本文主要是介绍从0开始写中国象棋-走一步棋(当门炮,马来跳)(C++),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在文章 从0开始写中国象棋-创建棋盘与棋子
中,我们已经可以看到象棋游戏的界面了。
这是因为,我们创建了棋盘(棋盘数组),并在棋盘上放置一些数字来表示棋子。
让棋子动起来
现在,我们打算让棋子动起来。
棋子动起来,其实很简单,比如开局 炮二平五。
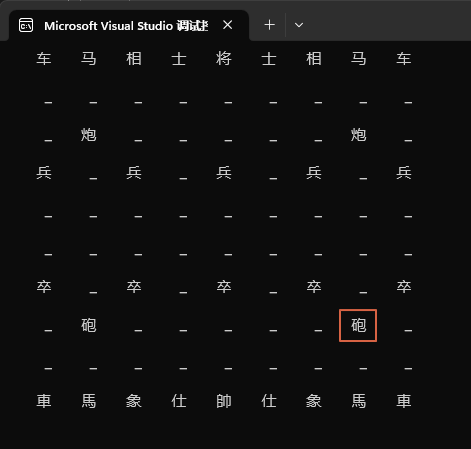
实际上就是棋子从棋盘上的一个位置移动到了棋盘的另一个位置。
实际上是棋盘在变化
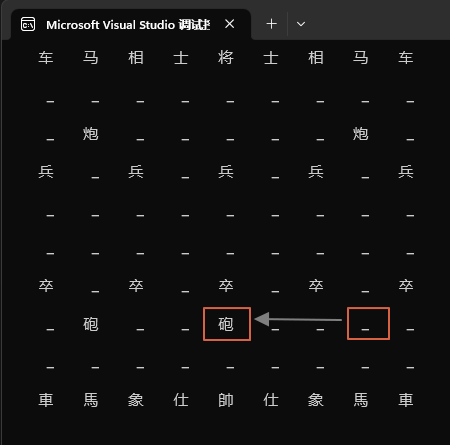
对应棋盘的变化就是,棋盘从:
变成了:
由于棋盘上的棋子就是一个一个的不同的数字,所以,从计算机的角度来说,走一步棋就是给二维数组的一个位置设置一个新数字。
也就是,起点位置元素重新赋值为0(表示这里没有棋子了,棋子走到其他位置去了);
终点位置元素重新赋值为炮的ID(表示炮走棋来到了这里)。
程序实现 GoAhead(OneStep)
现在我们希望告诉程序,走一步棋,从一个位置走到另一个位置,程序就能够实现这个目标。
由于这种需求是在下棋双方走棋的时候反复出现的,所以我们可以很方便的用函数来实现。
这个函数大概像下面这样:
bool GoAhead(from_row, from_col, to_row, to_col);其中,各个参数的意思是很明显的,我们就不解释了。
但是,函数返回值是bool,这个是干什么的呢?
因为用户可能会乱走棋,比如,蹩马腿了也要跳马,这个时候你就要告诉他不能走这步棋。这时候函数返回 false 。
现在让我们来实现这个函数:
bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col)
{//如果出发的地方没有旗子,就返回 falseif()
}这个时候我们才发现我们需要访问棋盘。
而棋盘是定义在main函数内的变量。我们访问不到。
怎么办?
C++全局变量
不在函数内定义的变量就叫全局变量。
为了能够让任何代码都访问到棋盘,我们在程序的一开始就定义棋盘。这样我们的函数就可以访问棋盘了。
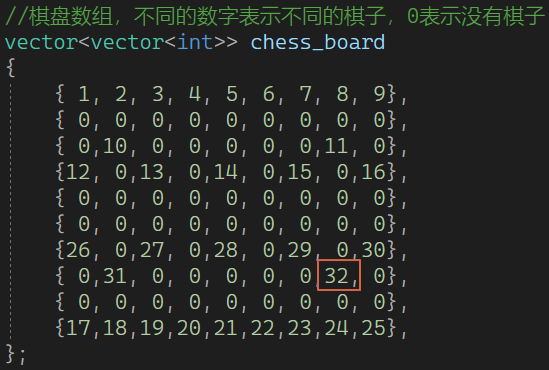
//棋盘数组,不同的数字表示不同的棋子,0表示没有棋子
vector<vector<int>> chess_board
{{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{ 0,10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,11, 0},{12, 0,13, 0,14, 0,15, 0,16},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{26, 0,27, 0,28, 0,29, 0,30},{ 0,31, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,32, 0},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25},
};bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col)
{//如果出发的地方没有旗子,就返回 falseif (chess_board[from_row][from_col] != 0){}else{return false;}
}谁能告诉我能否走到哪里?
现在的问题是,当走棋的起点有棋子的时候,这个棋子能否到达目的地位置?
也就是走棋的合理性问题。
这里门道就多了:马走日,相走田,车走直路,炮翻山,小卒一去不会还。
如何实现这样的需求呢?
C++的方式是使用多态来实现。伪代码像下面这样:
//棋子类的基类
struct chess_base
{// 纯虚函数,表示 chess_base 是一个抽象类,专门用来做基类;//GoAhead 用来给各个派生类来重新实现 overridevirtual bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col) = 0;
};struct Horse : public chess_base
{// 马实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){//ba la ba la ....return false;}
};struct King : public chess_base
{// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){//ba la ba la ....return false;}
};每个棋子都知道自己的规则,所以自己是知道能否走到目的地的。
这也就要求我们要替各个棋子来实现它们各自的走法。
棋子数组包含对象
之前,我们的棋子数组是不同位置(数组下标)表示不同棋子,棋子只有一个内容,就是它们的名字。
现在,我们希望用类对象来表示。名字只是棋子的一个成员变量。走棋GoAhead才是棋子的主要能力。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;//棋盘数组,不同的数字表示不同的棋子,0表示没有棋子
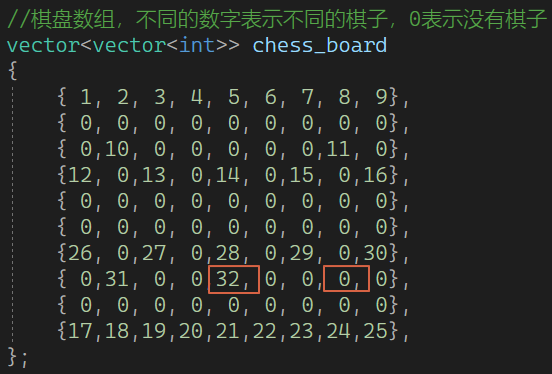
vector<vector<int>> chess_board
{{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{ 0,10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,11, 0},{12, 0,13, 0,14, 0,15, 0,16},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{26, 0,27, 0,28, 0,29, 0,30},{ 0,31, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,32, 0},{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25},
};//棋子类的基类
struct chess_base
{chess_base(const string& name1):name(name1){}// 纯虚函数,表示 chess_base 是一个抽象类,专门用来做基类;//GoAhead 用来给各个派生类来重新实现 overridevirtual bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col) = 0;string name;//棋子要显示的名字
};
//车 車
struct Chariot : public chess_base
{Chariot(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 马实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//ba la ba la ....return false;}
};
//马 馬
struct Horse : public chess_base
{Horse(const string& name1):chess_base(name1){}// 马实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//ba la ba la ....return false;}
};
//炮 砲
struct Cannon : public chess_base
{Cannon(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 马实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//ba la ba la ....return false;}
};
//将 帅
struct King : public chess_base
{King(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){//ba la ba la ....cout << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;return false;}
};
//士 仕
struct Official : public chess_base
{Official(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){//ba la ba la ....cout << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;return false;}
};
//相 象
struct Minister : public chess_base
{Minister(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){//ba la ba la ....cout << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;return false;}
};
//兵 卒
struct Soldier : public chess_base
{Soldier(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){//ba la ba la ....cout << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;return false;}
};vector<chess_base*> chess_man
{nullptr,//下标为0不用,编号从1开始//上方黑方棋子new Chariot("车"),new Horse("马"), new Minister("相"), new Official("士"), new King("将"), new Official("士"), new Minister("相"), new Horse("马"), new Chariot("车"),new Cannon("炮"),new Cannon("炮"),new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"),//下方红方棋子new Chariot("車"), new Horse("馬"), new Minister("象"), new Official("仕"), new King("帥"), new Official("仕"), new Minister("象"), new Horse("馬"), new Chariot("車"),new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"),new Cannon("砲"), new Cannon("砲"),
};int main(void)
{for (int row = 0; row < 10; row++){for (int col = 0; col < 9; col++){auto id = chess_board[row][col];if (id != 0){cout <<setw(5)<< chess_man[id]->name ;//输出一个棋子}else{cout<<setw(5) << "_";//表示棋盘上的一个位置}}cout << endl;cout << endl;}return 0;
}运行结果:

当门炮,马来跳
有了棋子对象之后,我们实现走棋就很好实现了。
// 当门炮 : 炮二平五 ID 为 32 从(7,7) 移动到 (7,4)chess_man[32]->GoAhead(7, 7, 7, 4);// 马来跳 : 炮8进7 ID 为 8 从(7,7) 移动到 (7,4)chess_man[8]->GoAhead(0, 7, 2, 6);此时,我们需要实现炮,马的 GoAhead 函数。
为了简单起见,我们不做合法性检查,让棋子直接在棋盘上从起点走到终点。
既然如此,其实所有棋子都是这样走棋的,我们把所有的棋子走棋都给实现了:
bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col)
{cout << "GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;
}完整的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;//棋盘数组,不同的数字表示不同的棋子,0表示没有棋子
vector<vector<int>> chess_board
{/* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8*//* 0*/{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9},/* 1*/{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},/* 2*/{ 0,10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,11, 0},/* 3*/{12, 0,13, 0,14, 0,15, 0,16},/* 4*/{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},/* 5*/{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},/* 6*/{26, 0,27, 0,28, 0,29, 0,30},/* 7*/{ 0,31, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,32, 0},/* 8*/{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},/* 9*/{17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25},
};//棋子类的基类
struct chess_base
{chess_base(const string& name1):name(name1){}// 纯虚函数,表示 chess_base 是一个抽象类,专门用来做基类;//GoAhead 用来给各个派生类来重新实现 overridevirtual bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col) = 0;string name;//棋子要显示的名字
};
//车 車
struct Chariot : public chess_base
{Chariot(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 马实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << "GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;}
};
//马 馬
struct Horse : public chess_base
{Horse(const string& name1):chess_base(name1){}// 马实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << "GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;}
};
//炮 砲
struct Cannon : public chess_base
{Cannon(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 马实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << "GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;}
};
//将 帅
struct King : public chess_base
{King(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout<<"GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;}
};
//士 仕
struct Official : public chess_base
{Official(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << "GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;}
};
//相 象
struct Minister : public chess_base
{Minister(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << "GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;}
};
//兵 卒
struct Soldier : public chess_base
{Soldier(const string& name1) :chess_base(name1) {}// 帅实现自己的走棋bool GoAhead(int from_row, int from_col, int to_row, int to_col){cout << "GoAhead " << from_row << "," << from_col << "," << to_row << "," << to_col << endl;//先保存原来的 ID, 为着放到终点auto id = chess_board[from_row][from_col];//离开之后,留下 0chess_board[from_row][from_col] = 0;//走到了目的地chess_board[to_row][to_col] = id;return false;}
};vector<chess_base*> chess_man
{nullptr,//下标为0不用,编号从1开始//上方黑方棋子new Chariot("车"),new Horse("马"), new Minister("相"), new Official("士"), new King("将"), new Official("士"), new Minister("相"), new Horse("马"), new Chariot("车"),new Cannon("炮"),new Cannon("炮"),new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"), new Soldier("兵"),//下方红方棋子new Chariot("車"), new Horse("馬"), new Minister("象"), new Official("仕"), new King("帥"), new Official("仕"), new Minister("象"), new Horse("馬"), new Chariot("車"),new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"), new Soldier("卒"),new Cannon("砲"), new Cannon("砲"),
};int main(void)
{// 当门炮 : 炮二平五 ID 为 32 从(7,7) 移动到 (7,4)chess_man[32]->GoAhead(7, 7, 7, 4);// 马来跳 : 炮8进7 ID 为 8 从(7,7) 移动到 (7,4)chess_man[8]->GoAhead(0, 7, 2, 6);for (int row = 0; row < 10; row++){for (int col = 0; col < 9; col++){auto id = chess_board[row][col];if (id != 0){cout <<setw(5)<< chess_man[id]->name ;//输出一个棋子}else{cout<<setw(5) << "_";//表示棋盘上的一个位置}}cout << endl;cout << endl;}return 0;
}运行效果
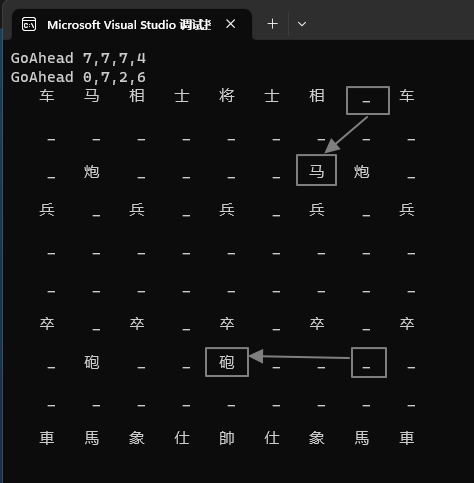
这篇关于从0开始写中国象棋-走一步棋(当门炮,马来跳)(C++)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




