本文主要是介绍《剑指offer》那些思路清奇的题目,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目:
- 《剑指offer》OJ🔗
- JZ70 矩形覆盖
- JZ39 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- JZ56 数组中只出现一次的两个数字
- JZ68 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- JZ82 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
- JZ53 数字在升序数组中出现的次数
- JZ38 字符串的排列
《剑指offer》OJ🔗
JZ70 矩形覆盖
当矩形长度为n时,矩形的覆盖情况可以是:
长度为n-1时的所有情况后边加一个竖着的矩形
长度为n-2时的所有情况后边加两个横着的矩形
所以与斐波那契数列类似。
class Solution {
public:int rectCover(int number) {if(number==0)return 0;int *num = new int[number+1];num[0]=1;num[1]=1;for(int i=2;i<=number;i++){num[i]=num[i-1]+num[i-2];}return num[number];}
};
JZ39 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
摩尔投票法
诸侯争霸,假设你方人口超过总人口一半以上,并且能保证每个人口出去干仗都能一对一同归于尽。最后还有人活下来的国家就是胜利。
初始化:候选人cand , 候选人的投票次数count = 0
遍历数组,如果count = 0, 表示没有候选人,则选取当前数为候选人 count++
如果count>0, 表示有候选人,如果当前数=cand,count++,否则
–count
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) {int cand=0;int count = 0;for(int i=0;i<numbers.size();i++)if(count==0){cand=numbers[i];count++;}else{if(numbers[i]==cand)count++;elsecount--;}return cand;}
};
JZ56 数组中只出现一次的两个数字
思路:两个相同的值异或为0,则所有值异或的结果是要找的两个值的异或的结果,异或结果中某一位为1,则要找的两个值这一位不同,根据这一位为0还是1,把数据分为两组,两组分别全部异或起来,两个结果就是要找的值,注意返回值类型,注意逻辑运算和比较运算的优先级。
vector<int> FindNumsAppearOnce(vector<int>& array) {int n=0; //所有值异或的结果for(auto e:array){n^=e;}int m=n; int i=0;while(1){if((m&1)==0){m=m>>1;i++;}elsebreak;}int n1=0,n2=0;for(auto e:array){if((e>>i&1)==0)n1^=e;elsen2^=e;}vector<int> a={n1,n2};if(n1>n2){a[0]=n2;a[1]=n1;} return a;}
JZ68 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
思路:
根节点作为当前节点开始,给定两值都比根节点小,两节点都在当前节点左子树,给定两值都比根节点大,两节点都在当前节点右子树,当前节点的值在给定值之间,当前节点就是解
int lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, int p, int q) {if(!root)return -1;if((p<=root->val&&q>=root->val)||(p>=root->val&&q<=root->val))return root->val;else if(p<root->val&&q<root->val)return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);elsereturn lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);}
JZ82 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
思路:递归,以根节点为当前节点,每次进入函数后sum减去当前节点的值,当当前节点为叶节点且sum为0,返回true
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {if(!root)return false;sum-=root->val;if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr&&sum==0)return true;return hasPathSum(root->left, sum)||hasPathSum(root->right, sum);}
因为找到一个解就满足,所以注意这里返回值的写法:
return hasPathSum(root->left, sum)||hasPathSum(root->right, sum);
JZ53 数字在升序数组中出现的次数
思路一:二分搜索
细节:通过< 和<= 分别找到数字第一次出现的下标和数字最后一次出现的下个位置的下标
如果数字不存在,都指向第一个大于数字的下边
int GetNumberOfK(vector<int> data ,int k) {int l1=0,r1=data.size();while(l1<r1){int mid=l1+(r1-l1)/2;if(data[mid]<k)l1=mid+1;elser1=mid;}int l2=0,r2=data.size(); while(l2<r2){int mid=l2+(r2-l2)/2;if(data[mid]<=k)l2=mid+1;elser2=mid;}return r2-r1;}
思路二:使用库函数
int GetNumberOfK(vector<int> nums ,int target) {return upper_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), target) - lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), target);}

返回一个迭代器,指向范围 [first,last) 中大于 val 的第一个元素
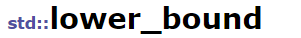
返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向范围 [first,last) 中不小于 val的第一个元素
JZ38 字符串的排列
思路:全排列,去重后返回。
class Solution {
public:vector<string> s;void Perm(string list, int k, int m){if (k == m){string temp;for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++){temp.push_back(list[j]);}if(find(s.begin(),s.end(),temp)==s.end())s.push_back(temp);}elsefor(int i=k;i<=m;i++){ swap(list[k],list[i]);Perm(list,k+1,m);swap(list[k],list[i]);}
}vector<string> Permutation(string str) {if(str.empty())return s;Perm(str,0,str.size()-1);return s;}
};
这篇关于《剑指offer》那些思路清奇的题目的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!