本文主要是介绍R语言绘制散点图结合边际分布图,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本博客主要介绍使用R语言利用ggplot绘制散点图,并且在图像的两边绘制边际分布图(包括边际直方图与边际密度函数)
我们这里介绍两种方法进行绘制:
- 主要使用
ggExtra结合ggplot2两个R包进行绘制。(胜在简洁方便) - 使用
cowplot与ggpubr进行绘制。(胜在灵活且美观)
下面的绘图我们均以iris数据集为例。
1. 使用ggExtra结合ggplot2
1)传统散点图
# library
library(ggplot2)
library(ggExtra)# classic plot
p <- ggplot(iris) +geom_point(aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, color = Species), alpha = 0.6, shape = 16) + # alpha 调整点的透明度;shape 调整点的形状theme_bw() +theme(legend.position = "bottom") + # 图例置于底部labs(x = "Sepal Length", y = "Sepal Width") # 添加x,y轴的名称
p

下面我们一行代码添加边际分布(分别以密度曲线与直方图的形式来展现):
2)密度函数
# marginal plot: density
ggMarginal(p, type = "density", groupColour = TRUE, groupFill = TRUE)

3)直方图
# marginal plot: histogram
ggMarginal(p, type = "histogram", groupColour = TRUE, groupFill = TRUE)

4)箱线图(宽窄的显示会有些问题)
# marginal plot: boxplot
ggMarginal(p, type = "boxplot", groupColour = TRUE, groupFill = TRUE)

5)小提琴图(会有重叠,不建议使用)
# marginal plot: violin
ggMarginal(p, type = "violin", groupColour = TRUE, groupFill = TRUE)

6)密度函数与直方图同时展现
# marginal plot: densigram
ggMarginal(p, type = "densigram", groupColour = TRUE, groupFill = TRUE)

2. 使用cowplot与ggpubr
1)重绘另一种散点图
# Scatter plot colored by groups ("Species")
sp <- ggscatter(iris, x = "Sepal.Length", y = "Sepal.Width",color = "Species", palette = "jco",size = 3, alpha = 0.6) +border() +theme(legend.position = "bottom")
sp
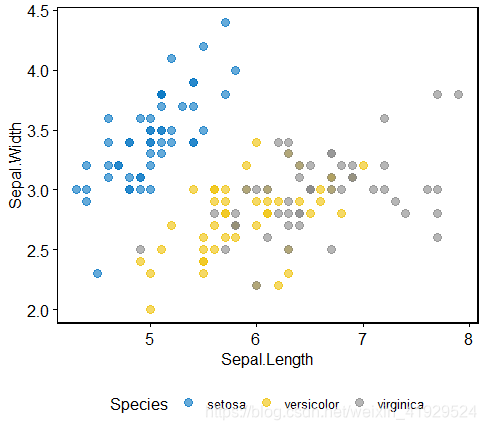
2)有缝拼接
① 密度函数
library(cowplot)# Marginal density plot of x (top panel) and y (right panel)
xplot <- ggdensity(iris, "Sepal.Length", fill = "Species",palette = "jco")
yplot <- ggdensity(iris, "Sepal.Width", fill = "Species", palette = "jco") +rotate()# Cleaning the plots
sp <- sp + rremove("legend")
yplot <- yplot + clean_theme() + rremove("legend")
xplot <- xplot + clean_theme() + rremove("legend")
# Arranging the plot using cowplot
plot_grid(xplot, NULL, sp, yplot, ncol = 2, align = "hv", rel_widths = c(2, 1), rel_heights = c(1, 2))

② 未被压缩的箱线图
# Marginal boxplot of x (top panel) and y (right panel)
xplot <- ggboxplot(iris, x = "Species", y = "Sepal.Length", color = "Species", fill = "Species", palette = "jco",alpha = 0.5, ggtheme = theme_bw())+rotate()
yplot <- ggboxplot(iris, x = "Species", y = "Sepal.Width",color = "Species", fill = "Species", palette = "jco",alpha = 0.5, ggtheme = theme_bw())
# Cleaning the plots
sp <- sp + rremove("legend")
yplot <- yplot + clean_theme() + rremove("legend")
xplot <- xplot + clean_theme() + rremove("legend")
# Arranging the plot using cowplot
plot_grid(xplot, NULL, sp, yplot, ncol = 2, align = "hv", rel_widths = c(2, 1), rel_heights = c(1, 2))
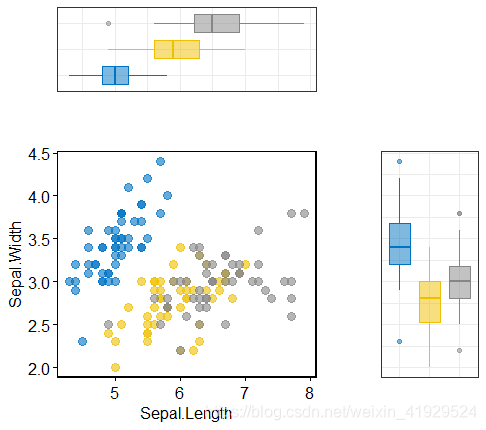
3)无缝拼接
# Main plot
pmain <- ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, color = Species)) +geom_point() +color_palette("jco")
# Marginal densities along x axis
xdens <- axis_canvas(pmain, axis = "x") +geom_density(data = iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, fill = Species),alpha = 0.7, size = 0.2) +fill_palette("jco")
# Marginal densities along y axis
# Need to set coord_flip = TRUE, if you plan to use coord_flip()
ydens <- axis_canvas(pmain, axis = "y", coord_flip = TRUE) +geom_density(data = iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width, fill = Species),alpha = 0.7, size = 0.2) +coord_flip() +fill_palette("jco")
p1 <- insert_xaxis_grob(pmain, xdens, grid::unit(.2, "null"), position = "top")
p2 <- insert_yaxis_grob(p1, ydens, grid::unit(.2, "null"), position = "right")
ggdraw(p2)

参考
- Articles - ggpubr: Publication Ready Plots——Perfect Scatter Plots with Correlation and Marginal Histograms
- Marginal distribution with ggplot2 and ggExtra
这篇关于R语言绘制散点图结合边际分布图的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



