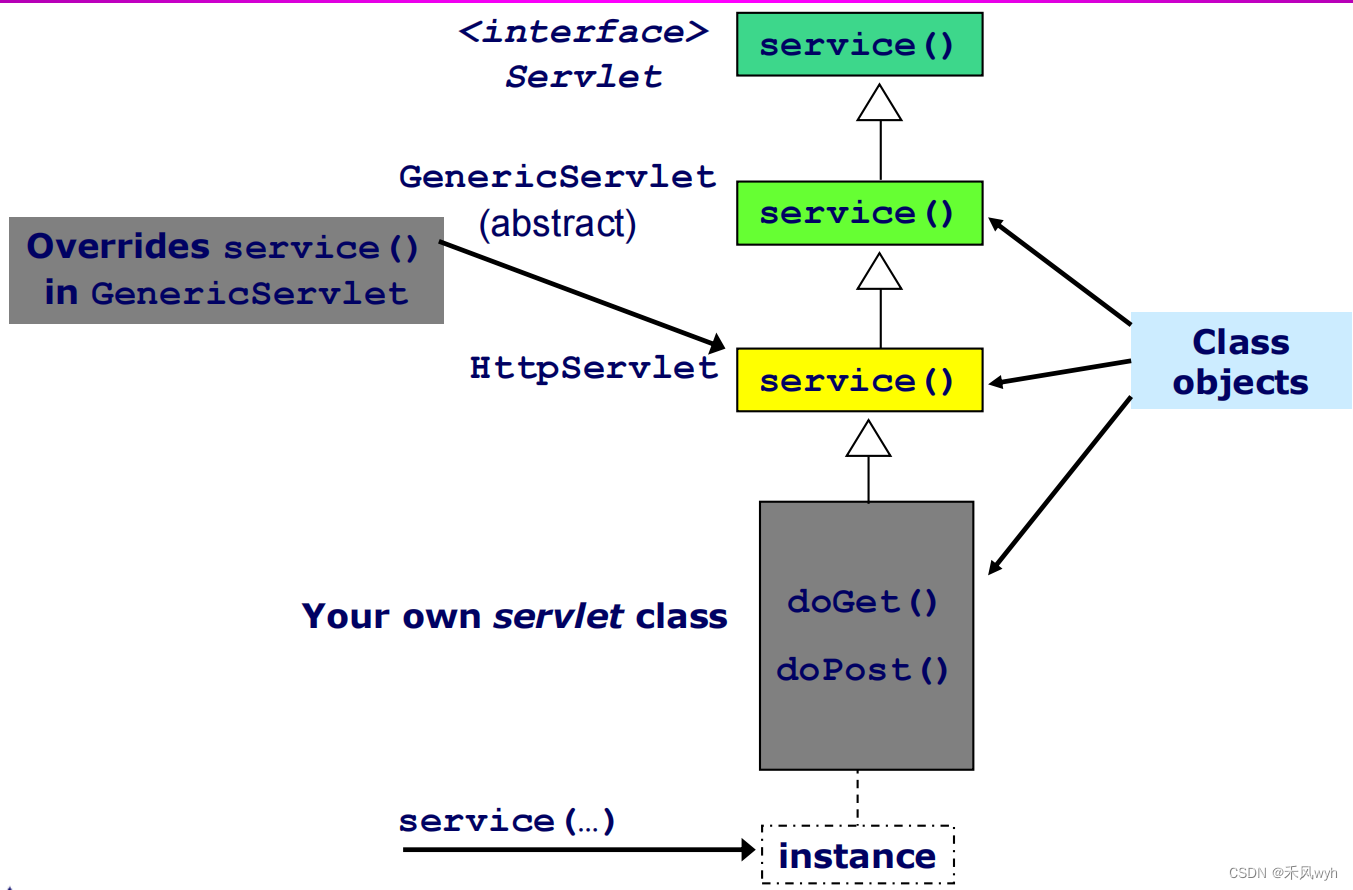
8. Servlet’s Life cycle
| Constructor (no arguments) | – not written or called by a developer – called by the container |
| public void init() | – called after constructor – called once, at the beginning (so potentially useful for initialisation of, e.g. databases) – can be overridden by the developer |
| public void service(…) | – rarely overridden by thedeveloper – called everytime |
| public void doGet() / public void doPost() | – must be written by the developer – must match the HTTP method in <form> in the HTML |
| public void destroy() | – must be written by the developer |
五、 Configuration Servlets To Run In Tomcat
1. Mapping names using the Deployment Descriptor (DD)
//For each servlet in the web application.
//Internal name of servlet can be “anything” following XML rules.
<web-app ...><servlet><servlet-name>…</servlet-name>//maps internal name to fully qualified class name (except without .class)<servlet-class>…</servlet-class>//maps internal name to public URL name e.g. /makebooking</servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>…</servlet-name><url-pattern>…</url-pattern ></servlet-mapping>
...
</web-app>2. Servlet Mapping Examples
- HTML:<FORM method=“post” action=“/servlet/MyTest.do”>- Server (webapps):WEB-INF/classes/Echo.class<servlet><servlet-name>......</servlet-name><servlet-class>.....</servlet-class></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>......</servlet-name><url-pattern>.......</url-pattern ></servlet-mapping>- HTML:<FORM method=“post” action=“/servlet/Test”>- Server (webapps):WEB-INF/classes/foo/Name.class<servlet><servlet-name>......</servlet-name><servlet-class>.....</servlet-class></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>......</servlet-name><url-pattern>.......</url-pattern ></servlet-mapping>
3. Example: A Small Form
//SmallForm.html
<html><title>Sending Form Information to a Servlet</title><body><form action="http://localhost:8080/servlet/elem004.ProcessSmallForm"method="post">//Can use absolute or relative URLs or pre-configured names.Please input your login: <br><input type="text" name="Login"><input type="submit" value="Login"></form></body>
</html>//the Deployment Descriptor (web.xml) and the servlet
<servlet><servlet-name>smallForm</servlet-name><servlet-class>SmallFormServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping><servlet-name>smallForm</servlet-name><url-pattern>/servlet/elem004.ProcessSmallForm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>4. Putting everything in the right place
| Level 1 | WEB-INF (folder) and .html, .jsp |
| Level 2 | (inside WEB-INF folder): web.xml and classes (folder) |
| Level 3 | (inside classes folder): servlet .class files (and other “business” class files e.g. JavaBeans) |
5. Servlet initialisation & Servlet Configuration object
6. Example: DD’s init parameters (web.xml for Tomcat)
<web-app xmlns=“http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee”xmlns:xsi=“http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance”xsi:schemaLocation=“http//java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2.4.xsd”version=“2.4”><servlet><servlet-name>Hello World Servlet</servlet-name><servlet-class>S1</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>lecturersEmail</param-name><param-value>paula.fonseca@qmul.ac.uk</param-value></init-param>//Container reads these & gives them to ServletConfig object.</servlet>
</web-app>out.println(getServletConfig().getInitParameter(“lecturersEmail”));Returns the servlet’s ServletConfig object (all servlets have this method).Getting a parameter value from the ServletConfig object; this code is in servlet.
7. Creating a servlet: ServletConfig and init(…)
| Step 1 | container reads the deployment descriptor |
| Step 2 | container creates new ServletConfig object |
| Step 3 | container creates name/value pair (Strings) for each servlet init-param |
| Step 4 | container passes references to these to the ServletConfig object |
| Step 5 | container creates new instance of the servlet class |
| Step 6 | container calls servlet’s init() method passing in reference to the ServletConfig object |
六、Thread Safety And Putting Things Together
1. Instance Variables
public class ExampletServlet extends HttpServlet {
private int age;
public void init() { age = 0; }
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws
IOException, ServletException {
age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter(“age”));
response.setContentType(“text/html”);
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println(“<HTML><BODY>You are ” + age + “ weeks old”);
out.println(“</BODY></HTML>”);
out.close();
}
}2. The 3 Threads access same Resources
3. Access – introducing the ServletContext object
<web-app ...> ...<servlet><servlet-name>...</servlet-name><servlet-class>...</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>...</param-name><param-value>...</param-value></init-param></servlet> ... + other servlets<context-param><param-name>HOP_Email</param-name><param-value>g.tyson@qmul.ac.uk</param-value></context-param>
...
</web-app>Note: Not inside any servlet. These are parameter namevalue pairs: both are strings.
4. To access web app parameters in servlet code
5. ServletContext also has attributes
6. Servlets – The Basics: Key Points & What we can’t do yet
| How to call a servlet in an HTML form | What a deployment descriptor does |
| How to write a servlet | Where to deploy files |
| How to access client information | Servlet life-cycle |
| Initialisation | – ServletConfig – ServletContext |
| Have a conversation with a client | – Shopping basket – Session object |
| Run any code before a servlet starts | – E.g. Database set up – Listeners |
| Send client information, or control, to another servlet/JSP | – Could be in another web server – Redirect and forward |
7. Extracting unknown parameters and multiple values
| String getParameter(String) | parameter name is known: – returns null if unknown parameter; – returns "" (i.e. empty string) if parameter has no value. |
| Enumeration getParameterNames() | obtain parameter names |
| String[] getParameterValues(String) | obtain an array of values for each one: – returns null if unknown parameter; – returns a single string ("") if parameter has no values. Case sensitive. |
8. Example: A Big Form
//BigForm.html
<form action="http://localhost:8080/servlet/elem004.ProcessBigForm"method="post">Please enter: <br><br>Your login: <input type="text" name="Login"> <br><br>Your favourite colour:<input type="radio" name="Colour" value="blue">Blue<input type="radio" name="Colour" value="red">Red<input type="radio" name="Colour" value="green">Green <br><br>//Single-value parameters.Which of these courses you are taking: <br><input type="checkbox" name="Course" value="elem001">ELEM001 <br><input type="checkbox" name="Course" value="elem002">ELEM002 <br><input type="checkbox" name="Course" value="elem003">ELEM003 <br><input type="checkbox" name="Course" value="elem004">ELEM004 <br><input type="submit" value="Send to Servlet">//Multiple-value parameter.
</form>
//After BigForm is processed.getParameterNames() returns parameters in no particular order.//ProcessBigForm.java
//More code here ...out.println("<table border=1>");// Obtain all the form’s parameters from the request object.Enumeration paramNames = req.getParameterNames();while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {String paramName = (String) paramNames.nextElement();// Obtain values for this parameter and check how many there are.String[] paramValues = req.getParameterValues(paramName);if (paramValues.length == 1) { // a single valueString paramVal = req.getParameter(paramName);out.println("<tr><td>" + paramName +"</td><td>"+ paramVal + "</td></tr>");}else { // If several values print a list in the table.out.println("<tr><td>" + paramName +"</td><td><ul>");for (int i = 0; i < paramValues.length; i++)out.println("<li>" + paramValues[i] + "</li>");out.println("</ul></td></tr>");}}out.println("</table>");out.close();
}
这篇关于【高级网络程序设计】Week3-2 Servlet的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




