本文主要是介绍寻找场景_柔性绿色无线接入网的负载均衡问题8.29,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
- 要素
-
- 柔性 elastic
-
- 绿色 green; energy-efficient
-
- 意图驱动 intent-driven
-
- 资源块 resource block
-
- 负载均衡 load balancing(among multiple base stations)
-
- 干扰管理 interference management(among multiple access networks)
1.大环境:智简6G无线接入网
1.1 IDN:意图转译网络intent-driven network
RAN:radio access network
ID-RAN:intent-driven RAN
IDN组成:
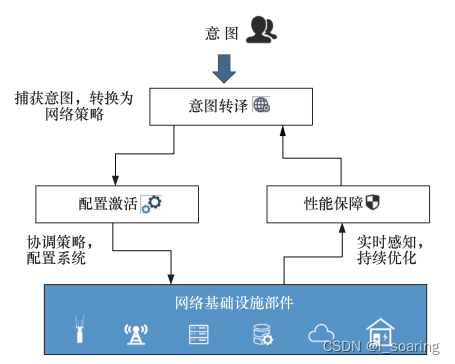
1.2 意图驱动无线接入网ID-RAN
ID-RAN系统架构
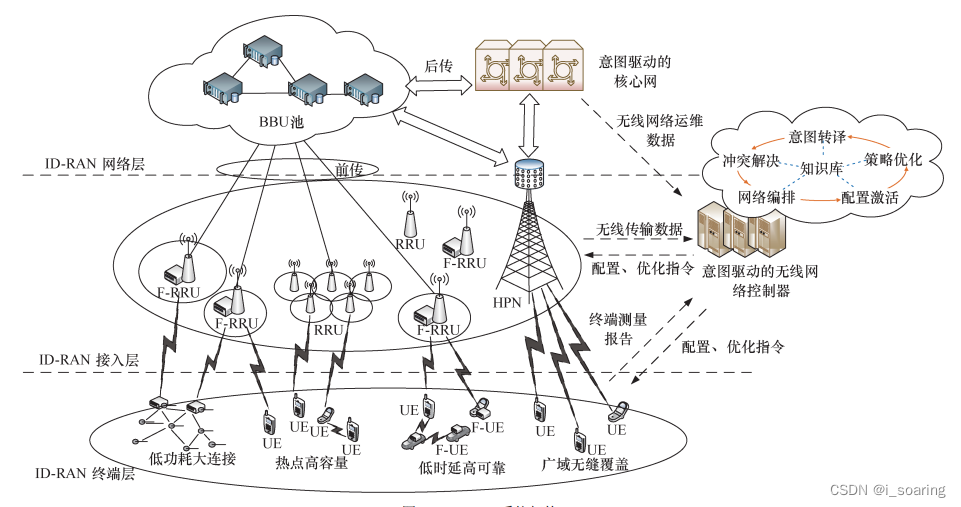
- 功能模块
- ①意图转译
②冲突解决
③网络编排
④配置激活
⑤策略优化 关键技术 - ①无线意图转译
②意图冲突解决
③意图组网柔性构建
④意图组网实施
⑤意图组网性能评估与优化
1.2.1 无线意图转译
转译三步:step1: NLP提取关键(命名实体识别NER, name entity recognition, e.g. BiLSTM-CRF, IDCNN-CRF, FudanNLP, etc.)
无线意图语言模型
[结果,操作,对象]
- 结果
- 业务类型
性能指标
期望状态
时空约束 操作 - 拓扑结构
接入模式
资源分配
网络约束 对象 - 物理节点
无线资源
缓存资源
计算资源
1.2.2 意图冲突解决
- 问题
- 网元参数调节冲突
无线网络资源分配不足
网络性能下降
本质:同种优先级对同种物理资源的争夺
目标:尽可能多满足意图多种网络优化目标(多目标联合优化)
算法:
①数值算法:多目标->单目标
<主要目标法、线性加权法、理想点法、分层序列法>
②智能算法:
<遗传算法、模拟退火算法、粒子群算法、
蚁群算法、Pareto 进化神经网络、模糊神经网络、
博弈论>
还有动态的多目标优化:
<非支配排序遗传算法、多目标粒子群优化算法>
(可以灵敏地检测环境的变化,并通过多样性引入机制、多样性保持机制、预测机制等应答方法有效响应环境变化,及时调整解集搜索方向,找到新环境下的 PS, Pareto Set解集)
1.2.3 意图组网柔性构建⭕⭕⭕
功能模块中网络编排环节,结合无线网络资源现状和网络配置经验,将无线意图转译输出的结构
随着云计算技术的发展,无线网络的终端测量数据以及信号传输过程中的大数据可以得到有效的存储,利用数据挖掘和 AI 技术挖掘数据的内在特征,并通过专家学习系统,获得同等或者超过人工运维的智能组网水平。强化学习旨在通过与环境频繁交互获得的奖惩值指导智能体的行为选择,并采用“试错”方式使智能体做出能够得到最大环境奖励的决策。考虑无线网络的时变性对组网策略自适应度的要求,可利用深度强化学习(DRL, deep reinforcement learning),通过采集网络环境高维数据,根据优化参考目标制定匹配于用户需求的组网策略,实现ID-RAN 的柔性组网过程
(终端数据-联邦学习;奖惩值、采集高维数据replay buffer?-DQN;)
基于DRL的意图组网策略构建:
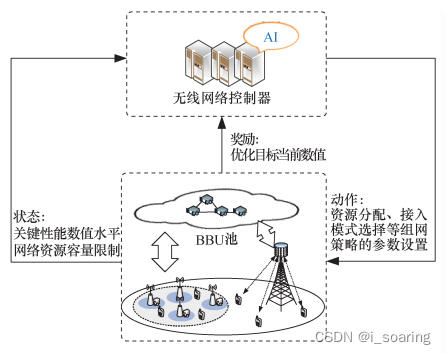
(BBU:基带单元Baseband Unite
RRU:射频拉远模块Remote Radio Unite)
RRH:远程无线电头remote radio head
1.2.4 意图组网实施
策略转换为无线网络基础设施控制指令
1.2.5 意图组网性能评估与优化
持续监测网络的实时性能状态
主动故障预测体验优化
将网络历史测量参数和性能数据输入到深度神经网络中,获得网络测量参数与关键性能状态等级的映射关系,从而通过实时测量参数预估网络关键性能指标(KPI, key performance indicator)参数可达到的数值等级
2.场景:绿色和柔性无线接入的软件定义超蜂窝架构
- 柔性 elastic
- 绿色 green; energy-efficient
- 意图驱动 intent-driven
- 资源块 resource block
- 负载均衡 load balancing(among multiple base stations)
- 干扰管理 interference management(among multiple access networks)
回顾
有些文献旨在从控制流量解耦的空中接口、基于云的RANs和软件定义的RANs的角度来更新RANs
本文
提出了一个软件定义的超蜂窝架构(SDHCA),确定了一种可行的方法来集成上述三个趋势,以实现绿色和弹性无线接入。进一步提出了实现SDHCA的关键实现技术,包括空接口分离、绿色基站操作和基站功能虚拟化,以及SDHCA的硬件测试平台
2.1 新兴RAN架构
蜂窝网络:分布式–>软件定义,静态功率可减小,绿色,5G用电巨量⭕⭕
控制\流量解耦的空中接口:
具有信号和数据分离的特点,旨在灵活有效地控制小单元,以提高吞吐量和基于BS睡眠的节能。为了使小区覆盖更适应业务动态,需要将部分控制信令功能与数据功能解耦,按需提供数据流量服务,同时控制平面始终“开”以保证基本覆盖。
基于云的RANs
将蜂窝网络改造为具有集中基带处理和远程无线电头(rhs)的大规模BSs,进一步发展为具有基于云的基带处理池[3]和BS功能虚拟化。
软件定义的RANs
从有线网络中得到启发的软件定义网络(SDN),将控制平面和数据平面分离,实现数据转发的集中优化。
三个视角需要深度融合
2.2 SDHCA:软件定义超蜂窝架构
software-defIned hyper-cellular ArchItecture
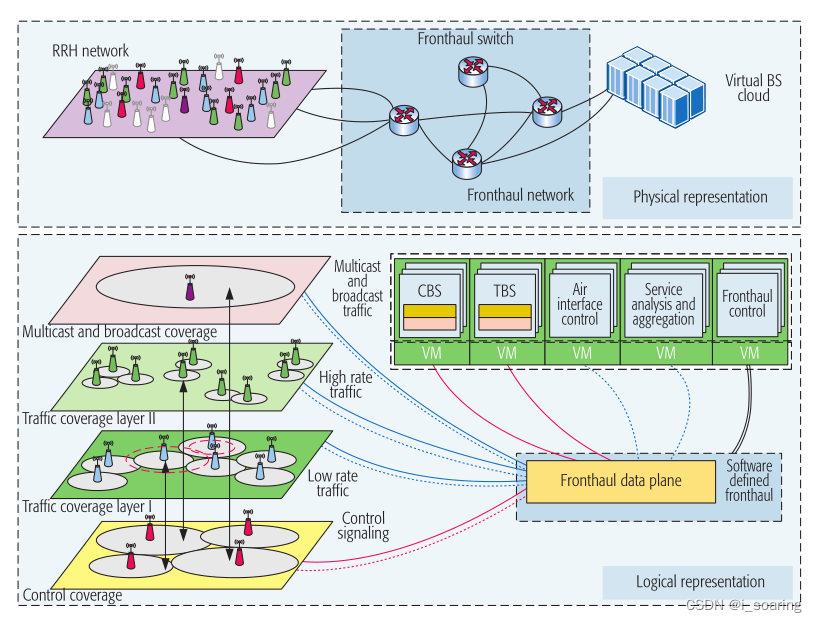
SDHCA设计基于空中接口分离、云RAN和SDN的深度融合。
它利用了云基础设施,云基础设施可以分为三个子系统:RRH网络、前运网络和虚拟BS (VBS)云。
为不同的用户流量类型提供了一个控制覆盖层和多个概念层。
2.2.1 关键特征
①控制\数据分离。the separation lies in three aspects:
a. air interface空中接口: CBS(control base station) takes charge of control coverage;TBS(traffic base station)takes charge of traffic coverage
b.infrastructure基础设施: software in charge of the network functions is separated from the hardware that forwards or transmits the data,一个RRH可以被动态配置为充当CBS或TBS,甚至两者兼有(即,在充当CBS时处理一些流量)。
c.plane decoupling平面解耦: control planes and data planes of SDF network are decoupled(SDF: software-defined fronthaul)
②CBS作为RAN控制器
CBS 关注移动用户,控制fronthaul network,TBS则是其覆盖范围的基础,so that CBS can have a global view of the RAN in the local geographic area, optimize the on-demand configuration and activation of the TBS so that the network resources(including spectrum resources and energy resources)can match the dynamic traffic in an elastic way⭕⭕
When the traffic load changes, a CBS can also control the cell zooming behavior of active TBSs to balance the load控制活跃TBS的单元缩放行为⭕⭕⭕
③通过虚拟化实现软件定义的网络功能
network functions e.g. air interface control空中接口控制, service analysis and aggregation服务分析和聚合, baseband sample generation基带采样生成, the fronthaul control plane前传控制平面 can be realized by virtual machines and the functions can be easily programmed and updated, allowing for felxible and efficient network operations, which potentially reduces computing energy consumption减少计算能源消耗⭕⭕
2.2.2 技术
①空中接口的分离
极端分离 extreme separation
功能分离√ functionality separation
functionality:网络向移动用户提供的基本功能集
including: synchronization, broadcast of system information, paging, multicast(low-rate data transmission), unicast(high-rate data transmission)
CBS in charge of synchronization, broadcast of system information, paging, multicast
TBS in charge of synchronization and unicast
②绿色基站操作
③基站功能虚拟化
3.场景:ERON:一种用于毫米波5G无线接入网络的节能柔性射频光架构
ERON: an energy-efficient and elastic RF-optical architecture for mmWave 5G radio access networks
- 柔性 elastic
- 绿色 green; energy-efficient
- 意图驱动 intent-driven
- 资源块 resource block
- 负载均衡 load balancing(among multiple base stations)
- 干扰管理 interference management(among multiple access networks)
本文提出了一种用于毫米波(mmWave)5G无线接入网络的弹性射频光网络(ERON)架构解决方案。ERON架构在无线电单元处使用光子增强多波束毫米波空间复用能力来实现能量效率和吞吐量弹性。硬件资源的集中化以及数据单元中RF和光资源的集中管理提供了高的资源共享增益。对ERON的光可调谐毫米波5G系统的能量效率的数值研究表明,ERON的能量效率比传统数字和混合RF波束形成实现高5倍。我们还进行了一项用户移动性感知网络资源研究,结果表明,与传统的无线接入网络实现相比,网络资源共享增益为10 dB
4.柔性RAN:一种适用于云无线接入网络的自适应多级柔性模型
Elastic-RAN: An adaptable multi-level elasticity model for Cloud Radio Access Networks
- 柔性 elastic
- 绿色 green; energy-efficient
- 意图驱动 intent-driven
- 资源块 resource block
- 负载均衡 load balancing(among multiple base stations)
- 干扰管理 interference management(among multiple access networks)
云无线电接入网络(C-RAN)通过采用基带单元(BBU)运行到云计算资源中 从而利用分布式系统的灵活性和云柔性的架构,越来越受到关注。C-RAN中的一个重大挑战在于协调计算资源以高性能和低基础设施成本处理传入请求的高度复杂性。在这方面,本文提出了柔性RAN模型,该模型为C-RAN提出了多层次的自适应柔性。
第一,我们探索多层次multi-level特性如下:
(i)BBU池的一个层次(即, 物理机器),考虑到特定BBU池的高流量;
(ii)由于处理传入请求的高CPU和内存需求,BBU本身(虚拟机)的另一个级别。
第二, 自适应 adaptive特征指的是可成型的柔性颗粒,这两个先前级别的资源都尽可能接近当前的加工需求。考虑到CPU和网络需求,我们评估了模拟不同负载分布的柔性运行实验。我们观察到,与传统的C-RAN相比,柔性RAN可以在执行时间上实现高达64%的增益。使用所提出的技术的蜂窝网络运营商将花费更少的能量,并且将具有根据其接入网络中的需求动态调整基带信号处理的解决方案。
云柔性是实现云中动态数量的BBU池的技术之一。为了实现动态扩大或减少资源数量的好处,C-RAN柔性的采用带来了几个挑战:
(i)资源的编排,其中实例的每次添加或删除都需要流程重组和通信拓扑的更新[8];
(ii)有效的负载平衡技术,用于在当前BBU之间分配负载,以提供敏捷处理和低基础设施成本[9,10];⭕⭕⭕
(iii)不同的负载需求可能会受到负载突然尖峰或下降的影响,因此产生假阳性或假阴性柔性作用[8];
(iv)柔性操作不会导致应用程序正常执行的性能下降,包括任务的分配和处理。
related paper:
[8] R. da Rosa Righi, V.F. Rodrigues, C.A. da Costa, G. Galante, L.C.E. De Bona, T. Ferreto, Autoelastic: Automatic resource elasticity for high performance applications in the cloud, IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 4 (1) (2016) 6–19.
[9] M.A. Marotta, N. Kaminski, I. Gomez-Miguelez, L.Z. Granville, J. Rochol, L. DaSilva, C.B. Both, Resource sharing in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks, IEEE Wirel. Commun. 22 (3) (2015) 74–82.
[10] T. Duan, M. Zhang, Z. Wang, C. Song, Inter-BBU control mechanism for load balancing in C-RAN-based BBU pool, in: Computer and Communications, ICCC, Chengdu, 2017.
[12] 根据负载动态映射资源 M. Qian, Y. Wang, Y. Zhou, L. Tian, J. Shi, A super base station based centralized network architecture for 5G mobile communication systems, Digit. Commun. Netw. 1 (2) (2015) 152–159.
[15] 呼叫接纳控制call admission control CAC算法 T. Sigwele, P. Pillai, Y.F. Hu, Call admission control in cloud radio access networks, in: International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, FiCloud, Barcelona, 2014.
[16] 负载分数用于决策(分布式\集中式) H. Taleb, M.E. Helou, K. Khawam, S. Lahoud, S. Martin, Centralized and distributed RRH clustering in cloud radio access networks, in: Computers and
Communications, ISCC, Heraklion, 2017.
[7] 一种集中式框架 S. Bhaumik, S.P. Chandrabose, M.K. Jataprolu, G. Kumar, A. Muralidhar, P.
Polakos, V. Srinivasan, T. Woo, CloudIQ: A framework for processing base stations in a data center, in: Mobile Computing and Networking, Istanbul, 2012, pp. 125–136.
[19] 云资源管理模型 A. Al-Dulaimi, S. Al-Rubaye, Q. Ni, Energy efficiency using cloud management of LTE networks employing fronthaul and virtualized baseband processing pool,
IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. PP (99) (2016) 1–12.
[20] 智能流量和弹性资源模型 T. Sigwele, P. Pillai, Y.F. Hu, iTREE: Intelligent traffic and resource elastic energy scheme for Cloud-RAN, in: Future Internet of Things and Cloud, FiCloud, Rome,
2015.
[21] 路由数据以实现网络负载平衡 M. Khan, R. Alhumaima, H. Al-Raweshidy, Quality of service aware dynamic BBU-RRH mapping in cloud radio access network, in: Emerging Technologies,
ICET, Peshawar, 2016.
[22] 启发式平衡负载 S. Scholz, H. Grob-Lipski, Reallocation strategies for user processing tasks
in future Cloud-RAN architectures, in: Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, PIMRC, Valencia, 2016.
[23] 云RRH:动态集中式任务调度算法 O. Chabbouh, S.B. Rejeb, N. Agoulmine, Z. Choukair, Service scheduling scheme based load balancing for 5G/HetNets Cloud RAN, in: Advanced Information Networking and Applications, AINA, Taipei, 2017.
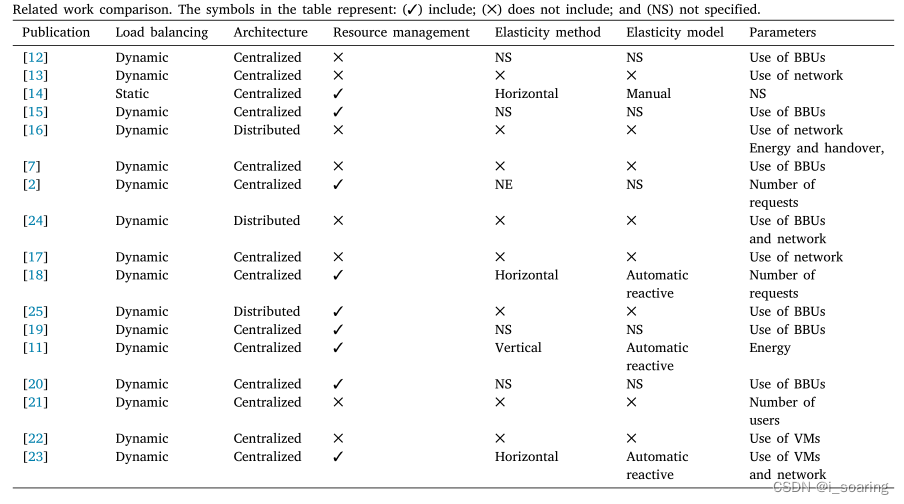
我们观察到,以前的绝大多数研究集中于创建和组合算法,以将RRH动态映射到BBU[2,7,9,11]。一些倡议还关注基于多个度量的负载平衡,以静态或动态地执行任务调度[2]。由于RRH的负载在一天中变化,因此该过程是相关的。此外,我们可以激活或停用BBU,因此执行RRH到仍在运行的BBU的新映射。然而,我们在C-RAN和柔性的联合分析中设想了三个主要挑战:
1.当大量传入消息发生时,我们观察到单个集中式BBU池中的网络瓶颈[2,7,11–23];
2.作者使用云柔性仅着眼于虚拟机(VM)级别,而没有物理机的概念及其最佳网络连接[2,7,11-25];
3.柔性颗粒不是自适应的,即 , 解决方案在柔性动作中始终使用相同数量的虚拟机,无论系统反应性和需求如何[2,7,11-25]。
考虑到上述差距和机遇,我们在本文中提出了柔性RAN模型,作为一种通过合并资源柔性和C-RAN来探索处理适应性的新方法。我们用两个主要概念探讨了加工适应性:多级和可调整大小的柔性颗粒。多级柔性指的是BBU池和BBU中资源的编排;“可调整大小的柔性颗粒”是指每个颗粒的柔性单位的动态定义,从而在充分处理输入负载的同时提高系统反应性。
4.1柔性RAN架构
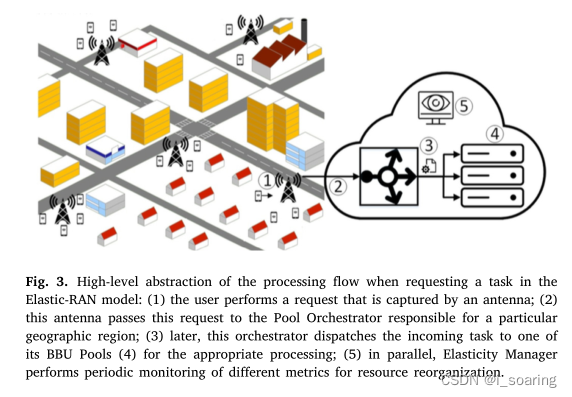
在柔性RAN模型中请求任务时处理流程的高级抽象:(1)用户执行由天线捕获的请求;(2) 该天线将该请求传递给负责特定地理区域的池协调器;(3) 随后,该编排器将传入任务分派到其BBU池(4)中的一个,以进行适当的处理;(5) 同时,柔性管理器对资源重组的不同度量进行定期监控。
负载分数 Load Score计算方法
自适应纹理 adaptive grain
多级柔性 multi-level elasticity
4.2 柔性RAN评估方法
总执行时间、能量和成本分析
5.基于C-RAN的BBU池中用于负载平衡的BBU间控制机制
[10] T. Duan, M. Zhang, Z. Wang, C. Song, Inter-BBU control mechanism for load balancing in C-RAN-based BBU pool, in: Computer and Communications, ICCC, Chengdu, 2017.
- 柔性 elastic
- 绿色 green; energy-efficient
- 意图驱动 intent-driven
- 资源块 resource block
- 负载均衡 load balancing(among multiple base stations)
- 干扰管理 interference management(among multiple access networks)
"4 C": centralized, cooperative radio, real-time cloud infrastructure, clean system
基于C-RAN的蜂窝系统打破了RRH和BBU之间的静态关系。此外,BBU池虚拟化技术使C-RAN能够处理动态调度和资源分配。特别是,由于集中式基带单元(BBU)池中的负载平衡能力,C-RAN可以解决蜂窝系统中流量分布不均匀的问题,例如潮汐的影响
5.1 C-RAN间BBU负载平衡的总体调度方案
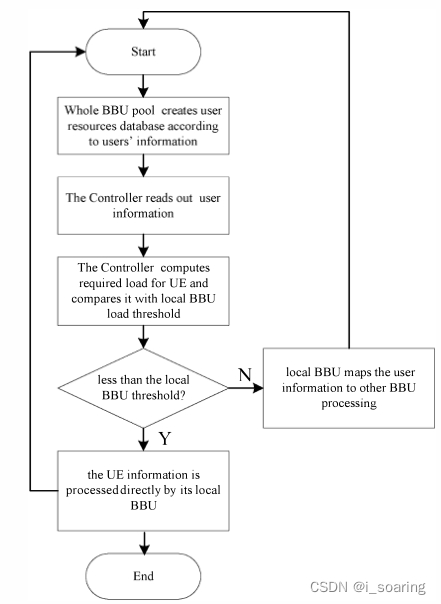
a Controller takes charge of all BBUs in a BBU pool
this mechanism is divided into 3 steps:
- initialize the user resource information
- RRU receive the request signal from user and send it to BBU pool, then BBU pool can read the information of the request signal and send the information to the Controller, at last, the Controller read the information and queries the load threshold of its local BBU
- Controller calculates the required load of UE, and compare it with the load threshold of the local BBU
- if possible, local BBU process, if not, local BBU maps the user information to other BBU by scheduling mechanism
5.2 C-RAN网络中BBU通信链路的建立
link establishment of BBU communication
- Controller sends scheduling command to the local BBU and other BBUs
- through scheduling command, local BBU gets the communication mode, and sends corresponding power and bandwidth, and then sends connection request to other BBUs during the delivery time of the scheduling command
- other BBUs read the scheduling command and get the communication mode, and receive the sending request message within the receiving time, and adjust the power and bandwidth according to the scheduling command, and send request response message to the local within delivery time
- local BBU’s receiving request response message makes sure the link between BBUs is established successfully
5.3 BBU池中特定的BBU间控制机制
从以上对整体调度方案的描述中,我们可以看到程序所有步骤中的一个重要点,即“本地BBU通过调度机制将用户信息映射到其他BBU处理”,它可以分为两个步骤:
首先,我们应该确保目的BBU的位置,这在本地BBU和其他BBU之间建立通信链路之前是必不可少的。
其次,我们应该设计从本地BBU到目标BBU的资源调度控制机制。
5.3.1 具体算法
定义:
i: source BBU node;
j: purpose BBU node
R(i,j): remaining bandwidth between i and j剩余带宽
b: user required bandwidth用户所需带宽
C(i,j): link capacity between i and j链路容量
E: link collection between the BBUs in the network链路集合
U(i,j): link bandwidth utilization of link (i,j)链路带宽利用率
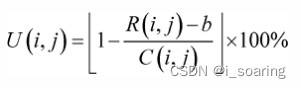
ω: service occupancy rate服务占用率 to measure the BBU’s remaining capacity for processing resources
k: services number of current node
N: total services number
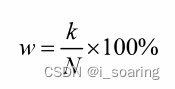
LSP:layered service provider分层服务提供程序,TCP/IP协议等的接口
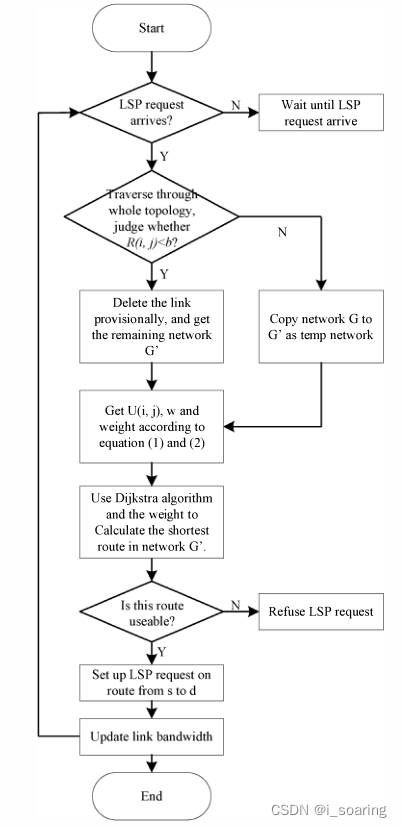
首先,为了找到LSP建立请求r(s,d,b)的最佳路由路径,图2中所示的具体算法步骤如下:
1)检测链路路径请求。如果存在要到达的构建请求r(s、d、b),则执行步骤2)。
2) 确保整个网络中的链路满足需求带宽,并将小于需求带宽b的链路剩余带宽标记为“忙”。获得名为G t的剩余网络。
3) 通过类型1)计算网络G中每个链路的带宽利用率U(i,j)。
4) 根据链路带宽利用率和服务占用率作为链路(i,j)的权重,我们使用Dijkstra算法确定剩余网络G t中节点对(s,d)之间的最短路径。如果路径存在,则进入步骤5),否则拒绝LSP建立请求,返回到步骤1),为下一个LSP建立要求做好准备。
5) 沿着从s到d的最短路径构建带宽需求为b单位的LSP,更新链路上的剩余带宽。
6) 返回步骤1),准备下一个LSP请求。
5.3.2 从源BBU到目的BBU的资源调度
在确认目的BBU后,控制器将执行资源调度指令。程序描述如下:
1)首先,确定是否需要调度。如果需要,源BBU将按需信号消息传递给控制器,控制器为其寻找最佳目的BBU。建立链接。
2) 源BBU将负载信息传递给目的BBU。
3) 删除链接。更新剩余带宽。
4) 返回步骤1),为下一个调度请求做准备。
5.4 仿真和讨论
DLB: dynamic load balancing
NDLB
The constraint is that all the services arrive according to the Poisson distribution
Poisson arrival rate is defined as the number of arrived services per unit time.
Per service payload refers to the ratio of per arrival service occupying its local BBU capacity
这篇关于寻找场景_柔性绿色无线接入网的负载均衡问题8.29的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




