本文主要是介绍日撸Java三百行 day11-12(顺序表),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1. 知识点
1.1 final 的使用
final关键字常用来修饰类、方法和引用。
修饰类:
格式:public final class 类名称 { // ··· }
该类不能有任何的子类,且其所有的成员方法都无法覆盖重写。
修饰方法:
格式:修饰符 final 返回值类型 方法名称(参数列表) { // 方法体 }
该方法就是最终方法,不能被覆盖重写。
修饰引用:
格式: final 引用类型 名称 = 值;
当引用类型为基本数据类型时,则引用为常量,其值无法修改;当引用类型为引用数据类型时,可修改其本身内容,但不能修改指向其的引用;当引用类型为类的成员变量时,由于成员变量具有默认值,所以final之后必须当场赋值。
这里使用到的是修饰一个基础数据类型的全局变量,final后其为常量,不能被修改。
public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;1.2 new关键字的使用
在Java中任何变量使用前都需要设置初值,Java提供了为类的成员变量赋予初值的功能:构造方法。
构造方法特殊性:
1) 构造方法名字必须与定义它的类名相同,没有返回类型。
2) 其调用是在创建一个对象时用new操作进行的,作用是初始化对象。
3) 每个类有可以有多个或没有构造方法。
4) 不能被static、final、synchronized、abstracth和native修饰,且不能被子类继承
然后再用new关键字加上构造方法来,创建一个对象。
比如:
public class SequentialList {public SequentialList() {}// Of the Constructor
}1.3 方法的Override
方法的重写是封装的特性之一,子类可以对在基类中的继承来的方法进行重写,从而扩充方法以达到自己的需求。但重写方法必须与被重写的方法的名称、参数列表、返回值类型相同,且不能使用比被重写的方法更严格的访问权限。
/************************ Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.**********************/
public String toString() {String resultString = "";if (length == 0) {return "empty";} // Of iffor (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {resultString += data[i] + ", ";} // Of for iresultString += data[length - 1];return resultString;
}// Of toString
这里顺便提一下public作用及有无static的区别:
public是访问修饰符(详解),主要做权限说明,表明该类或者该方法等是公共的,任何程序集都可以去调用到它。
用static修饰的方法,不可调用该类中的非静态成员和非静态方法;其不需要生成示例对象就可以直接调用成员,而且该静态方法(或变量)被该类创建的对象共享;其不能使用super对父类中的成员进行调用。不使用static的非静态方法调用方法或变量时没有限制。
2. 总代码
2.1顺序表的初始化和重置
package datastructure.list;/*** Sequential list.* * @author Yunhua Hu yunhuahu0528@163.com.*/
public class SequentialList {/*** The maximal length of the list. It is a constant.*/public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;/*** The actual length not exceeding MAX_LENGTH. Attention: length is not only the* number variable of Sequential list, but also the member variable of Array. In* fact, a name can be the member variable of different classes.*/int length;/*** The data stored in an array.*/int[] data;/*********************** * Construct an empty sequential list********************* */public SequentialList() {length = 0;data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];}// Of the first constructor/*********************** * Construct a sequential list using an array.* * @param paraArray* The given array. Its length should not exceed MAX_LENGTH. For* simplicity now we do not check it.********************* */public SequentialList(int[] paraArray) {data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];length = paraArray.length;// Copy data.for (int i = 0; i < paraArray.length; i++) {data[i] = paraArray[i];} // Of for i}// Of the second constructor/************************ Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.**********************/public String toString() {String resultString = "";if (length == 0) {return "empty";} // Of iffor (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {resultString += data[i] + ",";} // Of for iresultString += data[length - 1];return resultString;}// Of toString/************************ Reset to empty.**********************/public void reset() {length = 0;}// Of reset/************************ The entrance of the progarm.** @param args* Not used now.**********************/public static void main(String args[]) {int[] tempArray = { 1, 4, 6, 9 };SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray);System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + tempFirstList);tempFirstList.reset();System.out.println("After reset, the list is: " + tempFirstList);}// Of main}// Of class SequentialList输出:

2.2 顺序表的增删查改
对顺序表的增删查改,一定记得考虑false的情况。
package datastructure.list;/*** Sequential list.* * @author Yunhua Hu yunhuahu0528@163.com.*/
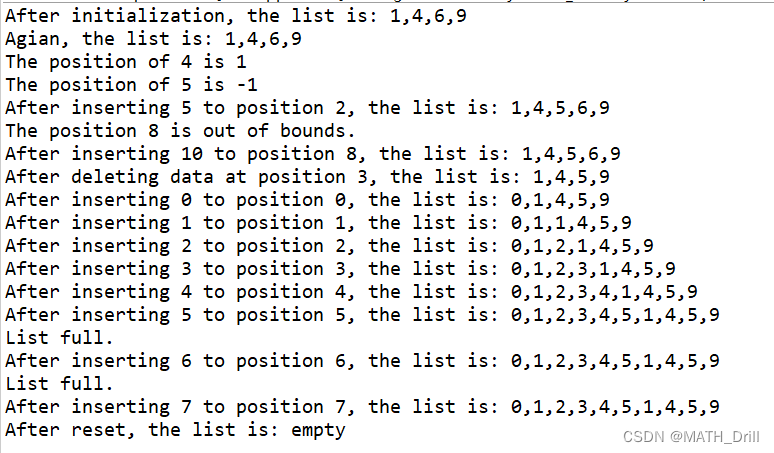
public class SequentialList {/*** The maximal length of the list. It is a constant.*/public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;/*** The actual length not exceeding MAX_LENGTH. Attention: length is not only the* number variable of Sequential list, but also the member variable of Array. In* fact, a name can be the member variable of different classes.*/int length;/*** The data stored in an array.*/int[] data;/*********************** * Construct an empty sequential list********************* */public SequentialList() {length = 0;data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];}// Of the first constructor/*********************** * Construct a sequential list using an array.* * @param paraArray* The given array. Its length should not exceed MAX_LENGTH. For* simplicity now we do not check it.********************* */public SequentialList(int[] paraArray) {data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];length = paraArray.length;// Copy data.for (int i = 0; i < paraArray.length; i++) {data[i] = paraArray[i];} // Of for i}// Of the second constructor/************************ Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.**********************/public String toString() {String resultString = "";if (length == 0) {return "empty";} // Of iffor (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {resultString += data[i] + ",";} // Of for iresultString += data[length - 1];return resultString;}// Of toString/************************ Reset to empty.**********************/public void reset() {length = 0;}// Of reset/************************ Find the index of the given value. If it appears in multiple positions,* simply return the first one.** @param paraValue The given value.* @return The position. -1 for not found.**********************/public int indexoOf(int paraValue) {int tempPosition = -1;for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {if (data[i] == paraValue) {tempPosition = i;break;} // Of if} // Of for ireturn tempPosition;}// Of indexOfpublic boolean insert(int paraPosition, int paraValue) {if (length == MAX_LENGTH) {System.out.println("List full.");return false;} // Of ifif ((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition > length)) {System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of bounds.");return false;} // Of if// Form tail to head. The last one is moved to a new position. Because length <// MAX_LENGTH, no exceeding occurs.for (int i = length; i > paraPosition; i--) {data[i] = data[i - 1];} // Of for idata[paraPosition] = paraValue;length++;return true;}// Of insertpublic boolean delete(int paraPosition) {if ((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition >= length)) {System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of bounds.");return false;} // Of if// Form head to tail.for (int i = paraPosition; i < length - 1; i++) {data[i] = data[i + 1];} // Of for ilength--;return true;}// Of delete/************************ The entrance of the program.** @param args* Not used now.**********************/public static void main(String args[]) {int[] tempArray = { 1, 4, 6, 9 };SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray);System.out.println("After initialization, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());System.out.println("Agian, the list is: " + tempFirstList);int tempValue = 4;int tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexoOf(tempValue);System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);tempValue = 5;tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexoOf(tempValue);System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);tempPosition = 2;tempValue = 5;tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);System.out.println("After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);tempPosition = 8;tempValue = 10;tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);System.out.println("After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);tempPosition = 3;tempFirstList.delete(tempPosition);System.out.println("After deleting data at position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {tempFirstList.insert(i, i);System.out.println("After inserting " + i + " to position " + i + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);} // Of for itempFirstList.reset();System.out.println("After reset, the list is: " + tempFirstList);}// Of main}// Of class SequentialList输出:
这篇关于日撸Java三百行 day11-12(顺序表)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






