本文主要是介绍【形式化方法】PartB:LA/LP Applications(N皇后问题),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
N-Queen Problem:
在作业3(挑战问题)中,我们在SAT之前解决了N个皇后的问题(4个皇后)。这个问题是关于把N个皇后放在一个N*N的棋盘上,这样就没有两个皇后互相威胁了。一种解决方案要求没有两个皇后共享同一行、列、对角线或反对角线。下图显示了N = 4的样本N -皇后谜题的解:
 这个问题的目标是在一个N*N棋盘,找出存在多少个解。
这个问题的目标是在一个N*N棋盘,找出存在多少个解。
SAT实现的基本思想是通过Bool值构造n-queen谜题约束。实际上,我们可以用LA来求解n-queen问题,它比SAT更容易理解,也更高效。其思路与求解子集和问题的思路相同。我们使用一个二维的0-1标志F来代表棋盘的每个单元格,F有值:
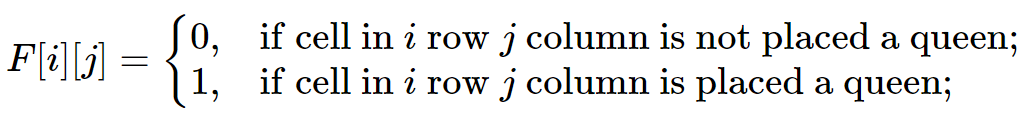 满足 0 < i <N, 0< j < N 。我们可以建立n-queen谜题的约束条件如下:
满足 0 < i <N, 0< j < N 。我们可以建立n-queen谜题的约束条件如下:
- 每一行只有一个皇后:
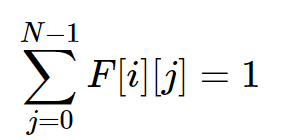 0 < i <N
0 < i <N - 每一列只有一个皇后:
 0 < j < N
0 < j < N - 每条对角线最多有1个皇后:
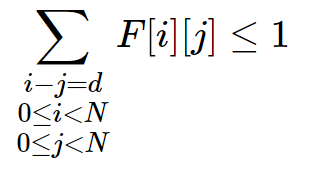 -N < d < N
-N < d < N - 每条反对角线最多有1个皇后:
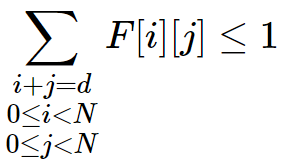 0 < d < 2N -1
0 < d < 2N -1
Exercise 11: 阅读queen.py Python文件中的代码,完成n_queen_la()方法,该方法使用0-1 ILA解决n-queen问题。您可以通过参考我们上面讨论的模型来构造约束,或者您可以提出您自己的约束。
# LA算法解决N皇后问题
def n_queen_la(board_size: int, verbose: bool = False) -> int:solver = Solver()n = board_size# Each position of the board is represented by a 0-1 integer variable:# ... ... ... ...# x_2_0 x_2_1 x_2_2 ...# x_1_0 x_1_1 x_1_2 ...# x_0_0 x_0_1 x_0_2 ...#board = [[Int(f"x_{row}_{col}") for col in range(n)] for row in range(n)]# only be 0 or 1 in boardfor row in board:for pos in row:solver.add(Or(pos == 0, pos == 1))# print(row)# @exercise 11: please fill in the missing code to add# the following constraint into the solver:# each row has just 1 queen,# each column has just 1 queen,# each diagonal has at most 1 queen,# each anti-diagonal has at most 1 queen.# raise Todo("exercise 11: please fill in the missing code.")for row in board:# print(row)solver.add(sum(row) == 1) # 约束1:一行只有一个皇后for col in board:# print(col)solver.add(sum(col) == 1) # 约束2: 一列只有一个皇后i = 0dia = []anti_dia = []# 对角线元素放到dia数组里面for row in board:j = 0for pos in row:if i == j:dia.append(pos)j = j + 1i = i + 1solver.add(sum(dia) <= 1) # 约束3:对角线最多只有一个皇后# print(dia)# 反对角线元素放到anti_dia数组里面i = 0for row in board:j = 0for pos in row:if i + j == n-1 :anti_dia.append(pos)j = j + 1i = i + 1# print(anti_dia)solver.add(sum(anti_dia) <= 1) # 约束4:反对角线最多只有一个皇后# count the number of solutionssolution_count = 0start = time.time()while solver.check() == sat:solution_count += 1model = solver.model()if verbose:# print the solutionprint([(row_index, col_index) for row_index, row in enumerate(board)for col_index, flag in enumerate(row) if model[flag] == 1])# generate constraints from solutionsolution_cons = [(flag == 1) for row in board for flag in row if model[flag] == 1]# add solution to the solver to get new solutionsolver.add(Not(And(solution_cons)))print(f"n_queen_la solve {board_size}-queens by {(time.time() - start):.6f}s")return solution_count
另一种解决N -queen问题的方法是使用回溯算法,但复杂度相对于棋盘大小N是指数级的。
Exercise 12:queen.py Python文件中的代码,在n_queen_bt()方法中有一个基于回溯的解决方案。尝试比较回溯算法和LA算法,通过改变棋盘大小N的值为其他值,哪一个更快?从结果中你能得出什么结论?
#回溯法解决N皇后问题
def n_queen_bt(board_size: int, verbose: bool = False) -> int:n = board_sizesolutions = [[]]def is_safe(col, solution):same_col = col in solutionsame_diag = any(abs(col - j) == (len(solution) - i) for i, j in enumerate(solution))return not (same_col or same_diag)start = time.time()for row in range(n):solutions = [solution + [col] for solution in solutions for col in range(n) if is_safe(col, solution)]print(f"n_queen_bt solve {board_size}-queens by {(time.time() - start):.6f}s")if verbose:# print the solutionsfor solution in solutions:print(list(enumerate(solution)))return len(solutions)
上述LA实现并不是求解n-queen问题的唯一算法。事实上,我们建立约束来描述问题的方式往往对算法的效率有很大的影响。
Exercise 13: 阅读queen.py Python文件中n_queen_la_opt()方法的代码。试着将此方法的效率与练习11中的实现进行比较。你的观察是什么?你能得出什么结论?
# LA优化算法解决N皇后问题
def n_queen_la_opt(board_size: int, verbose: bool = False) -> int:solver = Solver()n = board_size# We know each queen must be in a different row.# So, we represent each queen by a single integer: the column position# the q_i = j means queen in the row i and column j.queens = [Int(f"q_{i}") for i in range(n)]# each queen is in a column {0, ... 7 }solver.add([And(0 <= queens[i], queens[i] < n) for i in range(n)])# one queen per columnsolver.add([Distinct(queens)])# at most one for per anti-diagonal & diagonalsolver.add([If(i == j, True, And(queens[i] - queens[j] != i - j, queens[i] - queens[j] != j - i))for i in range(n) for j in range(i)])# count the number of solutionssolution_count = 0start = time.time()while solver.check() == sat:solution_count += 1model = solver.model()if verbose:# print the solutionsprint([(index, model[queen]) for index, queen in enumerate(queens)])# generate constraints from solutionsolution_cons = [(queen == model[queen]) for queen in queens]# add solution to the solver to get new solutionsolver.add(Not(And(solution_cons)))print(f"n_queen_la_opt solve {board_size}-queens by {(time.time() - start):.6f}s")return solution_countN = 4时,比较运行时间:
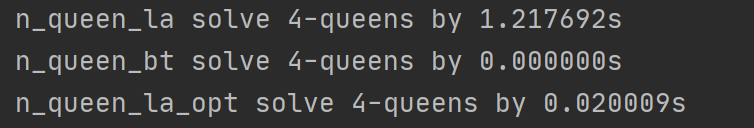
N = 5 时,比较运行时间:
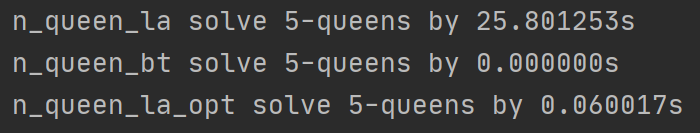
结论:
三种算法解决N皇后问题效率的比较: 用回溯法最快、LA优化算法其次、LA算法最慢
#中科大软院-hbj形式化课程笔记-欢迎留言与私信交流
#随手点赞,我会更开心~~^_^
这篇关于【形式化方法】PartB:LA/LP Applications(N皇后问题)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




