本文主要是介绍CS61b LECTURE 3 NOTE,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- CS61b LECTURE 3
- defining classes (定义类)
- Defining Classes
- Constructors
- The "this" Keyword
- The "static" Keyword
- Lifetimes of Variables
CS61b LECTURE 3
defining classes (定义类)
Defining Classes
Constructors
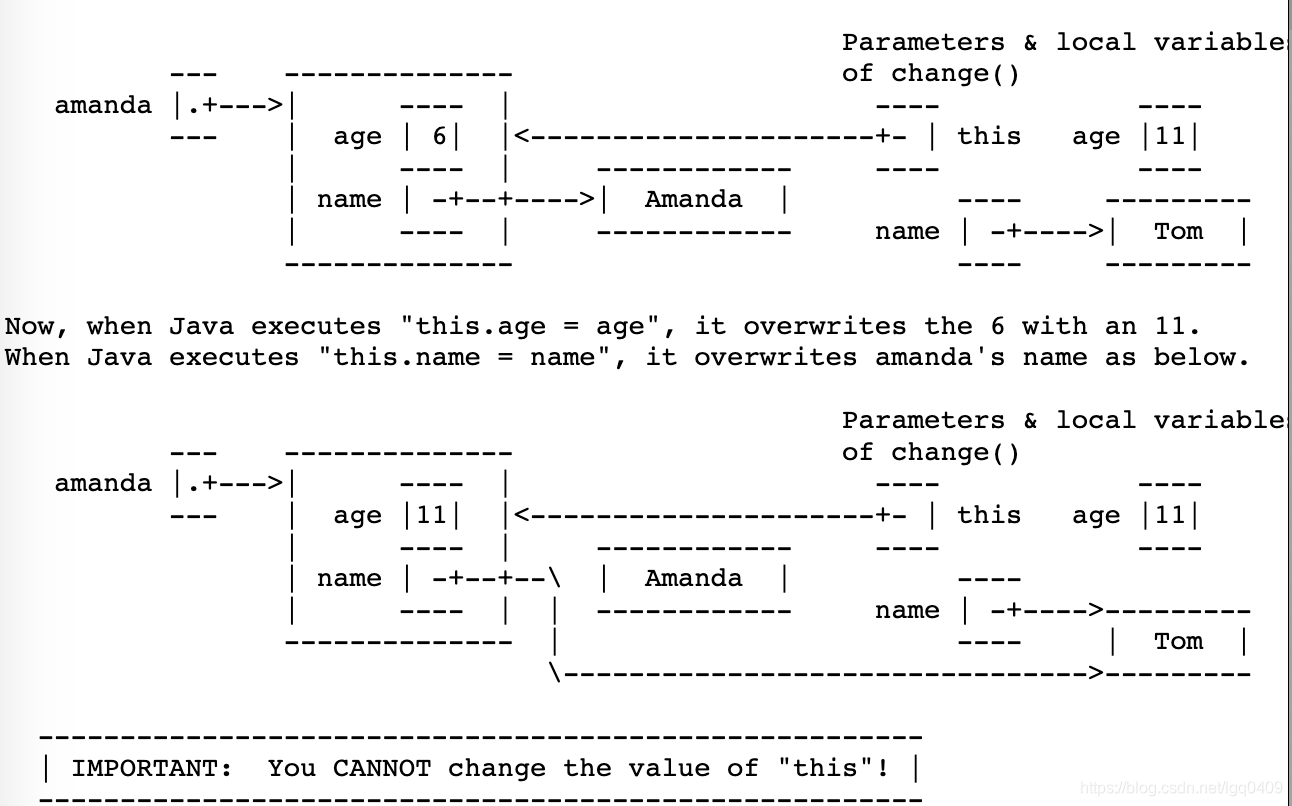
The “this” Keyword
A method invocation implicitly passes an object as a parameter called “this”.
The “static” Keyword
A static_field is a single variable shared by a whole class of objects; its value does not vary from object to object.
If we declare a field “static”, there is just one field for the whole class. Static fields are also called class_variables
System.in and System.out are other example of static fields.
Methods can be static too. A static method does not implicitly pass an object as a parameter.
The main method is always static.
Lifetimes of Variables
- A local variable (declared in a method) is gone forever as soon as the method in which it is declared finished executing.(If it references an object, the object might continue to exist, though.)
- An instance variable (non-static field) lasts as long as the object, the object lasts as long as there is a reference to it.
- A class variable (static field) lasts as long as the program runs.
An object is a repository of data.
Fields are variables that hold the data stored in objects. ( instance_variables)
class Human{public static int numberOfHumans;public static void printHumans() {System.out.println(numberOfHumans);}// call Human.printHumans()public int age;public String name;public void introduce() {System.out.println("I' m " + name + " and I' m " + age + " years old.");}public void copy(Human original) {age = original.age;name = original.name;}// copy original's fields into the object who calls the original// Constructors// A constructor is a method that constructs a Human. // The constructor won't actually contain code that dose the creatingpublic Human(String givenName) {numberOfHuman++;age = 6;name = givenName;}// A constructor// Java provides every class with a default constructor, which takes no parameters and does no initializing.// Warning: Once written your own constructor, the default constructor goes away. If you still want a default constructor, you must define it explicitly like below:public Human() {numberOfHumans++;}// override the default constructor public Human() {numberOfHumans++;age = 0;name = "Untitiled";}// Using "this" Keyword but DOES the SAME thing as abovepublic Human() {numberOfHumans++;this.age = 0;this.name = "Untitiled";}// if the parameters (local variables) of a method have the same name as the fields of an object, then the former have priority, and the "this Keyword" is needed to refer to the object's fieldspublic void change(int age) {String name = "Tom";this.age = age;this.name = name;
}
- construct 一个 Human对象
Human amanda = new Human(); // create amanda
amanda.age = 6; //set amanda's fields
amanda.name = "Amanda";
amanda.introduce(); //_Method_call
// Using the constructor:
Human amanda = new Human("Amanda");
amanda.introduce();
// look at the variable numberOfHuman, prefix it with the class name rather than the name of a specific object.
int kids = Human.numberOfHumans / 4; --------------| ---- |--- | age | 6| |amanda |.+--->| ---- | --------------- | name | -+--+---->| "Amanda" || ---- | -------------------------- a String objecta Human object
这篇关于CS61b LECTURE 3 NOTE的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



