本文主要是介绍278、Java基础54 - 数字与字符串【操作字符串】 2019.11.22,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
0、目录
- 1、JAVA常见字符串方法
- 2、获取字符
- 3、获取对应的字符数组
- 4、截取子字符串
- 5、分隔
- 6、去掉首尾空格
- 7、大小写
- 8、定位
- 9、替换
- 10、练习一:每个单词的首字母都转换为大写
- 11、练习二:英文绕口令
- 12、练习三:间隔大写小写模式
- 13、练习四:最后一个字母变大写
- 14、练习五:把最后一个two单词首字母大写
- 15、参考链接
1、JAVA常见字符串方法

2、获取字符
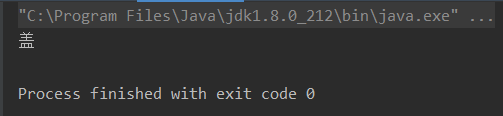
charAt(int index)获取指定位置的字符
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号";char c = sentence.charAt(0);System.out.println(c);}
}
- 输出结果
3、获取对应的字符数组
toCharArray()
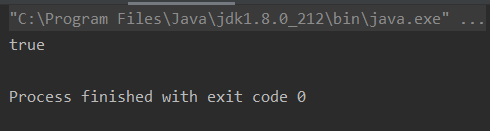
获取对应的字符数组
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了超神 的称号";char[] cs = sentence.toCharArray(); //获取对应的字符数组System.out.println(sentence.length() == cs.length);}
}
- 输出结果
4、截取子字符串
subString
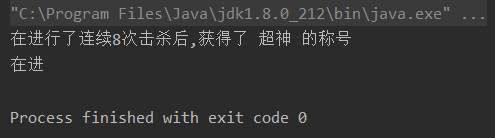
截取子字符串
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号";//截取从第3个开始的字符串 (基0)String subString1 = sentence.substring(3);System.out.println(subString1);//截取从第3个开始的字符串 (基0)//到5-1的位置的字符串//左闭右开String subString2 = sentence.substring(3,5);System.out.println(subString2);}
}
- 输出结果
5、分隔
split
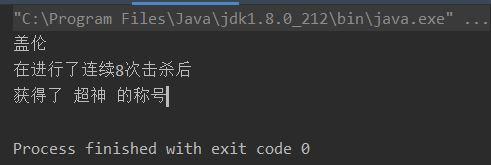
根据分隔符进行分隔
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号";//根据,逗号进行分割,得到3个子字符串String subSentences[] = sentence.split(",");for (String sub : subSentences) { // 增强for循环System.out.println(sub);}}
}
- 输出结果
6、去掉首尾空格
trim
去掉首尾空格
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = " 盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号 ";System.out.println(sentence);//去掉首尾空格System.out.println(sentence.trim());}
}
- 输出结果

7、大小写
toLowerCase 全部变成小写
toUpperCase 全部变成大写
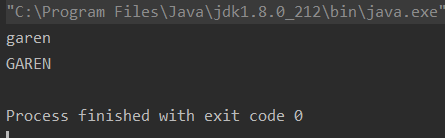
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "Garen";//全部变成小写System.out.println(sentence.toLowerCase());//全部变成大写System.out.println(sentence.toUpperCase());}
}
- 输出结果
8、定位
indexOf 判断字符或者子字符串出现的位置
contains 是否包含子字符串
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了超神 的称号";System.out.println(sentence.indexOf('8')); //字符8 第一次出现的位置System.out.println(sentence.indexOf("超神")); //字符串第一次出现的位置System.out.println(sentence.lastIndexOf("了")); //字符串最后出现的位置System.out.println(sentence.indexOf(',',5)); //从位置5开始,第一次出现,逗号的位置System.out.println(sentence.contains("击杀")); //是否包含字符串"击杀"}
}
- 输出结果

9、替换
replaceAll 替换所有的
replaceFirst 只替换第一个
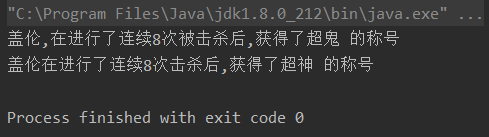
package character;public class TestString {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了超神 的称号";String temp = sentence.replaceAll("击杀", "被击杀"); //替换所有的temp = temp.replaceAll("超神", "超鬼");System.out.println(temp);temp = sentence.replaceFirst(",","");//只替换第一个System.out.println(temp);}
}
- 输出结果
10、练习一:每个单词的首字母都转换为大写
给出一句英文句子: “let there be light”
得到一个新的字符串,每个单词的首字母都转换为大写
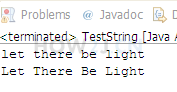
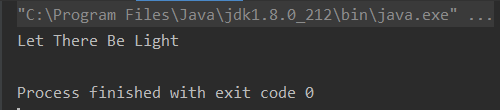
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {/** 思路:1.先按“ ”把字符串进行分割,获取一个字符串数组* 2.每个字符串转换字符数组,位置为0的字符,替换成对应的大写,改回成字符串* 3.最后用StringBuffer进行字符串的拼接,形成一个整体的字符串*/String str = "let there be light";String[] strArray = str.split(" ");for (int i = 0; i < strArray.length; i++) {char[] c = strArray[i].toCharArray();c[0] = Character.toUpperCase(c[0]);strArray[i] = new String(c);}StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();for (int i = 0; i < strArray.length; i++) {sb.append(strArray[i]);sb.append(" ");}String str2 = sb.toString();System.out.println(str2);}
}
- 输出结果
11、练习二:英文绕口令
英文绕口令
peter piper picked a peck of pickled peppers
汉语翻译:笛手彼得拿起一配克腌胡椒
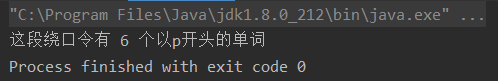
统计这段绕口令有多少个以p开头的单词
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String sentence = "peter piper picked a peck of pickled peppers";String temp[] = sentence.split(" "); // split分割字符串int count=0;for(String Temp:temp){ // 增强for循环if(Temp.charAt(0)=='p'){ // 获取字符串Temp指定索引位置0处的字符,是否为pcount++;}}System.out.printf("这段绕口令有 %d 个以p开头的单词",count);}
}
- 输出结果
12、练习三:间隔大写小写模式
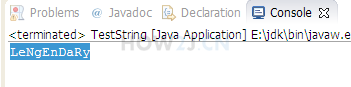
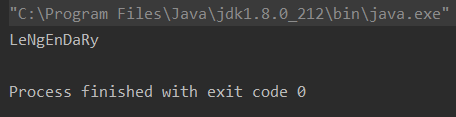
把 lengendary 改成间隔大写小写模式,即 LeNgEnDaRy
/** 思路:* 1.获取字符串的字符数组* 2.在0,2,4,...处进行字母大写,公差为2。* 3.循环更改对应位置的字符* 4.重新定义为字符串,输出*/
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "lengendary";char[] c = str.toCharArray(); // 获取字符串的字符数组cfor (int i = 0; i < c.length; i+=2) { // for循环整个字符数组,步长为2c[i] = Character.toUpperCase(c[i]); // 将步长为2的字符数组,全部转换为大写}String str2 = new String(c); // 将字符数组实例化成为一个字符串System.out.println(str2);}
}
- 输出结果
13、练习四:最后一个字母变大写
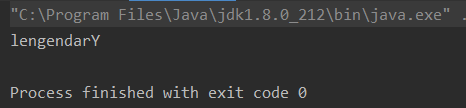
把 lengendary 最后一个字母变大写
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "lengendary";char[] c = str.toCharArray();for(int i=0; i < c.length; i++) { //循环赋值// 如果i等于数组长度减1,即i为元素最后一位数字,把此字母大写if(i == c.length-1) {c[i]=Character.toUpperCase(c[i]);}}String str1 = new String(c);System.out.println(str1);}
}
- 输出结果
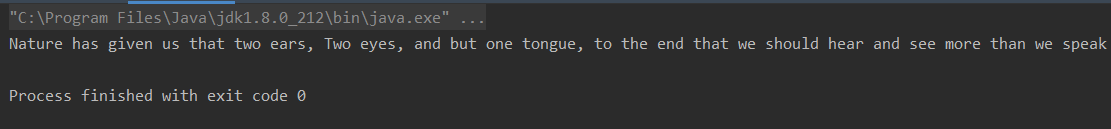
14、练习五:把最后一个two单词首字母大写
Nature has given us that two ears, two eyes, and but one tongue, to the end that we should hear and see more than we speak
把最后一个two单词首字母大写
/** 思路* 1.在字符串中寻找“two”最后一次出现的位置,就是单词首字母"t"字符所在的下标位置* 2.获取字符数组,在获取到的位置处更改字符为大写。* 3.重新定义为字符串,输出*/
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "Nature has given us that two ears, two eyes, "+ "and but one tongue, to the end that we should hear and see more than we speak";int index = str.lastIndexOf("two"); // 先在字符串中寻找“two”最后一次出现的位置(其实,这就是在寻找two单词首字母"t"出现的下标位置)char[] c = str.toCharArray(); // 获取字符数组c[index] = Character.toUpperCase(c[index]); // 将获取到two位置处的字符转换为大写str = new String(c); // 将字符数组c再次定义为字符串System.out.println(str); // 输出字符串}
}
- 输出结果
15、参考链接
[01] How2j - 数字与字符串系列教材 (七)- JAVA常见字符串方法
这篇关于278、Java基础54 - 数字与字符串【操作字符串】 2019.11.22的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





