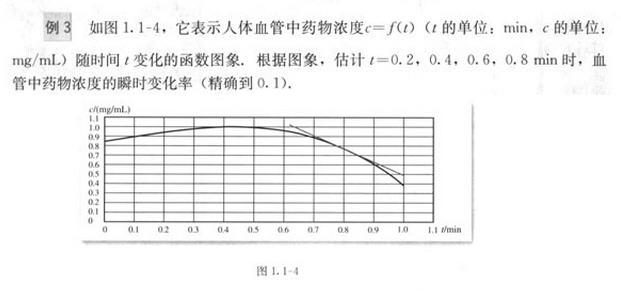
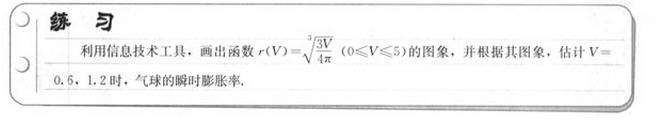
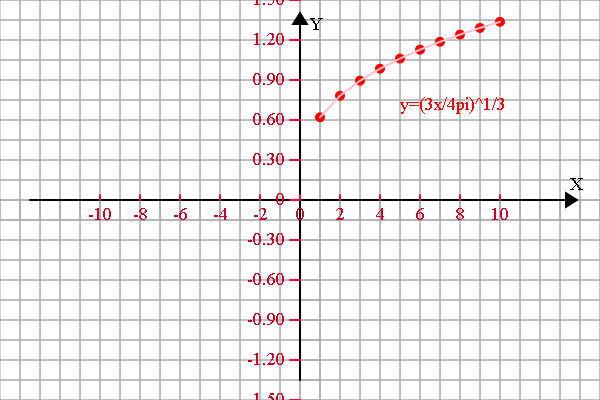
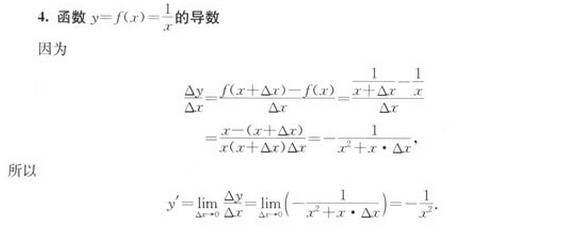
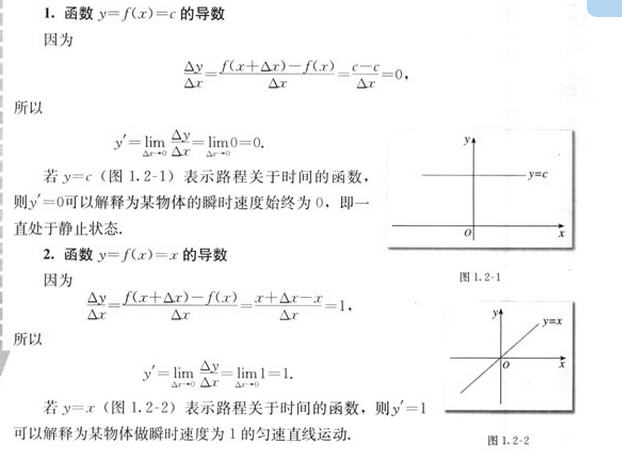
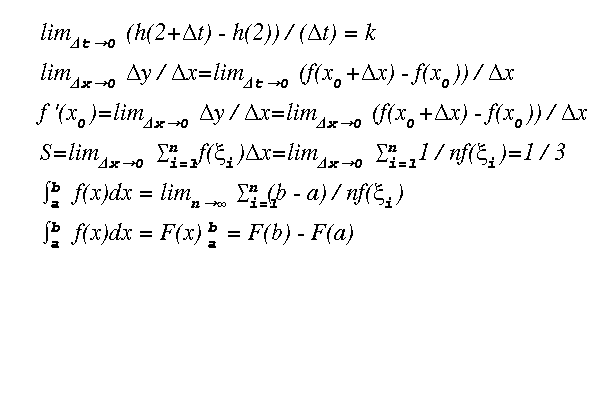本文主要是介绍[从头学数学] 第192节 导数及其应用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
剧情提要:
[机器小伟]在[工程师阿伟]的陪同下进入了[九转金丹]之第五转的修炼。
这次要研究的是[导数及其应用]。
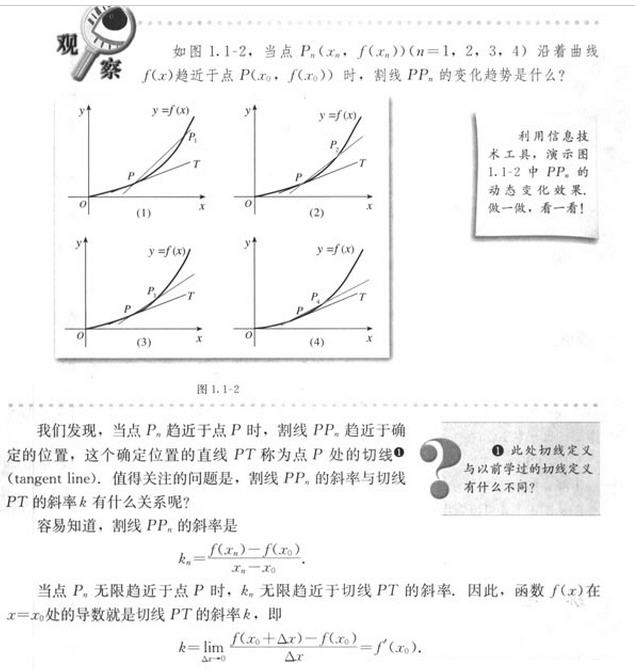



[机器小伟]在[工程师阿伟]的陪同下进入了[九转金丹]之第五转的修炼。
这次要研究的是[导数及其应用]。
正剧开始:
星历2016年04月23日 16:32:36, 银河系厄尔斯星球中华帝国江南行省。
[工程师阿伟]正在和[机器小伟]一起研究[导数及其应用]。
<span style="font-size:18px;">>>>
[-3.000001001396413, -2.999998999442255]
[4.999998999721811, 5.000000996346898]def taskFun(x):return x**2-7*x+15;def derivatives(x):epsilon = 1e-6;leftValue = taskFun(x-epsilon);rightValue = taskFun(x+epsilon);value = taskFun(x);leftLimit = (value-leftValue)/epsilon;rightLimit = (rightValue-value)/epsilon; return [leftLimit, rightLimit];def tmp():print(derivatives(2));print(derivatives(6));</span>
<span style="font-size:18px;">>>>
函数在0.6点的左、右导数分别是:[0.29068008811083956, 0.290679765257984]
函数在1.2点的左、右导数分别是:[0.1831169299526536, 0.18311682836724685]def taskFun(x):return (3*x/(4*math.pi))**(1/3);def derivatives(x):epsilon = 1e-6;leftValue = taskFun(x-epsilon);rightValue = taskFun(x+epsilon);value = taskFun(x);leftLimit = (value-leftValue)/epsilon;rightLimit = (rightValue-value)/epsilon; return [leftLimit, rightLimit];def tmp():a = [0.6, 1.2];for i in range(len(a)):print('函数在{0}点的左、右导数分别是:{1}'.format(a[i],derivatives(a[i])));</span>
<span style="font-size:18px;">>>>
函数在10点的左、右导数分别是:[0.07947403424246602, 0.07947403823926891]
>>> 1.05**10*math.log(1.05)
0.07947403625517714def taskFun(x):return (1+0.05)**x;def derivatives(x):epsilon = 1e-6;leftValue = taskFun(x-epsilon);rightValue = taskFun(x+epsilon);value = taskFun(x);leftLimit = (value-leftValue)/epsilon;rightLimit = (rightValue-value)/epsilon; return [leftLimit, rightLimit];#例1
def tmp():a = [10];for i in range(len(a)):print('函数在{0}点的左、右导数分别是:{1}'.format(a[i],derivatives(a[i])));</span>
<span style="font-size:18px;">>>>
函数在自变量取值为90处的左、右导数分别是:[52.83999450966803, 52.84000519623078]
函数在自变量取值为98处的左、右导数分别是:[1320.9993362579553, 1321.0006572990096]def taskFun(x):return 5284/(100-x);def derivatives(x):epsilon = 1e-6;leftValue = taskFun(x-epsilon);rightValue = taskFun(x+epsilon);value = taskFun(x);leftLimit = (value-leftValue)/epsilon;rightLimit = (rightValue-value)/epsilon; return [leftLimit, rightLimit];#例3
def tmp():a = [90, 98];for i in range(len(a)):print('函数在自变量取值为{0}处的左、右导数分别是:{1}'.format(a[i],derivatives(a[i])));</span>
<span style="font-size:18px;"> if (1) { var r = 20; config.setSector(1,1,1,1); config.graphPaper2D(0, 0, r); config.axis2D(0, 0,180); //坐标轴设定 var scaleX = 2*r, scaleY = 2*r; var spaceX = 2, spaceY = 0.3; var xS = -10, xE = 10; var yS = -10, yE = 10; config.axisSpacing(xS, xE, spaceX, scaleX, 'X'); config.axisSpacing(yS, yE, spaceY, scaleY, 'Y'); var transform = new Transform(); //存放函数图像上的点 var a = [], b = [], c = [], d = []; //需要显示的函数说明 var f1 = 'y=log_[2]x的导数', f2 = '', f3 = '', f4 = ''; var epsilon = 0.000001;var derivative = 0;//函数描点 for (var x = xS; x <= xE; x+=1) { derivative = (funTask(x+epsilon)-funTask(x))/epsilon;a.push([x, derivative]); } //存放临时数组 var tmp = []; //显示变换 if (a.length > 0) { a = transform.scale(transform.translate(a, 0, 0), scaleX/spaceX, scaleY/spaceY); //函数1 tmp = [].concat(a); shape.pointDraw(tmp, 'red'); tmp = [].concat(a); shape.multiLineDraw(tmp, 'pink'); plot.setFillStyle('red'); plot.fillText(f1, 100, -90, 200); } }}function funTask(x) {return Math.log(x)/Math.log(2);
}function funTask(x) {return 2*Math.pow(Math.E, x);
}</span>
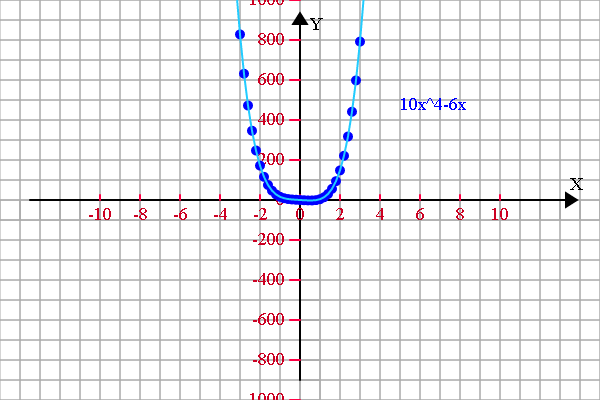
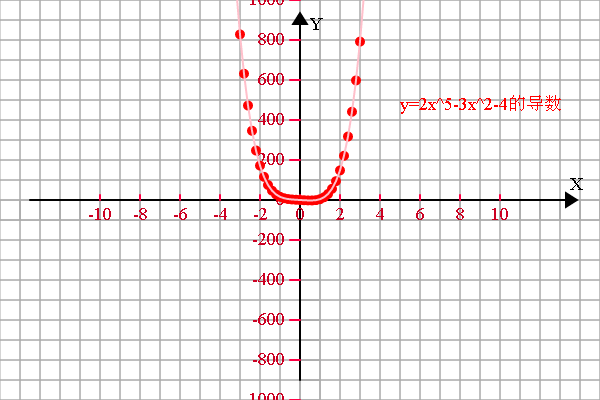
<span style="font-size:18px;"> if (1) { var r = 20; config.setSector(1,1,1,1); config.graphPaper2D(0, 0, r); config.axis2D(0, 0,180); //坐标轴设定 var scaleX = 2*r, scaleY = 2*r; var spaceX = 2, spaceY = 200; var xS = -10, xE = 10; var yS = -1000, yE = 1000; config.axisSpacing(xS, xE, spaceX, scaleX, 'X'); config.axisSpacing(yS, yE, spaceY, scaleY, 'Y'); var transform = new Transform(); //存放函数图像上的点 var a = [], b = [], c = [], d = []; //需要显示的函数说明 var f1 = 'y=2x^5-3x^2-4的导数', f2 = '10x^4-6x', f3 = '', f4 = ''; var epsilon = 0.000001;var derivative = 0;//函数描点 for (var x = xS; x <= xE; x+=0.2) { //derivative = (funTask(x+epsilon)-funTask(x))/epsilon;// a.push([x, derivative]); b.push([x, funTask_2(x)]);} //存放临时数组 var tmp = []; //显示变换 if (a.length > 0) { a = transform.scale(transform.translate(a, 0, 0), scaleX/spaceX, scaleY/spaceY); //函数1 tmp = [].concat(a); shape.pointDraw(tmp, 'red'); tmp = [].concat(a); shape.multiLineDraw(tmp, 'pink'); plot.setFillStyle('red'); plot.fillText(f1, 100, -90, 200); } //显示变换 if (b.length > 0) { b = transform.scale(transform.translate(b, 0, 0), scaleX/spaceX, scaleY/spaceY); //函数1 tmp = [].concat(b); shape.pointDraw(tmp, 'blue'); tmp = [].concat(b); shape.multiLineDraw(tmp, '#22ccFF'); plot.setFillStyle('blue'); plot.fillText(f2, 100, -90, 200); } }}function funTask(x) {return 2*Math.pow(x, 5)-3*Math.pow(x, 2)-4;
}function funTask_2(x) {return 10*Math.pow(x, 4)-6*x;
}
</span>
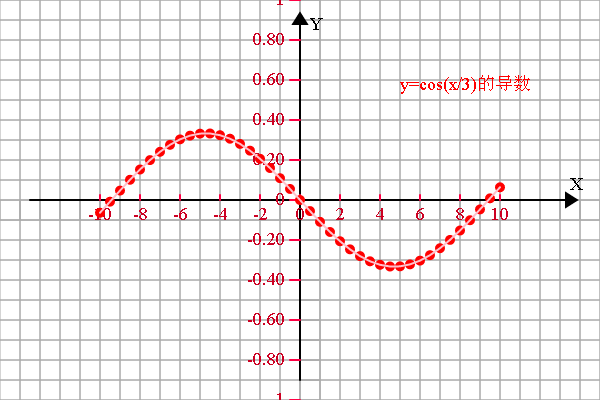
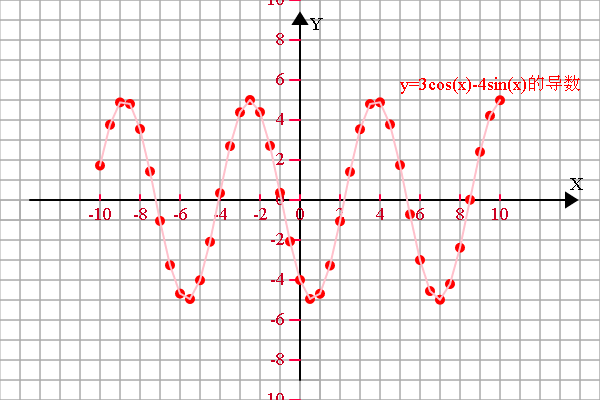
<span style="font-size:18px;"> if (1) { var r = 20; config.setSector(1,1,1,1); config.graphPaper2D(0, 0, r); config.axis2D(0, 0,180); //坐标轴设定 var scaleX = 2*r, scaleY = 2*r; var spaceX = 2, spaceY = 2; var xS = -10, xE = 10; var yS = -10, yE = 10; config.axisSpacing(xS, xE, spaceX, scaleX, 'X'); config.axisSpacing(yS, yE, spaceY, scaleY, 'Y'); var transform = new Transform(); //存放函数图像上的点 var a = [], b = [], c = [], d = []; //需要显示的函数说明 var f1 = 'y=3cos(x)-4sin(x)的导数', f2 = '10x^4-6x', f3 = '', f4 = ''; var epsilon = 0.000001;var derivative = 0;//函数描点 for (var x = xS; x <= xE; x+=0.5) { derivative = (funTask(x+epsilon)-funTask(x))/epsilon;a.push([x, derivative]); //b.push([x, funTask_2(x)]);} //存放临时数组 var tmp = []; //显示变换 if (a.length > 0) { a = transform.scale(transform.translate(a, 0, 0), scaleX/spaceX, scaleY/spaceY); //函数1 tmp = [].concat(a); shape.pointDraw(tmp, 'red'); tmp = [].concat(a); shape.multiLineDraw(tmp, 'pink'); plot.setFillStyle('red'); plot.fillText(f1, 100, -110, 200); } //显示变换 if (b.length > 0) { b = transform.scale(transform.translate(b, 0, 0), scaleX/spaceX, scaleY/spaceY); //函数1 tmp = [].concat(b); shape.pointDraw(tmp, 'blue'); tmp = [].concat(b); shape.multiLineDraw(tmp, '#22ccFF'); plot.setFillStyle('blue'); plot.fillText(f2, 100, -90, 200); } }}function funTask(x) {return 3*Math.cos(x)-4*Math.sin(x);
}function funTask(x) {return Math.cos(x/3);
}</span>
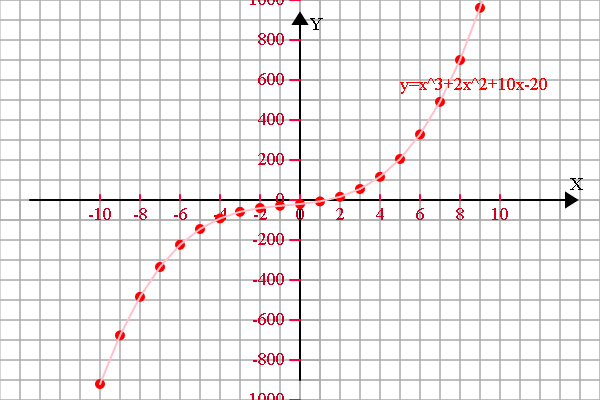
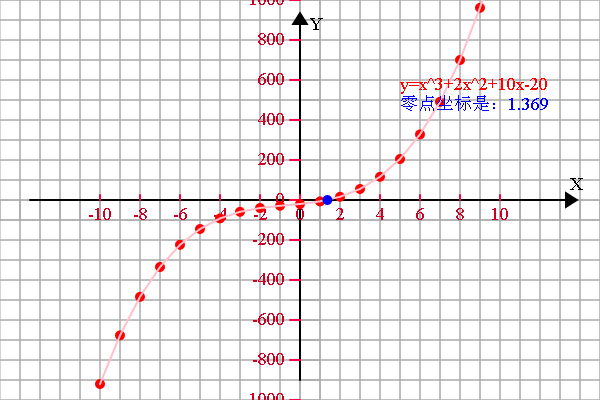
<span style="font-size:18px;"> if (1) { var r = 20; config.setSector(1,1,1,1); config.graphPaper2D(0, 0, r); config.axis2D(0, 0,180); //坐标轴设定 var scaleX = 2*r, scaleY = 2*r; var spaceX = 2, spaceY = 200; var xS = -10, xE = 10; var yS = -1000, yE = 1000; config.axisSpacing(xS, xE, spaceX, scaleX, 'X'); config.axisSpacing(yS, yE, spaceY, scaleY, 'Y'); var transform = new Transform(); //存放函数图像上的点 var a = [], b = [], c = [], d = []; //需要显示的函数说明 var f1 = 'y=x^3+2x^2+10x-20', f2 = '10x^4-6x', f3 = '', f4 = ''; var epsilon = 0.000001;var derivative = 0;//给定初始试探点var x0 = 4, xResult = 0;//函数描点 for (var x = xS; x <= xE; x++) { a.push([x, funTask(x)]); } //牛顿法求零点derivative = (funTask(x0+epsilon)-funTask(x0))/epsilon;xResult = x0-funTask(x0)/derivative;while (Math.abs((xResult-x0)/x0)>epsilon) {x0 = xResult;derivative = (funTask(x0+epsilon)-funTask(x0))/epsilon;xResult = x0 -funTask(x0)/derivative;}b.push([xResult, 0]);//存放临时数组 var tmp = []; //显示变换 if (a.length > 0) { a = transform.scale(transform.translate(a, 0, 0), scaleX/spaceX, scaleY/spaceY); //函数1 tmp = [].concat(a); shape.pointDraw(tmp, 'red'); tmp = [].concat(a); shape.multiLineDraw(tmp, 'pink'); plot.setFillStyle('red'); plot.fillText(f1, 100, -110, 200); } //显示变换 if (b.length > 0) { plot.setFillStyle('blue'); plot.fillText('零点坐标是:'+b[0][0].toFixed(3), 100, -90, 200); b = transform.scale(transform.translate(b, 0, 0), scaleX/spaceX, scaleY/spaceY); //函数1 tmp = [].concat(b); shape.pointDraw(tmp, 'blue'); } }}function funTask(x) {return Math.pow(x, 3)+2*Math.pow(x, 2)+10*x-20;
}
</span>
这是一张勉强能用的手写式,如果要想做成印刷上的多行立体形态,只怕是不容易。
当然,那就是公式编辑器的事了。
<span style="font-size:18px;"> if (1) {var mathText = new MathText();//希腊字母表(存此用于Ctrl C/V//ΑΒΓΔΕΖΗΘΙΚΛΜΝΞΟΠΡΣΤΥΦΧΨΩ//αβγδεζηθικλμνξοπρστυφχψωvar s = ['lim_[Δt->0](h(2+Δt)-h(2))/(Δt) = k','lim_[Δx->0]Δy/Δx=lim_[Δt->0](f(x_[0]+Δx)-f(x_[0]))/Δx','f \'(x_[0])=lim_[Δx->0]Δy/Δx=lim_[Δx->0](f(x_[0]+Δx)-f(x_[0]))/Δx','S=lim_[Δx->0]Ξ_[i=1]^[n] f(ξ_[i])Δx=lim_[Δx->0]Ξ_[i=1]^[n] 1/nf(ξ_[i])=1/3','[S]_[a]^[b] f(x)dx = lim_[n->[inf]]Ξ_[i=1]^[n] (b-a)/nf(ξ_[i])','[S]_[a]^[b] f(x)dx = F(x) |_[a]^[b] = F(b)-F(a)',];var x =40, y=40;var r1 = 40;var len = s.length;for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {if (s[i] == '') {if (x < 100) {x += 300;y-=r1*3;}else {x = 20;y += r1;}}else { mathText.printIntegral(s[i], x, y, '@');y+=r1;}} }/**
* @usage 数学表达式,代数式的书写
* @author mw
* @date 2016年03月12日 星期六 11:05:12
* @param
* @return
*
*/
function MathText() {//上标标记形式为...^[内容]...//分数不进行处理, 根式不进行处理,都转成指数式进行//特殊数学符号设想加\[alpha]进行转义,待续//可以进行指数上标代数式的书写//可扩展下标,待续this.setNormalFont = function() {plot.setFont("normal normal normal 24px Times Lt Std"); }this.setScriptFont = function() {plot.setFont("italic normal bold 16px Dark Courier ");}this.print = function(text, xPos, yPos, style, splitChar) {splitChar = splitChar ? splitChar : '|';xPos = xPos ? xPos : 0;yPos = yPos ? yPos : 0;style = style ? style : 'black';plot.save().setStrokeStyle(style).setFillStyle(style);var s = text ? text : '';if (s != '') {s = s.replace(/\/\//ig, '÷');s = s.replace(/\[>=\]/ig, '≥');s = s.replace(/\[<=\]/ig, '≤');s = s.replace(/\[!=\]/ig, '≠');s = s.replace(/\[PI\]/ig, 'π');s = s.replace(/\[+-\]/ig, '±');s = s.replace(/->/ig, '→');s = s.replace(/<-/ig, '←');s = s.replace(/<-/ig, '←');s = s.replace(/Ξ/g, '\u2211');}//字符串长度var len = s.length;//不同字体大小设置在此var r1 = 20;//单个字符暂存处var c;//文本显示位置var x = xPos, y = yPos;//正常文本暂存var s0 = '';//字符串打印长度var measure; //记录上一个x位置,可记录三层var xMem = [x, x, x];//记录每一层的左括号位置var bracketPos = [x, x, x];//记录括号层次var bracketsLevel = 0;//记录根号层次var radicalLevel = 0;//记录每一层根号的起始位置和层次数的数组...[[start, end, level], ...]var radicalSpan = [];//设置正常字体this.setNormalFont(); for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {if (s[i] == '_' && s[i+1] == '[') {//下标开始//下标标记形式为..._[内容]...if (s0 != '') { //先把正常字符打印出if (r1 != 20) { //字体字号大小还在上标状态r1 = 20;this.setNormalFont(); }measure = plot.measureText(s0);plot.fillText(s0, x, y, measure);s0 = '';x += measure;}var subScript = '';var j = 0;for (j = i+1; s[j]!=']'; j++) {if (s[j] != '[') {subScript+=s[j];}}if (r1 != 10) {//正常字体状态,需要改为上标字体r1 = 10;this.setScriptFont();}measure = plot.measureText(subScript);plot.fillText(subScript, x, y+8, measure);if (j < len-1 && s[j+1] == '^') {}else {x += 1.2*measure;}i = j;}else if (s[i] == '^'&&s[i+1] == '[') {//上标开始//上标标记形式为...^[内容]...if (s0 != '') { //先把正常字符打印出if (r1 != 20) { //字体字号大小还在上标状态r1 = 20;this.setNormalFont(); }measure = plot.measureText(s0);plot.fillText(s0, x, y, measure);s0 = '';x += measure;}var upperScript = '';var j = 0;for (j = i+1; s[j]!=']'; j++) {if (s[j] != '[') {upperScript+=s[j];}}//二次根式if (upperScript == '1/2' || upperScript == '0.5') { var x1, y1;if (i > 0 && s[i-1] == ')') {x1 = bracketPos[bracketsLevel];}else {x1 = xMem[bracketsLevel];}/* 存疑代码if (radicalSpan == []) {radicalLevel = 0;radicalSpan.push([x1, x, radicalLevel]);}else {var len = radicalSpan.length;for (var k = 0; k < len; k++) {if (x1 < radicalSpan[k][0]) {radicalLevel = radicalSpan[k][2]+1;break;}if (k >= len-1) {radicalLevel = 0;}}radicalSpan.push([x1, x, radicalLevel]);}*/y1 = y-20-5*radicalLevel; plot.save().setLineWidth(1);plot.beginPath().moveTo(x1-5, y+5).lineTo(x1-8, y-3).moveTo(x1-5, y+5).lineTo(x1+5, y1).moveTo(x1+5, y1).lineTo(x, y1).closePath().stroke();plot.restore();}//向量符号else if (upperScript == '->') {var x1, y1;if (i > 0 && s[i-1] == ')') {x1 = bracketPos[bracketsLevel];}else {x1 = xMem[bracketsLevel];}y1 = y-18-5*radicalLevel; plot.save().setLineWidth(1);plot.beginPath().moveTo(x1, y1).lineTo(x+2, y1).moveTo(x+2, y1).lineTo(x-5, y1-3).moveTo(x+2, y1).lineTo(x-5, y1+3).closePath().stroke();plot.restore();}else {if (r1 != 10) {//正常字体状态,需要改为上标字体r1 = 10;this.setScriptFont();}measure = plot.measureText(upperScript);plot.fillText(upperScript, x, y-8, measure);if (j < len-1 && s[j+1] == '_') {}else {x += 1.2*measure;}}//直接跳跃过上标字符区段i = j;}else {c = s[i];if (c == ')') {s0 += c;bracketsLevel -= 1;}else if (c == '(') {//如果整个括号被开根式,根号在括号左边bracketPos[bracketsLevel] = x + plot.measureText(s0); s0 += c;bracketsLevel+=1;//过了括号就是过了一道关,要刷新坐标xMem[bracketsLevel] = x + plot.measureText(s0);}else if (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '÷'|| c == '=' || c == ' ') {if (c == '*') {if (i > 0 && ((s[i-1] == ')' && /[0-9]/.test(s[i-2]) ||/[0-9]/.test(s[i-1]))) &&((s[i+1] == '(' && /[0-9]/.test(s[i+2])) || /[0-9]/.test(s[i+1]))) {//对于乘号前后都是数字的情况,把乘号改成叉号c = ' \u00D7 ';}else {//对于代数式中,乘号改为点号c = ' \u00B7 ';}}//如果是运算符后的数被开根式,根号在运算符右边if (c == '-' || c == '/') {s0 += ' '+c+' ';}else {s0 += c;}if (bracketsLevel < 3) {xMem[bracketsLevel] = x+plot.measureText(s0);} }else if (c == splitChar) { //隔字符if (bracketsLevel < 3) {xMem[bracketsLevel] = x+plot.measureText(s0)-3;}}else {s0 += c; } }}if (s0 != '') { //先把正常字符打印出if (r1 != 20) { //字体字号大小还在上标状态r1 = 20;this.setNormalFont(); }measure = plot.measureText(s0);plot.fillText(s0, x, y, measure);x += measure;}plot.restore();}//集合符号,集合表达式的书写this.printSet = function(text, xPos, yPos, style, splitChar) {//隔字符splitChar = splitChar ? splitChar : '|';var s = text ? text : '';xPos = xPos ? xPos : 0;yPos = yPos ? yPos : 0;style = style ? style : 'black';if (s != '') {//希腊字母表(存此用于Ctrl C/V//ΑΒΓΔΕΖΗΘΙΚΛΜΝΞΟΠΡΣΤΥΦΧΨΩ//αβγδεζηθικλμνξοπρστυφχψω//s = s.replace(/\[B\]/ig, '\u2208'); //∈s = s.replace(/\[NB\]/ig, '\u2209'); //不属于s = s.replace(/\[S\]/ig, '\u2286'); //包含于(是子集)s = s.replace(/\[SS\]/ig, '\u2287'); //包含s = s.replace(/\[ST\]/ig, '\u228A'); //真包含于(是真子集)s = s.replace(/\[SST\]/ig, '\u228B'); //真包含s = s.replace(/\[UU\]/ig, '\u222A'); //并集 ,由于U表示全集,又常为下标,此处错开s = s.replace(/\[I\]/ig, '\u2229'); //交集s = s.replace(/\[C\]/ig, '\u2201'); //补集s = s.replace(/\[INF\]/ig, '\u221E'); //无穷大s = s.replace(/\[NULL\]/ig, '\u2205');//空集s = s.replace(/\[&\]/ig, '\u2227');//且s = s.replace(/\[\|\]/ig, '\u2228');//或s = s.replace(/\[~\]/ig, '﹁');//非s = s.replace(/\[ALL\]/ig, '\u2200');//全称量词 Universal quantifiers = s.replace(/\[Exist\]/ig, '\u2203');//存在量词 Existential quantifier}return this.print(s, xPos, yPos, style, splitChar);}//微积分符号this.printIntegral = function(text, xPos, yPos, style, splitChar) {//隔字符splitChar = splitChar ? splitChar : '|';var s = text ? text : '';xPos = xPos ? xPos : 0;yPos = yPos ? yPos : 0;style = style ? style : 'black';if (s != '') {//希腊字母表(存此用于Ctrl C/V//ΑΒΓΔΕΖΗΘΙΚΛΜΝΞΟΠΡΣΤΥΦΧΨΩ//αβγδεζηθικλμνξοπρστυφχψω//s = s.replace(/\[S\]/ig, '\u222B'); //定积分符号 一次s = s.replace(/\[SS\]/ig, '\u222C');//定积分符号 二次s = s.replace(/\[SSS\]/ig, '\u222C');//定积分符号 三次s = s.replace(/\[INF\]/ig, '\u221E'); //无穷大}return this.print(s, xPos, yPos, style, splitChar);}}</span>本节到此结束,欲知后事如何,请看下回分解。
这篇关于[从头学数学] 第192节 导数及其应用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!